April 1, 2024
Hepatotropic Viruses
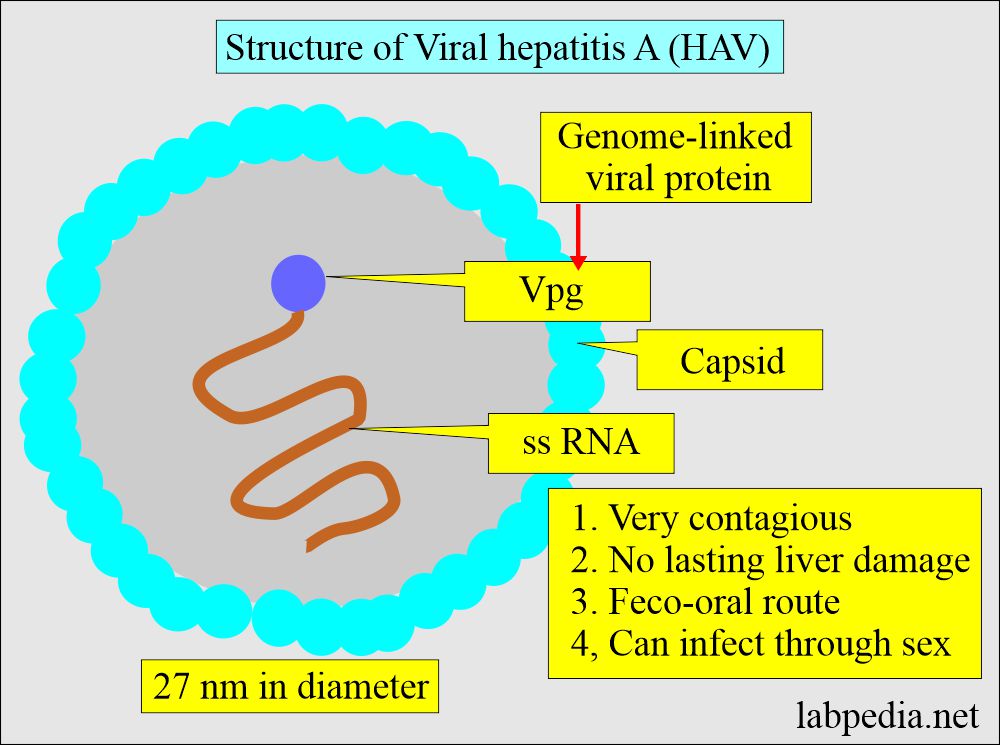
Hepatitis A Viral (HAV) infection
- This can be detected in the following samples:
- Feces
- Liver
- All body fluids (serum, other body fluids).
- These samples can be stored at 4 °C, and tissues may be stored at -20 °C.
- Diagnostic tests are:
- Anti-HAV IgM.
- Anti-HAV IgG.
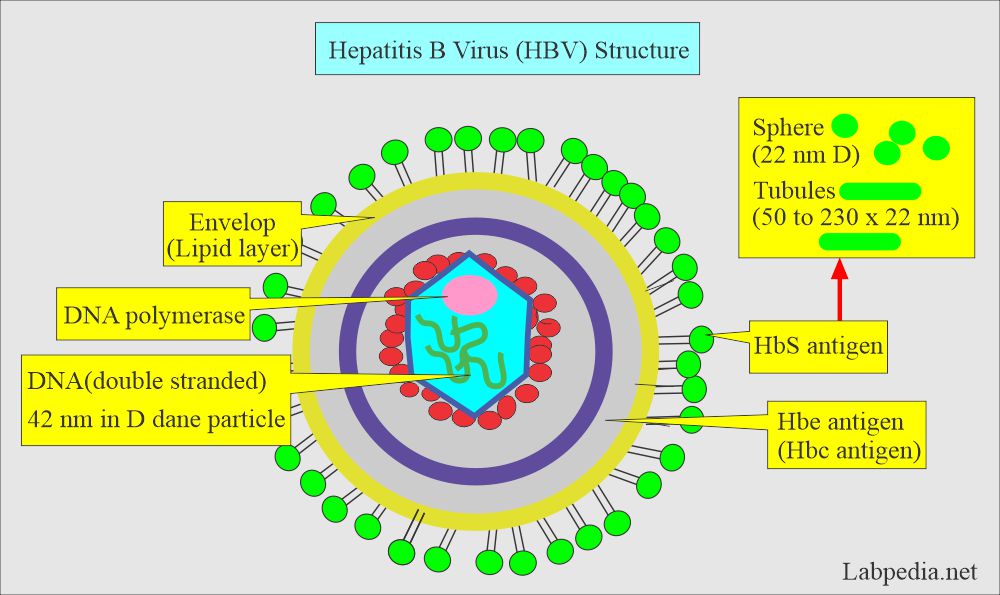
Hepatitis B viral (HBV) infection
- This virus can be detected in the following samples:
- Serum
- Whole blood
- Liver
- Body fluids
- Store serum and body fluids at 4 °C and store tissue at -20 °C.
