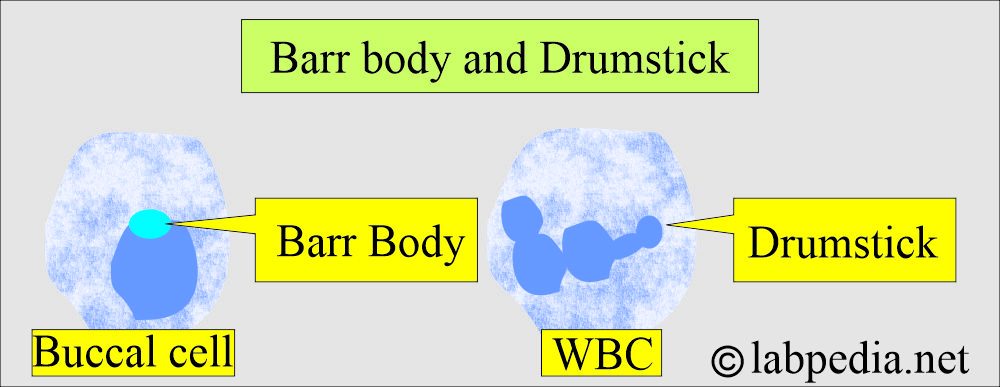
Barr Bodies detection and Drumstick
Barr Bodies
What sample is needed for Barr Bodies?
- Scrapings from buccal mucosa or the vaginal wall in some women.
- The buccal mucosa is scraped and smeared on the slide. It is fixed immediately. Make a monolayer of the cells.
- While the Drumstick test is performed on white blood cells (WBC) to detect the presence of the drumstick.
- The more specific method is a nucleic acid probe, which is more sensitive than Barr bodies.
What are the indications for Barr Bodies?
- This is an easy and cheap test.
- This screening test is for ambiguous genitalia (where the sex characteristics are unclear).
- It may be done for the delayed onset of puberty.
- This test may be used to diagnose Turner and Klinefelter syndromes.
- It helps in diagnosing sex chromosome abnormality.
What are the precautions for the Barr body sample?
- Don’t take the sample during the first week of a newborn’s life.
- Don’t take samples during the adrenocorticosteroids or estrogen therapy. This will lead to a decrease in the number of Barr bodies.
- Inadequate preparation may obscure the Barr chromosome bodies.
- 40% to 60% of the cells show identifiable Barr bodies.
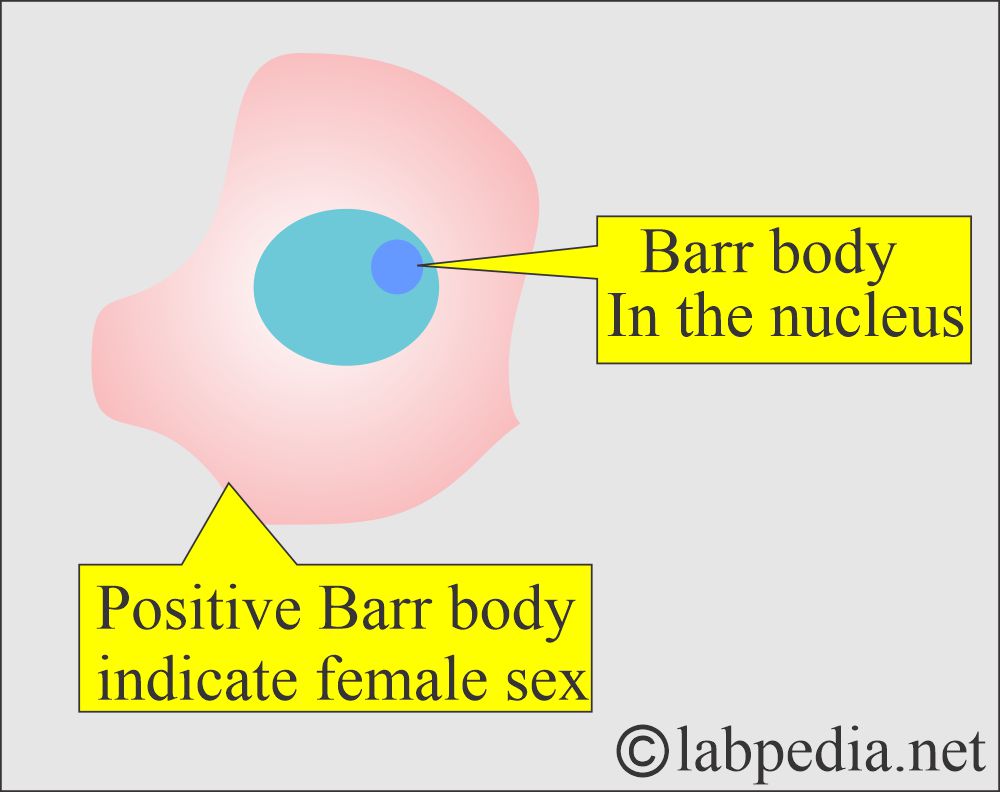
How will you define the Barr Bodies?
