Acid phosphatase and Prostatic phosphatase
Acid phosphatase and Prostatic phosphatase
What sample is needed for Acid phosphatase and Prostatic phosphatase?
- It is done on the patient’s serum, and tests are performed within one hour.
- How to get good serum: Take 3 to 5 ml of blood in a disposable syringe or a vaccutainer. Keep the syringe for 15 to 30 minutes and then centrifuge for 2 to 4 minutes to get the clear serum.
- The serum should be separated immediately from the RBCs and stabilized by adding disodium citrate monohydrate (10 mg/ml of the serum).
- Add acetic acid (5 mol/L) or 50 µL for 1 ml of the serum. This will lower the serum’s pH to 5.4, where the sample is stable.
- With all these precautions, the serum is stable at 37 °C (at room temperature) for several hours and one week if the serum is kept in the fridge.
- EDTA plasma is better because it stabilizes the acid phosphatase.
- A morning sample is preferred.
- The sample is stable for 24 hours at 2 to 8 °C.
- Try to do the test immediately.
- The enzyme will stabilize if serum is acidified below a pH of 6.5.
What Precautions are needed for Acid phosphatase and Prostatic phosphatase?
- Avoid hemolysis.
- It has poor stability in whole blood.
- ACP is unstable at room temperature >37 °C.
- Serum left at room temperature and exposed to air will decrease the acid phosphatase by even one hour.
- ACP is unstable if the pH is >7.0.
- The serum is separated immediately, and the test is performed within one hour.
- Or refrigerate the sample immediately.
- EDTA plasma is preferred because it stabilizes the AP.
- Avoid prostatic massage in the last 48 hours.
- Rectal examination, prostatic massage, urinary catheterization, or instrumentation of the prostate in the previous 2 days before the test may give false high values.
- Hemolysis falsely raised the value and should be rejected.
- The lipemic serum also gives a false value.
- 50% of the activity is lost if kept at room temperature.
- Drugs leading to elevated AP levels are:
- Androgens in females.
- Clofibrate and antilipiodemic drugs.
- Specimen received >15 minutes after the collection, and the hemolyzed sample gives false values.
What are the Indications for Acid phosphatase and Prostatic phosphatase?
- Diagnosing prostatic carcinoma requires advising the estimation of total acid phosphatase and the prostatic component.
- This test is more accurate in diagnosing advanced prostatic cancer than the early diagnosis.
- These two enzymes stage prostatic carcinoma and monitor the effectiveness of treatment.
- The test for acid phosphatase can be done on a vaginal swab in rape cases because the seminal fluid is rich in acid phosphatase.
- Acid phosphatase levels in rape cases peak between the first 12 hours and remain increased till <4 days.
How will you define Acid phosphatase?
- Acid phosphatase is a hydrolytic enzyme secreted by various cells.
- Acid phosphatase has five isoenzymes.
- The maximum amount is found in the semen (prostate).
- Acid phosphatase is also found in bone, liver, spleen, kidneys, RBCs, and platelets.
- Types of Acid phosphatase:
- Prostatic acid phosphatase.
- Bone acid phosphatase.
- Liver and spleen acid phosphatase.
How will you discuss the pathophysiology of Acid phosphatase and Prostatic phosphatase?
- Acid phosphatase (AP) includes all phosphatases with optimal activity below a pH of 7.0.
- The prostatic AP has an optimum pH range of 5 to 6.
- AP is unstable at temperatures>37 °C and pH levels>7.0.
- The prostatic AP in serum is labile and may lose >50% of the AP in one hour at room temperature.
- If you pacify the serum to a pH <6.5, it will stabilize the enzymes.
- Prostatic acid phosphatase (PAP):
- It is a tumor marker.
- When raised, it indicates metastatic prostatic carcinoma.
