Urine Potassium (K+), 24-Hours or Random sample
Urine Potassium (K+)
What sample is needed for Urine potassium (K+)?
- Collect 24 hours of urine.
- Procedure to collect 24-hour urine: Discard the first sample and note the time.
- Collect the rest of the urine for 24 hours and urinate the last sample into the container.
- Refrigerate the urine during collection.
What are the indications for Urine potassium (K+)?
- This study is done on renal and adrenal disorders.
- This is done for water and acid-base balance.
- This is done in support of hypercalcemia.
What are the precautions for Urine potassium (K+)?
- Potassium in the diet will affect the urinary potassium level.
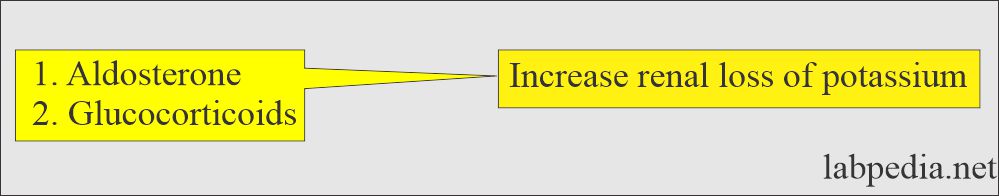
- Drugs that increase the potassium level are diuretics, salicylates, and glucocorticoids.
- Licorice increases potassium excretion in the urine.
How would you explain the pathophysiology of Urine potassium (K+)?
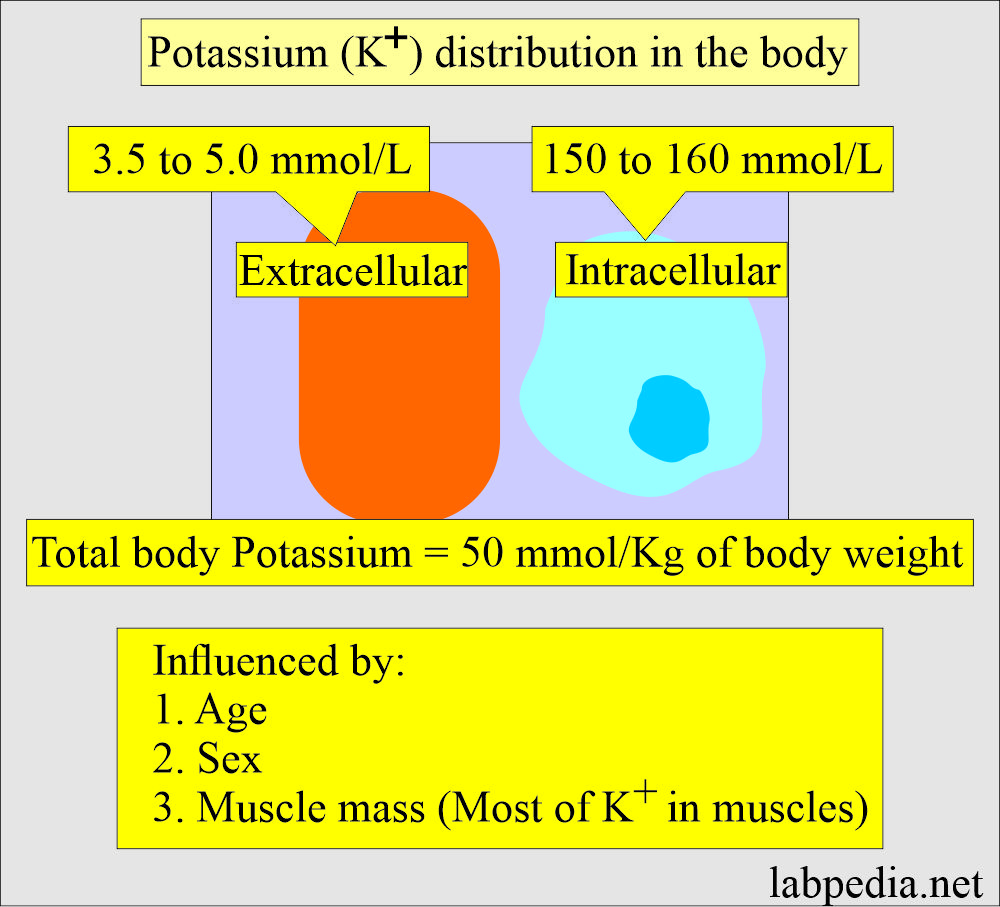
- Potassium is the major cation within the cells (Intracellular).