- Barr bodies and drumsticks both represents inactivated X chromosome in females where there are two XX chromosomes.
- Barr Bodies are used as a marker of the genetic sex or chromosomal abnormalities.
- Barr bodies or nuclear sexing is where buccal or vaginal smears are stained with cresyl violet and examined microscopically.
- A dense barr body on the nuclear membrane represents one of the X-chromosomes, occurring in 30% to 60% of females.
- Barr bodies are stainable structures.
- Barr bodies are present in the nucleus, and there are stainable sex chromosomes. The Barr body that appears for each X-chromosome.
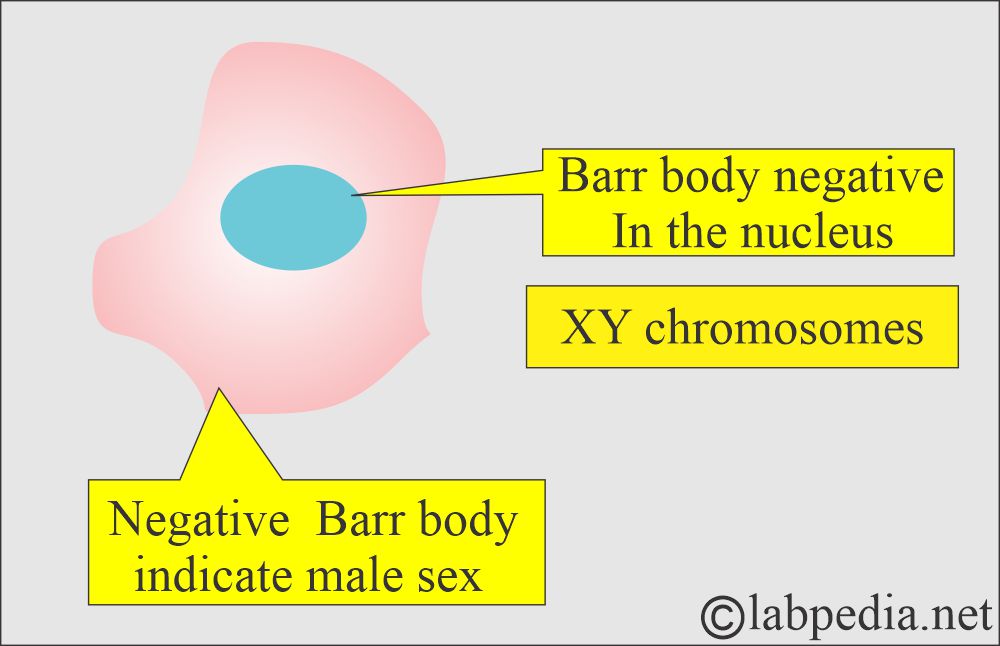
- Therefore, XX females will exhibit one Barr body, while males with XY chromosomes will display no Barr body.
- Therefore, if there are XXY, it will display two Barr bodies.
Discuss the history of the Barr Bodies?
- The Barr bodies are named after the discoverers, Murray Barr and E. C. C. Bertram, in the late 1940s.
- This is also called sex chromatin.
- Inactivated X chromosome is observable in many interphase cells as highly condensed intranuclear chromatin bodies, known as Barr bodies.
- The barr body is the inactive X chromosome in the female somatic cells.
- This is essentially a compact structure of the chromatin in the nuclei of female cells.
- The Barr body is a condensed form of chromatin, a dark-staining spot located at the periphery of the nucleus in each somatic cell of the human body.
