Mycobacterium Tuberculosis:- Part 4 – AFB Stain (Acid Fast Bacilli Stain), Procedure and Interpretations
AFB Stain (Acid Fast Bacilli stain)
What sample is needed for AFB stain?
- This can be done on any sputum sample, fluids, tissue, and urine.
- For the sputum, advise consecutive three samples to rule out Tuberculosis.
- Early morning sputum is preferred, and the minimum volume accepted is 2mL.
- Bronchial washing may be used, and the minimum volume needed is 2 mL.
- Pleural fluid may be used.
What are the Indications for AFB Stain?
- This is a special stain for the diagnosis of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in various specimens like sputum, caseous material, and tissue.
- The AFB smear stain was used to monitor the treatment of Tuberculosis.
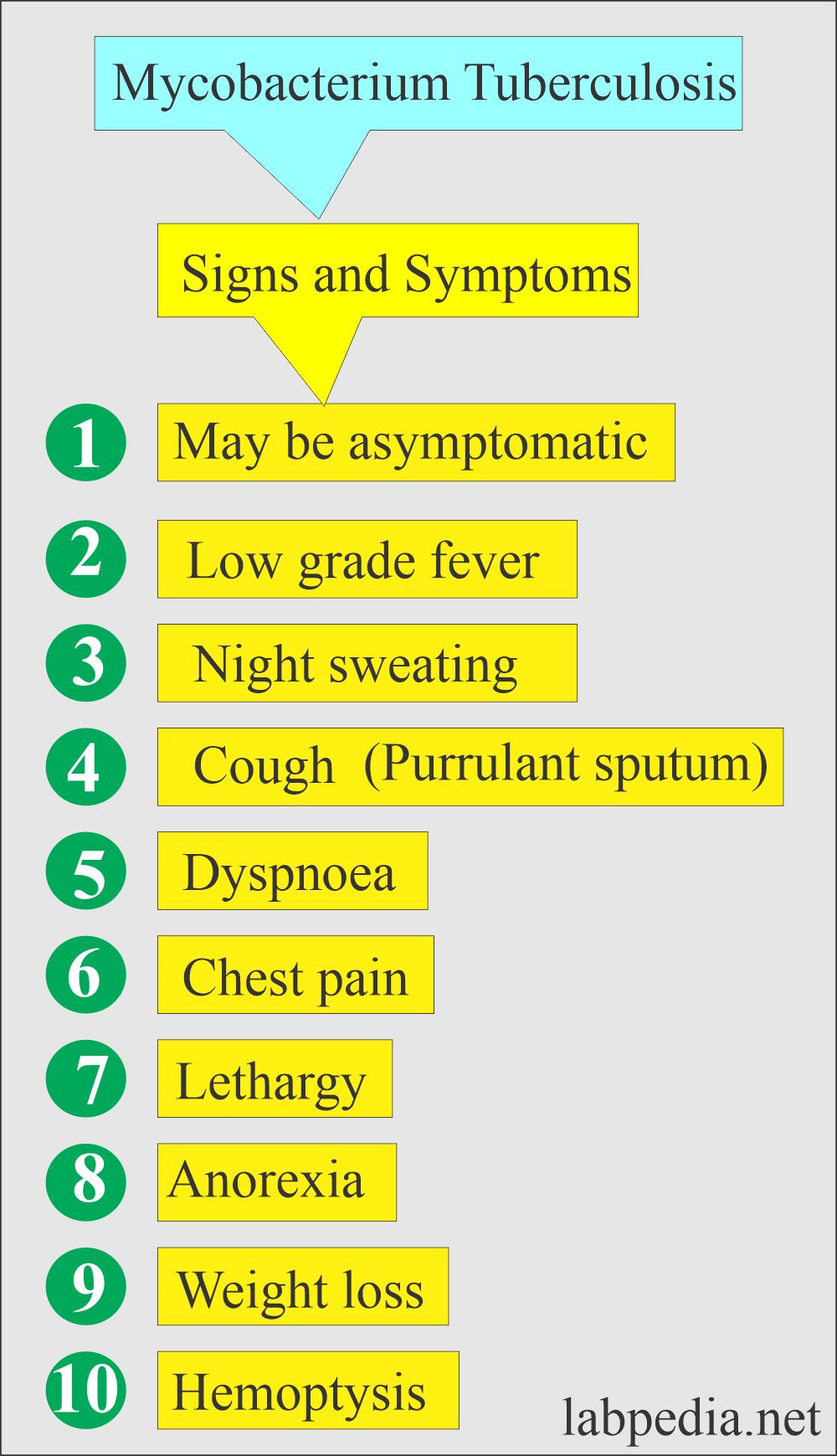
- The AFB stain on sputum is indicated in a patient with:
- A cough.
