Urine Protein (Proteinuria), Microalbuminuria
Urine protein (Proteinuria)
What sample is needed for Urine protein (Proteinuria)?
- A random urine sample can be used.
What are the indications for Urine protein (Proteinuria)?
- To find out the presence or absence of protein in the urine.
- This may be used as a screening test for kidney disease.
- It is an early marker of kidney disease.
- It is a predictor of cardiovascular risk.
- It differentiates between glomerular and tubular abnormality.
- It is advised in diabetes mellitus to find renal involvement.
How would you discuss the pathophysiology of Urine protein (Proteinuria)?
- Proteins will not be present in the urine of a healthy individual with normal renal function, but you may find only traces.
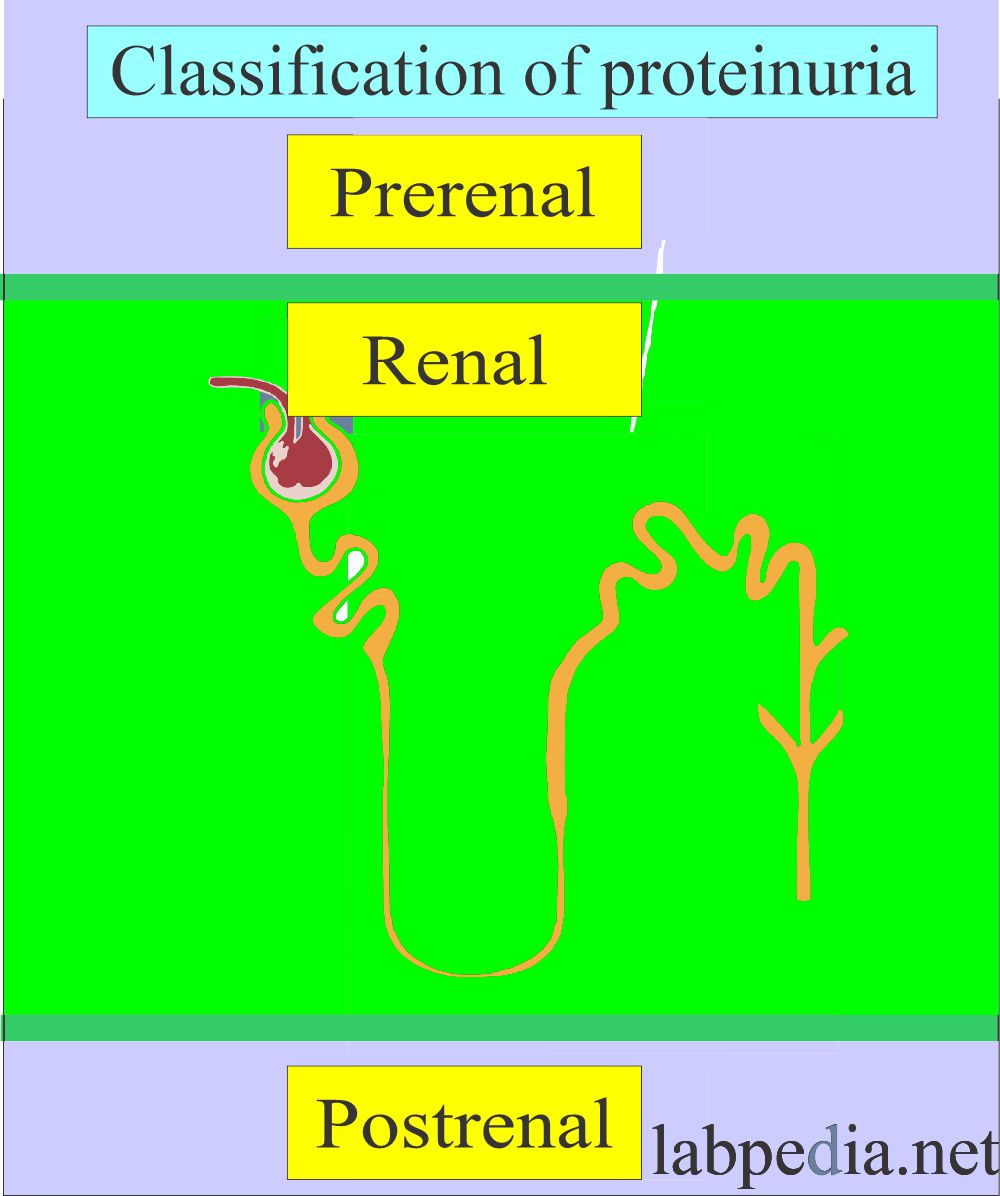
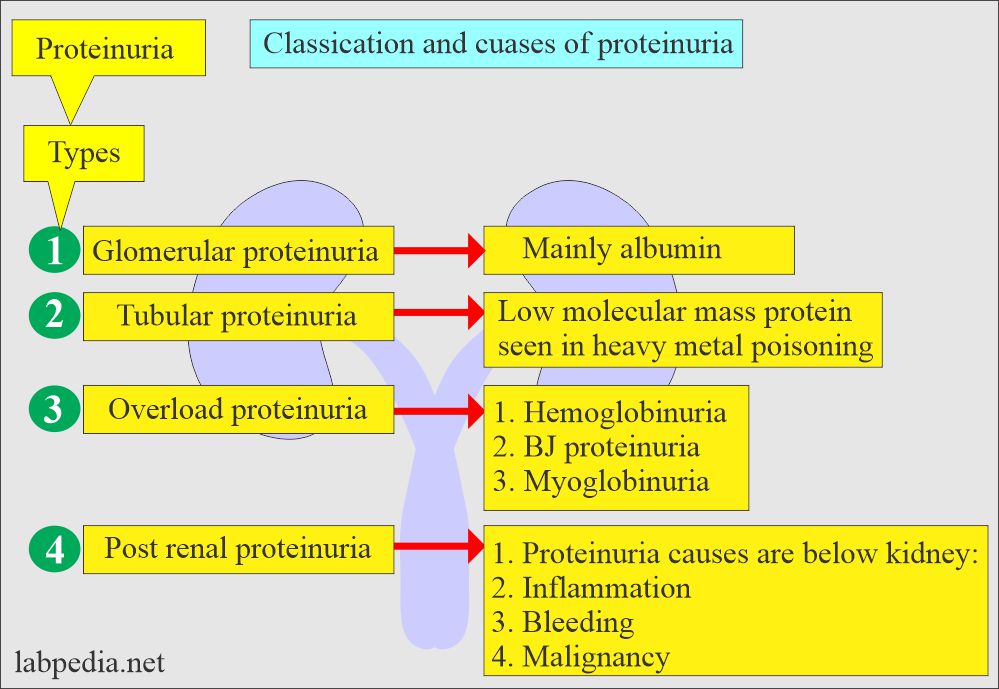
How will you classify Proteinuria?
- Pre-renal:
- This proteinuria is not indicative of renal disease.
- Low-molecular-weight plasma proteins like hemoglobin, myoglobin, and acute-phase proteins cause this transient condition.
- Another example is Bence-jones proteinuria in cases of multiple myeloma.
- Renal:
- This proteinuria is seen in renal diseases with glomerular or tubular damage.
- In the case of glomerular damage, there is an increased amount of albumin with RBCs and WBCs.
- Post-renal:
- This may be due to causes in the ureters, urinary bladder, prostate, and vagina.
- The causes are bacterial and fungal, which produce exudate-containing protein from the interstitial fluid.
- The blood, due to injury or menstrual cycle, contributes to protein.
- Prostatic fluid and spermatozoa may also contribute to protein.
