Summary of Normal Urine and Their Significance
Summary of Normal Urine
What are the Urine normal values?
| Urine substances to be checked | Normal values | Collection timings | Significance |
| Physical characteristics | |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Chemical characteristics | |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
It indicates the renal function |
|
|
|
It evaluates renal functions |
|
|
|
It is seen in the inherited disease |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
It helps to evaluate kidney function |
|
|
|
It helps to evaluate joint pain |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
It is part of acid-base balance |
|
|
|
It is part of acid-base balance |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
It is needed in the renal stone formation |
|
|
24-hour urine sample | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Negative |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
It diagnoses phenylketonuria |
| Microscopic characteristics | |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
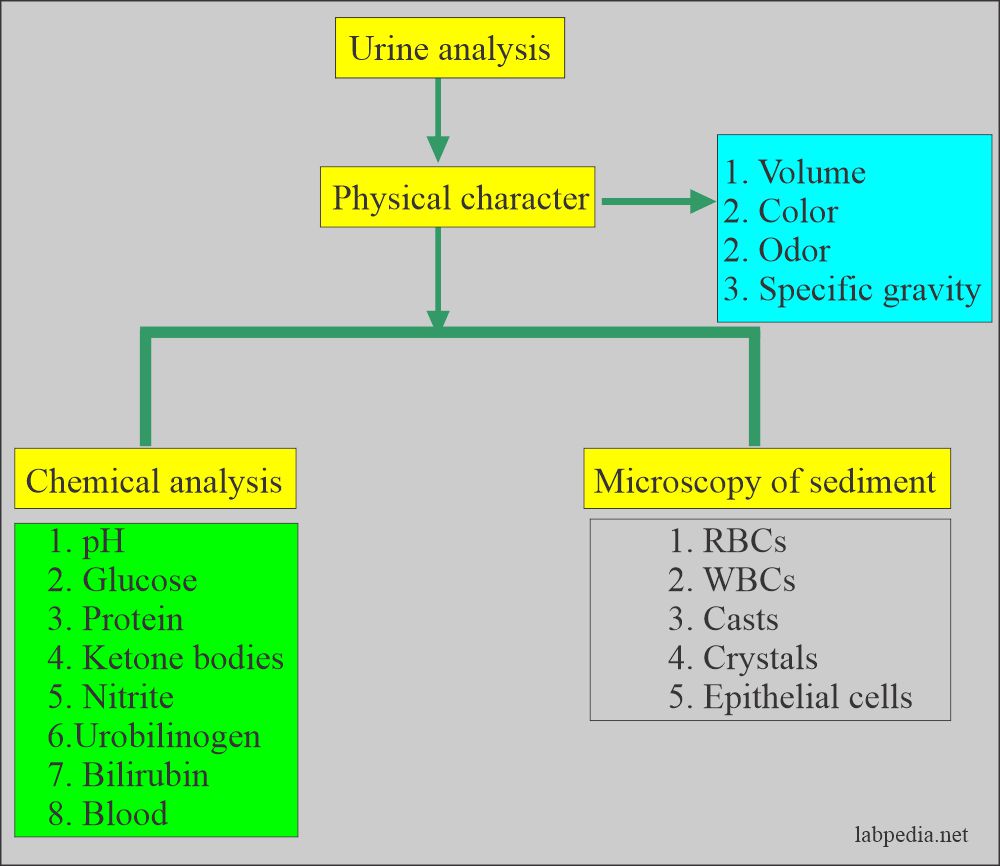
Summary of normal urine: Summary of the urine analysis
Questions and answers:
Q1: What is the significance of a waxy cast?
Q2: Is there any significance of the amylase in the urine?

Respected Doctor sahab,
Recently my sister’s 90 years old mother in law had a urine test.
Following is an excerpt from her urine test report:
“Urine r/e – sugar trace, 1 – 2 epi cells, 2 – 4 WBC, occ RBC. Urine culture: No growth”.
Instead of mentioning the number of RBC, the hospital has mentioned “occ RBC” .
1. What does “occ RBC” mean?
2. How many RBC is meant by “occ RBC”?
3. Does it indicate any serious condition?
I would be grateful if you kindly let me know.
Best regards.
Occasional RBC is normal. WBC 2 to 4, Epithelial cells 1 to 2 are normal. Sugar trace needs workup to rule out diabetes mellitus. There is no need to worry about RBC, WBC, and epithelial cells.
PUS CELL:4-6
BACTERIA: RARE
25 YEARS OLD AND 14 WEEKS PREGGY
Please repeat urine after 2 weeks. These pus cells are in normal range.
Dear Doctor Sir,
Hope you are doing good, recently my mother was diagnosed with diabetes, in her urine examination report it says a few things I want to clarify that:
Urine MICROSCOPIC EXAMINATION
1. Pus cells : 0 – 2 /HPF; is it normal or something to worry?
2. Red Blood Cells : Absent /HPF; HPF is normal or something alarming?
3. SUGAR : Present 1.0 %.
Is it expected that a person with diabetes has glucose/ sugar present in their urine?
WBC 0 t0 2 are normal. Mostly RBCs are absent in the urine. Only urine sugar is abnormal, and it appears in the urine when the blood sugar level is above 180 mg/dL. As a rule, urine should be negative for sugar. So you can control Diabetes mellitus by checking the urine sugar, which should always be negative.
GoodMorning sir can i ask what is my case. I had a resut of plus2 in Blood and my RBC is 0-2 and WBC is 0-2 may i ask if there is a problem? I already undergo urine culture but they found nothing on my Urine
I think your urine findings are normal unless you have any symptoms. Just drink at least 6 to 8 glasses of water for a few days. That is best if you drink water in the morning on an empty stomach.
Dear DR Riaz,
I recently had a Urinalyses test and my WBC was 6-10/HPF w/ WBC clumps present,
with a Urine culture of no growth in one day. Everything else is Negative.
Should I seek further Medical Advise.
In females, WBCs are more than in males. But clumps of WBCs indicate infection. You need to repeat urine analysis and culture. Do you have any symptoms like burning micturition?
Dr Riaz,
No burning or trouble urinating. No aches or pains in back. I’m a 70 year old Male, having Lazer therapy for a bad case of toe nail fungus and just had STREP
throat two weeks ago. Do you think this has a bearing on the WBC Thanks,,,
I am pregnant and I undergo a urinalysis test and the results says blood positive 1, ketones positive 1 and protein
Ketone indicates that you are not eating properly or vomiting. First, you improve your food and then check your urine again.
Dear Doctor Sir,
My sister’s age is 1 year and 5 months. Urine Routine Examination is done . The result is
Chemical Examination:
Urine for Specific Gravity >=1.030
Reaction(pH) 5.500
Albumin Nil
Sugar Nil
Phosphate Nil
Bilirubin Nil
Urobilinogen Absent
Nitrite Nil
ketone Nil
Microscope Examination :
Epithelial Cells 2-4 /HPF
RBC Nil /HPF
Pus Cells 2-4 /HPF
cellular Cast Nil /LPF
Granular Casts Nil /LPF
Hyaline casts Nil /LPF
Calcium Oxalate Nil
Triple Phosphate Nil
Uric Acid Nil
Amorphous phosphate Nil
Urates Nil
Is this Ok?
The urine looks normal.
A.o.A sir
My brothers age is 28
For about 4 months he is facing a problem. When he urinates the colour of urine is dark brown like coke but once in a month. Plz can you tell me the reason.
Most likely, hemoglobin is giving the color. But he needs to work up for hemoglobinuria. That is abnormal. Please consult a good physician to find the cause of hemoglobinuria.
Hemoglobin level in his test is ** traces
GOOD EVENING DOCTOR
MY RBC IS GIVEN 10-12/HPF
PUS CELLS 2-3 HPF
EPITHELIAL CELLS 1-2
CALCIUM OXALATE CRYSTALS 18/20HPF
pLEASE GIVE ME THE ANALYSIS REPORT
GOOD EVENING DOCTOR
MY RBC IS GIVEN 10-12/HPF
PUS CELLS 2-3 HPF
EPITHELIAL CELLS 1-2/HPF
CALCIUM OXALATE CRYSTALS 18-20/HPF
pLEASE GIVE ME THE ANALYSIS REPORT
This urine report only shows increased RBCs 10 to 12/HPF. This may be due to calcium oxalate crystalluria. Please drink more water, mainly empty stomach, at least 2 to 3 glasses. Then repeat urine after 2 to 3 weeks.
Hello. 56 year old male. I’ve been having abdominal pain recently (below navel) and have been treated for prostatitis over the past 2 years (several rounds of antibiotics, tamsulosin most of that time,
I can suggest an ultrasound abdomen. Or consult a physician to find the cause of pain.
Hello sir
My urin examination result is
Ph-5.5
Protein-Trace
Ketone-nil
Bilirubin candent
Glocous-nil
Rbc-nil
Wbc-nil
Cast-nil
Is report normal sir
Please check the presence of protein trace. I hope you are not diabetic?
