Acute Phase Protein:- Alpha-1-Antitrypsin (α1-antitrypsin)
Alpha-1-Antitrypsin
Acute Phase Protein
Acute-phase protein (Acute Phase Reactants)
- Acute-phase protein is raised in inflammatory conditions.
- When there is an increase in a protein called positive acute-phase protein.
- In the case of a decrease in the acute phase protein, it is called the negative phase protein.
- The acute phase proteins (positive) are proteins whose concentration increases in the plasma, and after the disease episode is over, it decreases and may become normal.
Alpha-1-antitrypsin (AAT, α1-antitrypsin)
Sample for Alpha-1-Antitrypsin
- It is done in the patient’s serum (collect 5 to 10 ml of blood).
- Serum electrophoresis may be advised.
Indications for Alpha-1-Antitrypsin
- In case of a family history of emphysema.
- Advised in children with cirrhosis and liver diseases.
- Advised for acute inflammation, infection, or malignancy (non-specific test).
- Drugs like oral contraceptives increase the AAT level.
Precautions for Alpha-1–antitrypsin (AAT, α1-antitrypsin)
- Serum level of AAT increases during pregnancy.
Definition of Alpha-1-Antitrypsin
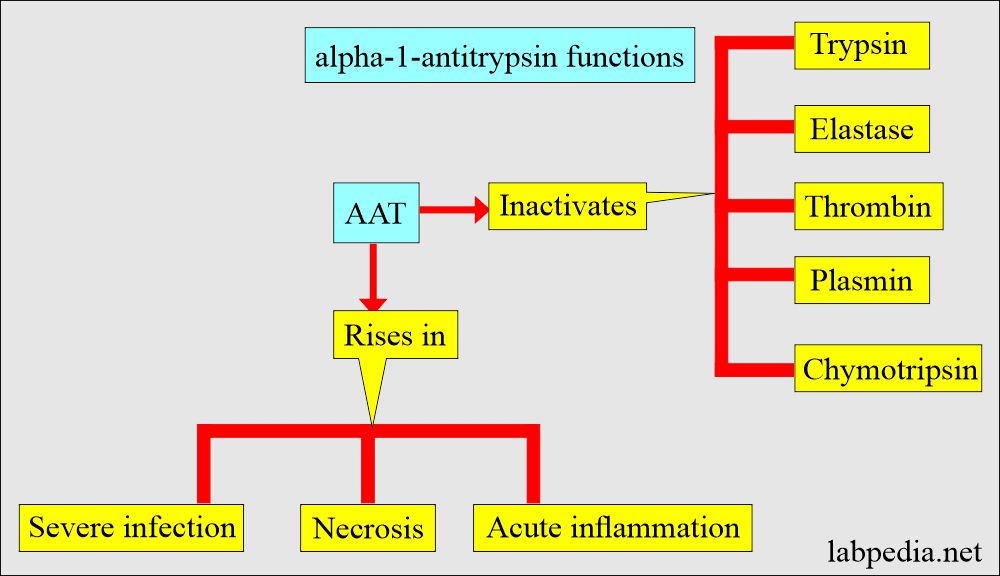
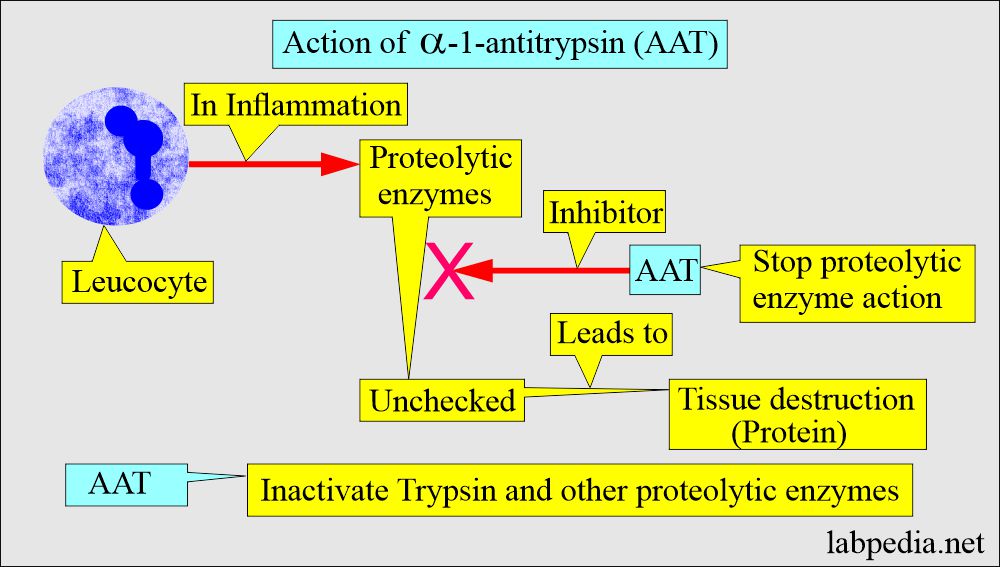
- Alpha-1-Antitrypsin (AAT) is a serine protease inhibitor that inactivates trypsin, but its important function is the inactivation of neutrophil elastase that breaks down the elastic fiber and collagen.