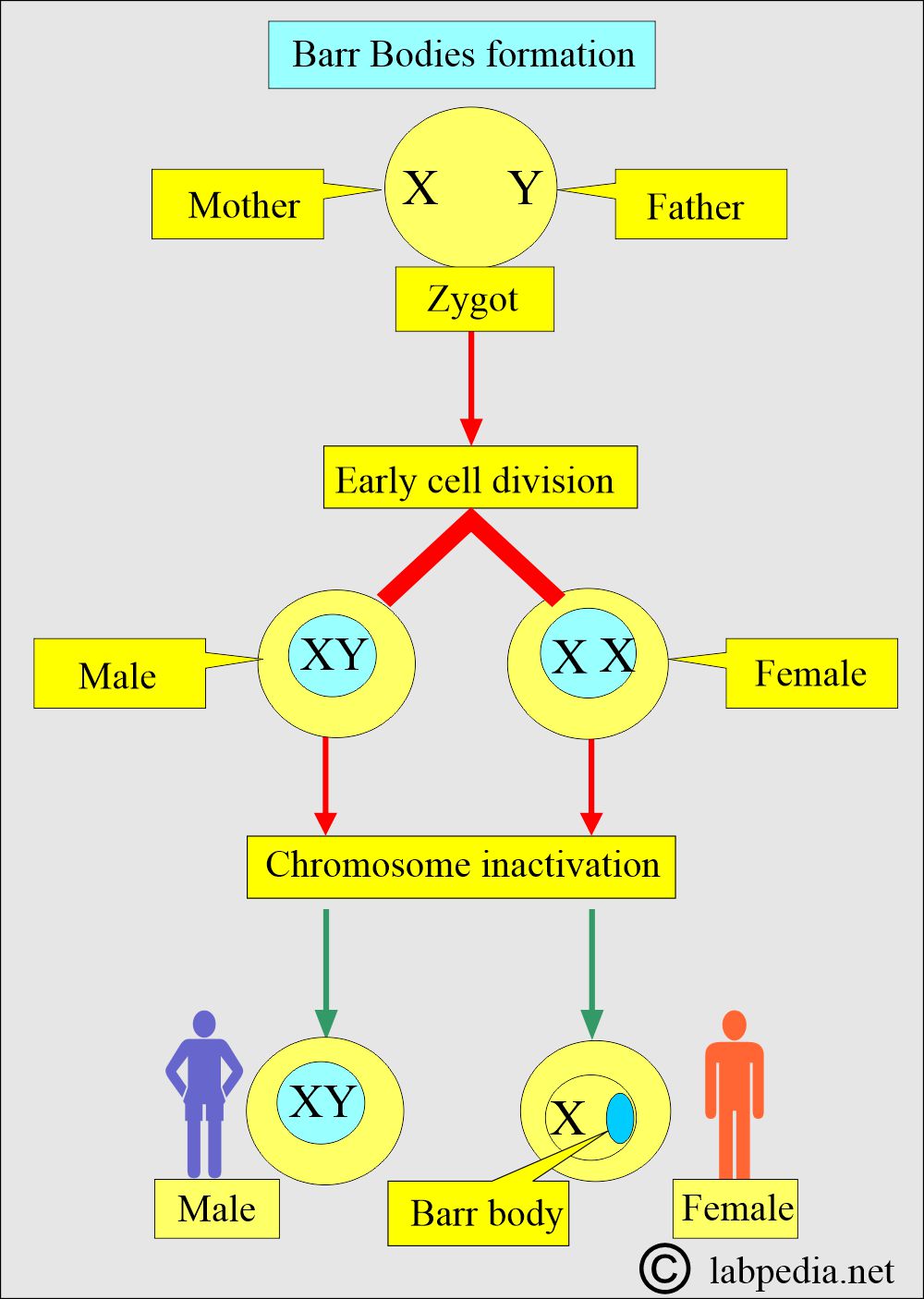
What is the mechanism of Barr Bodies Formation?
- This inactivation occurs very early in embryonic development, approximately 7 to 14 days after fertilization.
- One of the chromosomes, XX, specifically the X chromosome, is inactivated.
- Sometimes, one of the inactivated X chromosomes is donated by the father.
- The mother contributes to the other (X).
- This cell with an inactivated X chromosome gives the descendant the same structure.
- This helps determine sex where the infants’ physical features are unclear.
- Denver classification, total chromosomes are 46 in number:
- 22 pairs.
- One pair shows XX, indicating that it is female.
- Other pairs may show XY, indicating male.
- Therefore, the female XX chromosome has one Barr body and is considered chromatin-positive.
- While males have XY, so no Barr body, and are considered chromatin negative.
What are genetic abnormalities in both male and female?