- 98% of the potassium (K+) is found in the ICW (intracellular water) space.
- The extracellular water space (ECW), the potassium concentration is only 3.5 to 5 mmol/L.
- The concentration reaches about 150 to 160 mmol/L.
- Total body potassium (K+) in an adult male is about 50 mmol/Kg of body weight.
- Potassium concentration depends upon the following:
- Aldosterone.
- Glucocorticoids.
What are the functions of Potassium (K+)?
- Potassium is a vital electrolyte, and its important functions are:
- Nerve conduction.
- Muscles contraction.
- Fluid balance.
What is the role of Kidneys’ in Potassium (K+) regulation?
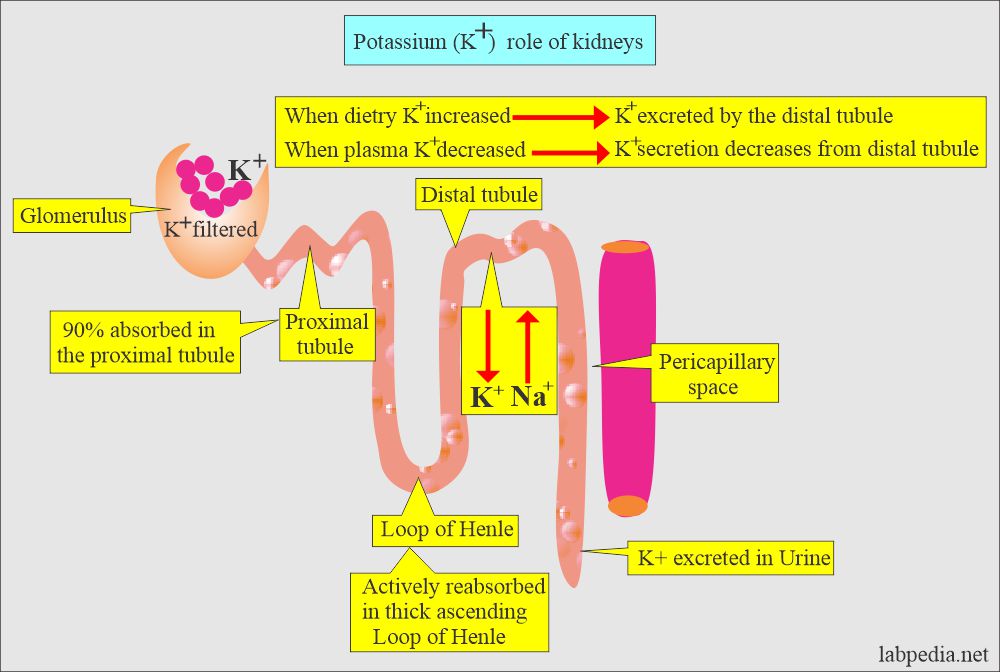
- Kidneys are important for the regulation of the K+ level.
- Kidneys can not reabsorb the potassium.
- Intake of potassium is balanced by the kidneys by the excretion of potassium in the urine.
- Proximal tubules reabsorb all the K+.
- Aldosterone additional K+ is excreted into the urine in exchange for Na+.
- The distal nephron is the main determinant of urinary K+ excretion.