I am 32 weeks pregnant. The followings are my results:
Name Results:
Protein, urine, qn 15.5 mg/dL
Creatinine, urine 100 mg/dL
Protein/creatnine, urine 0.16 mg/mg
Glucose, UA Negative
Bilirubin, UA Negative
Ketones, UA 20 mg/dL
Specific gravity, UA 1.018
Hemoglobin, ur, ql Negative
pH, UA 6
Protein Negative
Urobilinogen, UA <2.0 mg
Nitrite, UA Negative
Leukocyte esterase Trace
WBC 2 HPF
RBC NONE
Squamous cell counts 358 LPF
Mucus Rare
Protein 15.5 mg/dL
Creatinine 100 mg/dL
Protein/creatinine 0.16 mg/mg
You have proteinuria. You need supervision of the gynecologist till your delivery. What about you blood pressure?
Hi Doctor Riaz, my current results are
Specific gravity 1.010
Pus cells 3-6/hpf
Rbc 0-2/hpf
Epitheleal cells – few
Amorphous urates – few
Bacteria- moderate
Hi Dr. Riaz,
My current test is:
Pus cells: 3-6/hpf
RBC: 0-2/hpf
Epithelial cells: few
Amorphous Urates: few
Bacteria: Moderate
Your urine report is normal. Female may have pus cell or WBCs 5 to 7/HPF.
Hello Dr,
Here are my test results:
Color: Yellow
Appearance: Hazy
Reaction: 5
Specific Gravity: 1.010
Protein: Negative
Sugar: 3+
Pus Cells: 0-2/hpf
Red Blood Cells: 0-1
Epithelial/Renal Cells: Few
Am. Urates/Phosphates: FEW
Mucus Threads: FEW
Bacteria: Few
Do I have an illness I need to be aware of?
I think you have not noticed sugars 3+. It needs to check your blood glucose level. You need to rule out diabetes mellitus. Please also check your HbA1c.
Pus cells 2-3 hpf
Epithelial cells 1-3 hpf
Is this normal in my 20 months old baby boy CUE report
These findings are normal.
Hi Dr. Riaz
Here is my routine urinalysis result
Color pale straw
Transparency hazy
Reaction 6.0
Specific gravity 1.015
WBC (+2) 25-30 /HPF
RBC 0-1 /HPF
Squamous: many
Amorphous :urates few
Bacteria: few
Mucus threads: few
I want to know if there’s any problem n my result?
WBC 25 to 30 /HPF indicates urinary tract infection. Before taking antibiotics, please get urine culture and sensitivity report.
Doc urinary tract infection it can affect your baby? I am in 1st trimister pregnant.
Hi Doctor Riaz
My urine analysis result shows
Volumn – 5ml
Colour – Amber
Odor – Nill
Appearance – Clear
pH – 6.0
Protein – Trace
Ketones – Trace
Blood – +++
Specific Gravity – 1.030
My Blood Count
RBC – 4.2
Neutrophils – 36
Lymphocytes – 52
Platelets – 95
Please always write age. There is proteinuria and ketones in urine may be seen in starvation, vomiting or fasting. Blood count shows lymphocytosis and that may be seen in chronic infections. You have not written the ESR.
Hi Doctor Riaz,
Im 32 yrs old, female.
Can I ask ,
Heres my routine urinalysis
Color: yellow
Ph: 5.00
Transparency: turbid
Specific gravity: 1.019
Albumin: 1+
Sugar: negative
Ketones: negative
Urobilinogen: negative
Nitrite: negative
Bilirubin: negative
Erythrocytes: 2+
Leaukocytes: 3+
White blood cells: 60-70/HPF
Red blood cell: 0-2/HPF
Squamous Epithelial: Few
Bacteria: Few
Do I have an illness?
Thanks Doc.
This urine report is abnormal. There is proteinuria and urinary tract infection. You need consultation with the urologist/physician.
Hi Doctor Riaz,
Im Imran.
My daughter is age:5 yrs old,
Can I ask,
Here is my Daughter’s routine urinalysis
Color: Straw
Ph: 5.00
Transparency: turbid
Specific gravity: Nill
Albumin: Nill
Sugar: Negative
Ketones: negative
Urobilinogen: negative
Nitrite: negative
Bilirubin: negative
Pus cells:02-04/HPF
Epithelial cells: 10-12/HPF
She is suffering from Abdominal pain and burning urination.
please tell me the causes of too high epithetical cells and tretmet for this cause
Do I have an illness?
Epithelial cell 5 to 7/HPF are seen routinely. I do not think to worry.
For burning micturition, please get her X-RAY KUB (especially urinary bladder to rule our bladder stone).
Please get Xray for her urinary bladder for stones, that may cause burning micturition or infection may be the cause. I do not think epithelial cells have much significance.
Dear Doctor Sir,
I’m 18 years old girl. How is my report?
COLOUR – PALE YELLOW
APPEARANCE – CLEAR
SPECIFC GRAVITY – 1.010
REACTION (PH) – ACID (pH 6.0)
URINE PROTEINS (ALBUMIN) – NIL
GLUCOSE – NIL
BILIRUBIN – NIL
UROBILINOGEN- NORMAL AMOUNT
KETONE BODIES – NIL
PUS CELLS – 2-4
RED CELLS – OCCASIONAL
EPITHELIAL CELLS – +
CASTS – NIL
CRYSTALS – NIL
ORGANISMS – NIL
( Thank you, sir)
Your urine report is negative, no need to worry.
urin analysis:
color -yellow
appearance -s. turbit
spec. gravity -1.020
ph- 5.0
albumin -nil
suger -nill
ketones- -nill
bilirubin-nill
urobilinogen – nill
ascorbic acid-nill
nitrite- negative
blood- trace
microscopic exam:
pus cells- 3-5
red blood cells-1-3
epithelial cells -nill
casts – nill
crystals – nill
muscus threads – few
bacteria – few
other – nill
s. creatinine – 0.82
My age is- 38
Is this report is normal sir?
I will take this urine report normal, unless you have any signs and symptoms.
Sir, the symptoms are low urine flow and frequent urination.
You have not told your age. Check your HbA1C level and fasting blood sugar.
Hi, Dr. Riaz.
I’m 55 yo, female. My urinalysis text results are:
Color: Light Yellow
Transparency: Turbid
pH: 8.0
Specific Gravity: 1.000
Glucose: Negative
Protein: Negative
WBC: 60-70
RBC: 0-2
Epithelial Cells: Moderate
Bacteria: Rare
Mucous Threads: Few
Does the urine test result indicate infection? I’ve been having fever at 38 – 40 degrees Celsius for 3 days now but I don’t feel warm and no pain. What do I need to do?
Thank you.
Your urine report shows urinary tract infection. Best would be do urine culture before starting antibiotics. But you need antibiotics with consultation of physician.
Dr. Riaz, Assalam o Alaikum
i would like to know something about my report. please help me in this.
in urine chemical:
1. pH is 6 (is it acidic?) – however it is written (normal range is 5-8)
in urine microscopy:
1. RBC is Occasional / HPF – however it is written (normal range is 0-2 / HPF)
2. Leucocytes is Occasional / HPF – however it is written (normal range is 0-4 / HPF)
3. Squamous epith cell is NIL / HPF – however it is written (normal range is 0-4 / HPF)
4. Non Squamous EPI cell is NIL / HPF – however it is written (normal range is 0-4 / HPF)
5. Bacteria is FEW / HPF (is it serious?)
Your urine report is normal. No need to worry.
Need your opinion Doc. base on the result below. Thank you
Color – yellow
Clarity – hazy
Ph – 7.0
Glucose- negative
Protein – negative
Pus cell. – 1-3 /hpf
Red blood cell – 8-12 /hpf
Mucous thread – +++
Bacteria – ++
RBC Cast – 0-1 /lpf
Your urine shows presence of RBCs (8 to 12/HPF). You need to rule out of urinary stones or in case of female, menses contamination needs to rule out.
Hi Dr. I’m 35yrs. First trimester pregnant. Here is my results:
Urinalysis-
Appearance – amber and clear
pH -5.0
WBC- 1-2/hpf
RBC- 1-2
Yeast- nil
T.Vag- nill
Casts- nill
Epithelial cells- +
Culture:
Yielded scanty growth of staph aureus after 24hrs of incubation at 37°c.
Please sir Is any problem with me and is pregnancy safe?
Staph. aureus presence is not good. Please repeat urine analysis, and also ask for urine culture. Do you have urinary burning or other symptoms? Better consult urologist or gynecologist for the management.
No. There’s no urine burning but there is discharge.
Your urine culture shows the growth of Staph. aureus and not good. You need to consult urologist or gynecologist for further workup.
Hi Dr. I’m 35yrs. First trimester pregnant. Here is my results:
Urinalysis-
Appearance – amber and clear
pH -5.0
WBC- 1-2/hpf
RBC- 1-2
Yeast- nil
T.Vag- nill
Casts- nill
Epithelial cells- +
Culture:
Yielded scanty growth of staph aureus after 24hrs of incubation at 37°c.
Please sir Is any problem with me and is pregnancy safe?
Hi Dr.
