Urine Screening for Drug Abuse
Urine screening for Drug Abuse
What sample is needed for Drug abuse?
- One of the samples is urine.
- Urine should be taken in the presence of a technician or doctor.
- Saliva test: This is detectable in saliva within one hour of use.
- Hair follicle test: This is detectable in hairs in 5 to 7 days.
- Blood test: This is detectable within one hour of use.
What are the advantages of Urine testing?
- It is easy to get a urine sample, and this is not an invasive procedure.
- Some drug concentrations are higher in urine, which may not be detected in the blood.
- Drug metabolites are excreted for a longer period of time in the urine, indicating the drug’s past use.
- Urine test kits for drugs are easier and cheaper.
How will you get the sample from a drug abuser?
- The patient should wash their hands and wear gloves.
- Add bluing agents in the toilet to avoid adulteration of the urine sample.
- Avoid all sources of water in the toilet.
- The patient will provide a photo ID.
- The patient will leave all his belongings outside the toilet.
- Someone should be in the toilet while the patient is giving the sample, or he can wait just outside the door to listen to any abnormal sound.
- Check the urine volume (30 to 40 mL) and any abnormal color.
- The sample will be in sight of the technician/doctor and the patient all the time.
- The date and time are noted.
What are the critical alerts on the patient?
- Keep an eye that there is no tampering, like substitution, adulteration, or urine dilution.
- Avoid all unauthorized persons handling the specimen.
- The urine collection may be witnessed or unwitnessed.
What are the precautions for Drug abuse?
- Urine will detect heroin for 1 to 2 hours, a maximum of up to 2 to 5 hours after use.
- The minimum concentration should be 2000 ng/mL.
- Check for urine dilution by measuring creatinine, pH, and specific gravity.
- The following agents will give false results:
- Sodium chloride.
- Dilute urine due to low specific gravity.
- Acidic urine due to high pH.
- Alkaline urine due to low pH.
- Blood in the urine.
- Detergents in the container.
What are the indications for drug abuse?
- To diagnose drug abuse.
- Indicated in athletes, industrial workers, and professionals.
- It is used in toxicology to confirm clinical or postmortem diagnosis.
- To diagnose drug-induced signs and symptoms and differentiate from the trauma, infectious process, or metabolic disorder.
- To diagnose psychosis or drug abuse.
- It is used in prisoners to detect drug abuse.
- It is advised in the workplace for public safety.
- In routine, the following drugs are tested:
- Cocaine.
- Marijuana.
- Opiates (narcotics).
- Methadone.
- Barbiturates.
- Benzodiazepines.
- Amphetamines.
- Methamphetamines.
- Sedatives.
- Analgesics.
- Sympathomimetics.
- Phencyclidine
How will you perform drug abuse testing?
- Urine is the best sample for drug abuse, and the following tests are advised:
- Screening tests. These are simple, inexpensive, and rapid.
- Confirmatory tests. These are laborious and expensive.
How would you classify the drug abuse?
- CNS stimulants:
- It produces euphoria, depresses the appetite, and increases heart and respiration rates.
- These are cocaine and its derivatives, amphetamines, and methamphetamines.
- CNS depressant:
- These will lower heart rates and respiratory rates and reduce pain.
- These drugs are narcotics, sedatives, hypnotics, and tranquilizers.
- Psychoactive:
- These are also hallucinogenic drugs, cannabinoids, and phencyclidine.
- Antidepressant:
- These drugs include lithium, tricyclic depressant, etc.
What is the prevalence of drug abuse?
| Drug abuse | Prevalence % |
| Alcohol | 75% to 80% |
| Marijuana | 20% to 26% |
| Cocaine | 5% to 13% |
| Benzodiazepine | 1% to 5% |
| Barbiturates | 0.5% to 5% |
| Opiates | 0.1% to 2% |
| Phencyclidine | 0.1% to 2% |
| Amphetamines | 0.1% to 1% |
| Other stimulants | 0.8% to 2% |
| Sedatives and hypnotics | 0.6% to 2% |
Opiates
What are the several opiates used for addiction?
What do you know about Opiates?
- These are the substances with analgesia, sedation, and anesthesia.
- There is a high potential for addiction.
- Chronic use leads to tolerance for physical and psychological dependence.
- Acute use with overdose leads to respiratory acidosis with respiratory system depression, myoglobinuria, and possibly increased myocardial infarction indicators.
- A very high dose of opiates may lead to death due to cardiopulmonary failure.
- Treatment of an overdose of opiates is antagonists like naloxone.
- This was derived from the opium poppy.