- Diagnostic tests are:
- HB surface antigen.
- HB surface- antibody
- HBe antigen.
- HBe antibody.
- HBc-IgM antibody.
- HBc-antibody total (HBc-IgM and IgG).
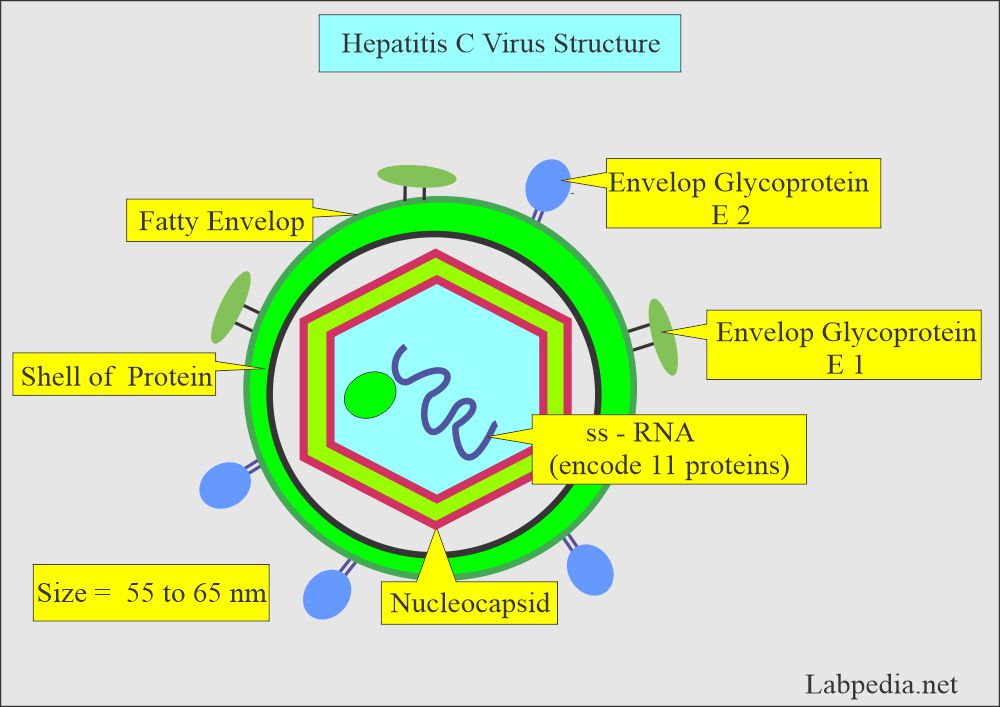
Hepatitis C viral (HCV) infection
- The virus can be detected in the following samples:
- Whole blood
- Serum
- liver tissue
- Body fluids
- Diagnostic tests are:
- Anti-HCV antibody.
- PCR for HCV antigen.
- Serum, blood, and body fluids can be stored at 4 °C and liver tissue at -20 °C.
