Alcohol and Its Complications
Alcohol and Its Complications
- Alcohol use is widespread in the Western world. Alcohol is easily available, and it is cheap as well. No doubt that there are so many side effects of alcohol.
What are the types of Alcohol complications?
- Social and financial.
- Health problems.
- Alcohol effects may be general or specific.
What are social and financial complications?
- Alcohol causes many social and family problems.
- Alcohol can lead to fights between husband and wife.
- Alcohol can change your behavior, and you may be rude to the neighbors and working fellows.
- Alcohol is the major cause of accidents.
- Alcohol can drain your finances.
- The economic impact is estimated to be >$ 100 billion per year regarding lost wages and productivity.
- Alcohol’s frequent use will make you unsocial.
- It is estimated that 80,000 Americans die because of alcohol every year, directly or indirectly due to alcohol abuse.
What are the health problems?
There are so many health issues. I will discuss them one by one.
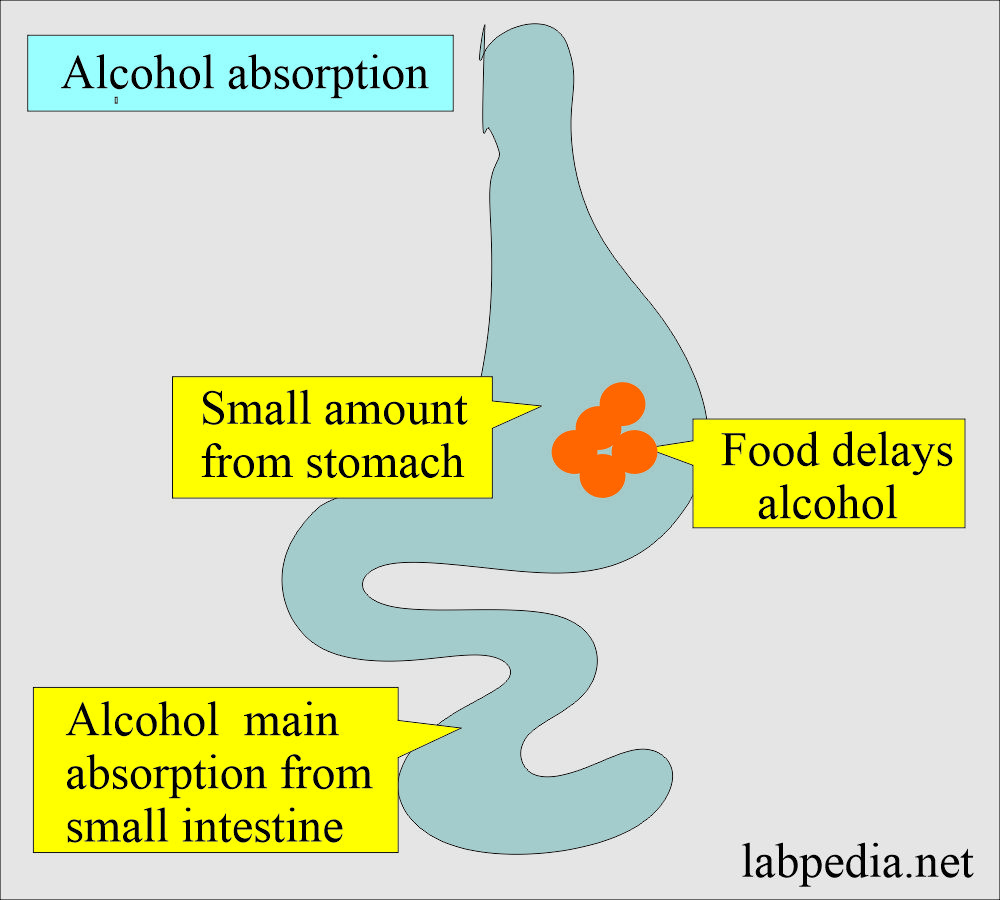
How is Alcohol absorbed?