- Night sweating.
- Anorexia.
- Fever.
- Hemoptysis.
- Unexplained weight loss.
- Fatigue and weakness.
- Chest pain.
- Advise AFB stain in high-risk patients like immunocompromised patients, alcoholics, or have recent exposure to TB patients.
What are the precautions for AFB stain?
- Brush the teeth and remove the denture if it is there.
- Rinse the mouth and take a deep cough sample.
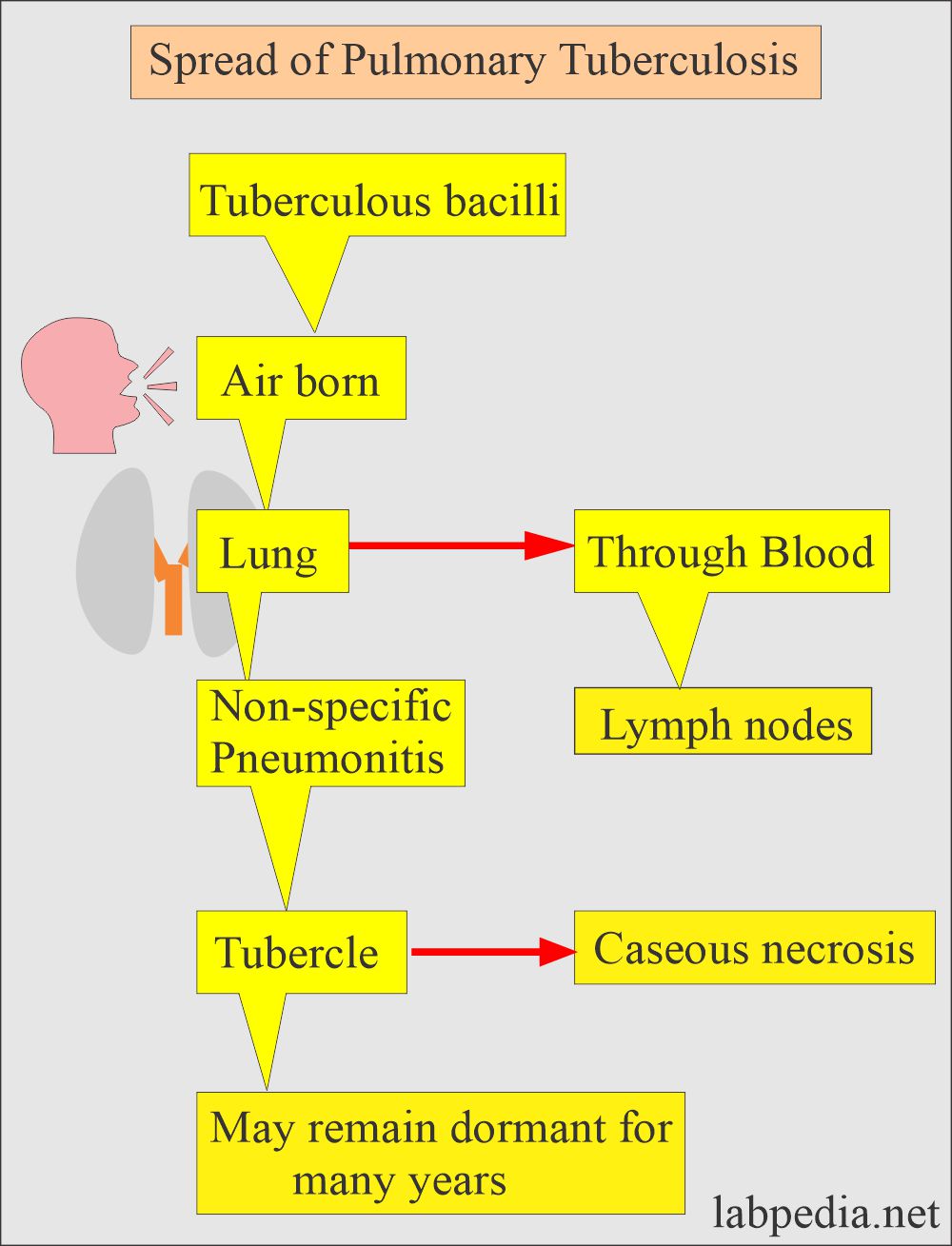
What is the epidemiology of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis?