- Naturally occurring modified opiates are:
- Opium.
- Morphine.
- Codeine.
- Heroin.
- Hydromorphone.
- Oxycodone.
- Chemically synthetic opiates are:
- Meperidine.
- Methadone.
- Propoxyphene.
- Pentazocine.
- Fentanyl.
- Some of these are:
- Heroin.
- Morphine.
- Oxycodone (Oxycontin).
- Hydromorphone (Dilaudid).
- Fentanyl (Duragesic).
- Acetylcholine, an impurity of heroin synthesis, has been suggested as an interesting biomarker of illicit heroin use.
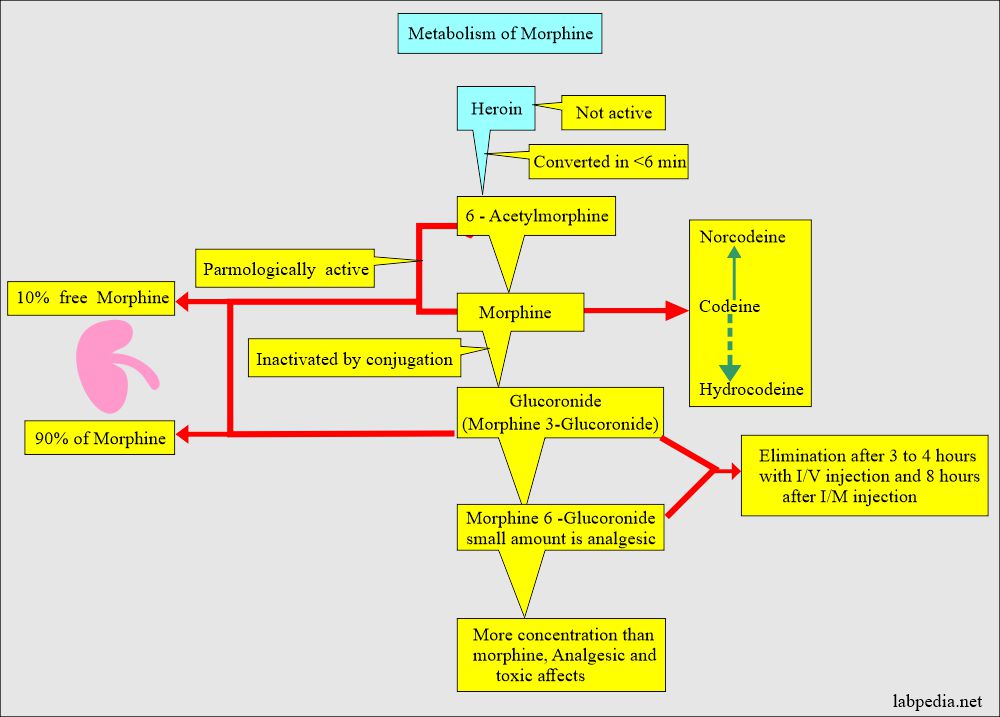
- Codeine and heroin are metabolized to morphine, which is then excreted in the urine.
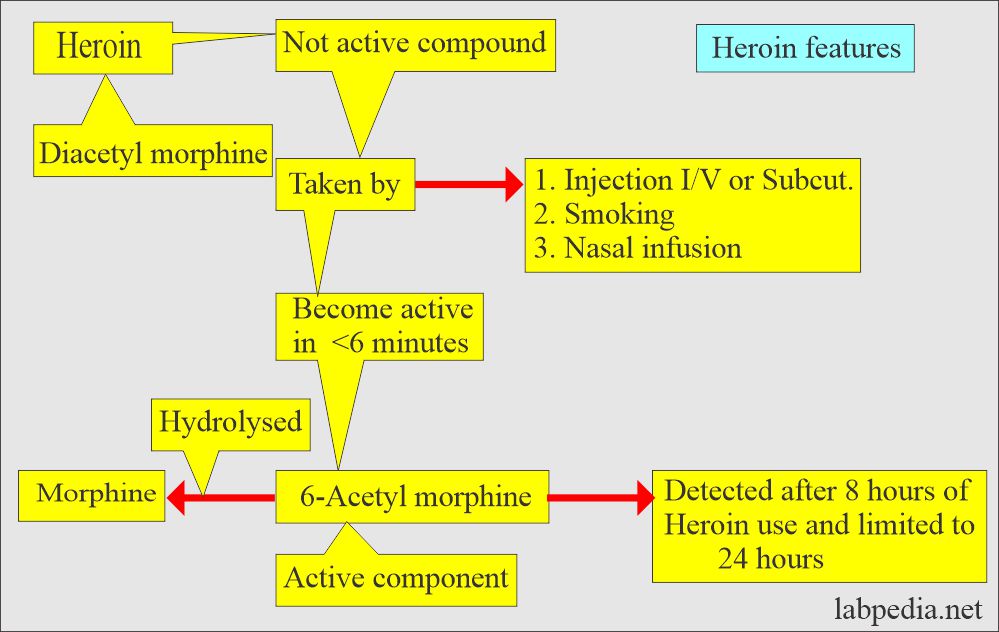
Heroin
How will you define Heroin?