I am 35 weeks pregnant. The followings are my results:
Colour – Yellow
Appearance – Slightly Turbid
S. G. (Refractometer) – 1.024
PH – 5.5
Protein – +50mg/dl
Glucose – Nil
Ketone Bodies – Nil
Bilirubin – Nil
Nitrite – Nil
Urobilinogen – slightly increased amount
PUS Cells – 35-40 /H. P. F
RD Cells – 10-15 /H. P. F
Epithelial Cells – +
Casts – Nil
Crystals – +Few calcium oxalate
Your urine report is not normal. There is proteinuria, increased WBCs, and presence of RBCs. Please see your gynecologist for the management as soon as possible.
hello doctor , just wanna check the interpretation of my recent urinalysis. im male.
bacteria – rare
epithelial cells – rare
amorphous sediments – few
mucus threads – rare
thanks.
hello doctor , just wanna check the interpretation of my recent urinalysis. im male.
color : yellow
transparency : clear
bacteria – rare
epithelial cells – rare
amorphous sediments – few
mucus threads – rare
thanks.
Your urine report is normal.
Hi Doc!
Urinalysis of a 4 year old/female
Color: Yellow
Transparency: Hazy
pH: 6.0
Specific Gravity: 1.025
Protein: Negative
Glucose: Negative
RBC: 0-2/HPF
Pus Cells: 1-2/HPF
Bacteria: Few
Epithelial Cells: Few
Mucus Threads: Moderate
Amorphous Urates: Occasional
Casts: None
Others: None
Is everything okay with my niece? Are the results normal? Thanks in advance!
Hi Doc!
Urinalysis of a 4 year old/female
Color: Yellow
Transparency: Hazy
pH: 6.0
Specific gravity: 1.025
Protein: Negative
Glucose: Negative
Red blood cells: 0-2/HPF
Pus cells: 1-2/HPF
Bacteria: Few
Epithelial cells: Few
Mucus threads: Moderate
Amorphous urates: Occasional
Casts: None
Others: None
Thank you!
This urine report is normal.
Hello doctor
Urieanalysis of 22 year old female,
Colour: pale yellow
Specific Gravity:1.020
Ph: 6.5
All Chemical Test : Negative
Microscopy Test Name. Unit: hpf
RBC: 0
Pus calls: 2.30
Epithelial cells: 1.40
Calcium oxalate monohydrate crystals: 0
Calcium oxalate dihydrate crystals: 0.10
Triple Phosphate crystals: 0
Uric acid crystals:0
Calcium Phosphate:0
Cystine crystals: 0
Leucine crystals: 0
Tvrosine crystals: 0
Amoronous urates crystals: 0
Amorphous phosphate crystals: 0
Hayline cast : 0.10
Hyaline-Granular casts: 0
GrAnITer CASIS: 0
RBC casts: 0
WBC casts:0
Fatty casts: 0
Waxy casts: 0
Microorganism Casts: 0
Yeast cells: 0
Bacteria Rod: 3.50
Bacteria Cocci: 53.60
Mucus: 13.30
Other : 0
This urine report is normal. Hyaline casts are shown, but protein is negative.
Hi Doctor
My MOM is 85. Her urine routine test result is as follows :
PHYSICAL EXAMINATION
Quantity Sufficient
Color Straw
Specific Gravity 1.010
Appearance Clear
Sediment Nil
Blood Nil
CHEMICAL EXAMINATION
Reaction Acidic
Urobilinogen Not-done
Excess of Phosphate Nil
Albumin (Protein) (+)
Sugar Nil
Acetone Bodies /Keton Bodies Not-done
Bile Salts Nil
Bile Pigment Nil
MICROSCOPIC EXAMINATION
Epithelial Cells 0-1 /HPF
Pus cells Plenty /HPF
RBC Nil /HPF
Amorphous Phosphate Nil
Hyaline Casts Nil
Granular Casts Nil
Cellular Casts Nil
Epithelial Casts Nil
RBC Casts Nil
Calcium Oxalate Crystals Nil
Uric Acid Crystals Nil
Sulphonamide Crystal Nil
Triple Phosphate Crystal Nil
Tyrosine Crystal Nil
Fungus Absent
Sperm Absent
Urate Absent
Bacteria Absent
Candida Absent
Trichomonas Vaginalis Absent
Urine for C/S : Colony Count >10 *5 CFU/ml and fund Esch. Coli
and prescribe an antibiotic Nitrofurantoin 500 mg for seven days twice daily.
My question : Is this treatment is perfect ?
My mother has loss of appetite. There is nothing tasty in tounge. and day after day she is gradually weak.
PLEASE DOCTOR, GIVE US A CONCISE SUGGESTION.
Your mother is suffering from urinary tract infection. She needs antibiotics for this infection. If in sensitivity Nitrofurantoin was the choice, then you can continue with this antibiotic. For apatite, I do not know how much your MOM is active. You can give her nutrition supplements like Glucerna etc.
Dear Doctor
Thank you very much for your reply.
How many days should take Nitrofurantoin.
How can I measure normal range of pus cell.
and how can I understand that my MOM out of urinary tract infection. that means in which test I identify it.
I would be grateful if you kindly let me know.
Best regards.
Antibiotics are usually given for 7 to 10 days. As regards the effectiveness of the antibiotic, please test urine after 5 to 6 days. There should be no pus cells.
Dear Doctor
Thank you very much for your quick response.
One question to you that is in which area of medical treatment your are specialist. This information is help for me.
I am retired professor of pathology.
Dear Doctor
Following is my MOM urine R/E Report. Please give me your valuable suggestion on this report and suggest if any medicine need further.
PHYSICAL EXAMINATION
Quantity Sufficient
Color Straw
Specific Gravity 1.000
Appearance Clear
Sediment Nil
Blood Nil
CHEMICAL EXAMINATION
Reaction Acidic
Urobilinogen Not-done
Excess of Phosphate Nil
Albumin (Protein) Trace
Sugar Nil
Acetone Bodies /Keton Bodies Not-done
Bile Salts Nil
Bile Pigment Nil
MICROSCOPIC EXAMINATION
Epithelial Cells 2-3 /HPF
Pus cells 0-2 /HPF
RBC 1-2 /HPF
Amorphous Phosphate Nil
Hyaline Casts Nil
Granular Casts Nil
Cellular Casts Nil
Epithelial Casts Nil
RBC Casts Nil
Calcium Oxalate Crystals Nil
Uric Acid Crystals Nil
Sulphonamide Crystal Nil
Triple Phosphate Crystal Nil
Tyrosine Crystal Nil
Fungus Absent
Sperm Absent
Urate Absent
Bacteria Absent
Candida Absent
Trichomonas Vaginalis Absent
Blessed day Doc !
Female 56 yrs old with Diabetes and Hypertension
Urinalysis :
Red cell = 14-17 /HPF
Crenated RBC = FEW
Is it okay ? Pls let me know.THANK you
RBCs are abnormal in the urine. You have not talked about WBCs. I think WBCS are not increased in the urine. She should take plenty of water and then again repeat urine test after 2 to 3 weeks.
Pus cell= 0-2/hpf
Pus cell= 0-2/hpf
What is crenated RBC ?
No need for medication ? Just increase fluid intake ? And then after a week…repeat a urine test ? THANK you doc…
Blessed day doc !
Female 47 yrs old
Urinalysis :
Color = Yellow
Turbidity = Hazy
SP.GV = 1.005
Ph = 6.0
Protein = Negative
Glucose = Negative
Pus cell = 1-4/ hpf
Red cell = 6-9/hpf
Epithelial cells= Few
Mucus Thread = Moderate
Bacteria = Few
Is it okay ? THANK you Doc for being kind and you are a big help !!!
Hi doc I’m female 32 y/o
Color:yellow
Transparency: slightly hazy
Blood +1
Leococyte+1
Bilirubin negative
Urobilinogen normal
Ketone negative
Glucose negative
Protein negative
Nitrites negative
WBC 10-15 /hpf
Rbc 5-10 /hpf
Epithelial-few
Mucus thread few
Bacteria moderate
Amorphous urates few
Kindly help me what is the result doc, I’m still waiting for the result of my urine culture and sensitivity. Is there something wrong to me doc.thank you in advance
Your urine report shows RBCs and WBCs,indicating urinary infection. But you have to keep in mind about the menses. In case of menses, no need to worry.
Blessed day doc !
Female 47 yrs old / Menopause
Urinalysis :
Color = Yellow
Turbidity = Hazy
SP.GV = 1.005
Ph = 6.0
Protein = Negative
Glucose = Negative
Pus cell = 1-4/ hpf
Red cell = 6-9/hpf
Epithelial cells= Few
Mucus Thread = Moderate
Bacteria = Few
Is it okay ? THANK you Doc for being kind and you are a big help !!!
Hello Doc!
May I ask if my Urine Test result is normal Thank you!
Color- STRAW
Appearance- HAZY
Pus Cell- 10-12
RBC- 0-2
Epithelial- MODERATE
Am. Urates/Phosphates- RARE
Mucus- FEW
Bacteria- FEW
Thank you in advance!
Your urine shows 10 to 12 WBC/HPF, that is not normal. If you do not have any urinary symptoms, then please repeat urine after 2 weeks. Meanwhile take plenty of water.
Blessed day doc !
Female 47 yrs old / Menopause
Urinalysis :
Color = Yellow
Turbidity = Hazy
SP.GV = 1.005
Ph = 6.0
Protein = Negative
Glucose = Negative
Pus cell = 1-4/ hpf
Red cell = 6-9/hpf
Epithelial cells= Few
Mucus Thread = Moderate
Bacteria = Few
Is it okay ? THANK you Doc for being kind and you are a big help !!!