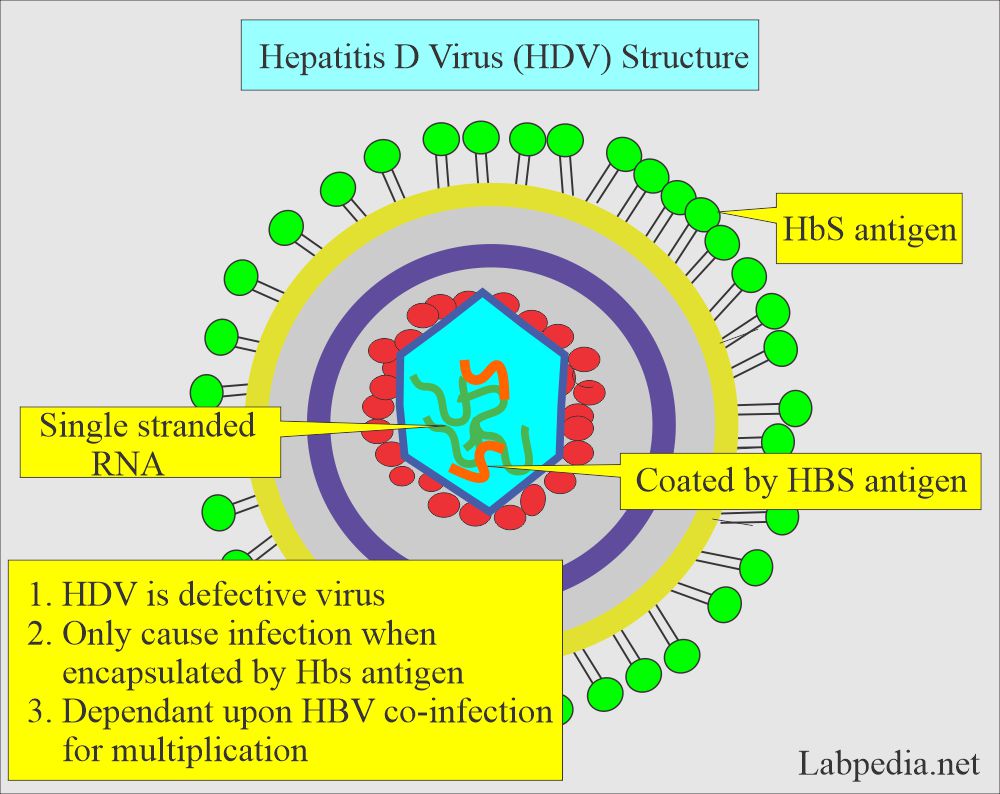
Hepatitis Delta Virus (HDV) infection
- The Hepatitis D virus is also called delta hepatitis. It was discovered in 1977.
- A partially defective virus must enter the HBV to penetrate the hepatocytes.
- So HBV will be present before the patient develops Hepatitis D infection.
- HBV is needed as a helper to start the infection.
- The Hepatitis D virus can be detected in the following samples:
- Whole blood
- Serum
- Liver tissue
- Diagnostic tests are:
- Anti-D IgM.
- Anti-D IgG.
- The whole blood and serum can be stored at 4 °C and liver tissues at -20 °C.
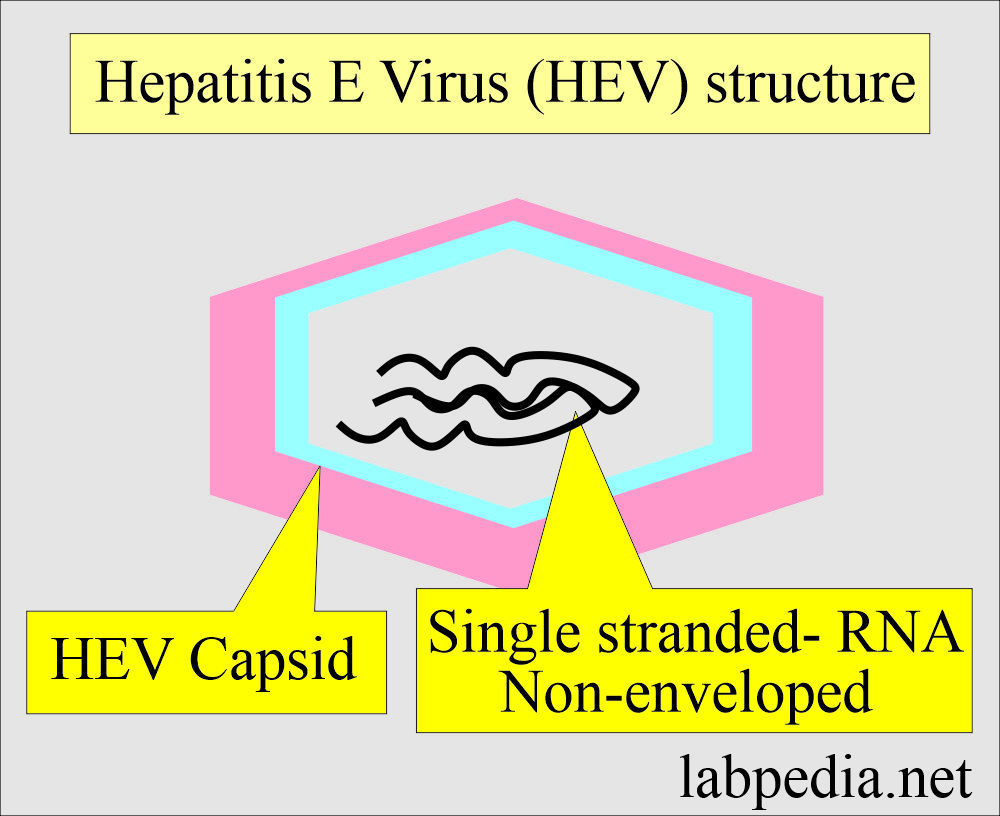
Hepatitis E virus (HEV)