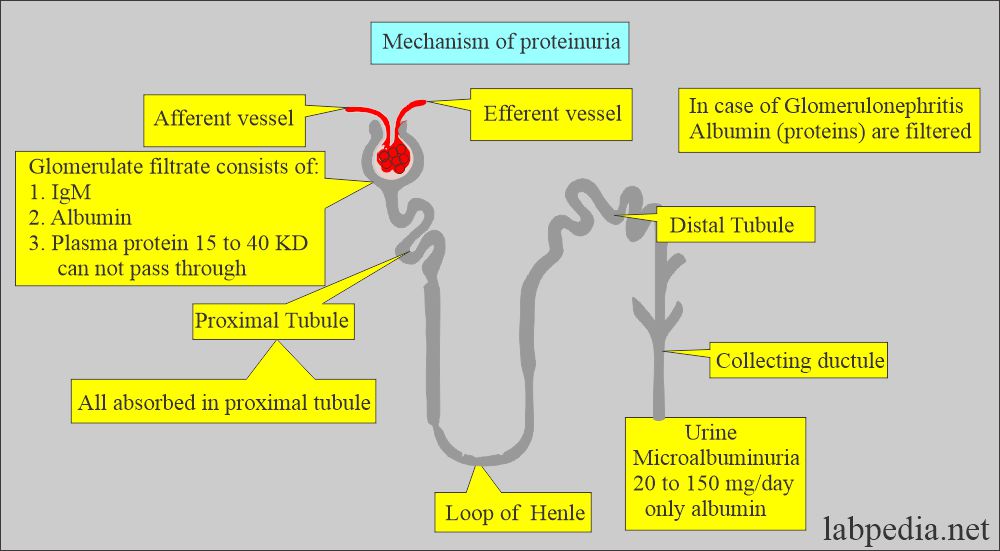
What is the mechanism of protein in the urine?
- Urine is formed by the ultrafiltration of plasma across the glomeruli.
- Plasma protein with molecular weight >40,000 is retained in the plasma.
- Normally, the glomerular membrane does not allow protein filtration into the urine because of narrow spaces in the glomerular membrane.
- The majority of the albumin presented to the glomeruli is not filtered.
- The convoluted tubules reabsorb much of the Protein (albumin) filtered by the glomeruli.
- In glomerulonephritis, the glomerular membrane is injured, and there are larger spaces from which protein, particularly albumin (which is smaller in size), can easily pass in the urine.
- Albumin is 1/3 of the urinary protein.
- Albumin is filtered through the glomeruli very easily compared to plasma globulin.
- In pathologic conditions, Albumin is abundant.
- Urine Albumin is used as the protein marker of glomerular permeability.
- The term proteinuria is often used synonymously with Albuminuria.
- Protein is the single most important parameter for renal dysfunction.
- If more than a trace of protein is found in urine, advise 24-hour urinary protein.
What is the normal urine protein (proteinuria)?
- Spot urine protein = 0 to 8 mg/dl
- While 24 hours of protein is <150 mg/dl
- Another source
- <10 mg/dL or
- 100 mg/24 hours of urine.
Source 1
- The limits of detection by the strips are:
- Albustix , Multi stix = 15 to 30 mg/dL.
- Chemstrip = 6 to 30 mg/dL.
- In the case of microalbumin:
- Albsure = 2 to 3 mg/dL
- Micral = 1.5 to 2 mg/dL
- Micro-Bumintest = 4 to 8 mg/dL
How will you detect proteinuria?
Spot test:
- In this test, protein is detected by dipstick or biochemically in the random urine sample.
- Usually, 24 hours urine sample is needed.
- Urine protein assays are sensitive to all types of proteins like albumin, globulins, and Bence-Jones protein.
- Most assays can detect a minimum of 3 mg/dL of protein in the urine.
- A urine dipstick is most commonly used. This is most sensitive to albumin.
- The dipstick can detect albumin when it is about 18 mg/dL.
Sulfosalicylic acid precipitation method:
- First, centrifuge the urine.
- Add 3 mL of 3% sulfosalicylic acid (another reference says 20%) to 3 mL of centrifuged urine.
- Mix well and observe cloudiness; the photometry can also read this.
How will you read the sulfosalicylic acid test?
| Grade based on turbidity | Degree of Turbidity |
Protein % in mg/dL |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
How will you compare the various proteinuria tests?
| Grade of urine protein | Multistix/Albustix | Sulfosalicylac acid | Chemstrip |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
What is the sensitivity of the various test strips?
- Multistix/Albustix = 15 to 30 mg/dL of albumin.