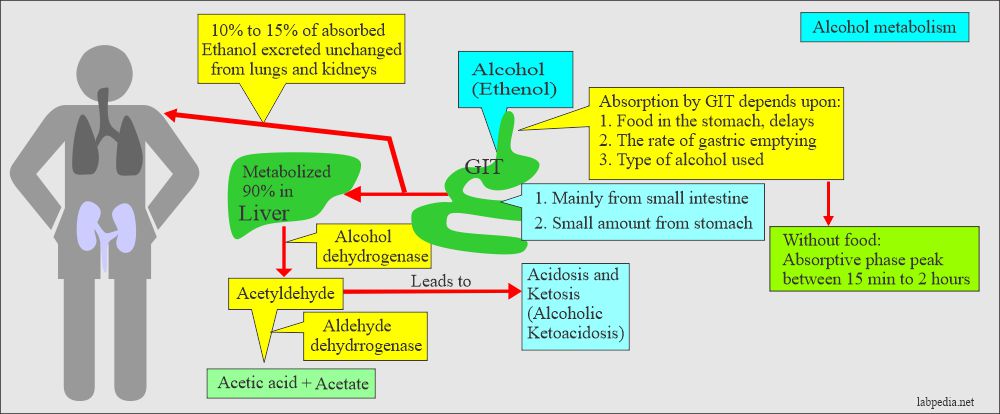
- Alcohol is absorbed from the small intestine and a small amount from the stomach. Food will delay the absorption of alcohol.
- Without food, alcohol is absorbed in just 15 minutes, and this absorption may even delayed to 2 hours.
- 50% show peak in 30 minutes and 75% in 60 minutes (within 40 to 70 minutes on an empty stomach). The maximum late absorption may be 2 hours in a few cases.
- The liver metabolizes 75% of the absorbed alcohol to acetaldehyde.
- Once the peak level is achieved then, its excretion (disappearance) is linear (15+5 mg/dL/hour).
- 15% is excreted unchanged through the kidneys and lungs.
- Alcohol intoxication will lead to:
- Disorientation.
- Confusion.
- Euphoria.
- Euphoria will progress into unconsciousness, and paralysis and a rising alcohol level will lead to death.
- Alcohol causes a depressant effect on the central nervous system.
- Ethanol depresses the CNS and ultimately may lead to coma and death.
| The alcohol concentration in the blood | Affect on the body |
| <50 mg/dL | Euphoria and decreased inhibitions |
| 100 to 300 mg/dL | Incoordination and decreased orientation |
| >400 mg/dL | Coma and death |
- CNS dysfunction is more pronounced when:
- Absorptive phase: Ethanol concentration in the blood is increasing.
- Elimination phase: When the level of alcohol is declining.
- Alcohol causes diuresis by inhibiting the secretion of the ADH (antidiuretic hormone) by the posterior pituitary.
- It also inhibits oxytocin secretion because this property is used to stop uterine contractions in premature labor.
- Alcohol blood concentration level of 100 mg/dL has been established to limit car/truck driving in most states in the United States.
The Normal Level Of Alcohol And Interpretations:
| Clinical interpretation (Blood alcohol level) | Level of the alcohol in the blood |
| Negative | Not detected in the blood |
| Considered negative | <10 mg/dL |
| Considered negative by the USA transportation | <20 mg/dL |
| Considered positive | >40 mg/dL |
| Considered drunk driver (in most states) | >80 mg/dL |
| Toxic level | |
| The toxic level of ethanol | >100 mg/dL |
| Fatal level of ethanol | >300 to 400 mg/dL |
| The toxic level of methanol | >20 mg/dL |
| The toxic level of isopropanol | >40 mg/dL |
What is the effect of Alcohol on pregnancy?
- Alcohol used during pregnancy leads to fetal alcohol syndrome.
- The ancient Greeks made a law that a pregnant lady should not drink alcohol. It is found that alcohol, even wine and beer, can lead to certain congenital disabilities.
- A glass of wine may lead to fewer chances of making a baby.
- Everyone has a different tolerance for alcohol; the best way is to avoid alcohol during pregnancy until their babies are born.
- The lady taking even beer, 60% of the ladies become infertile compared to ladies not drinking wine or beer.
- Studies show that a lady taking even one glass or less has a 30% lower chance of becoming pregnant.
- Alcohol also affects men by lowering their testosterone levels, and sperm are unhealthy.
What is the effect of alcohol on sleep?