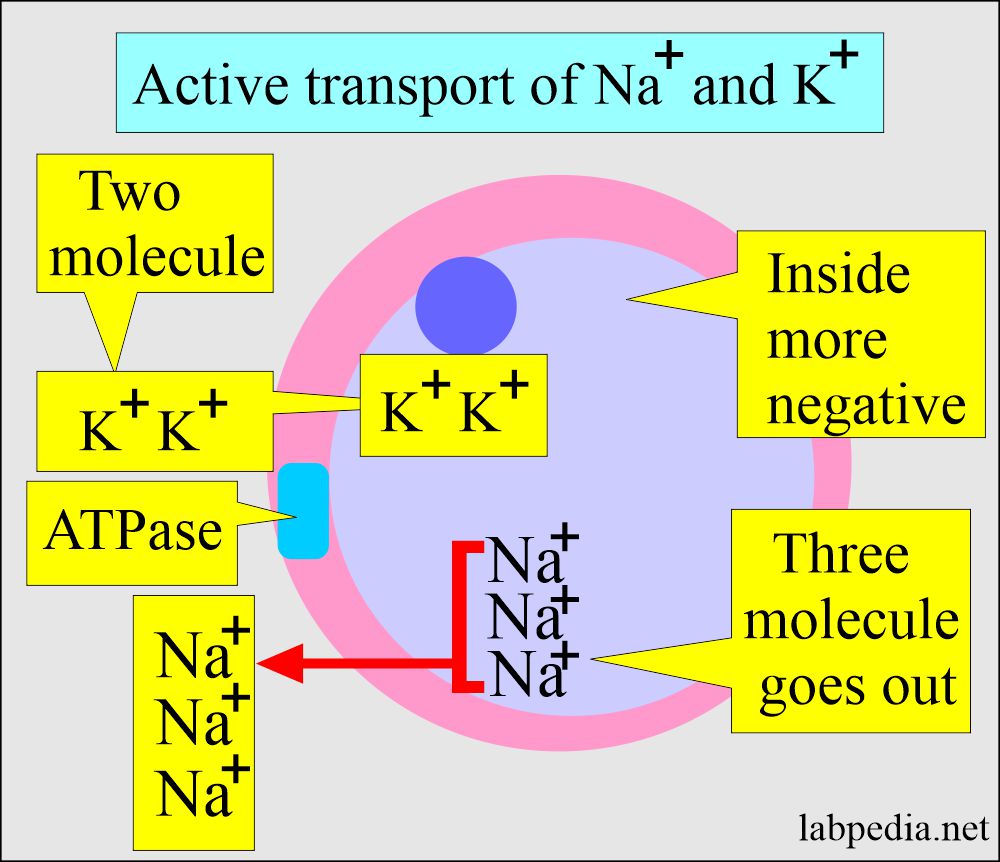
- Even if an excess of K+ is taken, this is still excreted in the urine except in patients with renal failure, where the K+ level may enter the toxic level. This is an active process that depends upon ATPase activity.
- This is the amount of potassium excreted in the urine.
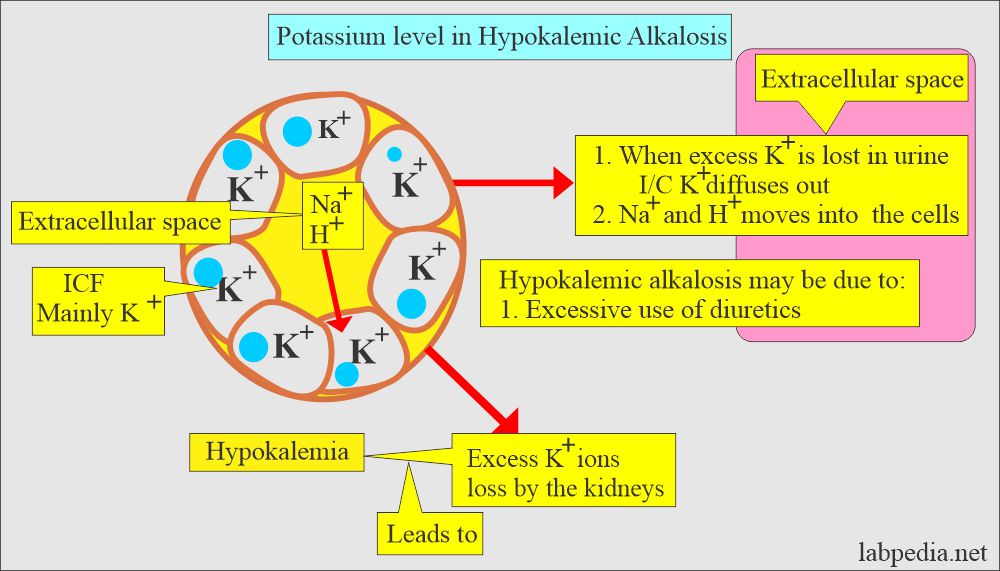
What is the level of Potassium (K+) in Alkalosis?
- In the case of Alkalosis, there is increased secretion of Potassium in the urine.