- Most common abnormalities of X chromosomes.
- Normal female = XX, One X is active and other one becomes Barr body.
- Normal Male = XY, no Barr body because there is only one X chromosome.
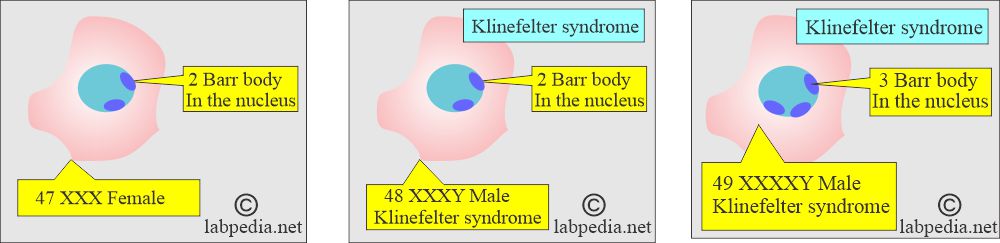
- Klinefelter syndrome = XXY, so there will be one bar body.
- Turner syndrome = XO, so no Barr body.
How will you perform the Procedure for Barr bodies?
- Take epithelial cells from the buccal mucosa or vaginal smear.
- Make a monolayer cell slide.
- Fix these cells with the fixative.
- Stain with cresyl violet.
- Examine under the microscope.
- There is a dense body (Barr body) on the nuclear membrane; it represents one of the X-chromosomes.
- This will be seen in 30% to 60% of the female somatic cells (other than the reproductive cells).
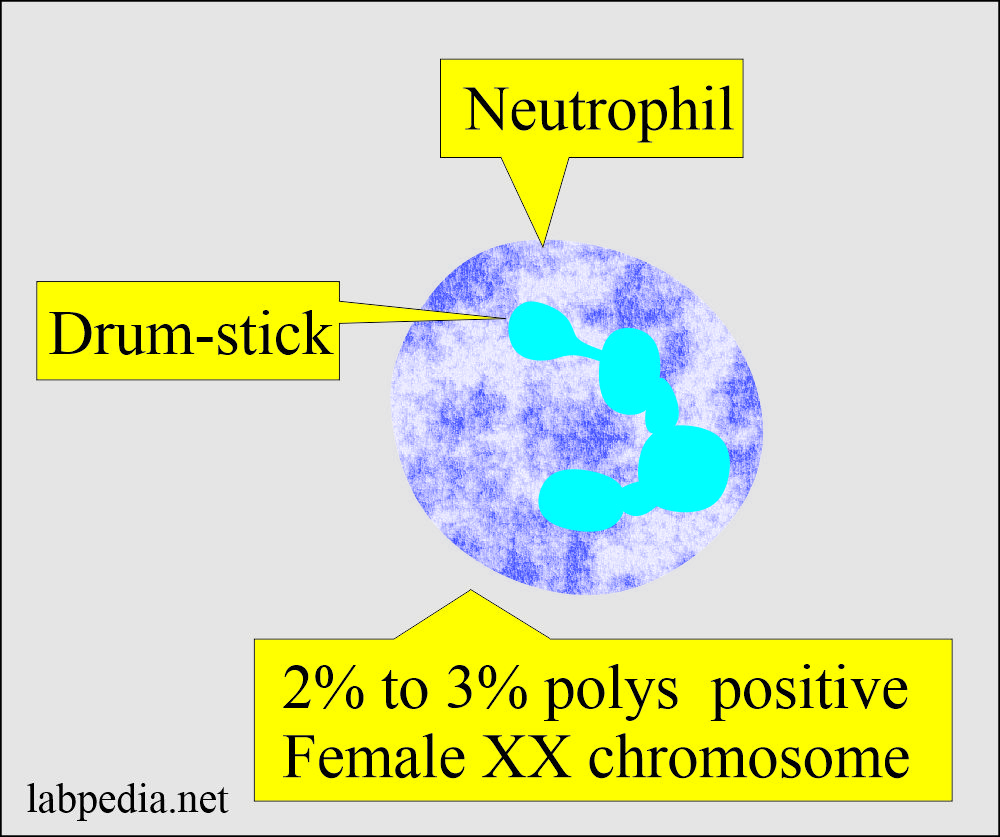
Drumstick in the neutrophils:
- The drumstick is the drum-shaped nuclear appendage seen in 2% to 3% of the neutrophils in females, indicating 2 X chromosomes. This can be confirmed by karyotyping.
