Urine For Pus cells, WBC, Eosinophils, Mononuclear cells, Pyuria
Urine For Pus cells
What sample is needed for Urine Pus cells?
- The test sample is urine.
Indication Urine For Pus cells
How will you discuss the pathophysiology of Urine For Pus Cells?
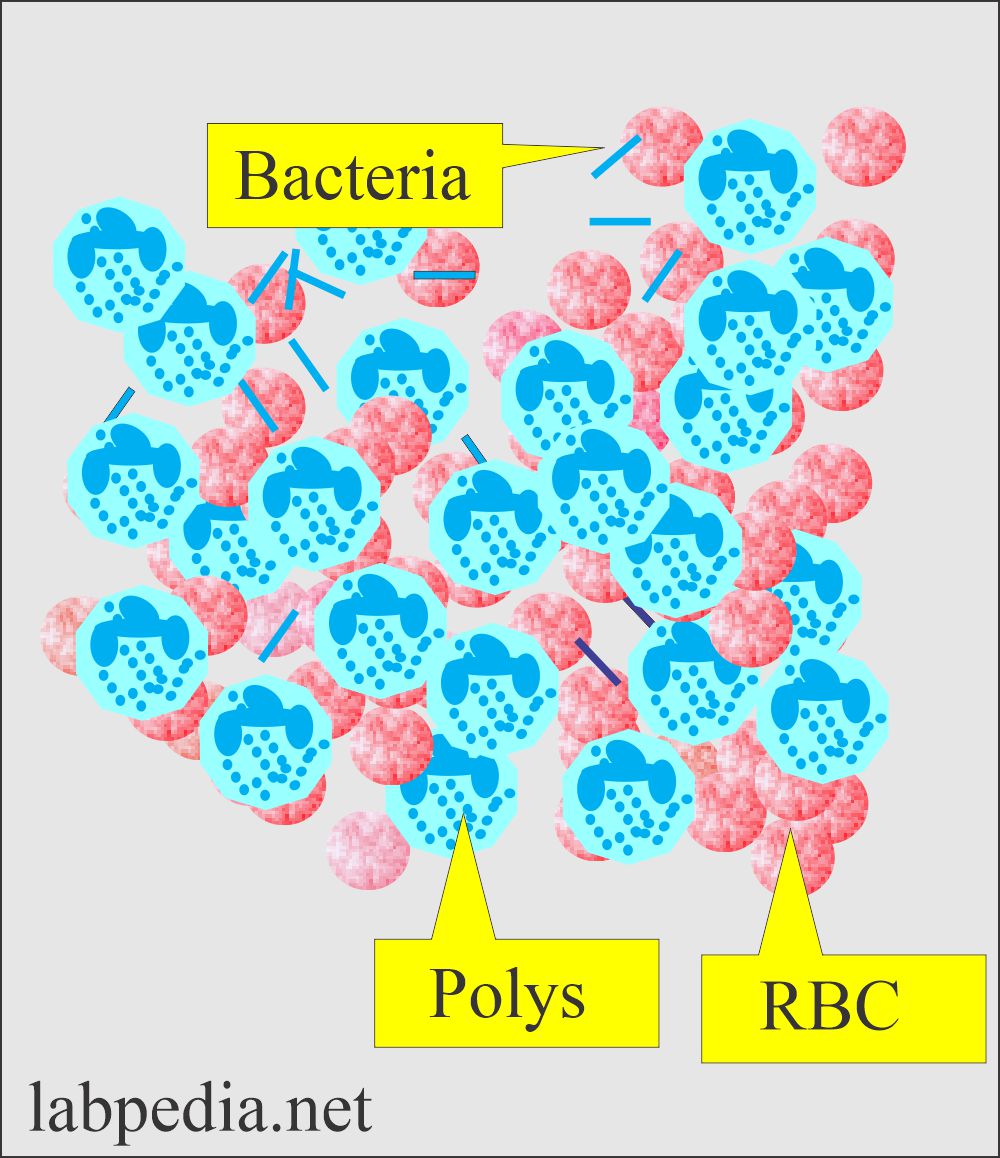
WBC (White blood cells, Pyuria):
- WBCs may originate from any part of the urinary tract.
- WBC is larger than RBC, around 12 µm in diameter.
- The predominant white cells are neutrophils.
- Identifying neutrophils is easy because of the granular cytoplasm and multilobate nucleus.
- These are reported to be an average of 10 fields under high power.
- Neutrophils lyse rapidly in alkaline urine and lose nuclear details.
- WBCs can migrate to the site of infection or inflammation.
- An increase in WBCs in urine is called Pyuria.
- WBCs in the urine indicate infection or inflammation in the urinary tract.
- There may be sterile pyuria.
Eosinophils (Eosinophiluria):
- Eosinophil is suggestive of interstitial nephritis and does not favor urinary tract infections.
- Eosinophils are also seen in drug-induced interstitial nephritis.
- Few eosinophils may be seen in urinary tract infections and renal transplantation rejection.
- The urine sediment slide is prepared by cytospin and stained with Wright’s stain or Hansel’s stain.
- The percentage of >1% eosinophils in urine is significant.
