White blood cell:- Part 2 – Total Leukocyte Count Procedure (TLC), TLC Solution Preparation
White blood cell
Total leucocyte count procedure (TLC)
What sample is needed for Total leukocyte count (TLC)?
- EDTA blood is required.
- Oxalate or citrated blood can also be used.
What are the Indications for Total leucocyte count (TLC)?
- To differentiate between acute and chronic infection.
- To follow the patient with chemotherapy.
- To find the effect of drugs.
What is the principle of white cell count (total leucocyte count, TLC)?
- Blood is diluted with a solution (acetic acid) that causes the lysis of RBCs.
- Acetic acid does not affect the WBCs.
- Gentian violet is added to differentiate the WBCs.
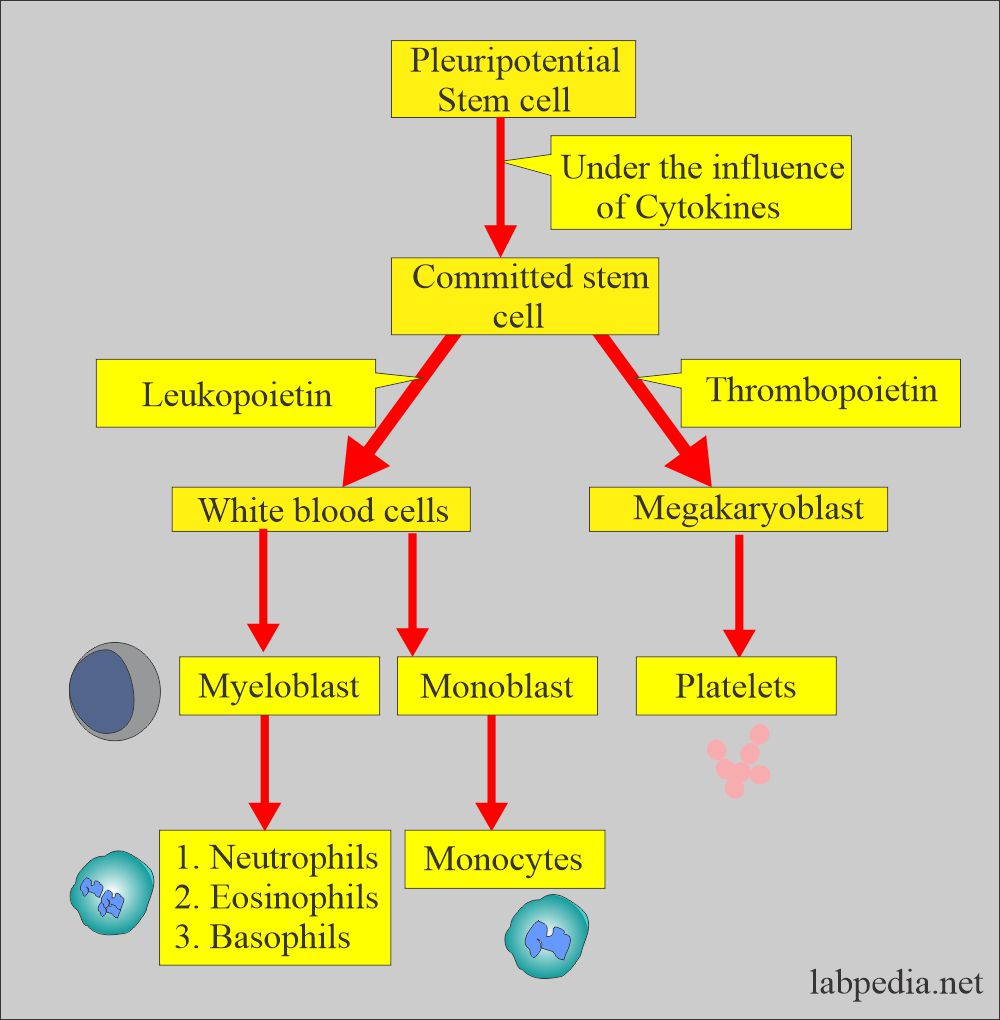
How will you discuss the pathophysiology of Total leucocyte count TLC)?