- Heroin metabolism shows that it is not an active compound but becomes active after conversion to 6-acetylmorphine.
- 6-Acetylmorphine and morphine are pharmacologically very active substances.
How will you detect morphine in the urine?
- The detection of morphine in the urine may be the result of:
- Intake of heroin.
- Morphine.
- Codeine.
- Poppy seeds intake.
- Heroin may be present until 5 days in urine after the last dose. (Some say 3 to 4 days).
Cocaine
How will you define cocaine?
- These are alkaloid salts, which can be taken by injection, insufflation, or inhaled in vapors.
- The half-life of cocaine is 0.5 to 1 hour. Because of the short half-life, repeated doses are given.
What is the mechanism of Cocaine action?
- This is an effective local anesthetic with few adverse effects in a therapeutic dose.
- This potent CNS stimulator leads to excitement and euphoria.
What are the complications of Cocaine?
- Acute toxicity is associated with hypertension, seizures, arrhythmias, and myocardial infarction.
How will Cocaine be excreted?
- The hepatic product of cocaine is benzoylecgonine, which is excreted in the urine.
- The presence of this metabolite in urine is a sensitive and specific indicator of cocaine intake.
- After a single intake, this can be detected in the urine for up to 3 days.
- It can be detected in chronic cases up to 20 days in the urine after the last use.
What is the duration of some of the drugs appearing in the urine?
| Drugs | Screening cut-off value | Duration of detection |
| Heroin | 2000 ng/mL | 1 to 2 hours |
| Cocaine | 300 mg/dL | 2 to 4 days |
| Opiates | 300 ng/mL | 2 to 4 days |
| Marijuana | 50 ng/mL | 30 to 60 days |
| Amphetamines | 1000 ng/mL | 2 to 3 days |
| Methadone | 300 ng/mL | 8 to 60 hours |
| Barbiturates | 200 ng/mL | up to 30 days |
| Benzodiazepines | 200 ng/mL | up to 40 days |
| Alcohol | 20 ng/mL | 12 hours |
| Tricyclic antidepressant | 1000 ng/mL | 1 to 3 days |
| PCP | 25 ng/mL | 2 to 3 days |
| Methaqualone | 300 ng/mL | up to 7 days |
| Phencyclidine | 25 ng/mL | <3 days |
| LSD (Lysergic acid diethylamide) | 0.5 ng/mL | <12 to 24 hours |
What are the Signs and Symptoms of Opiates?
- All opiates (Morphine, Codeine, Hydroxymorphine and Oxycodone, hydrocodone, hydrocodone) have the common S/S.
- Heroin action is very rapid in onset.
- These have an analgesic effect.
- Signs and symptoms are:
- Sedation.
- Pinpoint pupil.
- Constipation.
- Euphoria
- Respiratory depression.
- Orthostatic hypotension.
- Decreased intestinal motility leads to constipation.
- There are nausea and vomiting.
- Bradycardia.
- Morphine overdose (intoxication) leads to :
- Coma.
- Miosis.
- Respiratory depression.
What are the withdrawal Symptoms of opiates?
- Dilated pupil.
- Tachycardia.
- Lacrimation and rhinorrhea.
- Irritability and restlessness.
- Diaphoresis.
- These symptoms can be decreased by methadone ( an opiate antagonist). Another used drug is clonidine.
How will you diagnose opiates?
- Commercial kits are available.
- Gas chromatography. This is one of the accepted methods.
- Latex Agglutination Inhibition.
- Thin Layer Chromatography.
- Radioimmunoassay (RIA).
- High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC).
- Mass Spectrophotometry (GC/MS).
- Radioimmunoassay (RIA) is rapid and cheap.
- Morphine and Codeine are found after heroin use.
- A single urine test is enough to diagnose various drugs like cocaine, opiates, barbiturates, amphetamines, methadone, oxycodone, benzodiazepines, cannabinoids, methadone, and tricyclic antidepressants.
How will you treat opiates?
- Treat intoxication due to opiates with opiate antagonists like Naloxone.