- It is the NANB virus with incubation time, clinical signs and symptoms, and epidemiology, which is like HAV infection.
- HEV is thought to be a calicivirus.
- HEV is a nonenveloped, single-stranded RNA virus.
- Till 1994, no serological tests for HEV were available.
- HEV diagnostic tests are:
- HEV antigen identified in hepatocytes.
- HEV can be identified in the stool by immunoelectron microscopy.
- Serum is positive for anti-HEV antibodies IgM, which is short-lived.
- Anti-HEV IgG was also found to appear immediately after IgM.
Other Viruses
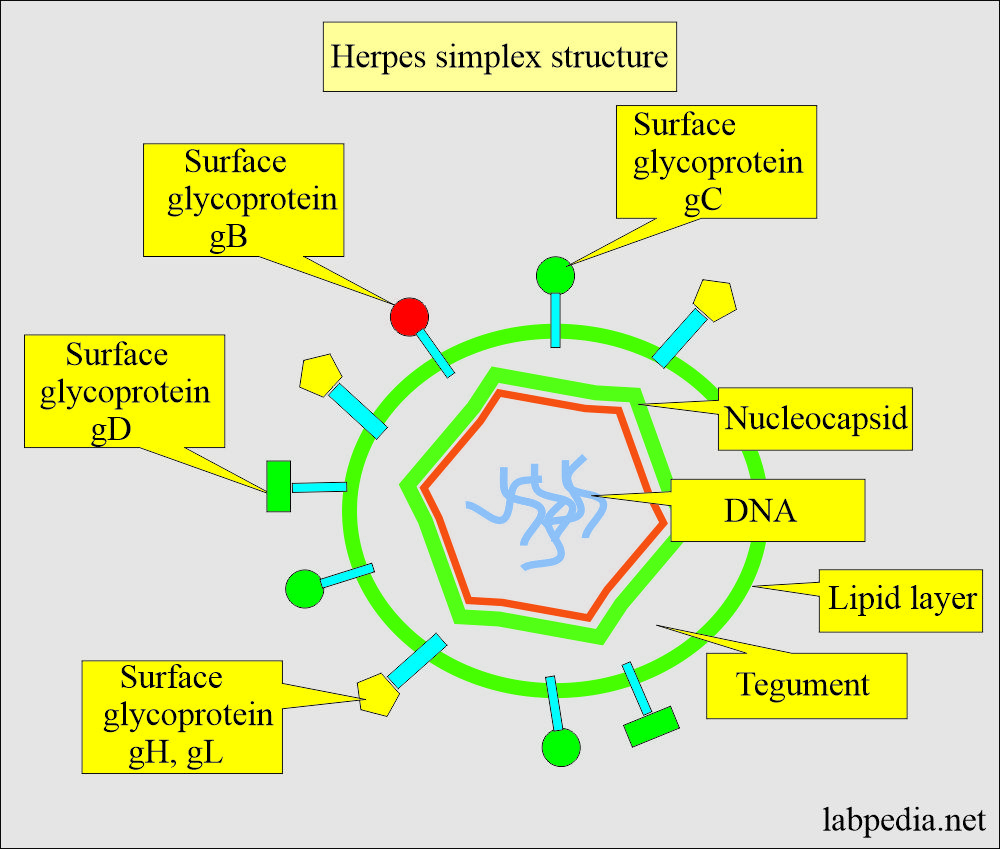
Herpes Simplex (HSV) infection
- Most cases are caused by HSV type 2, and there are significant numbers of HSV type 1.