- White blood cells develop from the stem cells in the bone marrow.
- Stem cells differentiate into:
- Granulocytic series cells. The granulocytes got the name due to the presence of distinct granules in the cytoplasm of these cells.
- Leucocytes live from 13 to 20 days; after that, they are destroyed in the lymphatic system and may be excreted from the body in feces.
- Leucocytes fight infections and defend the body by a process called phagocytosis.
- WBC serves as an excellent indicator of the various disease processes.
- The granulocytic series consists of:
- Polymorphonuclear leucocytes (Neutrophils).
- Eosinophils.
- Basophils.
- Monocytes.
- Non-Granulocytic cells:
- Lymphocytes.
- B-lymphocytes.
- T-lymphocytes.
- NK cells.
- Monocytes.
- Lymphocytes.
How will you divide White blood cells?
- Phagocytic cells:
- Polys.
- Eosinophils.
- Basophils.
- Monocytes.
- White blood cell:
- B- lymphocytes.
- T-lymphocytes are:
- T-helper cells (CD4+)
- T-cytotoxic cells (CD+)
- T-effector cells (CD4+)
How will you prepare the Total leucocyte count (TLC) solution?
What is the principle of the TLC method?
- Blood is diluted with a fluid that causes the RBCs to hemolyze, but the WBCs remain intact, and then these are counted in the Neubauer chamber.
- Gentian violet lightly stains the leucocytes and allows those to be counted.
What chemicals (Reagents) are needed for TLC solution?
- Glacial acetic acid = 2 ml.
- Gentian violet (1%) = 1 ml.
- Distal water = 97 ml.
- This is a 2% solution of acetic acid.
- Add 2 ml of glacial acid (2 + 1), 1 mL gentian violet (1 %), and add 97 ml of distle Water to make up to 100 ml solution.
- Gentian violet is added until the color is pale blue-violet.
What is the procedure for Total leucocyte count?
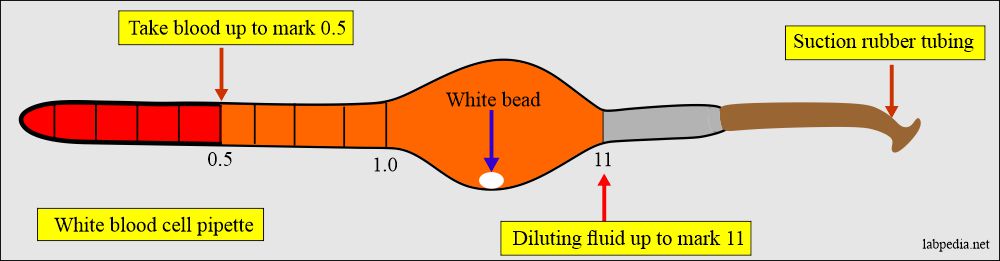
How will you count the total leukocyte count using the pipette method?
- This pipette (also called Thoma pipette) long stem is divided into two parts:
- The long stem is marked with 0.5 and 1.0
- While the short arm after the bulb is marked 11.
- Its central portion is a bulb or a globular shape with one white bead in it.
- Rubber tubing is attached to suck the blood.
- Ultimately, the blood dilution to the TLC fluid is at 1:20.
How do we perform the pipette method for total leukocyte count (WBC)?
- Take the TLC pipette, which has a white bead inside.
- Fill the blood into the 0.5 marks and then add the TLC solution.
- Fill the pipette with the TLC solution to point 11.
- Remove the rubber tubing.
- Seal both ends or hold it between two fingers.
- OR can put this pipette on the mechanical device to shake it.
- Shake for 1 minute or preferably for 2 minutes.