- Chemstrip = 6 mg/dL of albumin (in 90% of the cases).
What are the causes of urine proteinuria?
Pre-renal causes:
- Multiple myelomas.
- Intravascular hemolysis.
- Muscle injury.
- Infection and inflammation.
Renal causes:
- Glomerular diseases:
- Amyloidosis.
- Immune-complex disease.
- Diabetic nephropathy.
- Hypertension.
- Pre-eclampsia.
- Strenuous exercise.
- Dehydration.
- Toxic agents.
- Orthostatic or postural.
- Tubular diseases:
- Drug toxicity is like toxic agents and heavy metals.
- Fanconi’s syndrome.
- Viral infection (severe).
Post-renal causes:
- Lower urinary infection.
- Menstrual contamination.
- Vaginal secretion.
- Injury or trauma.
- Prostatic fluid.
- Presence of spermatozoa.
Microalbuminuria
How will you define microalbuminuria?
- This indicates diabetic nephropathy.
- There is reduced glomerular filtration, and eventually, there is renal failure in diabetes mellitus type 1 and type 2.
- Diabetes complication is first indicated by microalbuminuria.
- These complications are controlled by controlling the diabetic glucose level and hypertension.
- Microalbuminuria is also associated with cardiovascular disease.
Values are reported as the albumin excretion in µg/minute or mg/24 hours.
- Microalbuminuria is significant when:
- It is 20 to 200 µg/minute Or
- 30 to 300 mg/24 hours Or
What are the causes of microalbuminuria?
- Diabetic nephropathy.
- Hypertension.
- Infection and inflammation.
- Kidney disease (Glomerular diseases).
- Metabolic syndrome.
- Cardiovascular diseases.
What are the normal values of microalbuminuria?
- Normal = <30 mg/day.
- Microalbuminuria = 30 to 300 mg/day.
- Albumin to creatinine ratio = 30 mg or higher.
What is the Normal urine picture?
-
Physical features Chemical features Microscopic findings - Color = Pale yellow or amber
- Appearance = Clear to slightly hazy
- pH = 4.5 to 8.0
- Specific gravity = 1.015 to 1.025
- Blood = Negative
- Glucose = Negative
- Ketones= Negative
- Protein = Negative
- Bilirubin = Negative
- Urobilinogen = Negative (±)
- Leucocyte esterase = Negative
- Nitrite for bacteria = Negative
- RBCs = Rare or Negative
- WBC = Rare or Negative
- Epithelial cells = Few
- Cast = Negative (Occasional hyaline)
- Crystal = Negative (Depends upon the pH of the urine)
- Bacteria = Negative Albumin: creatinine ratio is >3.4 mg/mmol.
- See more details on the urinary protein.
Questions and answers:
Question 1: When will you call microalbuminuria?
Question 2: Can you see normal protein in the urine?

We are planning to analyze neurotransmitters with urine that collecting with dry urine spot. To stabilize urine in our collection devices, may I ask what composition and substances should be used for the stabilizer? Kindly inform me of its formula. Thank you.
Please see the following link:
https://www.labpedia.net/urine-analysis-part-2-urine-formation-urine-sample-types-and-urine-preservatives/
1. thanks for the useful information
2. Just a short comment and will appreciate a feed back ;
a. urine strips are now in 13 parameters which include MICROALBUMIN AND CREATININE – giving better detection of albumin in the 10micro range.
b. PYROGALLOL red calorimetric method by Watanabe is quantitative for micro albumin in urine and CSF., simple, cost effective. Please try this method
Our readers can try these kits. There are so many strips that are available.
Can we use pyroglallol method for urine albumin,urine protein, urine microalbumin? As it detect major protein present in urine
Please see the following reference, and this may answer your question.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4992489/
my urine total protein is 14mg/dl when done today morning urine sample. however 2 days back i did microalbumin test which came to be 0.6 mg/dl.
is it cause of concern?
Sure, you need workup of the kidneys, like blood urea and creatinine level. Rest I hope you are not diabetic. Still, I will ask you to do HbA1c.