Bone Marrow Trephine biopsy (Bone biopsy) Part 2
Bone Marrow Trephine biopsy
What sample is needed for a Bone Marrow Trephine biopsy?
- The bone marrow is aspirated, and a trephine bone biopsy is taken.
What are the indications for bone marrow biopsy?
Bone marrow aspiration and biopsy are advised in the following ways:
- To confirm the megaloblastic anemia.
- To confirm the diagnosis of Leukemia.
- To confirm the diagnosis of multiple myeloma.
- It is advised in bone marrow hypoplasia.
- This can be done for the culture of the organism.
- For the diagnosis of metastatic infiltrate.
- To diagnose bone disorders, such as Paget’s disease and bone cancer.
- Bone tumor-like osteoma can be diagnosed.
- This can give an idea about osteomalacia or osteoporosis.
- Metastatic cancer infiltrates from the lung, breast, prostate, or any other organ.
- To differentiate benign lesions of the bone, such as a benign cyst.
- To find the causative agent of osteomyelitis.
- To diagnose chronic bone pain in a specific area.
- To evaluate any abnormality seen on X-ray.
What are the precautions for bone biopsy?
- Stop the blood-thinning medicines (aspirin, warfarin, etc.)
- Avoid bone biopsy in pregnant women.
- Stop all medication, even including herbal medicine, which may thin the blood.
- Ask about any allergy to anesthetic drugs.
What are the complications of Bone Marrow Trephine biopsy?
- Sometimes the needle may break into the bone.
- Rarely is there a bone infection.
- There may be local hemorrhage or bleeding.
- There may be an injury to the nerve or blood vessels.
How will you perform bone biopsy?
- This procedure is the same as Bone marrow aspiration; a Trephine biopsy is done to take bone tissue.
- Local anesthesia is applied.
- This gives more information about the abnormalities of bone marrow cellularity and is more helpful for diagnosing Aplastic marrow.
- Adequate bone biopsy measures around one inch.