Your urine report is almost normal except few RBCs are seen. I will suggest repeating urine after 3 weeks. Take plenty of water.
No infection ? Why is there blood ? No need for medication ? Just increase fluid intake ? And then after a week…repeat a urine test ? THANK you doc…
WBC 5.9High
Urine RBC Value 13.7High
Urine Epithelial Cells Value 8.0High
Urine Bacteria Slight
Urine Hyaline Casts (Auto)5.37High
Urine Protein- Trace
Culture negative
Urine report is not clear to me. RBC 13.7 high. WBC 5.9 high. Please ask the lab what they means by high.
Age 27 Male
TEST(s) RESULT(s) REFERENCE RANGE(s)
COLOR YELLOW PALE YELLOW -YELLOW
APPEARANCE CLEAR CLEAR
SPECIFIC GRAVITY 1.010 1.005 – 1.025
pH 7.5 5-8
PROTEIN NEGATIVE NEGATIVE (gm/L)
GLUCOSE NEGATIVE NEGATIVE (mmol/L)
ACETONE (KETONE BODIES) NEGATIVE NEGATIVE (mmol/L)
BILE PIGMENT NEGATIVE NEGATIVE (umol/L) UROBILINOGEN 3.4 UMOL/L 3-16 (umol/L)
BLOOD NEGATIVE NEGATIVE (/ul)
NITRITE NEGATIVE NEGATIVE
PUS CELL 0-1 0-4 (HPF)
RED CELL NIL 0-2 (HPF)
EPITHELIAL CELL 0-1 0-4 (HPF)
CAST NIL NIL (LPF)
CRYSTAL NIL NIL (HPF)
BACTERIA NIL NIL (HPF)
YEAST NIL NIL (HPF)
MUCUS NIL NIL (HPF)
This urine report is normal.
Hi Doc,
I’m 27 years old. 37 weeks pregnant may I ask if there’s something wrong on my urinalysis test.
Color: Light Yellow
Transparency: Slightly Hazy
Sp. Gravity : 1.005
Ph: 6.50
Protein: Negative
Glucose:negative
Bilirublin: negative
Blood(ery/hb) :negative
Leucocytes: +++
Nitrite,: negative
Urobilinogen:negative
Ketone: negative
Rbc: 1-3 /hpf
Wbc:6-8 /hpf
Epithelial cells: moderate
Bacteria: few
Leucocytes are three plus and few RBCs. But nitrite is negative. WBCs are 6 to 8/HPF. Please repeat your urine from different lab. Because this urine report is confusing, and reports does not tally with each other.
Blessed day doc !
Female 47 yrs old / Menopause
Urinalysis :
Color = Yellow
Turbidity = Hazy
SP.GV = 1.005
Ph = 6.0
Protein = Negative
Glucose = Negative
Pus cell = 1-4/ hpf
Red cell = 6-9/hpf
Epithelial cells= Few
Mucus Thread = Moderate
Bacteria = Few
No infection ? Why is there blood ? No need for medication ? Just increase fluid intake ? And then after a week…repeat a urine test ? THANK you doc…
Salaam Doctor,
Wailkum salam, Thanks,
Blessed day doc !
Female 47 yrs old / Menopause
Urinalysis :
Color = Yellow
Turbidity = Hazy
SP.GV = 1.005
Ph = 6.0
Protein = Negative
Glucose = Negative
Pus cell = 1-4/ hpf
Red cell = 6-9/hpf
Epithelial cells= Few
Mucus Thread = Moderate
Bacteria = Few
No infection ? Why is there blood ? No need for medication ? Just increase fluid intake ? And then after a week…repeat a urine test ? THANK you doc…big help.
Female 19 years old
Urine examination Result :
Albumin – nil
Sugar – nil
Pus cells- -6-8/HPF
Epithelial cells- 12-15/HPF
RBC- 0-1/HPF
Motile bacteria -present (+)
Urine report looks to be normal. Only Pus cells 6 to 8/HPF is seen. I will suggest repeating urine from different lab after 2 weeks.
Female 47 yrs old / Menopause
Urinalysis :
Color = Yellow
Turbidity = Hazy
SP.GV = 1.005
Ph = 6.0
Protein = Negative
Glucose = Negative
Pus cell = 1-4/ hpf
Red cell = 6-9/hpf
Epithelial cells= Few
Mucus Thread = Moderate
Bacteria = Few
No infection ? Why is there blood ? No need for medication ? Just increase fluid intake ? And then after a week…repeat a urine test ? THANK you doc…big help.
Female 32
Urinalysis result
Color : yellow
Clarity: Sl. Hazy
Ph: 6.0
Specific gravity: 1 030
Protein: trace
Blood: neg
Glucose: neg
Ketones: neg
Bilirubin: neg
Nitrite : neg
Leukocytes: neg
Urobilinogen: 0.2
Epithelial cells: 2+
Bacteria: 1+
Mucus: 1+
Wbc: 0-3
Rbc: 0-3
Casts: none
Crystals: none
Yeast: none
Trichomonas: none seen
There is mild proteinuria. Please drink plenty of water and repeat your urine after one month.
Blessed day !
Female 47 yrs old / Menopause
Urinalysis :
Color = Yellow
Turbidity = Hazy
SP.GV = 1.005
Ph = 6.0
Protein = Negative
Glucose = Negative
Pus cell = 1-4/ hpf
Red cell = 6-9/hpf
Epithelial cells= Few
Mucus Thread = Moderate
Bacteria = Few
No infection ? Why is there blood ? No need for medication ? Just increase fluid intake ? And then after a week…repeat a urine test ? THANK you doc…big help.Female 47 yrs old / Menopause
Urinalysis :
Color = Yellow
Turbidity = Hazy
SP.GV = 1.005
Ph = 6.0
Protein = Negative
Glucose = Negative
Pus cell = 1-4/ hpf
Red cell = 6-9/hpf
Epithelial cells= Few
Mucus Thread = Moderate
Bacteria = Few
No infection ? Why is there blood ? No need for medication ? Just increase fluid intake ? And then after a week…repeat a urine test ? THANK you doc…big help.
Hi doctor md Riaz, my father 55 years old urine analysis is hear
Color – pale yellow
Apperance-clear
Sediment – present
Spefic gravity : – – –
Reaction – acidic
Alubin – trace
Sugar-nil
Rbc – nil
Pus cells :6-8/hpf
Elipthical cells :2-3/hpf
Casts-nil
Crystals – nil
Others – nil
He is diabetic including mediation with insulin, hypertension
Is the report is normal sir
Your father urine shows proteinuria, that is the complication of diabetes mellitus. Please also check eyes of your father to rule out retinopathy. He needs complete workup for diabetes complications.
Hi doc…
Female 47 yrs old / Menopause
Urinalysis :
Color = Yellow
Turbidity = Hazy
SP.GV = 1.005
Ph = 6.0
Protein = Negative
Glucose = Negative
Pus cell = 1-4/ hpf
Red cell = 6-9/hpf
Epithelial cells= Few
Mucus Thread = Moderate
Bacteria = Few
No infection ? Why is there blood ? No need for medication ? Just increase fluid intake ? And then after a week…repeat a urine test ? THANK you doc…big help.
Hi doctor md Riaz, my father 55 years old urine analysis is hear
Color – pale yellow
Apperance-clear
Sediment – present
Spefic gravity : – – –
Reaction – acidic
Alubin – trace
Sugar-nil
Rbc – nil
Pus cells :6-8/hpf
Elipthical cells :2-3/hpf
Casts-nil
Crystals – nil
Others – nil
He is diabetic including mediation with insulin, hypertension
Is the report is normal sir
His creatine is 1.9 will it decreases, doctor prescribed renolife tablet, will it works to reduce creatine and kidney function
Hi Sir,
I’m 37 yrs old female
My Urine routine report says as following:
Colour: Pale yellow
Appearance: Slightly cloudy
pH: Acidic
Albumin: Trace
Sugar: Nil
Pus Cells: 10-12/HPF
Epithelial Cells: 3-7/HPF
RBC: 2-4/HPF
Cast: Nil
Crystal: Nil
Bacteria: Present
I have sedentary life style due to office work load, have continuous lower left abdominal pain since pregnancy, and have constipation due to irregular eating and sleeping habits.
After (1st baby) delivery (at the age 33/34yrs old) also the pain continues till now. I have taken urine routine and USG (60 days USG alone), 6 months, and also 2 year after delivery. No adhesion or fluid found in USG and that report said everything normal. But Urine routine had RBC and Epithelial cells previously. Then Dr suggested me to drink more water.
Now 3 years after at 37yo, the same present. Please suggest. I’m well hydrated now.
Note: Since, I’m in Kerala, everyone including hospitals staff suggested me to consult and take ayurvedic medicine after delivery. As per them after 45 days, I consulted and that Ayur.Dr. suggested me that I have to take medicines for 2 months. For first month, so many medicines (tablets, capsules, kashayam, arishtam, health mix, for stamina) for 1 month, and I took and felt well. For second month, she changed some medicines and newly included some tablets (in which I found some metalic powders and crystals in a tablet) which I need to add and mix with khsayam (a liquid). The liquid added with tablet I drank, but it has sediments of that metal. I was shocked and didn’t take that medicine again. I discontinued all ayur medicines and informed that ayur dr. She again added some more tablets. I just take one and stopped taking those medication.