- Another antagonist is Nalmefene, which is synthetic in origin.
Amphetamines
How will you define Amphetamines?
- Amphetamine and methamphetamine are therapeutic drugs used for:
- Narcolepsy.
- Attention deficit disorder.
- Obesity
- These are stimulants with a high rate of drug abuse.
What is the route of administration of Amphetamines?
- Amphetamines are readily absorbed from the GIT and widely distributed throughout the body.
- These are converted into more polar substances in the liver and easily excreted in the urine.
- These are mostly excreted in 48 hours.
- Possible routes are:
- Oral.
- Injections.
- Inhalation.
- Insufflation.
What is the mechanism of action of Amphetamines?
- Amphetamines are sympathomimetic amines that stimulate the CNS and produce excitement.
- It increases the release and blocks the uptake of some of the neurotransmitters.
- It induces euphoria and alertness and boosts energy.
- It induces loss of apatite and reduces the sense of fatigue.
What are the complications of Amphetamines?
- It leads to addiction. One can develop psychological and physiological addiction.
- It induces irritability, anxiety, and insomnia.
- It may lead to blurred vision.
- Increases blood pressure and cardiac palpitation.
- It increases body temperature.
- It may lead to anxiety, paranoid behaviors, and psychosis.
Barbiturates
What is the mechanism of action of Barbiturates?
- These are CNS depressants.
- These are used as anxiolytic, anticonvulsants, anesthetic, and muscle relaxant drugs.
- These drugs bind to chloride channel molecules of GABA receptors and induce sedation, mood alteration, and euphoria.
- The duration of action of these barbiturates is divided into the:
- Short-acting.
- Ultra-short-acting.
- Lonf-acting.
- Intermediate-acting.
- Once absorbed, these are metabolized in the liver.
- There will be oxidation and glucuronide conjugation.
What is the mode of administration of Barbiturates?
- The most common routes are oral and parenteral.
What are the complications of Barbiturates?
- There may be drowsiness.
- Mental impairment.
- Ataxia.
- Dysarthria.
- In case of high doses may lead to coma and cardiovascular and respiratory depression.
Benzodiazepines
What is the mode of action of the Benzodiazepines?
- It is like barbiturates.
What is the mode of administration of Benzodiazepines?
- These can be given orally or parenterally.
What are the side effects of Benzodiazepines?
- These are like barbiturates but are milder.
- There is physical dependence, and the patient may have withdrawal symptoms like:
- Agitation.
- Irritability
- Insomnia.
- Muscle tension.
- Psychosis and seizures.
What is the metabolism of Benzodiazepines?
- In the liver, benzodiazepine is converted into active and inactive forms.
- The half-life of the parent drugs is less than that of metabolites.
Cannabinoids
What is the source of Cannabinoids?
- Cannabinoids are found in the hemp plant, from which marijuana is formed.
What is the mechanism of action of cannabinoids?
- In Marijuana, THC is the psychoactive ingredient that leads to euphoria and relaxation effects, which is the reason for its abuse.
- It is highly lipophilic and is converted into more than 20 metabolites.
- Urinary metabolites 11-nor-Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol9-carboxylic acid (THC-COOH) is used to detect in the urine.
- 70% of the THC is excreted in the feces and urine within 72 hours.
- In addicts, the half-life may be >10 days.
What is the mode of administration of Cannabinoids?
- It can be used for inhalation and also can be ingested.
- THC is nonlethal when it is used alone.
What are the side effects of Cannabinoids?
- Some of the patients may have side effects like:
- Tachycardia.
- Respiratory distress.
- Behavior and mental abnormalities.
- Long-term use leads to tolerance and mild withdrawal symptoms.
Phencyclidine
How will you define Phencyclidine?
- It is a potent hallucinogenic agent.
What is the mode of action of Phencyclidine?
- It antagonizes the glutamate receptors and may block dopamine uptake as well.
- This drug is lipophilic, so it can be stored for a longer period in the brain and adipose tissue.
- Metabolism occurs in the liver through oxidative hydroxylation and conjugation; it is cleared from the kidneys.
What are the other phencyclidines?
- Cyclohexamine.
- Phenylcyclohexylpyrrolidine.
- Thienylcyclohexylpiperidine.
What is the mode of administration of Phencyclidines?
- These substances can be taken orally.
- Intravenously.
- Smoked in combination with marijuana or tobacco.
What are the side effects of Phencyclidine?
- Tachycardia.
- Paranoia.
- Psychosis.
- Respiratory depression.
- There is mydriasis (dilatation of the pupil).