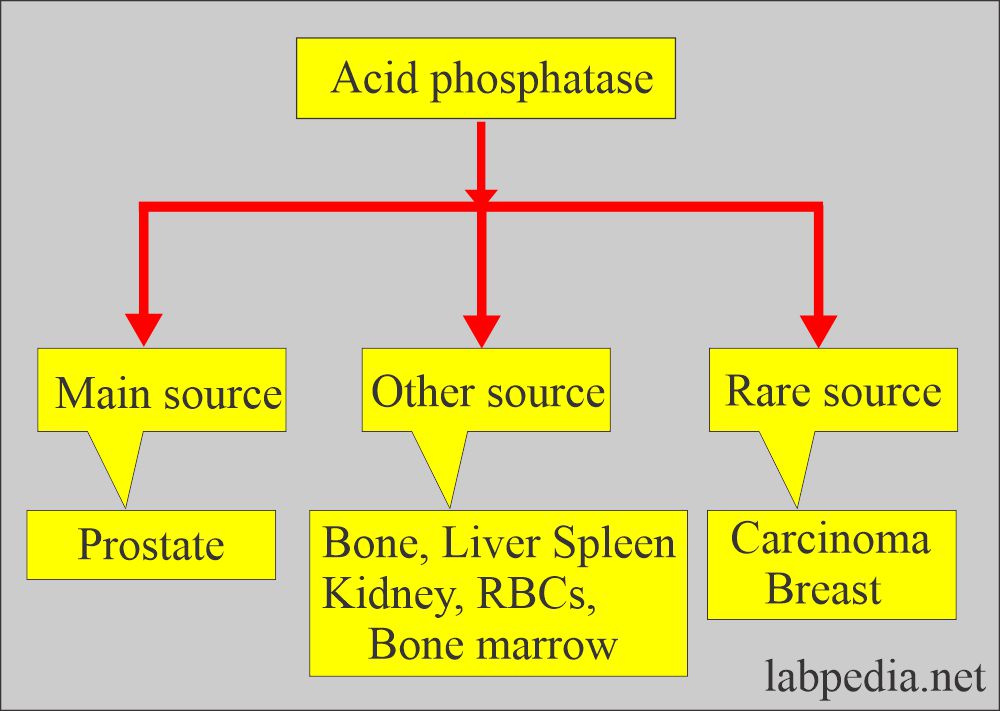
What are the sources of Acid Phosphatase?
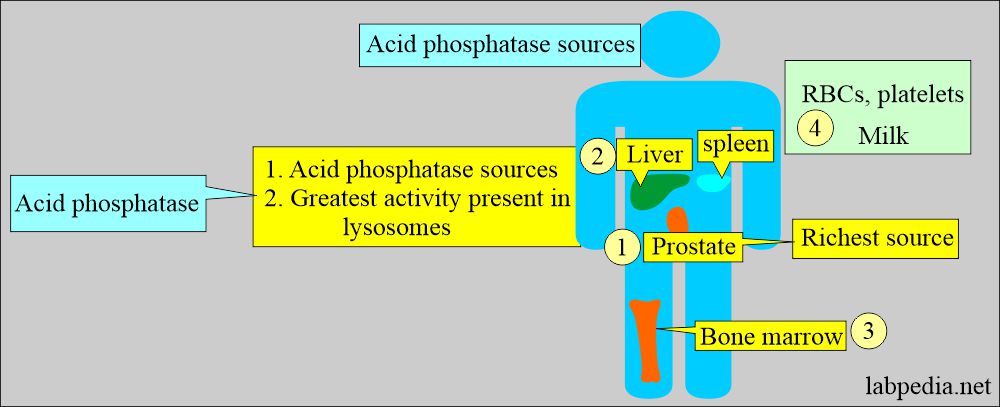
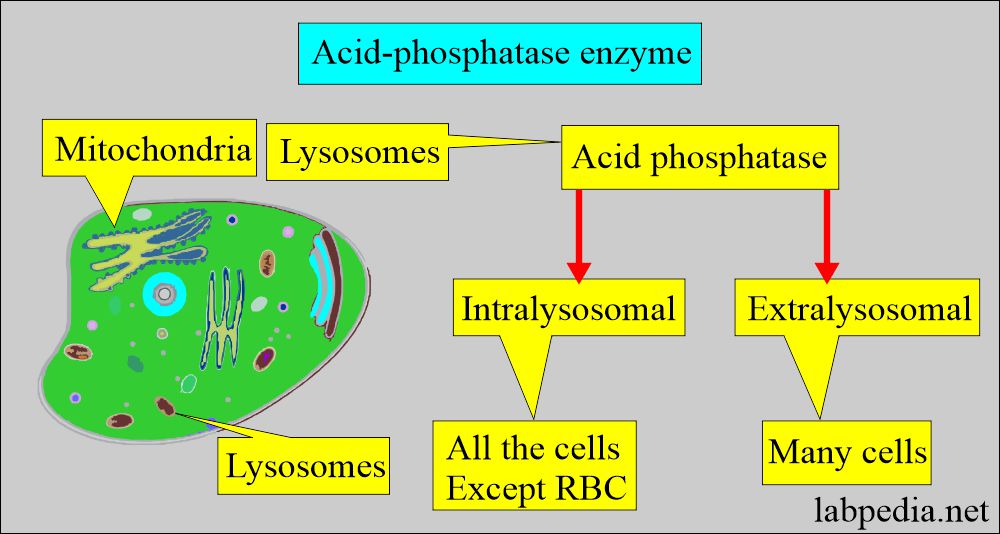
- Acid phosphatase enzymes are found in various tissue lysosomes like the Prostate, bone, kidney, platelets, semen, liver, and spleen, except RBCs.
- The prostate is the richest source. The majority of AP arises from the RBCs and prostatic tissue.
- Extralysosomal AP is also found in many cells.
- High levels are also found in white blood cells, such as monocytes and lymphocytes.
- Total acid phosphatase consists of a one-half prostatic component and the rest of the liver, disintegrating platelets and RBCs.
- The prostate has 100 times more acid phosphatase activity than other tissues, so it is the richest source.
- Acid phosphatase (AP), derived from the prostate, has an optimum pH range of 5 to 6.
- All phosphatases have optimal activity below a pH of 7.0
The difference in activity between acid phosphatase and alkaline phosphatase as regards pH:
| Acid phosphatase | Alkaline phosphatase | |
| pH | At pH 5.0 = Optimum reaction | At pH>7.0 = Optimum reaction |
- As the prostatic component (PAP) is not raised in early prostatic diseases, this is not a good screening enzyme.
What is the significance of Acid-phosphatase?
- Acid phosphatase is a lysosomal enzyme, so the prostatic enzyme is found in the lysosome of the prostatic epithelium and is a glycoprotein.
- Once prostatic cancer spreads, AP’s level rises significantly when there is metastasis, particularly in the bone.
- The raised level in 80% of the patients with metastasis is age-related.
- It is raised in Prostatic carcinoma, particularly its prostatic component.
- Total AP is raised in Bone diseases.
- Prostatic acid phosphatase needs to be differentiated from non-prostatic sources like RBCs source.
- Total AP = AP after tartarate inhibition = Prostatic AP.
- Some of the inhibitors discriminate between prostatic and nonprostatic AP.
- Prostatic AP is inhibited by the dextrorotatory tartrate ions when there is no action on the RBC isoenzyme AP.
- RBC AP is inhibited by formaldehyde and cupric ions, whereas prostatic AP is resistant.
What are the Normal values of Acid phosphatase and prostatic component?
- Total acid phosphatase
- 2.5 to 3.7 ng /mL or 2.5 to 3.7 µg/L.
- or less than 3.0 mg /L.
- Prostatic acid phosphatase = <2.5 ng/mL (0 to 0.6 U/L).