- This can be diagnosed by:
- Skin biopsy lesion
- Vitreous humor
- Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
- Serum
- Diagnostic tests are:
- Cultural is the gold standard,
- HSV antigen 1.
- HSV antigen 2.
- Stored body fluids at 4 °C and tissue at -20 °C.
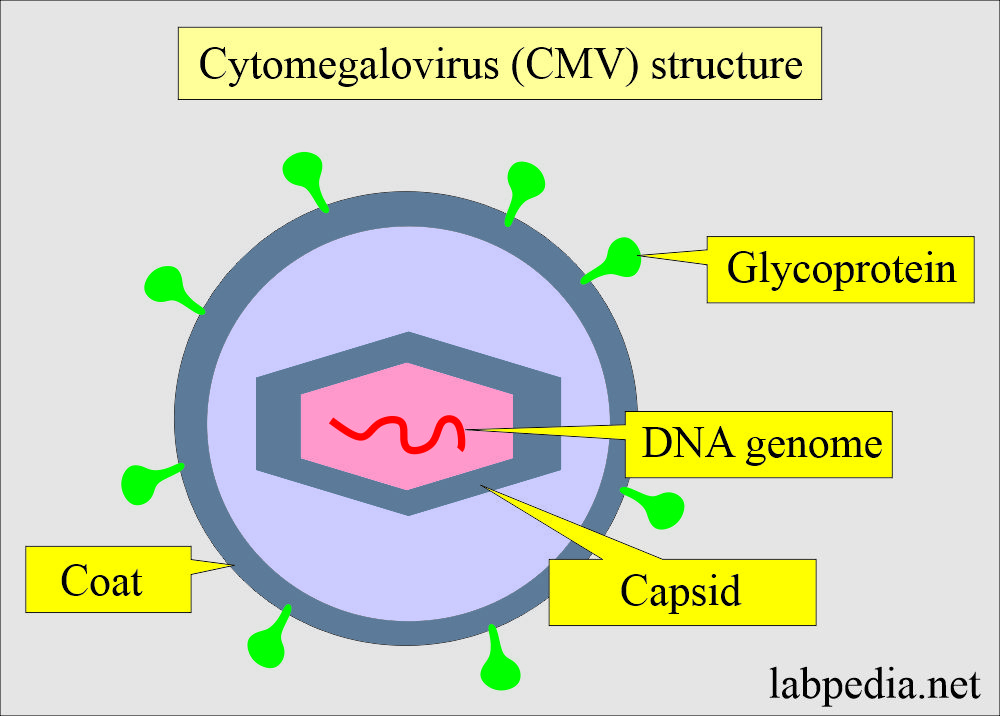
Cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection
- CMV is a part of the herpesvirus group.
- CMV infection is widespread, as serological evidence of infection varies from 30% to >90% of the population.
- There is a lower incidence in the USA and Western Europe.
- CMV infection is seen in:
- Fetal and early childhood.
- Young adults and late adolescents.
- This can be diagnosed from:
- Whole blood
- Serum
- Urine
- Tissues
- Diagnostic tests:
- Culture is the most sensitive method.
- CMV-IgM indicates the most recent infection.
- CMV-IgG indicates past infection.
- Store all fluids at 4 °C and tissues at -20 °C.
Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) infection
- EBV is a member of the herpes virus.
- This can be diagnosed with the following samples:
- Whole blood
- Tissue
- saliva
- Diagnostic tests are:
- Monospot heterophilic agglutination test.
- Viral capsid antigen-antibody test for IgM and IgG.
