Vitamin C (Ascorbic acid)
Vitamin C (Ascorbic acid)
What sample is needed for Vitamin C?
- Serum or plasma can be used.
- The whole blood for vitamin C is stable for 3 hours when refrigerated.
- Deproteinized the serum or plasma with metaphosphoric acid (5 g/dL) or trichloroacetic acid (10 g/dL).
What are the precautions for Vitamin C?
- Avoid hemolysis.
- Avoid exposure to light.
- Use the fresh sample, as it will deteriorate if kept longer.
- Keep at a low temperature or on ice to avoid oxidation.
- Avoid exposure to air as it will oxidize to dehydroascorbic acid.
What are the indications for Vitamin C estimation?
- It helps to diagnose scurvy.
- In case of delayed wound healing.
- In the case of renal stone formation.
- To assess the chronic diseases.
How will you define vitamin C?
Vitamin C, or ascorbic acid, is a water-soluble vitamin essential for various bodily functions:
- Immune support.
- Collagen synthesis.
- Antioxidant activity.
- Since the human body cannot synthesize it, vitamin C must be obtained from dietary sources or supplements.
How would you discuss the pathophysiology of Vitamin C (Ascorbic acid)?
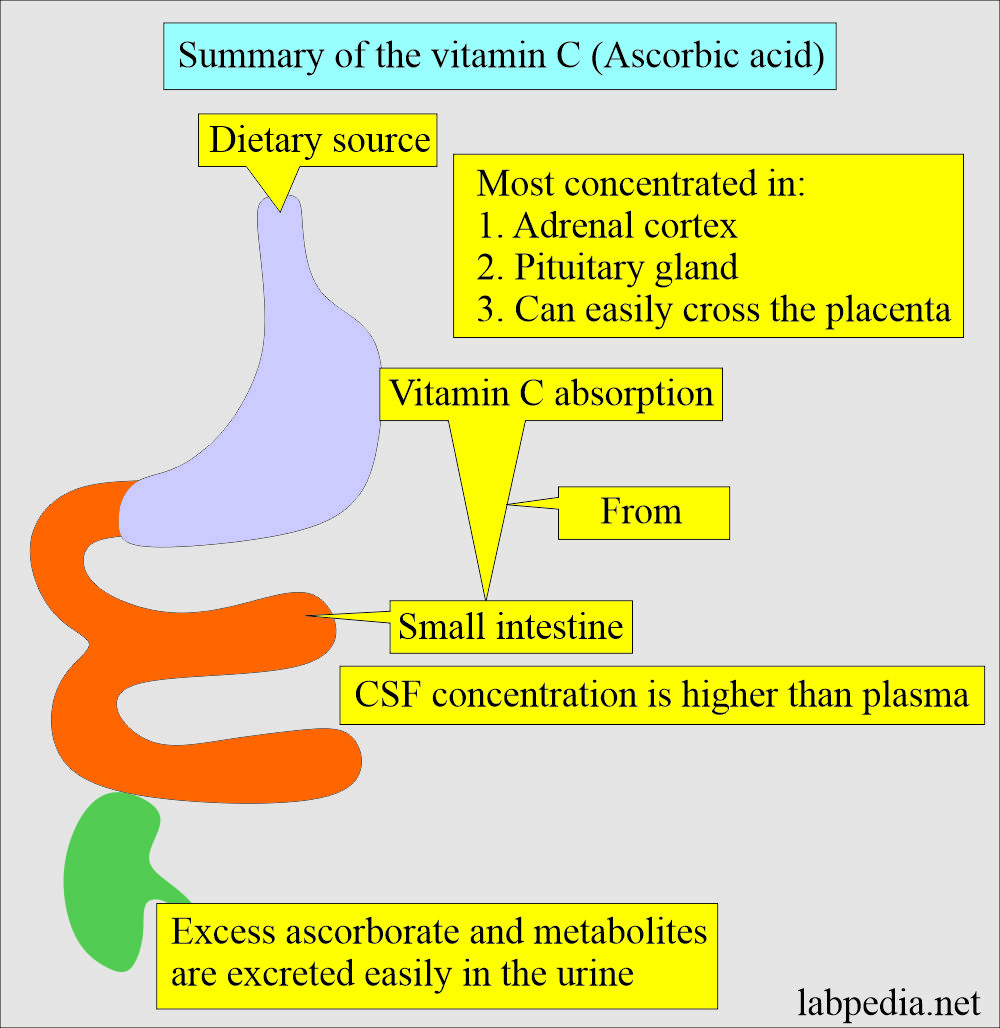
- Plants and some animals can synthesize Vitamin C, but humans cannot. Therefore, dietary intake is important for humans.
- This white crystalline solid is easily soluble in water and easily absorbed from the stomach and intestine.
- These are strong reducing compounds, and the source is dietary ingestion.
- Body stores can last for months.