- Before putting it into formalin, make touch preparation.
- Put this biopsy into buffered formalin.
- It needs fixation for 12 to 24 hours.
What tests are done on bone marrow and bone biopsy?
- Bone marrow smears and touch preparation may be stained by the Wright-Giemsa stain.
- A special stain, such as Prussian blue, is used for iron.
- Paraffin sections are stained with hematoxylin-eosin, PAS stain, and a reticulin stain.
- Can do immunochemistry and molecular diagnostics.
- Flow cytometry was also performed.
- Molecular genetics studies are done for:
- PCR for detection of viral DNA and RNA.
- Fluorescent in-situ hybridization (FISH).
- Detection of the chromosomal abnormalities.
- Bone marrow/biopsy material may be used for culture.
- Can do electron microscopy (E/M).
- Can do tissue culture.
What is the interpretation of the Bone marrow?
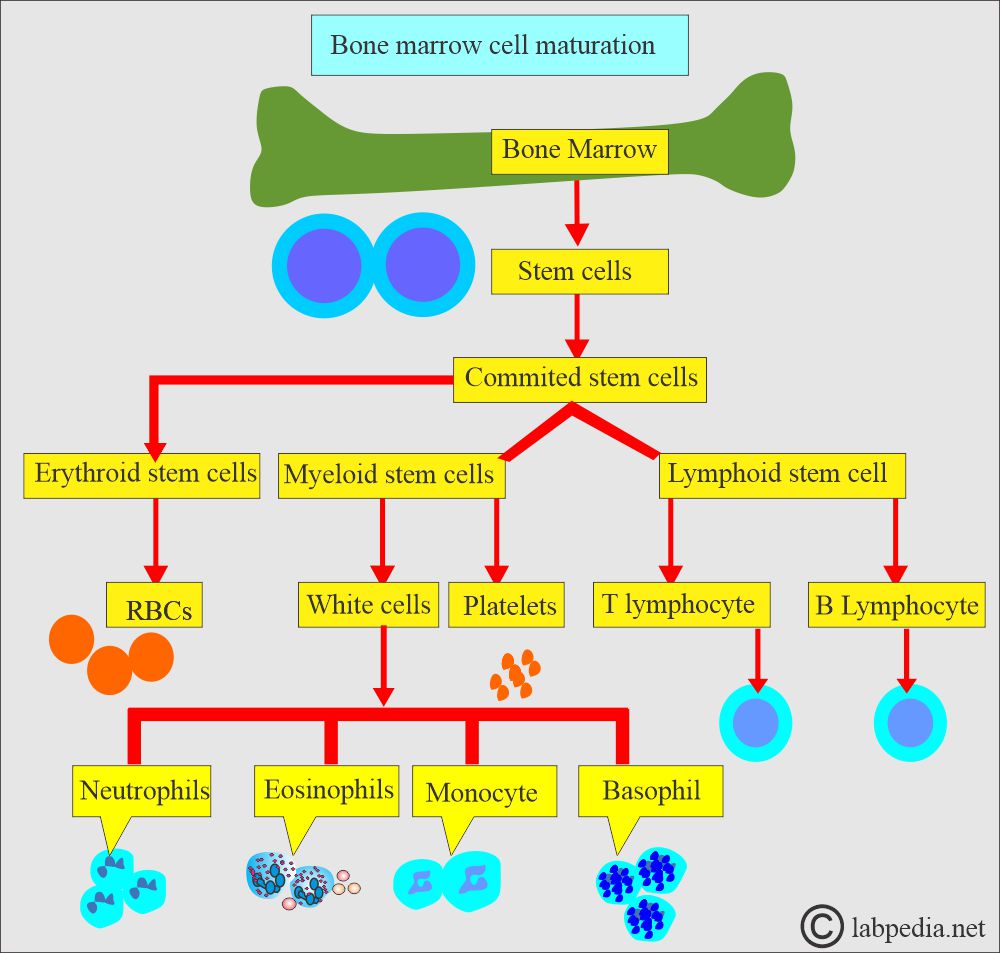
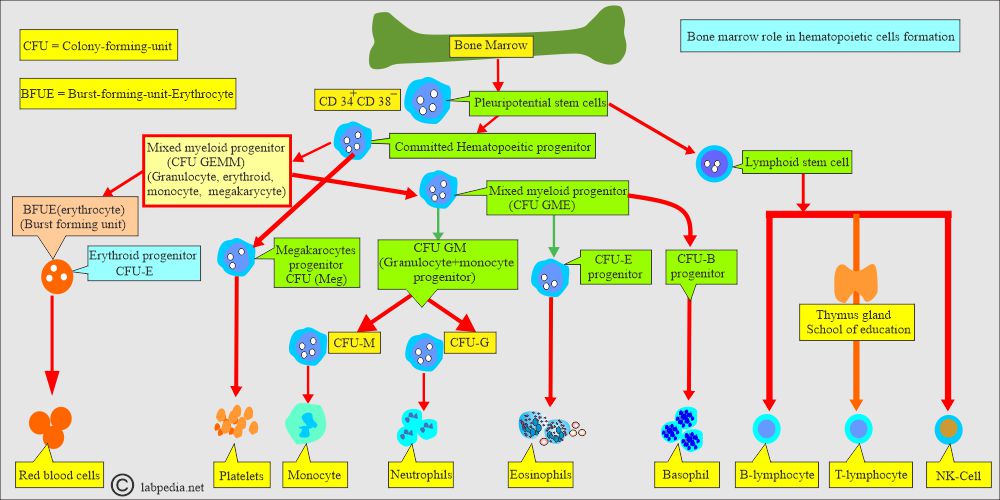
- Myeloid, erythroid, megakaryocytes, and lymphoid series cells.
What will you see in normal bone marrow?
- Cellularity to fat ratio at birth = 100%.
- It declines ∼10% each decade.
- Young children = 9:1.
- Young adults = 2:1.
- Middle-aged = 1:1.
- In old people, it gradually decreases = 1:9.
- Bone marrow stainable iron = It is seen in reticuloendothelial cells and normoblasts or sideroblasts.
- Flow-cytometry = It will differentiate:
- T- lymphocytes and B-lymphocytes.
- Degree of maturation as pre-B or mature B-lymphocytes.
- Detects the presence of cytokines or other receptors.
- Please see more details in the Bone marrow examination.
What is the difference between bone marrow aspiration and trephine biopsy?
| Feature | Bone marrow aspiration | Bone marrow trephine biopsy |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Questions and answers:
Question 1: What stain can be done on bone biopsy?
Question 2: Why bone biopsy is done?