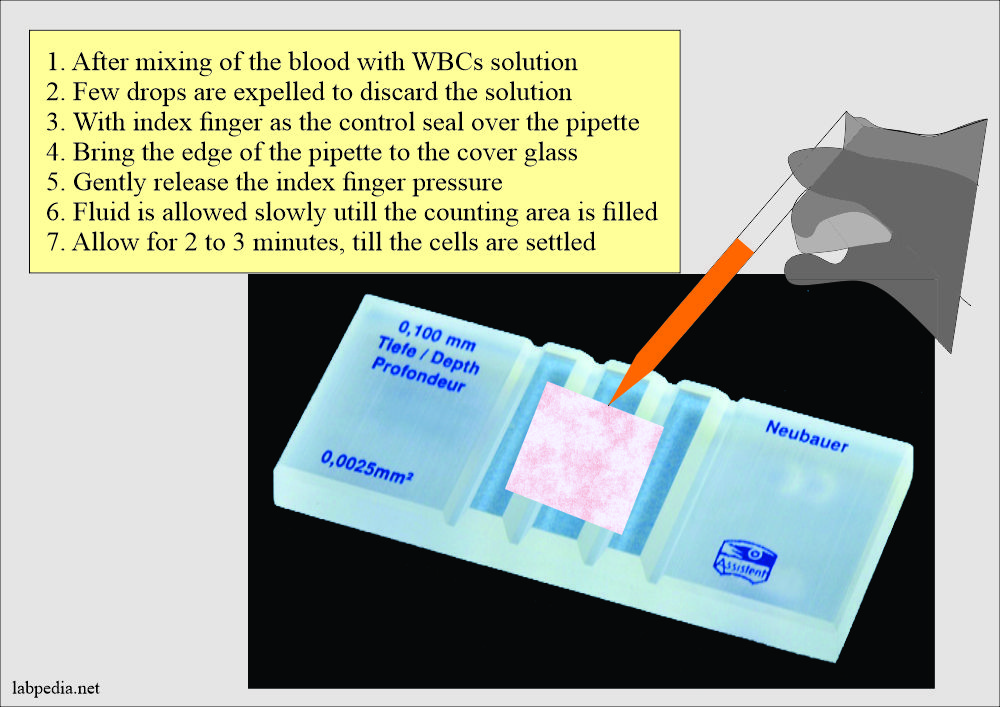
- Shaking is important before filling the Neubauer chamber.
- After thoroughly mixing, discard the first few drops and gently fill the chamber until the platform is filled.
- The capillary action will draw the fluid.
- Allow the chamber on the microscope stage for 2 to 3 minutes till the cells are settled.
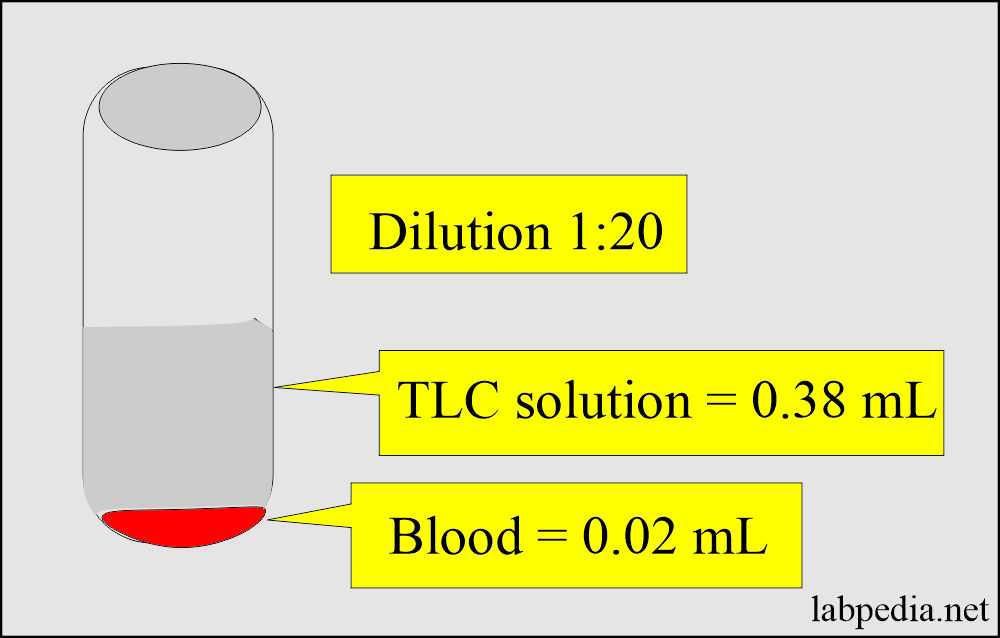
How do you perform the tube method for total leucocyte count?
