What is HbA1c?
HbA1c
How will you Define HbA1c?
- HbA1c measures the average blood glucose level over 3 months period.
- It is reported as a % or an estimated average glucose.
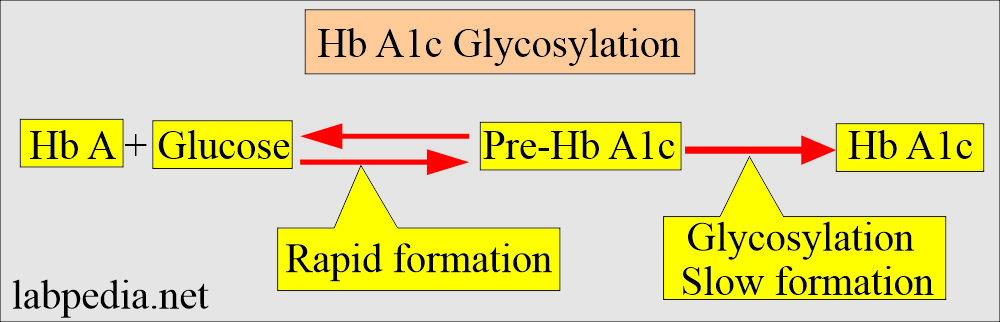
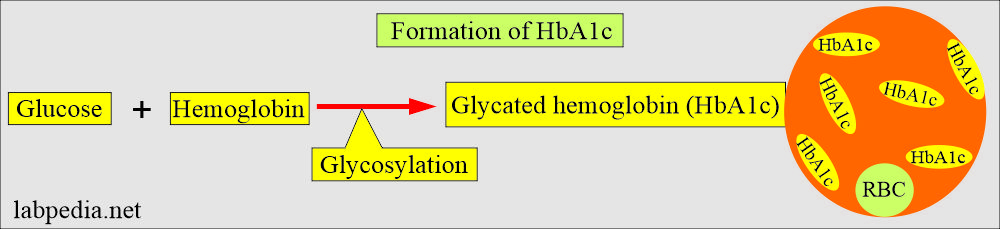
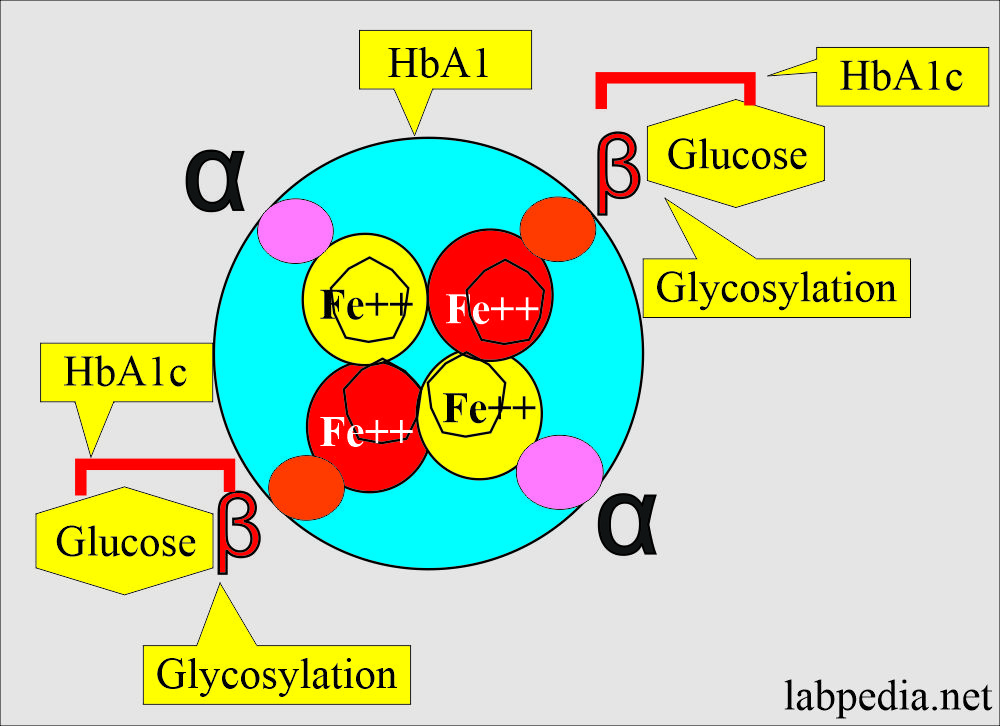
- Hemoglobin has the sugar residue attached to the Red blood cells. HbA1c is the major fraction (80% ) of glycated hemoglobin.
- HbA1c is also called:
- Glycosylated hemoglobin.
- Glycohemoglobin.
- Glycated protein
Discuss the pathophysiology of HbA1c?
- Glycated hemoglobin is essentially irreversible, and its concentration depends upon the following:
- The lifespan of the RBCs is an average of 120 days.
- Blood glucose concentration.
- The rate of the formation of glycated hemoglobin is directly proportional to the concentration of the blood glucose level.
- Glycated hemoglobin concentration represents the integrated values for glucose over the preceding 6 to 8 weeks.
- Day-to-day changes do not influence glycated hemoglobin in the blood glucose level.
- This process of glycosylation occurs when the RBCs are exposed to blood glucose.
- Initially, there is a bond between the RBCs, and glucose is labile but later on becomes stable.
What is normal HbA1c?
- In case of no diabetes = 5.6% or less
- Prediabetic = 5.7 to 6.4%
- Diabetics = 6.5 or more
How will you explain the Diabetic goal of HbA1c?
- Good diabetic control = <7%.
- Fair diabetic control = 8% to 9% (another reference = 6% to 8%).
- Poor diabetic control = >9% (another reference = >8%).
| HbA1c % | Mean plasma glucose level mg/dL | Advice needed |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
What are the goals of diabetes mellitus patients?
- Newly diagnosed patients should try to keep HbA1c below 7%.
- In such patients, the average glucose level is 154 mg/dL.
- When HbA1c is around 8%, then the average glucose is 183 mg/dL.
- HbA1c of 9% will have an average glucose level of 212 mg/dL.
- HbA1c of 10% will have average glucose of 240 mg/dL.
- Ideally, one should try to keep the HbA1c level around 7%.