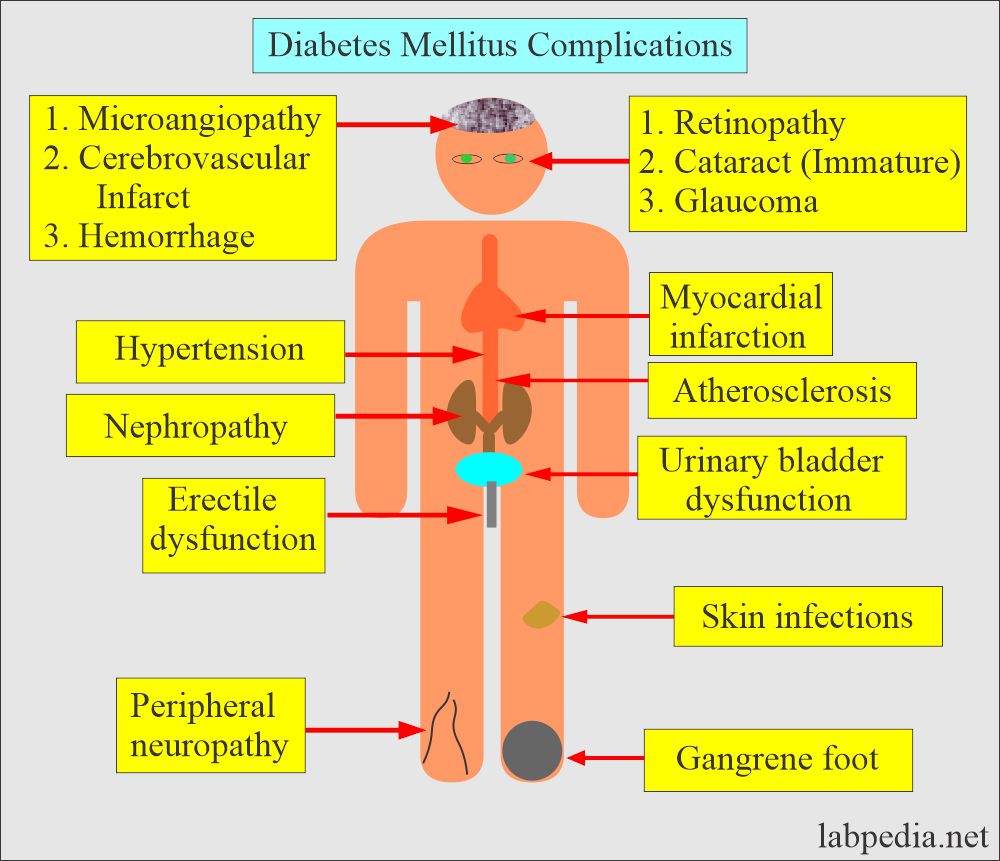
Difference Between Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus, and Complications
Difference Between Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Type 1 Diabetes mellitus is mostly seen in the younger age group
- While type 2 is seen in most adults and older people.
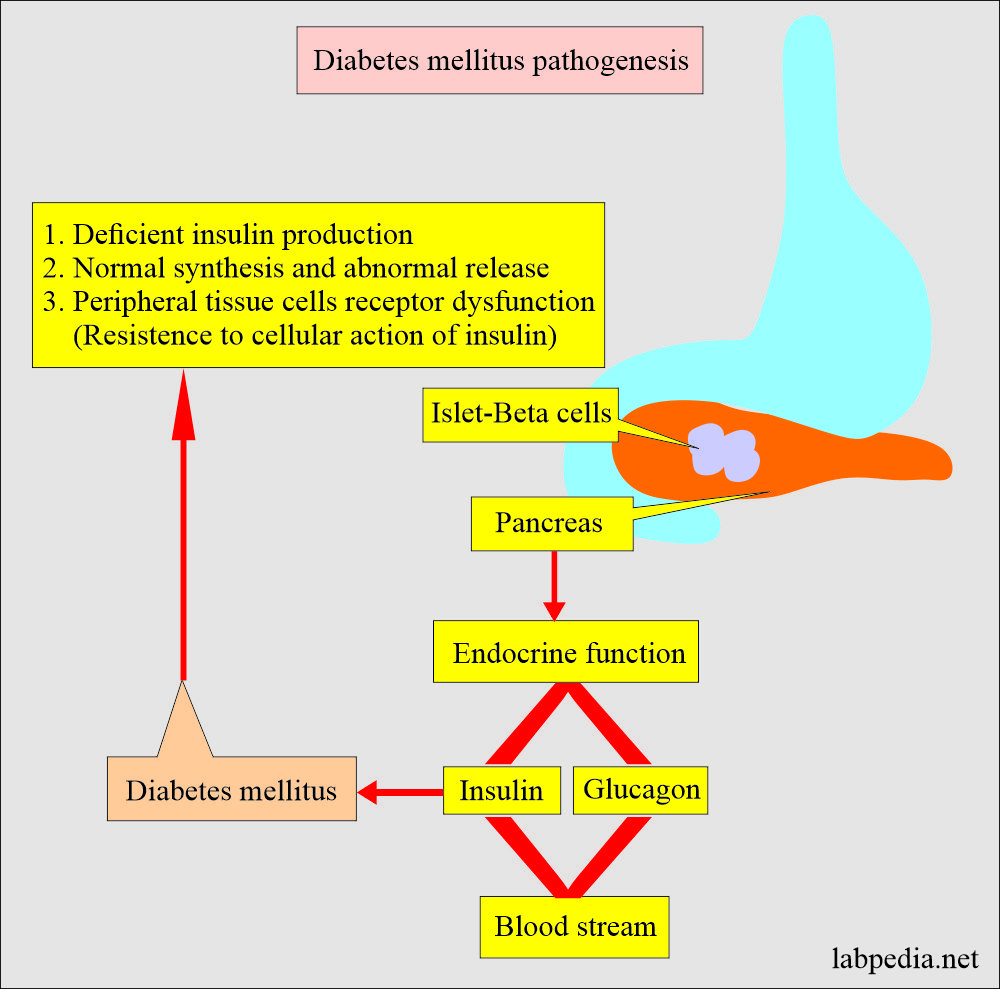
What is the pathogenesis of diabetes mellitus?
How will you differentiate between diabetes mellitus type 1 and type 2?
| Differentiating points | Type 2 Diabetes mellitus | Type 1 Diabetes mellitus |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
This may be as follows:
|
|
|
|
|