- Take 0.02 mL of blood and mix it with diluting fluid.
- Take 0.38 mL of TLC dilution fluid in a small tube and mix it with the blood (1:20 dilution).
- Mix them very well.
- The dilution will be the same.
- This tube method is more accurate than the Thoma pipette technique.
- In case of low WBC count, fill the pipette to mark 1, and this will give a dilution of 1:10 OR
- Take 0.1 mL blood and 0.9 mL diluent solution (1:10 dilution).
- In the case of a high WBC count, make a higher dilution.
How will you calculate Total leucocyte count (TLC)?
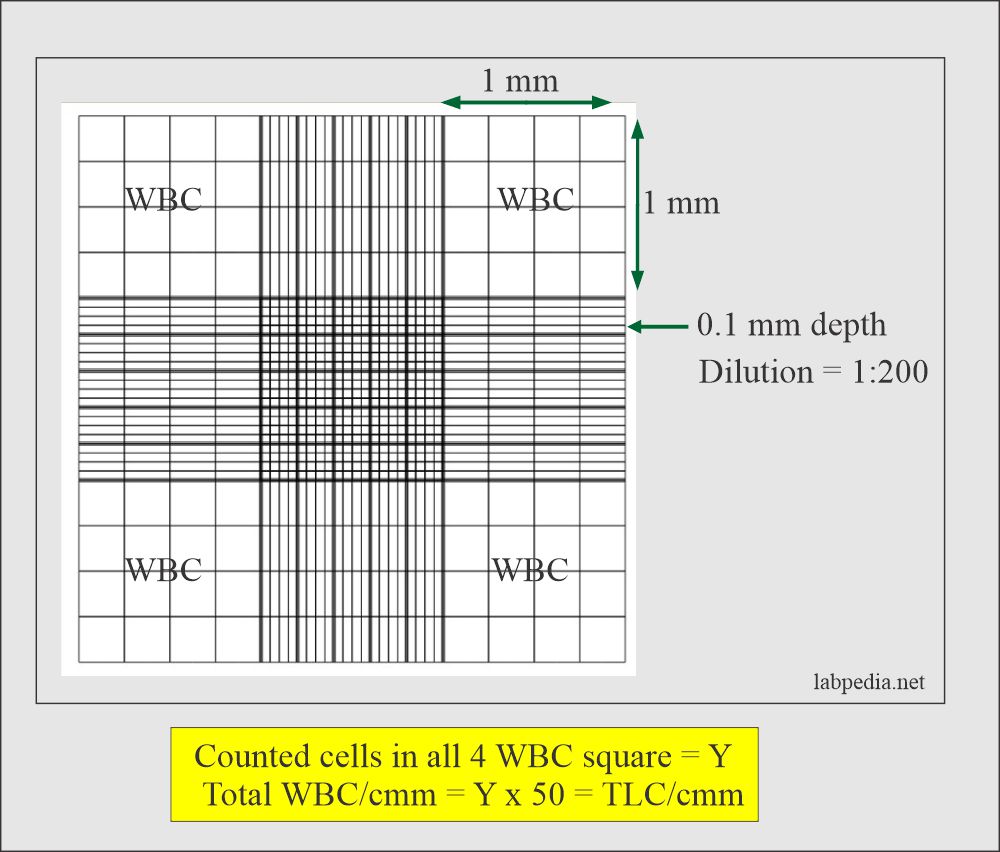
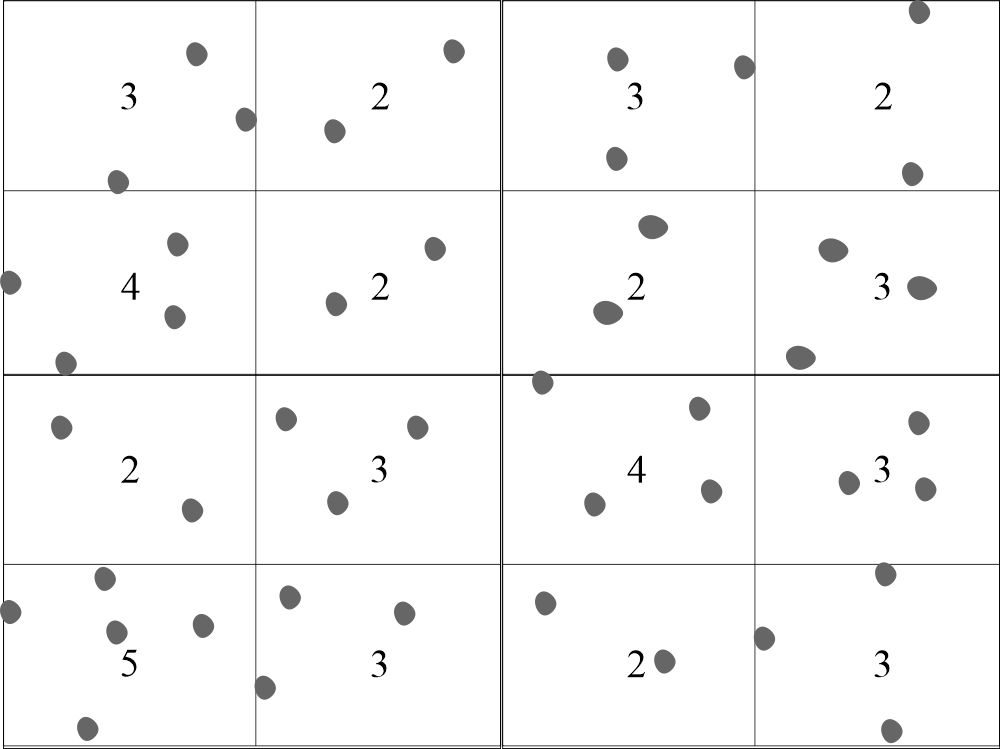
- Count the cells in the Neubauer chamber. These are counted in the four large corner squares labeled as WBC, and if the number is Y.
- One large area is 1 x 1 mm, and the depth is 0.1 mm.
- Total area counted in 4 large squares = 4 x 1 x o.1 = 0.4 µL (4/10).
- Y x 10/4 is the total WBC in the cell in 1 µL.
- Now, dilution is 1:20.
- Number of WBC in 1µL = Y x 10 x 20/4 = Y x 50 = Total WBC count.
- Total TLC = counted cells (Y) x 50 = TLC/cmm.
- If the count is low <4000/cmm, then use the dilution 1:10.
What is the source of errors for TLC count?
- If there are microclots in the sample.
- If inadequate mixing is done.