- Alcohol is the most common cause of sleep disturbance.
- At night, instead of the alcohol, take the milk for better sleep.
What is the effect of Alcohol on the brain?
- Some people believe that alcohol is poison for the brain.
- Alcohol causes damage to the brain cells.
- Drinking a significant amount of alcohol can lead to significant loss of memory.
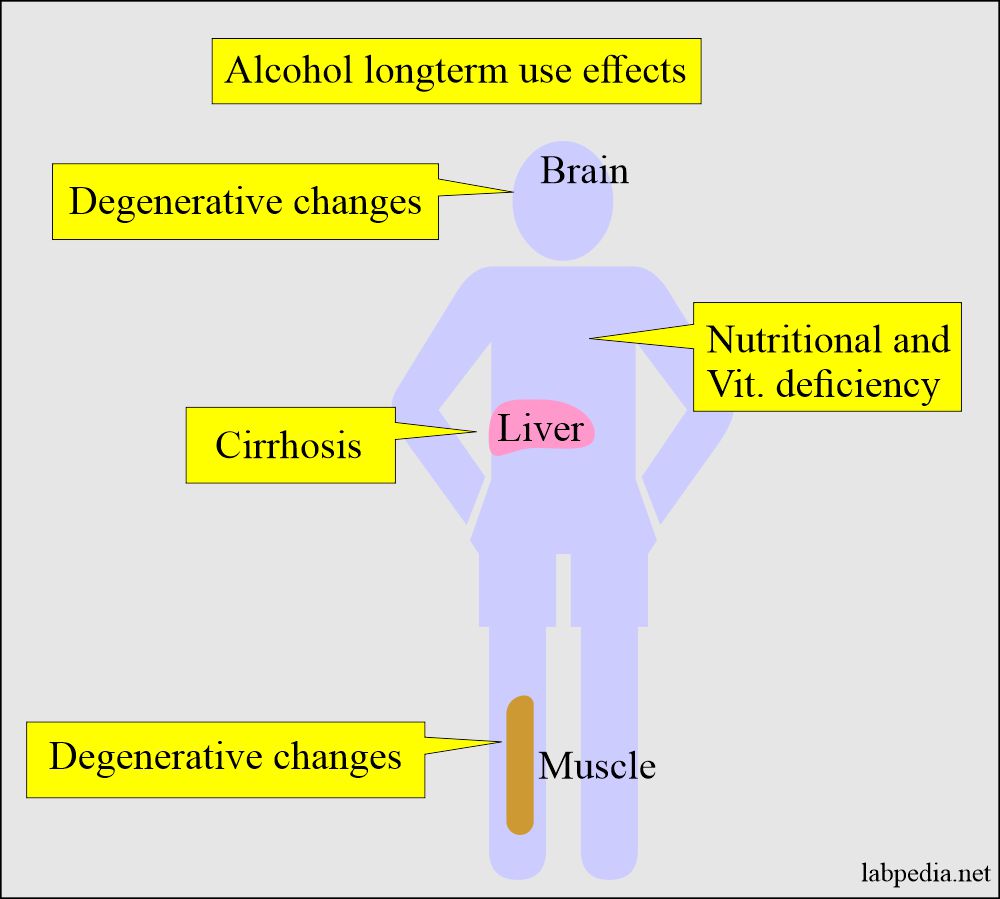
What is the summary of the complications of alcohol?
- Cirrhosis of the liver.
- The degenerative changes in the brain.
- Dementia.
- Depression.
- Seizures like epilepsy.
- Alcoholic neuropathy.
- The degenerative changes in the skeletal muscles.
- Chronic alcoholics may have nutritional and vitamin deficiencies.
- Anemia.
- Cancers.
- Cardiovascular diseases.
- Gout.
- Hypertension.
- Increased risk for infections like tuberculosis, HIV, and pneumonia.
- Gastritis and pancreatitis.
How will you assess the alcoholics?
You can advise the following tests to evaluate the damage caused by alcohol.
- Gamma GT (GGT) = It increases before the onset of pathologic changes.
- AST (SGOT) = It will increase in case of liver cell injury.
- ALT (SGPT) = It is more specific for the liver cell injury.
- HDL = It may be increased in small amounts of use.