Mononuclear cells:
- Mononuclear cells like lymphocytes, macrophages, and histiocytes may be present in small numbers.
- These cells are not identified in the wet preparation.
- Increased numbers of lymphocytes may be seen in the early stages of renal transplantation rejection.
- For mononuclear cells, the supravital stain is needed.
- Or, Add acetic acid to enhance nuclear details.
Lymphocytes:
- These are seen in kidney transplant rejection.
- An increased number of lymphocytes indicates early signs of kidney rejection.
- Also, plasma cells may be seen along with lymphocytes.
What are the symptoms of a urinary tract infection?
- Increased infrequent urination.
- There is blood in the urine (hematuria).
- The urine color is cloudy.
- There is a burning sensation.
What are the causative agents of UTI?
- The most common is E.coli. About 80% of UTIs are due to these bacteria.
- Staphylococcus is a common cause in young sexually active females.
- Klebsiella and Enterobacter are also common causative agents.
- Sometimes Candida may also cause UTI.
What is the evidence of pyuria?
- There is a positive leukocyte esterase test. The sensitivity is 70% to 95%.
- There is a positive nitrite test even in fresh urine. This test specificity is quite high, but sensitivity is only 50%
- There is a reagent strip that finds evidence of urinary tract infection.
- The ultimate diagnosis is culture:
- A count of 100,000 bacteria is a significant number to call a urinary tract infection.
- A count of 10,000 bacteria is considered contamination.
What are the normal WBCs (Urine For Pus cells)?
- Male = pus cell(WBC) = < 4 /HPF.
- Female = pus cell (WBC) = 5 to 7 /HPF.
What are the causes of increased WBCs in urine?
- Bacterial infection of the urinary tract.
- Cystitis.
- Prostatitis.
- Urethritis.
- Acute Appendicitis.
- Chronic pyelonephritis.
- Glomerulonephritis.
- Tuberculosis.
- Bladder Tumors.
- An autoimmune disease like SLE.
- Note: When there are clumps of WBCs, these should be reported, suggesting urinary tract infection.
- In urinary bladder infection, there are WBCs and very few RBCs.
Normal urine picture:
| Physical features | Chemical features | Microscopic findings |
|
|
|
- Please see more details in the Urine analysis.
Questions and answers:
Question 1: When will you see eosinophils in the urine?
Question 2: What is the cause of lymphocytes in the urine?

Please send this information to my email address
Please send me the email address. I can send link there
Thanks alot Sir, the write up are help and would like you to help me with the link download or send me with some of the textbooks your referenced
Dear
I have to consult a number of books. I can quote a few of those.
1. Urine analysis and body fluids by Susan King Strasinger.
2. Clinical laboratory science. The basics and routine techniques by Jean Jorgenson Linne.
3. A manual of Laboratory diagnostic tests by Frances Fischbach
Please see this link:
https://www.labpedia.net/urine-analysis-part-6-microscopic-findings/
Hi
I had my urine results today. Everything looks fine except of one result The Urine WBC/hpf where the results show 4-5. I am male 38yo. Is this normal?
I will take it normal unless you have any urinary signs or symptoms. Also, repeat the urine after 3 to 5 days. Also, ask the lab if there are clumps of WBCs, then I will call it infection.
My urine routine exam was done on 18 August 2020.my pus cells are 5-7 WBC/HPF.I have pain on left back side above the pelvis girdle and also urge to urinate.Please recommend some allopathic medicine for pus infection and any other examination like ultra sound etc
Please consult urologist, burning micturition is mostly seen in infection or stones. Ultrasound will also help.
Hi i had my urine test today . everything was nomal except my leucocyte esterase wad positive and pus cell was 5-7 wbc/hpf.
I this normal . should i get worried
I have replied.
Hi i had my urine test today . everything was nomal except my leucocyte esterase wad positive and pus cell was 5-7 wbc/hpf.
I this normal . should i get worried.iam female
In female usually, 5 to 7 WBC/HPF are normal, to consider the leucocyte esterase, I will suggest to repeat urine test and ask them to rule out any presence of clumps of WBC. If they find a few clumps, then you can have culture and sensitivity of urine.
Hi. I had a Urine test today showing Uric Acid (+) while Blood test showed Serum Uric Acid 4 mg/dl which is normal. Which test should concern me. Thanks
This is not necessary to see a uric acid crystal in the urine and blood uric acid to be high. Uric acid crystals in the urine depend upon the diet.
Hi
My father’s PUS level is between 20 -30. Can you please let me know what the cause of this high value and what are the remedies? Thank you.
Please what you mean by PUS level. Is it the number of pus cells in the urine or?
Hello, In My Microscopic Report of Urine test, I have found my pus cells/WBC is 116.00 P/μlwhere the normal reference is (0-9) P/μl. Should I get worried about it? Or Are there are any typing mistakes? Is this possible for 116.0 P/μl?
The best way will be to do a urine culture and then start antibiotics.
AoA i am male 27 year old .
Yesterday my urine test wbc 6_8 please tell me
AoA i am male 27 year old .
Yesterday my urine test wbc 6_8 please tell me .thanks
Would you please take more water and test the urine again? Because this number is not so significant, if they find clumps of WBCs, it is a urinary tract infection.