Please suggest does taking such (even though approved) medication once/twice in a day cause damage to the cells? Or, this report could be due to some other problem within me?
Your urine shows mild proteinuria. As regards your pain, i think they should do intravenous pyelography, that may give some clue about your pain. Rest as regard ayurvedic medications are not recommended because no research is done on these medications. These drugs, no bodies know about their side effects. As regards water please take 2 glass of water empty stomach.
Blessed day doc…
Female 47 yrs old / Menopause
Urinalysis :
Color = Yellow
Turbidity = Hazy
SP.GV = 1.005
Ph = 6.0
Protein = Negative
Glucose = Negative
Pus cell = 1-4/ hpf
Red cell = 6-9/hpf
Epithelial cells= Few
Mucus Thread = Moderate
Bacteria = Few
No infection ? Why is there blood ? No need for medication ? Just increase fluid intake ? And then after a week…repeat a urine test ? THANK you doc…big help.
PHYSICAL
– COLOR LIGHT YELLOW
– APPEARANCE TURBID
– SPECIFIC GRAVITY 1.030
-REACTION ACIDIC
SUGAR – NEGATIVE
ALBUNIM POSITIVE 1+
EPITHELIAL CELL – MANY
PUS CELL – 20-25/HPF
RCB 2-3/HPF%
AMORPHOUS URATES/PHOSPATE – FEW
BACTERIA – FEW
MUCUS THRED – FEW
Your urine shows proteinuria and urinary infection. Please consult the physician. Also get urine culture if you have not started antibiotics. Please aways mention the age.
Blessed day doc…
Female 47 yrs old / Menopause
Urinalysis :
Color = Yellow
Turbidity = Hazy
SP.GV = 1.005
Ph = 6.0
Protein = Negative
Glucose = Negative
Pus cell = 1-4/ hpf
Red cell = 6-9/hpf
Epithelial cells= Few
Mucus Thread = Moderate
Bacteria = Few
No infection ? Why is there blood ? No need for medication ? Just increase fluid intake…And then after a week…repeat a urine test ? THANK you doc…big help.
Blesses Day Dr.
32 Male
Colour YELLOW
Specific Gravity 1.025
PH 5.0
Proteins +
Glucose NIL
Ketones NIL
Urobilinogen NORMAL
Bilirubin NIL
Blood (Chemical Test) +++
Nitrite NEGATIVE
Pus Cells NUMEROUS /HPF
RBC’s 18-20 /HPF
Epithelial Cells 0-1 /HPF
Casts NIL /HPF
Amorphous Phosphate/Urates NIL
Mucous PRESENT /HPF
Bacteria NIL /HPF
Yeast Cells NIL /HPF
Crystals NIL
There is urinary tract infection. Please ask for urine culture and sensitivity. Also get ultrasound to rule out any other abnormality like stones etc.
Good day Doc!
I’m a 31 year old Male suffering from painful urination. I just want to be open here. Recently I had an unprotected sex with a girl and after 8-10 days i started experiencing burning and painful sensation when urinating. Doctor prescribed me antibiotics for UTI without any urine test. After taking the medicine the pain did not subside instead it became extreme painful. After 3-4 days taking the antibiotics I went to the doctor again. He prescribed me Azithromycil for 3 days and also asked me to have a urine test done. Below are the result of the test:
Physical examination
Color and Appearance- Yellow
Appearance- Clear
Specific Gravity- 1.020
PH- 7.0
Glucose- Negative
Ketone- Negative
Protein- Negative
Blood- Trace
Bilirubin- Negative
Urobilinogen- Normal
Nitrite- Negative
Leukocytes- Negative
Microscopic Examination
Pus Cells 1-2
RBC’s 6-8
Epithelial cells 1-2
Bacteria- Absent
Yeast Cells- Absent
Trichomonas Vaginalis- Absent
Mucus Threads- Absent
Crystals- Absent
Casts- Absent
Doc, please let me know if I have to worry about the test and what steps I take from here on. Please note that I have been feeling a little better less pain and less burning while urinating but the pain is still causes me uncomfortable after taking Azithromycin.
Your immediate response is highly appreciated.
Please check Gonorrhea by urethral smear. Your history suggests Gonorrhea.
Hello Doc!
Will gonorrhea be cured? Is Azithromycin the right antibiotic for this?
Hello Doctor, my one year old female child:
Leukocytes 6-8 (0 – 5)
Cells of squamous epithelium FEW (0 – 5)
Bacteria FEW (0)
Salts-amorphous urates FEW (0)
Small epithelium cells 3-5 (0 – 1)
THANK YOU
I think this urine report is normal. For the leukocytes, please repeat the urine after 2 weeks. Give plenty of water.
Hi doc…
Female 47 yrs old / Menopause
Urinalysis :
Color = Yellow
Turbidity = Hazy
SP.GV = 1.005
Ph = 6.0
Protein = Negative
Glucose = Negative
Pus cell = 1-4/ hpf
Red cell = 6-9/hpf
Epithelial cells= Few
Mucus Thread = Moderate
Bacteria = Few
No infection ? Why is there blood ? No need for medication ? Just increase fluid intake…And then after a week…repeat a urine test ? THANK you doc…big help.
Crystal haematobium ova
candida, t vaginals, casts
Are all N subscript 2 a
Please are they positive
Hello doc I’m 20 and I had this from last urine test
Crystal haematobium ova
candida, t vaginals, casts
Are all N subscript 2 a
Please are they positive
When these are present are abnormal. Why there are so many things positive in one urine sample. Please repeat urine from different lab.
Hello Doctor, my 5 years urine analysis results are :
Color: Yellow
Aspect; Turbid
Specific gravity: 1.020
PH: 6
Protein: positive
Glucose: negative
Ketones: positive
WBC/hpf : 35-37
RBC/hpf :1-3
Epithelial cells/hpf : 0-2
Crystals : Granular cast
She is having high fever and vomiting, She was prescribed Suprax for 14 days
I’m worried about proteins being +
Please advise
Hello Doctor, my 5 years urine test results are :
Color: Yellow
Aspect; Turbid
Specific gravity: 1.020
PH: 6
Protein: positive
Glucose: negative
Ketones: positive
WBC/hpf : 35-37
RBC/hpf :1-3
Epithelial cells/hpf : 0-2
Crystals : Granular cast
She is having high fever and vomiting, She was prescribed Suprax for 14 days
I’m worried about proteins being +
Please advise
There is urinary tract infection. Ketones are positive due to vomiting. I think they should have done urine culture and sensitivity before starting the antibiotics. This urine report Favour UTI (urinary tract infection). When symptoms subside, repeat the urine examination.
What does amorphous : urates 3+ mean in Urine test?
Urine amorphous has very little clinical value. These are seen when one eats more meat, dehydration, and fever. These are seen in acidic urine.
.
Hi Dr Raz
Does below results for my baby girl means she has UTI?
Age/Sex: 10mos/F
GROSS EXAMINATION
Color : Yellow
Transparency : Hazy
Reaction (ph) : 5.0
Specific Gravity : 1.010
Blood : NEGATIVE
Protein : NEGATIVE
Sugar : NEGATIVE
Leukocyte : +3
Urine Ketone : NEGATIVE
Urine Urobilinogen :NORMAL
Urine Bilirubin : NEGATIVE
Nitrite : NEGATIVE
MICROSCOPIC EXAMINATION
RBC : 0-1/HPF
PUS Cells >50/HPF
Epithelial Cells : OCCASIONAL
Bacteria : OCCASIONAL
Mucus Threads : OCCASIONAL
Thank you
Pus cells >50/HPF indicate urinary infection. Urine is hazy which means infection. I will suggest for culture and sensitivity before starting antibiotics.
Hi Dr. Riaz,
son (12 years):
Hb (g/dl): 15.0
Hkt(%) 42.8
Tromb: 248000
Ges. Leuko: 6000
%gran: 45
%L/M: 55
MCHC: 35.0g/dL
Blood sugar: 98 mg/dL (not fasted)
CRP: 11 mg/L
Urine protein + BB
Thank you
There is mild increase in lymphocytes and urine shows protein. These finding may be seen during fever. You have not told that why these tests were done. If there is fever, then please repeat urine and CBC after the fever is over.
There was no fever. My son has had abdomen pain for about 4 weeks. The doctor has indicated constipation and given Movicol for past 4 weeks.
Hi Dr. Diaz, I am concerned about bacteria appearing “few” on my urinalysis. Is this Normal?
Male 24 years old.
Color: Light Yellow
Transparency: Clear
Specific Gravity: 1.020
Protein: Negative
Glucose: Negative
Reaction pH: 6.0
Pus Cells: 0-2/HPF
RBC: 0-2/HPF
Ephithelial Cells: Few
Mucus Thread: Few
Bacteria: Few
Yeast Cells: None
Calcium Oxalate: None
Pus Cells in clumps: None
Uric Acid Crystals: None
Amorphous Urates: None
Few bacteria are normal. Because if there is urinary infection, then you will find increased pus cells.
hi doc…my mother is 43 this is her urine r/e report…is it something to worry about or is it ok?