- Mycobacterium Tuberculosis is a very common disease throughout the world.
- Roughly 1.86 billion people are infected with TB.
What are the signs and symptoms of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis?
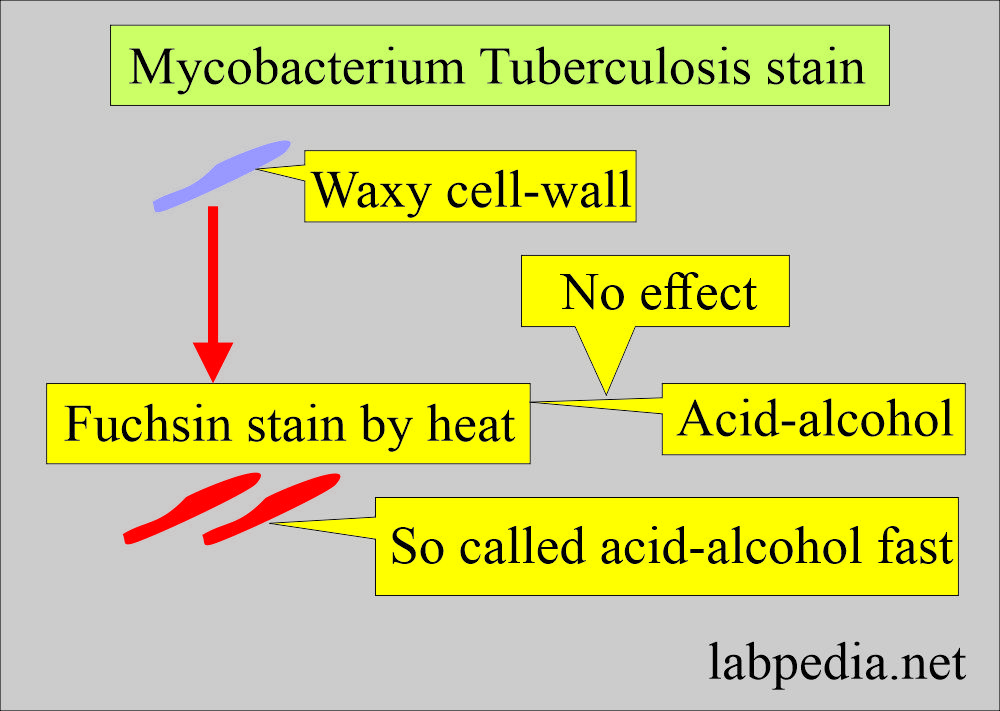
What is the principle of AFB stain?
- Acid-fastness is related to the composition of the bacterial outer capsule.
- The outer capsule (cell wall) is lipid-laden.
- These lipids consist of:
- Mycolic acid is a large fatty acid.
- Mycosides. Mycolic acid is bound to carbohydrates and forms glycolipids.
- Cord factor. It is formed by two mycolic acids and attached to the disaccharide molecule. It is only found in virulent strains.
- Sulfatides. It is a mycosides attached to sulfates and disaccharides.
- Wax-D. It is a complex mycoside, and its function is as an adjuvant. It increases the antibody formation to the antigen.
- Once this capsule takes up the dye fuchsin, it is not decolorized by acid alcohol, which is acid-alcohol fastness.
What are the Reagents of AFB (Ziehl-Neelsen) stain?
- Carbol fuchsin:
- Basic fuchsin = 10 grams.
- Ethanol or methanol = 100 mL.
- Phenol = 5 grams.
- Distilled water = 1000 mL.
- Method to prepare:
- Mix the ethanol with basic fuchsin. Try to mix until it is completely dissolved.
- Dissolve phenol carefully into the water.
- Mix the rest of the water and mix it well.
- It can be stored at room temperature for an indefinite time.
- Acid alcohol 3% V/V:
- Absolute Ethanol or methanol 680 mL.
- Hydrochloric acid concentrated = 30 mL.
- Distilled water = 290 mL.
- Method to prepare: Mix alcohol with water.
- Now, slowly add HCL to the above solution.
- Malachite green 5 g/L (0.5% W/V):
- Malachite green = 5 grams.