- Improper filling of the chamber.
- If the dilutions are improper.
- Mistakes in the calculations.
What are the normal values of total leucocytes?
Source 2
- Adult /child = 5000 to 10,000 /cmm
- Child ≤2 years = 6200 to 17000 /cmm.
- Newborn = 9000 to 30,000 /cmm
Other sources
- At birth = 10,000 to 25,000/cmm
- Infants = 8000 to 15,000/cmm
- Adults = 4000 to 10,000/cmm
- Pregnant ladies = 12,000 to 15,000/cmm
What are the causes of increased TLC (Leucocytosis)?
- Mostly in the case of infections that may be bacterial or viral.
- Localized infections are:
- Meningitis.
- Pneumonia.
- Abscess.
- Tonsillitis.
- Generalized infections:
- Septicemia.
- Acute rheumatic fever.
- Cholera.
- Localized infections are:
- In the case of leukemias.
- After the strenuous exercise.
- Pain and anorexia.
- Epileptic seizures.
- Emotional reaction.
- Mild leucocytosis in pregnancy.
- Acute hemorrhage.
- Intoxications like:
- Poisoning by drugs, chemicals, and venoms (black widow spider).
- Metabolic diseases include uremia, acidosis, eclampsia, and acute gout.
- Parenteral proteins and vaccines.
- Acute hemolysis of red blood cells.
- Myeloproliferative diseases.
- Tissue necrosis:
- Burns.
- Gangrene.
- Necrosis of the tumor.