- Another reference:
- Adult 0.13 to 0.63 units/L at 37 °C
- or 2.2 to 10.5 units/L (SI units).
- Child 8.6 to 12.0 units/mL at 30 °C.
- Newborn 10.4 to 16.4 units /mL at 30 °C.
- Another source:
- Prostatic AP = 0 to 0.6 U/L.
- RIA = 3 µg/L.
- Immunoassay = <20 µg/L.
What causes Moderately raised Acid phosphatase levels other than prostatic carcinoma?
- Niemann-Pick disease.
- Gaucher’s disease.
- Prostatitis and Benign prostatic hyperplasia ( BPH ).
- Urinary retention.
- Any cancer that has given metastasis to the bones.
- Myeloid Leukemia.
- Multiple myelomas.
- Paget disease.
- Sickle cell anemia.
- Renal diseases.
- Liver diseases like cirrhosis.
- Thrombocytosis.
- Hyperparathyroidism.
What are the causes of the raised level of Acid phosphatase?
- Significantly raised level seen in prostatic carcinoma.
- Benign prostatic hyperplasia. It is seen in 5% to 10% of the cases.
- Prostatitis.
- Prostatic infarct can increase Acid phosphatase levels for a short time.
- Metastatic carcinoma of the prostate.
- Metastases to the bones.
What is the variation of Acid phosphatase in the case of carcinoma prostate?
- AP values vary according to the methodology, such as RIA and immunoassay.
- The level of AP is related to the clinical staging of prostatic carcinoma.
- 5% to 10% of prostatic carcinoma confined to the prostate has an elevated level of AP.
- 20% to 25% of prostate carcinomas show elevated values with the extension of prostatic adenocarcinoma outside the prostate capsules without distant metastasis.
- 75% to 80% of the cases show elevated AP with bone metastasis.
What is the significance of acid phosphatase for prostatic carcinoma?
| Stage of the prostatic carcinoma | % positivity | Acid phosphatase level |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
How will you compare Acid phosphatase/PSA according to the stage of prostatic carcinoma?
| Clinical stage of prostate cancer | Acid phosphatase levels raised | Prostatic specific antigen (PSA) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
What are the Important facts about the acid phosphatase?
- After the surgery, its level will drop in 3 to 4 days.
- With estrogen, therapy takes 3 to 4 weeks to drop the level.
- Acid phosphatase is not recommended for prostatic carcinoma screening because its level is not usually significantly raised until the tumor metastases.
- Acid phosphatase is not advised in routine to diagnose prostatic carcinoma, in case the following parameters are recommended:
- Per-rectal digital examination.
- Transurethral ultrasound image.
- Histologic examination of the prostatic biopsy.
- Total body scan.
- The Prostatic specific antigen is advised.
What is the medicolegal importance of acid phosphatase?
- There is a high concentration of AP in the semen, so its measurement is important in rape cases.
- Take the vaginal swab, keep it in 2.5% of broth, and store it at 4 °C or room temperature.
- Result: In noncoital ladies, its value is 10 U/L, and in the coital lady is >50 U/L.
- However, PSA is more specific and sensitive than acid phosphatase.
What is the importance of acid phosphatase for layman?
- This test is advised for the diagnosis of prostatic cancer.
- It can be advised in case of rape on the vaginal swab.
Questions and answers:
Question 1: What is the value of prostatic phosphatase for the diagnosis of prostatic carcinoma.
Question 2: What is the pH for the acid phosphatase activity.

Fantastic
Thanks.
The figures’ subtitles say Alkaline phosphatase instead of Acid Phosphatase
Thanks, corrected.
What about acid phosphatase in sarcoidosis?
Particularly hepatic one!!
Acid phosphatase’s primary source is the prostate. I do not think acid phosphatase has any diagnostic value in sarcoidosis, particularly if the liver is involved.
good job.