- Distilled water = one liter.
- Mix the malachite green in the water till it is completely dissolved.
- This solution has been stable for several months.
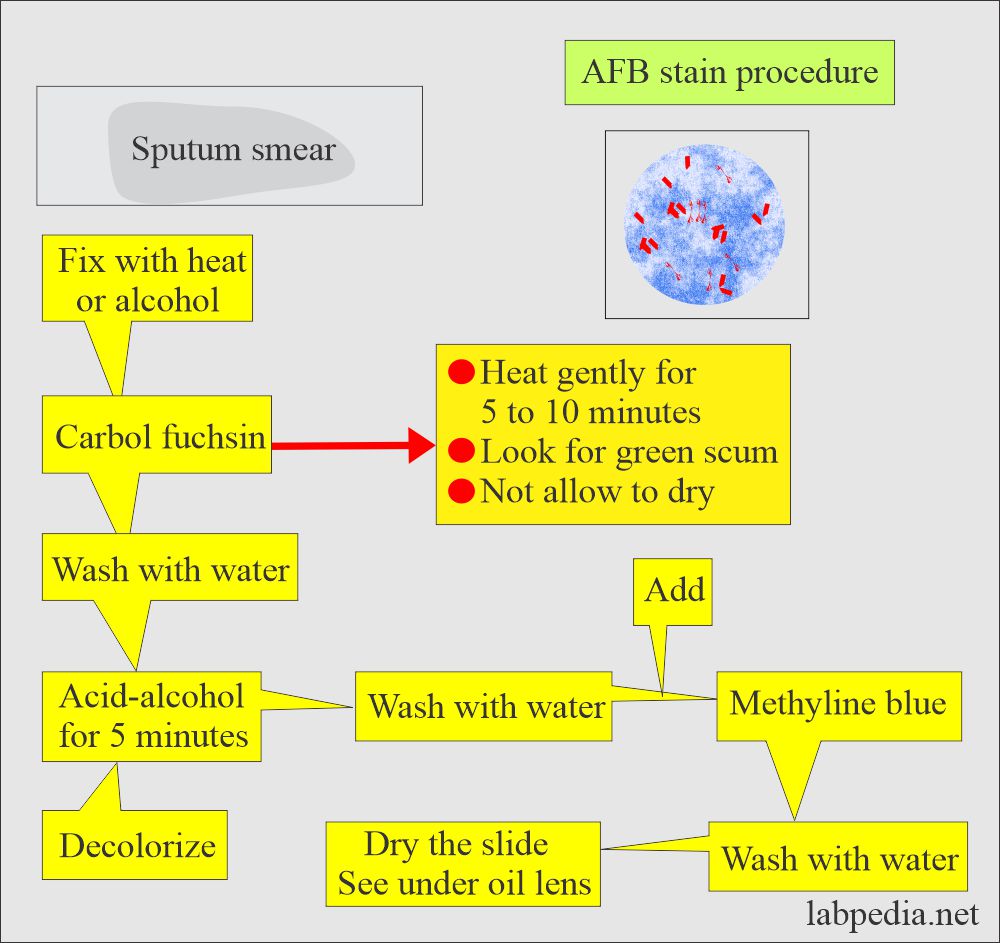
How would you describe the AFB (Ziehl-Neelsen acid-fast) staining procedure?
- The tissues/sputum are smeared on the slides.
- Always take deep cough sputum and avoid saliva.
- Then smear from the sputum is fixed by heat or alcohol.
- Heat fixes cells on a glass slide.
- Flood the slide with a carbol fuchsin stain.
- Heat the slide gently (around 60 °C) until it steams (5 min).
- You can see green scum.
- Avoid overheating.
- Pour off the carbol fuchsin.
- Wash slides thoroughly with water.
- Decolorize with acid-alcohol (5 min).
- Wash slides thoroughly with water.
- Flood slide with methylene blue (or malachite green 1 to 2 minutes) counterstain for 1 minute.
- Wash with water.
- Blot excess water and dry in hand over bunsen flame.