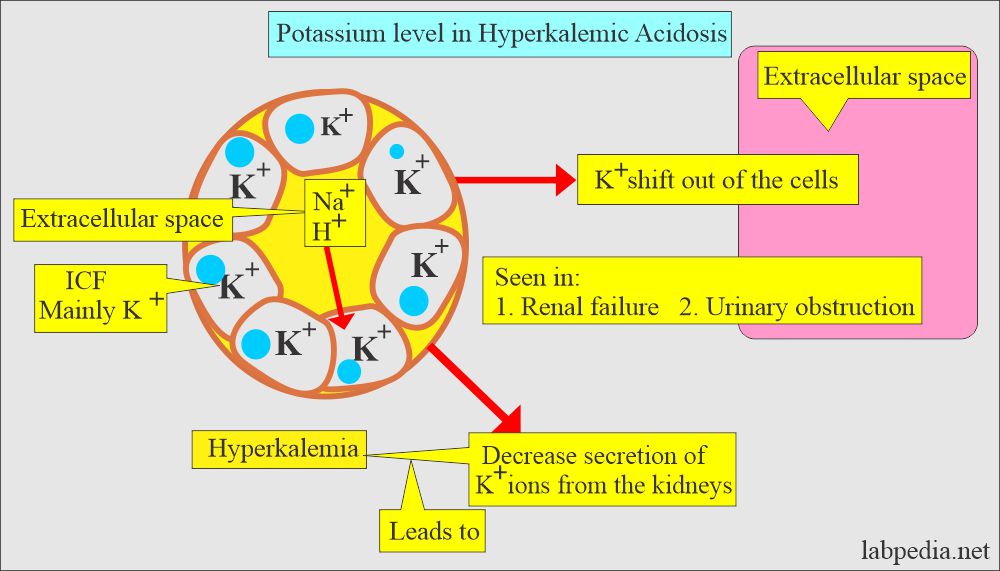
What is the role of Potassium (K+) in acidosis?
- In the case of acidosis, there is decreased potassium secretion in the urine.
What are the important facts for Urine Potassium (K+)?
- Urine potassium (K+) concentration is important in diagnosing hypokalemia.
- Urine potassium (K+) concentration <20 mmol/L with hypokalemia is suggestive of inadequate intake of potassium (K+) or nonurinary loss.
- Meanwhile, a urine potassium (K+) level of >20 mmol/L is consistent with urinary loss.
- Urine K+ >30 meq/day is inappropriate in hypokalemic patients and strongly suggests a hyperaldosteronism state.
- Spot urine test K+ > Na+ is also suggestive.
- Urine K+ <30 meq/day reflects renal K+ retention as seen in diuretic use or gastrointestinal loss.
- Urine potassium (K+) has little value in the differential diagnosis of hyperkalemia.
What are the causes of depletion of Potassium (K+)?
- Potassium (K+) depletion occurs when the potassium (K+) output exceeds intake.
- A small amount of potassium (K+) is lost in the stool in normal conditions.
Causes of potassium (K+) retention in the body:
- Potassium (K+) accumulates in the body when the intake of potassium (K+) increases the output because of some abnormality in the potassium (K+) homeostasis.
- Under normal conditions, kidneys can compensate for the imbalance.
- High potassium (K+) intake leads to potassium retention only when the kidney’s functions are disturbed.
| Decreased potassium (K+) excretion | Increased potassium (K+) intake |
|
|
What is the normal Urine Potassium (K+)?
Source 1
| Age | meq/day |
| 6 to 10 years | |
| Male | 17 to 54 |
| Female | 8 to 37 |
| 10 to 14 years | |
| Male | 22 to 57 |
| Female | 18 to 58 |
| Adult | 25 to 125 |
- Values vary with diet.
Source 2
- 25 to 100 meq / L / day (25 to 100 mmol/day).
- Values vary with diet.
What are the causes of increased urine Potassium (K+) Hyperkaluria?
- Diuretic therapy.
- Cortisone therapy.
- Drugs like penicillin and carbenicillin
- Thiazides.
- Chronic renal failure.
- Starvation.
- Hyperaldosteronism.
- Renal tubular acidosis.
- Cushing’s syndrome.
- Alkalosis.
- Excessive intake of licorice.
What are the causes of decreased Urine Potassium (K+) Hypokaluria?
- Diazoxide.
- Amiloride.
- I/V glucose infusion.
- Dehydration.
- Malnutrition.
- Diarrhea.
- Vomiting.
- Malabsorption.
- Addison disease.
- Acute renal failure where urinary K will be low, but the patient will have hyperkalemia.
What is the diagnostic value of urinary Potassium (K+)?
- It helps to differentiate between renal and non-renal causes of potassium imbalance.
- Urine potassium-to-creatinine ratio helps with potassium losses.
Questions and answers:
Question 1: What is the value of urine potassium (K+) in hyperkalemia?
Question 2: Is there any value of urine potassium (K+) in the hypokalemia?