- Vitamin C is a reducing agent in several hydroxylation reactions in the body.
- This exists in two forms:
- L-ascorbic acid.
- Dehydroascorbic acid (Ascarbone).
- This form is more labile and biologically active.
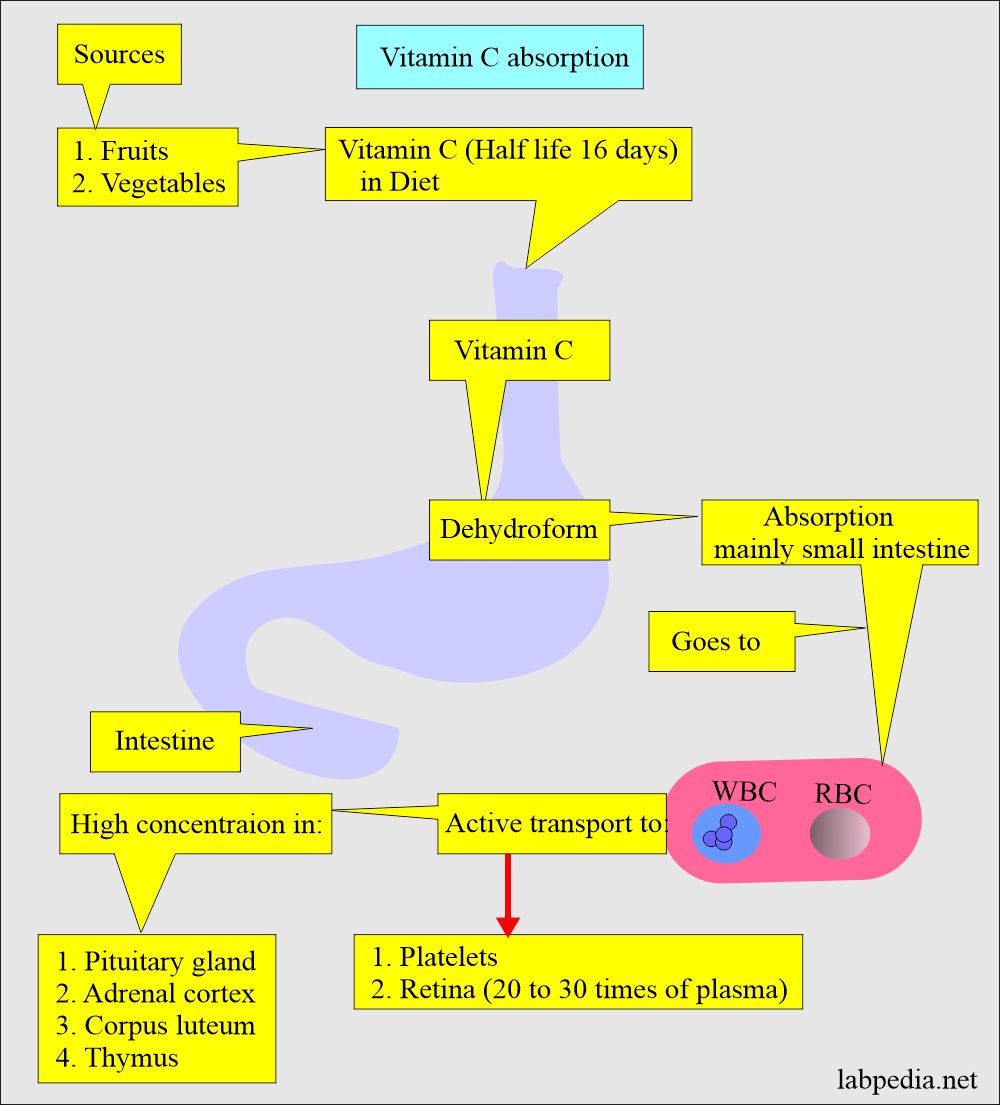
- Absorption is mainly from the stomach and small intestine.
- This has passive entry into the WBCs and RBCs.
- Active entry is into glandular tissue like the pituitary gland, adrenal cortex, corpus luteum, and thymus.
- At the same time, concentration in the retina is 20 to 30 times more than in tissue.
- Vitamin C is excreted in the urine. Its excretion is increased by:
- Aspirin.
- Aminopyrine.
- Barbiturates.
- Paraldehyde.
- Hydantoin.
What are the functions of Vitamin C?
- Vitamin C has a very important function in our body.
- It is a water-soluble vitamin.
- This is essential for converting proline and lysine in procollagen to hydroxyproline and hydroxylysine.
- Vitamin C is essential in the formation and stabilization of the collagen.
- Vitamin C may be involved in the stimulation of the synthesis of collagen.
- It is a powerful antioxidant that protects from oxidative stress and free radical damage.
- It boosts the immunity.
- It helps in wound healing.