Color Yellow
Appearance Clear
Specific Gravity 1.005
pH 8.0
Protein Negative
Glucose Negative
Urine Ketone Negative
Bilirubin Negative
Hemoglobin+++
Urobilinogen0.2
Nitrite Negative
Leucocyte esterase++
Microscopic=
W.B.C. 10-12 / HPF
R.B.C. 20-24 / HPF
Epithelial Cells 0-1 / HPF
Casts Nil
Crystals Nil
Pathologist Comments : Pus cells are increased.
Your mother urine shows abnormalities. There is hemoglobin in the urine indicating hemolysis in the urinary tract. There is hematuria and pus cells are borderline. Please get X-Ray (KUB) and ultrasound to rule out the stones/any other abnormality.
Hello Dr. Riaz,
My age is 33. Is the report below a cause for concern, or is it satisfactory?
Colour: Straw
Appearance: Slightly hazy
Sp.gravity: 1.015
Micro Organism: Present (+)
Epithelial cells: 3-4 (Squamous)
Pus cells: 2-3
Casts: Nil
Crystals: Nil
Micro Organism: Present (+)
Yeast cells: Nil
I think your urine was checked late, otherwise this urine report is normal.
Sir, the specimen was collected at 08:59 AM and the same was checked & analyzed at 02:42 PM.
Hello Doctor, can you please give suggestion,
my Daugther age 3
Colour PALE YELLOW
Appearance CLEAR
Reaction (PH) ACIDIC
Sugar NIL
Urine Albumin NIL
Pus Cells 8 – 10 /HPF
RBC 1 – 2 /HPF
Epithelial Cells 2 – 4 /HPF
Casts NIL
Crystals NIL
Bacteria NOT SEEN
Only WBCs are 8 to 10/HPF. And occasional RBCs. Please repeat urine analysis after one week from another lab. Meanwhile just wait and give her no medications.
Hi Dr. Riaz, My 10-years-old girls urine test was:
Cast 2/LPF
Small Round Cell 20/LPF
Crystal 92/LPF
Bacteria 25/HPF
Yeast like cell 23/ul
everything else was within the reference range. Should I worry?
This urine report is confusing. I do not know what they mean by small round cells. Crystal may be seen normally. Bacteria and yeast may be seen normally. please clarify the small round cells.
Urine Test Result
Colour Reddish
Specific Gravity 1.020
pH 5.0
Urine Albumin Positive (+)
Urine Glucose Nil
Urobilinogen Positive (++++)
Ketone Bodies Present (+)
Bilirubin Present (+++)
Blood Positive (+)
Leukocytes Positive (+++)
Pus Cells 10-12
Epithelial Cells 4-5
RBCs 15-20
Casts Hyaline cast seen
Crystal Nil
Bacteria Present
Yeast Cells Absent
There is hematuria, and urinary infection. please ask for urine culture. I hope the patient is not diabetic. If not diabetic, then patient is fasting or having vomiting. Also please get serum bilirubin level. I will suggest consulting the physician.
Hi Dr. I’m 32 yrs old male. This is my results from urinalysis. My symptoms is that in a cold room temperature I urinate frequently if i drink 2- 3 glasses of water before going to bed. Maybe every 30 mins when I’m resting in bed. But no symptoms of burning and struggling when urinate. Also to add my ECG and chest X-ray are normal.
Urinalysis Result
Physical and Chemical Analysis:
Microscopic Analysis
Color : YELLOW
Transparency: SLIGHTLY HAZY
Blood: NEGATIVE
Bilirubin NEGATIVE
Urobilinogen: NORMAL
Ketones : NEGATIVE
Glucose :NEGATIVE
Protein NEGATIVE
Netrite: NEGATIVE
Leukocyte NEGATIVE
pH 6.0
Sp. Gravity: 1.030
WBC: 2-3 HPF
RBC: 2-4 HPF
Bacteria: MODERATE /HPF
Epithelial Cells: RARE. /LPF
Amorphous Urales: NONE /LPF
Mucus Thread: MANY /HPF
Others:
Coarse Granular cast: 1-4 /LPF
Fine Granular cast 1-2 /LPF
What could be the problem? Thank you Dr.
Your urine report is confusing. Urine protein is negative. There are granular cast. Overall, your urine report is normal. I think repeat after one month and also check your HbA1c and fasting blood glucose.
35 yr old female:
03/17/2024 4:28 PM
NRBC %: 0.0 /100 WBC
Hct: 40.4 % — Normal range between ( 38.0 and 47.0 )
Hgb: 13.7 gm/dL — Normal range between ( 12.0 and 16.0 )
MCH: 32.8 pg — Normal range between ( 26.0 and 33.0 )
MCHC: 33.9 gm/dL — Normal range between ( 31.0 and 36.0 ) MCV: 96.7 Femtoliters — Normal range between ( 82.0 and 100.0 ) MPV: 11.0 Femtoliters — Normal range between ( 8.6 and 11.7 ) RBC: 4.18 x10e6/mcL — Normal range between ( 4.20 and 5.40 ) WBC: 9.33 x10e3/mcL — Normal range between ( 4.30 and 11.00 ) Plt: 193.0 x10e3/mcL — Normal range between ( 150.0 and 375.0 ) RDW-CV: 12.4 % — Normal range between ( 11.5 and 14.5 ) NRBC #: 0.00 x10e3/mcL
CBC no Diff: CBC no Diff
Urinalysis
03/17/2024 4:31 PM
Ur Clarity: Cloudy
Ur Bacteria: Few
UR Glucose: Negative mg/dL Ur Ketones: Negative mg/dL
Ur Nitrite: Positive
Ur Protein: 100 mg/dL
Ur RBC: 1291 /HPF — Normal range between ( 0 and 5 )
Ur WBC: 1122 /HPF — Normal range between ( 0 and 5 )
Ur WBC Clumps: Many /HPF
Ur Squam Epithelial: 2 /HPF — Normal range between ( 0 and 5 ) Ur Mucous: Few /LPF
Ur Color: Amber
Ur Leuk Est: Trace
Ur Bili: Negative mg/dL
Ur Blood: Large
Ur Urobilinogen: 4.0 mg/dL
Ur Spec Grav: 1.025 — Normal range between ( 1.005 and 1.030 ) Ur pH: 5.0
Chemistry
03/17/2024 4:56 PM
Estimated Creatinine Clearance: 64.26 mL/min
03/17/2024 4:28 PM
Creatinine: 0.98 mg/dL — Normal range between ( 0.50 and 1.00 ) Anion Gap: 6 mmol/L
BUN/Creat Ratio: 21
Alk Phos: 49 units/L — Normal range between ( 45 and 117 )
ALT: 20 units/L — Normal range between ( 13 and 56 )
AST: 11 units/L — Normal range between ( 15 and 37 )
T Bili: 0.4 mg/dL — Normal range between ( 0.2 and 1.0 )
CO2: 25 mmol/L — Normal range between ( 21 and 32 )
Glucose Level: 91 mg/dL — Normal range between ( 74 and 106 ) Lipase Lvl: 32 units/L — Normal range between ( 13 and 75 )
TP: 7.2 gm/dL — Normal range between ( 6.4 and 8.2 )
BUN: 21 mg/dL — Normal range between ( 7 and 18 )
Chloride: 108 mmol/L — Normal range between ( 98 and 107 ) Calcium: 9.1 mg/dL — Normal range between ( 8.5 and 10.1 ) Albumin. Level: 4.2 gm/dL — Normal range between ( 3.4 and 5.0 ) Potassium: 4.4 mmol/L — Normal range between ( 3.5 and 5.1 ) Sodium: 139 mmol/L — Normal range between ( 136 and 145 )
A/G Ratio: 1
eGFR Pediatric: Not Reported
eGFR Cr: 77 mL/min/1.73m2
This was really too much detailed tests. There is urinary infection, which shows RBCs and WBCs. Please also get urine culture before starting the antibiotics. You have not mentioned the age of the patient.
how about the below Dr. Riaz
COLOR: Light Yellow
Trasparency: Sl. Turbid
PH: 6.5
Specific gravity: 1.005
Sugar: Begative
Protein: Negative
Epithelial: None Seen
Mucus Threads: None Seen
PUS CELLS: 0-1 /HPF
RBC: 3-6 /HPF
AMORPHOUS URATES: None Seen
AMORPHOUS PHOSPHATES: None Seen
Bacteria: Occasional
CAST: None Seen
CRYSTALS: None Seen
YEAST Cells: None Seen
Others: No Dysmorphic RBC Seen
I will take this report normal. I will suggest you take plenty of water at least 8 glasses. Again, repeat urine after one month and see still RBCs are seen or disappeared.
Thank you. Dr. Diaz.
Good Evening Doctor
I am from Nepal. My Name is Sunil and I am 46 years old. Today early monring i have my Urine Routine Test and i need your review / suggestion on the report which is provided below:
My Urine Routine Test / Analysis Result:
Colour : Light Yellow
Transparency : Clear
Reaction (pH) : Acidic
Glucose : NIL
Albumin : +
Epithelial Cell : 1-2 (/Hpf)
Pus Cell : 0-2 (/Hpf)
RBC (Red Blood Cell) : Nil (/Hpf)
Hope for your response on this.