- EBV nuclear antigen (EBNA).
- EBNA-IgG
- EA-D
- Store the fluid at 4 °C and the tissue at -20 °C.
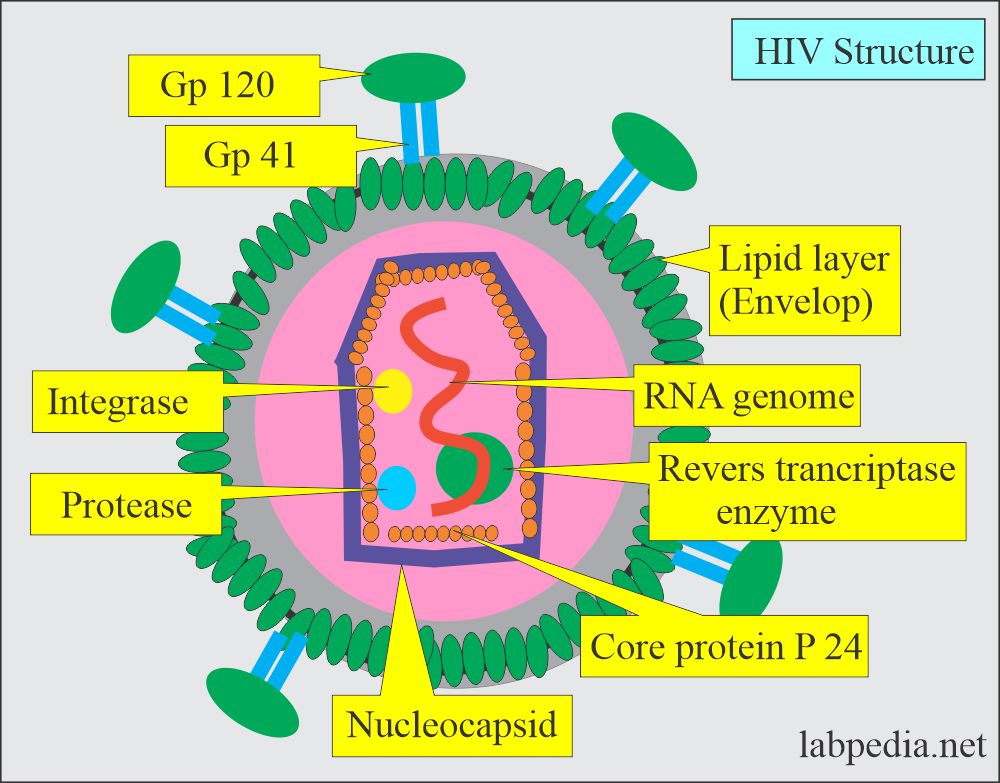
Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV-1)
- This can be diagnosed by:
- Whole blood
- urine
- Body fluids
- Diagnostic tests are:
- HIV antibody test by ELIZA.
- Western blot test.
- p24 antigen capture assay. This will detect before the seroconversion and also assesses the progression of AIDS.
- Oral fluids for the detection of HIV antibodies, kits by the name of Orasure, Orapette, and Omni sal are available.
- Urine for the HIV antibody test.
- Store fluids at 4 °C and tissue at -20 °C.
Human papillomavirus (HPV)
- This can be diagnosed from:
- Cervical smears
- Biopsy or scrapings
- Tissue from anogenital area
- Diagnostic tests are:
- Colposcopy and Vinegar acetic acid will give white color to the affected area.
- PAP smear will give abnormalities of the cells and see the virus-infected cells.
- Biopsy.
- HPV cervical test.
- DNA test (PCR, southern blot hybridization).
- Store the tissue at -20 °C.
Rotavirus Infection
- This can be diagnosed from:
- Feces (isolate the nucleic acid)
- This can be stored at 4 °C.
- Diagnostic tests are:
-
- Stool for rotavirus antigen.
- ELIZA
-
Varicella-Zoster Virus
- This can be diagnosed from:
- Whole blood
- Skin Lesions
- Diagnostic tests are:
- Usually, this is diagnosed by the clinician as a typical skin lesion, a vesicular dermal lesion.
- Culture of the virus.
- PCR from the lesion.
- Store fluids at 4 °C and tissues at -20 °C.