- Plays a role in neurotransmitter synthesis and cognitive function.
- It helps in the absorption of the iron.
What are the sources of vitamin C?
- The best sources of Vitamin C are:
- Citrus fruits. This is the major source.
- Berries.
- Melons.
- Green pepper.
- Tomatoes.
- Raw cabbage.
- Leafy green vegetables.
- Potatoes.
- Heat can lead to the loss of vitamin C.
What is the mechanism for the Vitamin C absorption?
- Vitamin C is mainly absorbed in the small intestine.
- Ascorbate is sensitive to heat and oxygen; fresh and uncooked foods have the highest concentration.
What will the presentation of Vitamin C deficiency be?
How will you discuss the Scurvy?
History of scurvy:
- In 1747, a naval surgeon found that citrus fruits help scurvy patients.
- This anti-scurvy agent was isolated in 1932 and was vitamin C.
- It was given the name ascorbic acid because of its antiscorbutic effect.
What are the Clinical effects of scurvy?
- Several months are needed before the scurvy develops.
- Vitamin C deficiency leads to Scurvy, which will show clinically:
- Hemorrhagic disorder. There may be bruising and ecchymosis.
- Impaired college synthesis leads to petechiae and bruising.
- There are swollen and bleeding gums.
- There is a loss of teeth.
- There is impaired healing.
- There is anemia.
- There is weakness in the lower extremities.
How will you summarize the scurvy?
- Early weakness, lassitude, and irritability.
- Vague aches and pain.
- In the late stage, hemorrhage into the skin, GI tract, and urinary tract.
- There are osteoporotic changes in the bone.
- Defective tooth formation.
- There is anemia.
- There is delayed wound healing.
- There may be a fever.
What is the normal Vitamin C (Ascorbic acid)?
Source 1
- Vitamin C = 0.4 to 1.5 mg/dL
- Deficiency level = <0.2 mg/dL
Other sources
- Daily requirements of vitamin C:
- Infants
- 0 to 6 months = 40 mg/day
- 7 to 12 months = 50 mg/day
- Children
- 1 to 3 years = 15 mg/day
- 4 to 8 years = 25 mg/day
- 9 to 13 years = 45 mg/day
- Adolescents
- Girls 14 to 18 years = 65 mg/day
- Pregnant teens = 80 mg/day
- Breastfeeding teens = 115 mg/day
- Boys 14 to 18 years = 75 mg/day
- Adults
- Men age 19 and older = 90 mg/day
- Women age 19 years and older: = 75 mg/day
- Pregnant women = 85 mg/day
- Breastfeeding women = 120 mg/day
- Vitamin C normal range = 0.2 to 2.0 mg / 100 ml.
- Deficiency when a level is < 0.2 mg/dL.
- Vitamin C level in Leucocytes = 20 to 53 µg/108 leucocytes.
- Deficient value when it is <10 µg / 108 leucocytes.
- Urinary excretion of vitamin C = 8 to 27 mg/day.
What is the clinical presentation of the deficiency of Vitamin C?
- Prolonged deficiency leads to Scurvy.
- There is an inadequate formation of intercellular substances in the connective tissue leads to the following:
- Swollen, tender, and sometimes bleeding into the joints.
- Gums are swollen.
- Infantile scurvy, also knew Barlow’s disease, will show bayonet rib syndrome.
- There is vascular fragility leads to:
- Cutaneous bleeding usually starts in the lower thigh and may spread to the buttocks, abdomen, arms, and legs.
- Petechial hemorrhage may lead to a large bruise.
- There is an ocular hemorrhage.
- Bleeding in the GI tract, kidneys, conjunctiva, and brain.
- Hemorrhage of the gingiva.
- There may be dental loss and even fractures.
- There is delayed wound healing.
- Other glands like salivary, lacrimal, and parotid may be involved.
- There may be femoral neuropathy and edema of the lower extremities.
What is the presentation of the toxicity of Vitamin C?
- Large doses of vitamin C for allergies and colds are not recommended.
- Large doses do not cause any problems except GI upset.
- Increased oxalate stones in the kidney and urinary bladder due to urine acidification.
What is the presentation of the clinical effects of increased Vitamin C?
- When vitamin C is more than>2000 mg/day, it may cause:
- Diarrhea.
- Nausea and dyspepsia.
- Over absorption of iron.
- A stone formation is like oxalate stones due to the increased secretion of oxalate.
- There may be increased secretion of urates.
- Effect on diabetes tests and occult blood.
How can you measure Vitamin C?
- This can be measured by:
- Photometric system
- Fluorometric and HPLC techniques can be used.
How will you treat for Vitamin C deficiency?
- The daily dose of 10 mg of vitamin C is sufficient to treat the clinical signs of scurvy.
Questions and answers:
Question 1: What is the complication of vitamin C deficiency?
Question 2: What is the complication of toxicity of vitamin C?