There is proteinuria. I hope you are not diabetic. Please have a workup for any issue in the kidneys.
good day doctor,
I am 25weeks pregnant and this is my urinalysis result. I get my urine sample after my OGTT will it affect my results?
color Yellow
Transparency Cloudy
reaction 6.0
SP-Gravity 1.030
Albumin Trace
Glucose Negative
Epithelial Cells ++++
Mucus Threads +++
Pus cells 8-12/HPF
Red blood cells 3-5/HPF
Bacteria ++++
You have proteinuria which needs to be treated. For RBC and Pus cells, please repeat urine after 2 weeks. I hope your blood pressure is normal. Better to consult gynecologist.
Good evening Dr. Riaz,
Thanks for your efforts in sharing your valuable feedback and guidance.
I am 40 yr male, kindly find below my Urine routine report. Please let me know if anything to worry. Is RBC occasional is normal?
General Examination
Colour
((Naked eye examination))
Pale Yellow Pale Yellow
Transparency (Appearance)
((Naked eye examination))
Clear Clear
Reaction (pH)
((Automated Photoelectric colorimetry))
5 4.5-8
Specific gravity
((Automated Photoelectric colorimetry))
1.010 1.010-1.030
Chemical Examination
Urine Protein (Albumin)
((Automated Photoelectric colorimetry/Sulpho
salicylic acid method))
Absent Absent
Urine Glucose (sugar)
((Automated Photoelectric colorimetry/Benedict’s
Test))
Absent Absent
Urine Ketones (Acetone)
((Automated Photoelectric colorimetry/Rothera’s
method))
Absent Absent
Bile salts
(Hay’s Sulphur method)
Absent Absent
Bile pigments
(Automated Photoelectric colorimetry/Fouchet’s
method)
Absent Absent
Urobilinogen
((Automated Photoelectric colorimetry/Ehrlich’s
aldehyde method))
Normal Normal
Nitrite
((Automated Photoelectric colorimetry))
Negative Negative
Microscopic Examination
Red blood cells Occasional /hpf Absent
Pus cells (WBCs) 2 – 4 /hpf 0-5
Epithelial cells 2 – 3 /hpf 0-4
Crystals Absent Absent
Cast Absent Absent
Amorphous deposits Absent Absent
Bacteria Absent Absent
Trichomonas Vaginalis Absent
Your urine report is normal. Occasional RBCs may be seen.
Result Trends
Results limited to those after Jul 18, 2019. Results found from Oct 9, 2019 – Jul 18, 2024.
Rachel S B Date of Birth: Jan 1982
Oct 9, 2019 – Jul 18, 2024 (Table 1 of 1)
Component Oct 9, 2019 Feb 3, 2023 Jul 18, 2024
Color, Urine
Normal Range: Yellow
Yellow Straw Straw
Ketones, Urine Normal Range: Negative mg/dL
Negative mg/dL Negative mg/dL Negative mg/dL
Urobilinogen, Urine Normal Range: <2.0 mg/dL mg/dL
Negative mg/dL Normal mg/dL Normal mg/dL
Blood, Urine
Normal Range: Negative
Negative
Trace
Negative
WBC, Urine Normal Range: None Seen,
0-2 /HPF 0-2 /HPF 0-2 /HPF
RBC, Urine Normal Range: None Seen,
0-2 /HPF 0-2 /HPF 2-5 /HPF
Squamous Epithelial Cells, Urine Normal Range: None Seen,
Rare /HPF Rare /HPF Rare /HPF
Bacteria, Urine
Normal Range: None Seen /HPF
Rare /HPF Rare /HPF
Mucus, Urine Normal Range: None Seen /LPF
Slight /LPF Slight /LPF
Clarity, Urine Normal Range: Clear
Clear Clear Clear
Specific Gravity, Urine Normal Range: 1.005 – 1.030
1.018, 1.036, 1.024
pH, Urine Normal Range: 5.0 – 7.5 pH
7.0 pH 5.5 pH 7.5 pH
Leukocytes, Urine Normal Range: Negative Negative Negative Negative
Nitrite, Urine Normal Range: Negative Negative Negative Negative
Protein, Urine Normal Range: Negative mg/dL
Negative, mg/dL, Negative mg/dL, Abnormal 10 mg/dL
Glucose, Urine Normal Range: Negative mg/dL Negative mg/dL Negative mg/dL Negative mg/dL
Bilirubin, Urine Normal Range: Negative Negative Negative Negative
Your report was too long, but any how I do not see any abnormality.
Hello, hope you are great. My daughter is 6 years old. We had to do urine test as sometimes she doesn’t go to the toilet often and holds urine for hours. Here is her test results. Is this normal ?
Proteins are high?
Proteins 27mg!dl
Density 1.029
PH 5.0
protein negative
Glucosa Negative
Ketones Negative
Billirubin Negative
Blood Negative
Leykocytes Negative
Nitrats Negative
Urobilinogen Negative
Sediments > without abnormal elements.
Urine report of your daughter is just normal. But you have to repeat urine for urine protein. Urine protein must be worked to find the reason.
Sometime there is orthostatic proteinuria.
Hello, we repeated urine protein, it is again 20 mg dl in biochemical part but then in urinalysis protein is negative. GFR of blood is 149 for her. And we always did urine first thing in the morning. IS there something wrong with the kidneys? Thank you doctor
Please let me know the age. Is there any history of diabetes?. You have to do 24 hours urinary protein. Rest GFR is normal. Normal GFR is 90 or above.
She is 6 years old. No diabetes.
Thank you
39 Year Old, Female
URINE BIOCHEMISTRY
Urine Creatinine Random 4.30 mmol/L
Urine Microalbumin (Random) <5 mg/L
Comment:
URINALYSIS
Urine Colour Yellow
Urine Clarity Clear
Urine Chemistry
pH 6.5
Specific Gravity 1.010
Nitrite Negative
Protein Negative
Glucose Negative
Ketones Negative
Urobilinogen Negative
Bilirubin Negative
Leukocytes Negative
Erythrocytes Negative
Urine Microscopy
White Blood Cells 0 cells/µL
Red Blood Cells 0 cells/µL
Epithelial Cells 8 cells/µL
Casts Nil
Crystals Nil
Bacteria Nil
Yeasts Nil
Your reports are in the normal range.
But my Epithelial Cells reading is high.. it’s ok?
Please doctor have a look on this report
Physico Chemical Analysis
Colour Pale Yellow Pale yellow
Appearance Clear Clear
Sp. Gravity 1.003 – 1.030 1.030
Ph: 4.5 – 8.0 5.5
Glucose NIL Trace
Proteins NIL NIL
Blood NIL ++
Ketones NIL Trace
Nitrites NIL Negative
Bilirubin NIL NIL
Urobilinogen Normal Trace
Microscopic Analysis
Pus Cells M: 0-3 F: 0-5 /HPF 2-4
Red Blood Cells 0 – 2/HPF 3-4
Epithelial Cells M: 0-3 F: 0-10/HPF 6-8
Crystals NIL/HPF NIL
Casts Nil/LPF
Physico Chemical Analysis
Colour Pale Yellow Pale yellow
Appearance Clear Clear
Sp. Gravity 1.003 – 1.030 1.030
Ph: 4.5 – 8.0 5.5
Glucose NIL Trace
Proteins NIL NIL
Blood NIL ++
Ketones NIL Trace
Nitrites NIL Negative
Bilirubin NIL NIL
Urobilinogen Normal Trace
Microscopic Analysis
Pus Cells M: 0-3 F: 0-5 /HPF 2-4
Red Blood Cells 0 – 2/HPF 3-4
Epithelial Cells M: 0-3 F: 0-10/HPF 6-8
Crystals NIL/HPF NIL
Casts Nil/LPF
Age 42 and having urine burn problem:
Kindly Look into it.
Physico Chemical Analysis
Colour Pale Yellow Pale yellow
Appearance Clear Clear
Sp. Gravity 1.003 – 1.030 1.030
Ph: 4.5 – 8.0 5.5
Glucose NIL Trace
Proteins NIL NIL
Blood NIL ++
Ketones NIL Trace
Nitrites NIL Negative
Bilirubin NIL NIL
Urobilinogen Normal Trace
Microscopic Analysis
Pus Cells M: 0-3 F: 0-5 /HPF 2-4
Red Blood Cells 0 – 2/HPF 3-4
Epithelial Cells M: 0-3 F: 0-10/HPF 6-8
Crystals NIL/HPF NIL
Casts Nil/LPF
Please write only positive findings.
Physico Chemical Analysis
Colour Pale Yellow Pale yellow
Appearance Clear Clear
Sp. Gravity 1.003 – 1.030 1.030
Ph: 4.5 – 8.0 5.5
Glucose NIL Trace
Proteins NIL NIL
Blood NIL ++
Ketones NIL Trace
Nitrites NIL Negative
Bilirubin NIL NIL
Urobilinogen Normal Trace
Microscopic Analysis
Pus Cells M: 0-3 F: 0-5 /HPF 2-4
Red Blood Cells 0 – 2/HPF 3-4
Epithelial Cells M: 0-3 F: 0-10/HPF 6-8
Crystals NIL/HPF NIL
Casts Nil/LPF
Please write your age and write only positive findings.