- Alpha-1-Antitrypsin is an autosomal recessive deficiency.
- It is located on chromosome 14.
- It is a serine protease inhibitor.
Pathophysiology of Alpha-1-antitrypsin (AAT, α1-antitrypsin)
- This is a naturally occurring protease inhibitor.
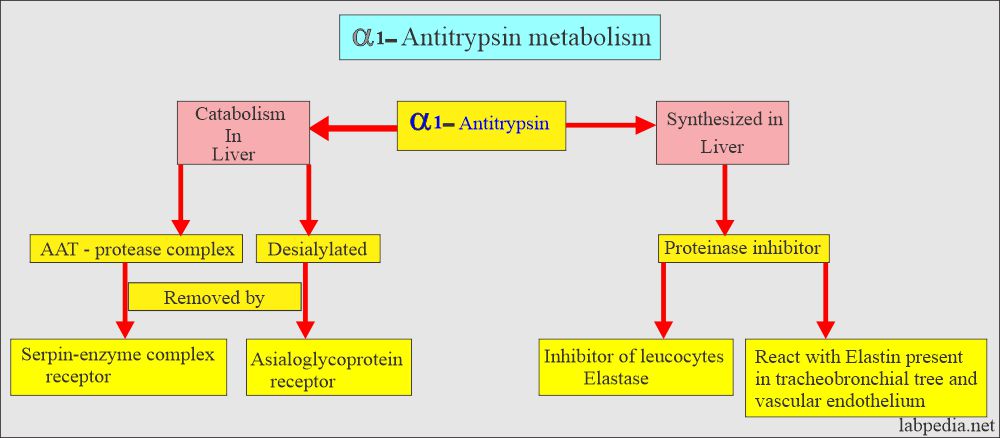
- This is synthesized and catabolized in the liver.
- Alpha-1-Antitrypsin (AAT) is synthesized in the liver.
- It comprises 90% of the globulins that migrate on electrophoresis in the alpha-1 region.
- This is an important inhibitor of neutrophil elastase that is produced in phagocytosis by these cells.
- This enzyme reacts with elastin in the tracheobronchial tree and vascular endothelium.
- This enzyme prevents the loss of elastic tissue function.
- The Alpha-1-Antitrypsin (AAT) deficiency has been associated with two different diseases:
- Pulmonary emphysema in adults is relatively common.
- Cirrhosis in children is relatively rare.