- Acute myocardial infarction.
- Necrosis due to bacteria.
- Physiologic conditions are:
- Emotional stress.
- Exercise.
- Obstetrical labor.
- Menstruation.
What are the causes of decreased total leucocytes (neutropenia)?
- This may be seen in fever, malaise, and chills.
- Bacterial Infections:
- Bacterial.
- Septicemia.
- Miliary tuberculosis.
- Typhoid fever.
- Paratyphoid fever.
- Tularemia.
- Brucellosis.
- Viral infections are:
- Hepatitis.
- Influenza.
- Infectious mononucleosis.
- Psittacosis.
- Rubella.
- Measles.
- Hematological diseases:
- Aleukemic leukemia.
- Pernicious anemia.
- Gaucher’s disease.
- Felty’s syndrome.
- Aplastic anemia.
- Deficiency of vitamin B12.
- Drugs and chemicals:
- Antibiotics.
- Analgesics.
- Sulphonamides.
- Antithyroid drugs.
- Arsenicals.
- Marrow depressant.
- Bone marrow disorders:
- Malignant infiltration of the bone marrow.
- Bone marrow aplasia.
- Bone marrow depression by radiations.
- Autoimmune diseases like SLE.
- Critical value = <2500 or >30,000 /cmm ( These are panic values).
Questions and answers:
Question 1: What is the role of gentian violet in TLC solution?
Question 2: What are the markings on Thoma pipette?
- Please see for more details in complete blood count (CBC) part 1.

Very essential information
Thanks.
Sir plz upload lecture on leukemia
I am working on acute leukemias. You will find daily updates.
I have updated acute leukemias. I hope you will like it.
Send a WBC calculation process
Please see at the end of “White blood cell. part 2”.
You made this topic very easy for me
Thanks.
It is so helpful for me
Thanks.
It is 100% easy than to read it from university manual.
Thanks.
Perfectly OK sir
Thanks.
What is 10 in wbc count formula?
Total area counted in 4 large squares = 4 x 1 x o.1 = 0.4 µL (4/10).
x10 comes from above formula.
How about when the number are very high like erythrocytes we use the R squares.
When you have a chance, Can you please elaborate on that? We use it to count sperm concentration of frozen samples used for artificial insemination.we dilute the sample 1:200.
Normal concentrations can range between 100.000 to 2’000.000 per cc.
Please see this link, I hope this may help you.
https://www.labpedia.net/semen-part-1-semen-analysis-semen-examination-and-semen-counting-procedure/
That was exactly what i was looking for. Thank you !
We were correct but wanted to double check. use a dilution 1:200 so will add one extra 0.
Frozen semen is stored under liquid nitrogen that is -196C or 320F and will deteriorate at temperatures over -140C or -220F so that referral page of frozen semen you gave me the frozen semen at -20 should be corrected. I hope this can be my 5 cent contribution to your page…. if you want to.
Thanks again. Great work
Thanks, I am happy that the issue is solved.
Please what is the implications of ovefilling the chamber
And what is the implications of trapping air bubbles in the chamber
You will get the wrong result because of the dilution inconsistency.
Same here, I found it very useful
Thank You Sir
Welcome
I’m really confused on how to count the WBC
Please follow the instructions given on this topic.
https://labpedia.net/white-blood-cell-part-2-total-leukocytes-count/
Thank for your effort on
Thanks.
How can we control a typhoid in africa
1. Good hygiene.
2. Mostly, the cooks are carriers; they need to be given antibiotics. Ampicillin is the most successful antibiotic and should be used in large doses.
3. The oral vaccine in 3 doses is the best way to avoid typhoid fever. Everyone at home should use this vaccine dose every year.
Very useful information, thank you.
Thanks.
Is the concentration of WBC obtained from the RBC lysate method and Ficol gradient method from a healthy individual are same? If not what are values.
Please see this reference.
https://jnm.snmjournals.org/content/58/supplement_1/810
what is clinical significance of this test?
Total leukocytes count differentiates acute and chronic infections. TLC helps to reach the diagnosis of various diseases.
Very intresting indeed
Thanks.
Thanks 👍
Thanks.