Physico Chemical Analysis
Colour Pale Yellow Pale yellow
Appearance Clear Clear
Sp. Gravity 1.003 – 1.030 1.030
Ph: 4.5 – 8.0 5.5
Glucose NIL Trace
Proteins NIL NIL
Blood NIL ++
Ketones NIL Trace
Urobilinogen Normal Trace
Microscopic Analysis
Pus Cells M: 0-3 F: 0-5 /HPF 2-4
Red Blood Cells 0 – 2/HPF 3-4
Epithelial Cells M: 0-3 F: 0-10/HPF 6-8
Crystals NIL/HPF NIL
Casts Nil/LPF
Your report is confusing. Please write your age and only write positive findings. Then I can give you some advice.
Sure sir, I am 42 years old and having urine burning problem
Sure sir, I am 42 years old and having urine burning problem, please let me know if u find any problem, thanks
Colour Pale Yellow Pale yellow
Appearance Clear Clear
Sp. Gravity 1.030
Ph: 5.5
Glucose Trace
Proteins NIL
Blood NIL ++
Ketones Trace
Urobilinogen Trace
Microscopic Analysis;
Pus Cells M: 2-4
Red Blood Cells 3-4
Epithelial Cells M: 6-8
Sure sir, I am 42 years old and having urine burning problem, please let me know if u find any problem, thanks, please ignore the previous one
Colour Pale Yellow Pale yellow
Appearance Clear Clear
Sp. Gravity 1.030
Ph: 5.5
Glucose Trace
Proteins NIL
Blood ++
Ketones Trace
Urobilinogen Trace
Microscopic Analysis;
Pus Cells M: 2-4
Red Blood Cells 3-4
Epithelial Cells M: 6-8
There are few issues in urine report. There is glucose in traces. Blood is positive (++), although RBCs are only 3 to 4/HPF. For glucose, I will suggest checking your fasting blood glucose level. For blood ++ in the urine also indicates bleeding in the urinary tract and burning urination. Please repeat urine from different lab.
Thanks a lot Doctor JAZAKALLAH
Thanks. You are welcome.
Female 48 yrs old
Menopause/Endometriosis
Urinalysis :
Color = Light Yellow
Character = Clear
Ph = 5
Specific Gravity = 1.005
Protein = Negative
Glucose = Negative
Epithelial Cells = Rare
Mucus Thread = Rare
Wbc = 0-2
Rbc = 0-2
Bacteria = Rare
Amosphous Urates = Rare
Doc…I feel that every time I urinate…there is always residual urine. What should I do?
Thank you doc…
Hello doctor I can’t get a straight answer from my Dr and they so there’s no infection. My urine is very strong smelling and lingers in the bathroom even after I have flushed.
Female 49 years old
Glucose NEG
Bilirubin NEG
Ketones 5
Spec gravity 1.025
Hemoglobin NEG
pH 6.0
Protein 30
Uribilinogen 2.0
Nitrite POS
Leukocyte estrace TRACE
Appearance cloudy
Color amber
WBC 2
RBC 33
Bacteria 4+
Squamous 18
Mucous rare
Ca oxalate crys, ur sed, Ql 2+
Blood was done and my parathyroid hormone is 130 which usually also is a sign of UTI and I’ve never head thyroid abnormalities or throws issues.
My dr is saying I don’t need tx at this time but these numbers seem like they are indicating otherwise.
Your urine shows proteinuria, and blood (Hematuria). But there is no evidence of infection. I think nitrate positive may be due to late urine testing. I think you should have ultrasound abdomen and consultation with urologist. It needs explanation. I have no idea about your age.
Female 48 yrs old
Menopause/Endometriosis
Urinalysis :
Color = Light Yellow
Character = Clear
Ph = 5
Specific Gravity = 1.005
Protein = Negative
Glucose = Negative
Epithelial Cells = Rare
Mucus Thread = Rare
Wbc = 0-2
Rbc = 0-2
Bacteria = Rare
Amosphous Urates = Rare
Doc…I feel that every time I urinate…there is always residual urine. What should I do?
Thank you doc…
Rajla devi (80 Years) 01-Oct-2024
Color Light pale
Sediment Absent
Appearance clear
Pus cells 3-5/HPF
Epithelial cells +
Red blood cells nil
Calcium oxalate nil
Specific gravity Q.N.S
Reaction(ph) Acidic
Protein nil
Sugar nil
phosphate nil
Bile salt Negative
Bile pigment Negative
Please advise is the result ok?
Your urine report is normal. No need to worry.
Female 48 yrs old
Menopause/Endometriosis
Urinalysis :
Color = Light Yellow
Character = Clear
Ph = 5
Specific Gravity = 1.005
Protein = Negative
Glucose = Negative
Epithelial Cells = Rare
Mucus Thread = Rare
Wbc = 0-2
Rbc = 0-2
Bacteria = Rare
Amosphous Urates = Rare
Doc…I feel that every time I urinate…there is always residual urine. What should I do?
Your urine report is normal. For residual urine, please consult urologist/nephrologist.
Okay Doc…THANK you
You are welcome.
What is the reason why there is residual urine?
Is it dangerous if there is always residual urine?
Thank you doc…
Male, 35 years
I have done 2 urine tests at a gap of 3 months. Except the presence of bacteria now, everything thing else is same for both reports. Also I did abdomen USG and found 2 kidney stones. There is slight discomfort in bladder area
Blood – trace (10cell/uL)
Leukocyte – trace (15 cell/uL)
WBC – 3-4
RBC – 3-5
Epithelial cell – 2-3
Bacteria – present (was absent in earlier report)
There is hematuria and that may be due to stones. I do not think about urinary tract infection, because WBC are in the normal range. If the urine is left for more than 2 hours, then you may see bacteria, but these have no significance.
Thankyou sir for the reply.
I did a urine test today. And the results were completely normal . No RBC,blood,WBC etc. But still I feel discomfort in bladder area. I drink a lot of water 5-6 litres easily and hence urinate a lot. Can this be a reason for the bladder discomfort.
Hi Doctor!
I hope you’re doing well. Please give me some advise and read my UA Result. Thank you!
Im Keer/ Female/29/ 25 wks Pregnant.
Color – Light Yellow
Transparency – Hazy
Ph – 6.5
Specific Gravity – 1.025
Protein – Negative
Glucose – Negative
RBC/hpf – 2-5/hpf
WBC/hpf – 10-25/hpf
Epithelial Cells – Abundant
Mucus Thread – Rare
Amorphous material – Rare
Bacteria – Many
Thank you.
Your urine report is normal. There are RBCs and pus cells. You need urine culture and treatment for it. Please also check your blood glucose level to avoid gestational diabetes,
Thank you Dr. Riaz
WElcome.
Hi Doctor!
I hope you’re doing well. Please give me some advise and read my baby’s UA Result. Thank you!
Im Ravinder my 2 year baby / Female/.
Color – P. Yellow
Appearance –Clear
Odour – Present
Ph – 7.5
Specific Gravity – 1.025
Ketones – +
Protein – ++++
Bilirubin – Nil
Glucose – Nil
Nitrite – Nil
Urobilinogen – Nil
Blood/Leukocytes – Nil
RBC– nil
Epithelial cells – 3-5
Bacteria/Crystal/Casts– Nil
Thank you.
Your baby has proteinuria. Ketone may be positive if your baby having diarrhea, vomiting and not eating foods. For protein in the urine, we need further workup like ultrasound abdomen. Please consult doctor for protein in the urine.
Hello,
Can you advise on these levels for a pediatric patient?
Glucose – neg
Bilirubin – neg
pH – 6.5
Ketone – trace
Protein – trace
Leukocytes – neg
Appearance – clear
Urobilinogen – normal
Blood – neg
Nitrite – neg
Specific Gravity – >=1.030
Color – yellow
Bacteria – none
WBC – 1
Hyaline Casts – 0
RBC – 8
Squamous Epithelial Cells – 0
Thank you!
I think your baby having vomiting or diarrhea, or fever that explain ketones and protein. Otherwise, this urine is normal. Please repeat urine when he is fully healthy.
Doctor please my sister did a urinalysis and there were presence of yeast 2 plus and bacteria to 2 plus. Please is it a serious problem
Please check if the urine was left in the lab for longer time before the urine examine. That could be the reason. If you leave urine for longer time, it will lead to growth of bacteria and yeast.
Lab has not mentioned about the presence of WBCs.
The WBCs was only 10
Your question is not clear. WBC only 10. Please let me know the age and exact WBC number/HPF.
Hi doc…Male…43 yrs old.
Urine test :
Color = Yellow
Appearance = Slightly Turbid
Ph = Acidic
Specific Gravity = 1.010
Sugar = +
Albumin = Negative
Bilirubin = Negative
Nitrite = Negative
Urobilinogen = Normal
Ketones = ++
Blood = +++
Leukocytes = Negative
Pus cells = 4-5
Rbc = 25-30
Epithelial cells = Nil
Crystals = Nil
Amorphous = Nil
Bacteria = Nil
Miscellaneous = Nil