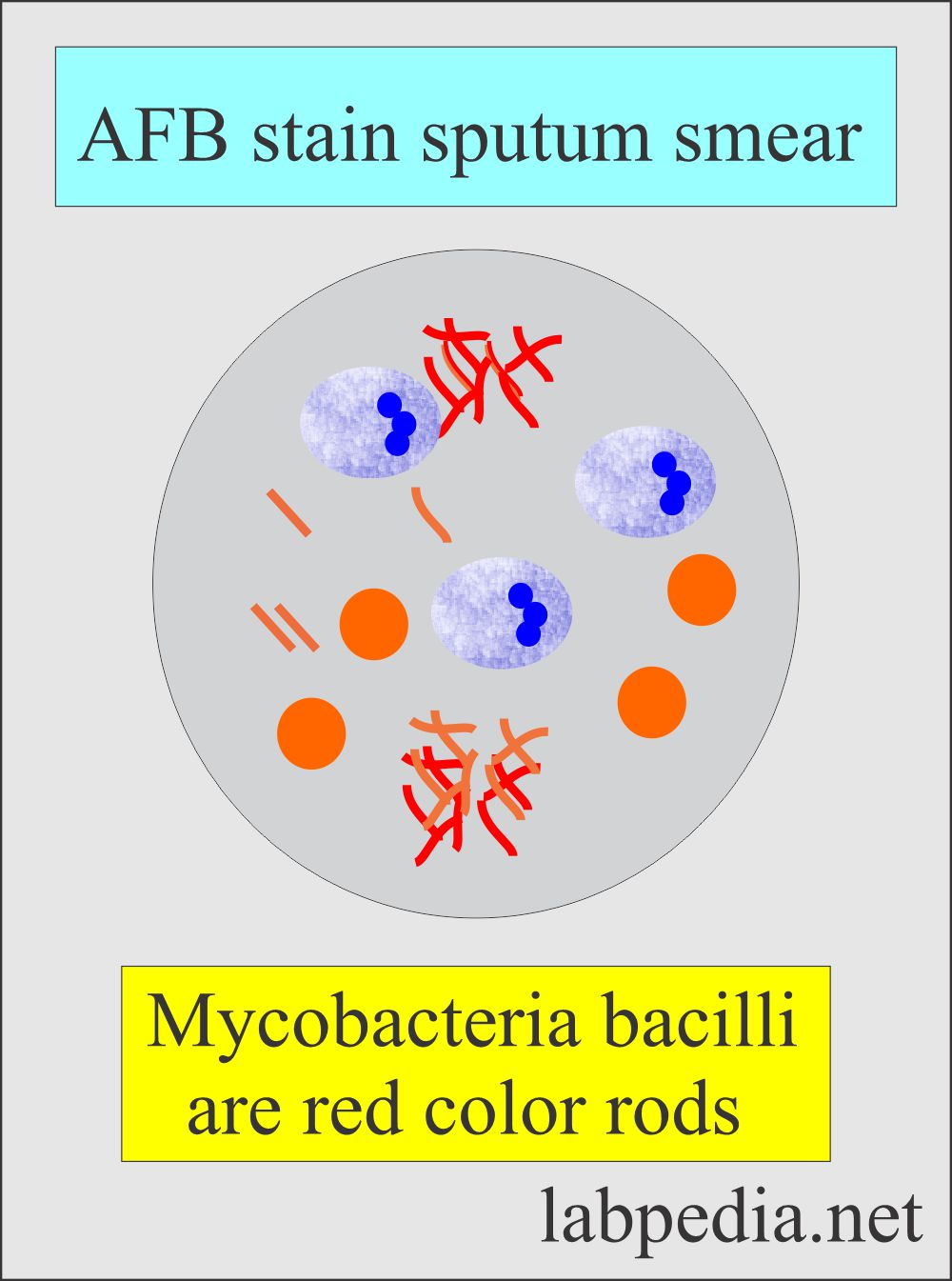
What is the result of the AFB stain?
The positive result is:
- The acid-fast bacilli are red color rods, and the background is blue.
- When these rods are seen, they indicate active tuberculosis.
- The culture may confirm a positive AFB stain.
When will you see a negative AFB stain?
A negative result means that:
- There is no infection.
- The number of bacteria was not sufficient to be seen under the microscope.
- Symptoms may be due to some other cause.
How will you report the AFB stain?
| Presence of AF bacilli | Positivity report | Another system |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Questions and answers:
Question 1: What is the purpose of acid-fast stain?
Question 3: How you can report the AFB stain?


Nice notes
Thanks.
Iam a medical laboratory technician and i love the page
Thanks.
This is best explanation
Thanks.
What if the lab tech is color blind to red color?
Then he has to use the urine dipstick. It will show if there is hematuria.