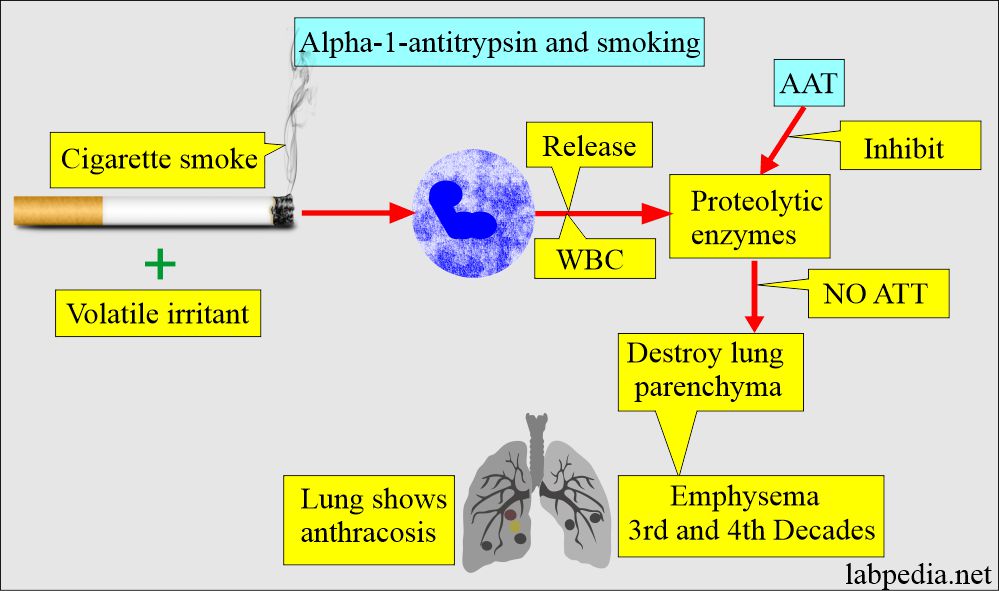
- Its deficiency leads to premature emphysema.
- Its concentration increased much to fold in acute inflammation. It is increased in:
- Acute inflammatory disorders.
- Chronic inflammatory disorders.
- Stress.
- Any infection.
- Thyroid infection.
- Cigarette smoke and volatile irritants lead to the release of proteolytic enzymes from the white blood cells.
- This is a disease called AAT deficiency, which is an inherited condition.
- This disease can transfer from parents to children.
- ATT is a protein that protects the lung. It is formed in the liver.
Signs and symptoms of Alpha-1-Antitrypsin (AAT) deficiency:
- There is tiredness.
- There is weight loss.
- Repeated lung infections.
- There is shortness of breath and wheezing.
- There may be a vision problem.
- There may be tachycardia on standing.
- This is increased in acute and chronic inflammation.
Normal level of Alpha-1–antitrypsin (AAT, α1-antitrypsin)
- Newborn = 145 to 270 mg/dL.
- Adult = 78 to 200 mg/dL.
- Adult > 60 years = 115 to 200 mg/dL.
- Serum electrophoresis showed 90% of ATT in the α1-globulin.
- Another source:
- 85 to 213 mg/dL (0.85 to 2.13 g/L).
- Another source:
- 100 to 200 mg/dL (18.4 to 36.8 µmol/L) by nephelometry.
Alpha-1-Antitrypsin (AAT) is decreased in:
- The level is typically <50 mg/dL.
- Severe liver diseases.
- Malnutrition.
- Prematurity.
- Renal losses like nephrosis.
Normal level of Alpha-1–antitrypsin (AAT, α1-antitrypsin)
- Newborn = 145 to 270 mg/dL.
- Adult = 78 to 200 mg/dL.
- Adult > 60 years = 115 to 200 mg/dL.
- Serum electrophoresis showed 90% of ATT in the α1-globulin.
- Another source:
- 85 to 213 mg/dL (0.85 to 2.13 g/L).
- Another source:
- 100 to 200 mg/dL (18.4 to 36.8 µmol/L) by nephelometry.
Alpha-1–antitrypsin decreased in the following:
- The level is <50 mg/dL.
- Emphysema of the lungs.
- In severe liver diseases.
- Malnutrition.
- Prematurity.
- Renal losses in nephrosis.
- G I losses have been seen in pancreatitis and protein-losing diseases.
- Exudative dermatopathy.
Alpha-1–antitrypsin (AAT) increased in the following:
- Acute and chronic infections, as an acute phase protein.
- In malignancies like cervical cancer and lymphoma.
- Use of birth control tablets.
Test value for the layman:
- In the case of patients with emphysema.
- In children, if they develop cirrhosis or liver diseases.
Questions and answers:
Question 1: What is the role of Alpha-1–antitrypsin (ATT) deficiency?
Question 2: What is the role of Alpha-1–antitrypsin (AAT)?