- It is not found in males.
- There is a lower incidence of the drumstick in Klinefelter syndrome (XXY) as opposed to the extra barr body.
- Double drumsticks are exceedingly rare and have no diagnostic value.
Normal Barr Body
- Male = No barr bodies are seen.
- Female = Barr’s body is positive.
| Number of Barr bodies | Possible sex character |
|
|
|
|
|
|
How will you differentiate the Barr body and the drumstick?
| Characteristics | Barr body | Drumstick |
| Definition | Inactive one X chromosome | Nuclear projection in WBC |
| Gross features | It is a dense chromatin dot in the nucleus | Drumstick-like projection |
| Where to see | All female somatic cells | 3% to 5% of the female WBC |
| Differentiate male and female | Female (XX) only (male =XY) | Female only |
| Diagnostic value |
|
Cytological sex differentiation |
What is the normal value of Drumstick?
- Drumstick positive in females (2% to 3% of polys) indicates the presence of two X chromosomes.
- Drumstick negative in males.
- If <10% of cells contain the Barr Bodies in patients with female sex organs, chromosomal karyotyping is recommended to find any abnormality.
How will you interpret the Barr Body?
- This Barr body test is advised to screen ambiguous or doubtful sex characters.
Turner’s syndrome
How will you define Turner’s syndrome?
- Female (XO) will have no barr body.
- This is a chromosomal sexual abnormality in females.
- These patients have a single chromosome deletion, resulting in only 45 chromosomes instead of the normal 46 chromosomes.
- What are the clinical features of Turner’s syndrome?
- There is a deficiency of secondary sexual features and small genitalia.
- There may be a webbing of the neck, coarctation of the aorta, and short fingers.
- They don’t mensurate and usually lack ovaries.
- How will you diagnose Turner’s syndrome?
- Buccal smear for Barr bodies will be negative.
- If Barr’s body is positive, then advise chromosomal karyotyping, as these patients may have a mix of 50% positive and 50% negative cells for Barr’s bodies.
Klinefelter syndrome
How will you define Klinefelter syndrome?
- A male with (XXXY) will have a barr body.
- What is the clinical presentation of Klinefelter syndrome?
- The person appears to be male, but the chromosomes indicate an XXY or XXXY karyotype.
- Their external genitalia are normal, except for the presence of small testes.
- There are decreased body hairs, and may be gynaecomastia.
- There is a mental deficiency, but they may have normal intelligence.
- Mostly, these patients are sterile.
- How will you diagnose Klinefelter syndrome?
- The biopsy will confirm the diagnosis, showing atrophic semniferous tubules.
- Chromosomal karyotyping is the method of choice.
- Females with XXX chromosomes will have two barr bodies.
- The female cell with four X chromosomes has three barr bodies.
NOTE:
If needed, the result should be confirmed by chromosomal karyotyping.
Questions and answers:
Question 1: What precautions are needed for Barr bodies detection?
Question 2: What is the difference between Barr body and drumstick?

Thank you
Thanks
Thank you for your sharing.
You are welcome
can you please Explain some reasons why cytogenetic diagnosis using Barr body analysis may yield false positives results?
I have described the precautions. Also, it depends upon the cell slide preparation; if you make a thick smear, there are chances of a false-positive result. Rest in case of doubt; please go for chromosomal karyotyping.
I was told that I had fusial labia (actually up to age 6 where I could not use the restroom). I also looked ‘in between”. I was diagnosed as a transsexual in the early 1980s as a teenager but when I took a buccal smear when I was 17 it showed I had 2% of sex chromatin and that I may have a Y chromosone hidden somewhere. I was told then that all biological women were supposed to have 20% of sex chromatic where males had between 2% and 4%. What exactly does that mean and does that mean I could be intersex (given the labia fusion and looking in between genders and the low sex chromatin?) ? Thanks
I think you need to consult the physician. Also, it would be best if you did a chromosome analysis. Mapping the chromosomes will give a better idea about the presence or absence of chromosome Y. Also, that will decide the number of chromosomes as well.
Is the presence of barr body related to an individual’s intelligence quotient in any way?
(A zoology teacher told us that more the number of barr bodies, lesser the IQ- implying that females are supposedly less intelligent than men)
He may be right because mostly genetic abnormalities have an extra X-chromosome.
I was direly in need of this test. Thank you Professor (Sir) for your kindness posting it.
You are welcome, and thanks.