Urine for Phosphorus (Phosphates), 24 hours Urine sample
Urine for Phosphorus (Phosphates)
What sample is needed for Urine Phosphorus?
- The test sample is urine.
- Collect urine for 24 hours.
How will you collect a 24-hour urine sample?
- Note down the time and empty the urinary bladder.
- Now, all the urine samples will be collected until 24 hours have passed.
- Empty the urinary bladder when the time is finished.
What preservative will you use for urine?
- Acidify with HCL, and If pH <3 Then, urine is stable for 6 months.
- The vial should be washed with acid.
- Containers should be detergent-free.
- Instruct the patient to void the first sample and note the time.
- After that, all the samples will be collected until 24 hours have passed.
- Now, void the last sample in the container.
- Refrigerate the urine sample during collection.
What are the indications for urine for Phosphorus?
- It helps in finding kidney problems.
- It helps to find the causes of kidney stones.
- Phosphorus levels will give an idea about renal or bone disease.
- Advised to assess the parathyroid function.
How will you discuss the pathophysiology of Phosphorus?
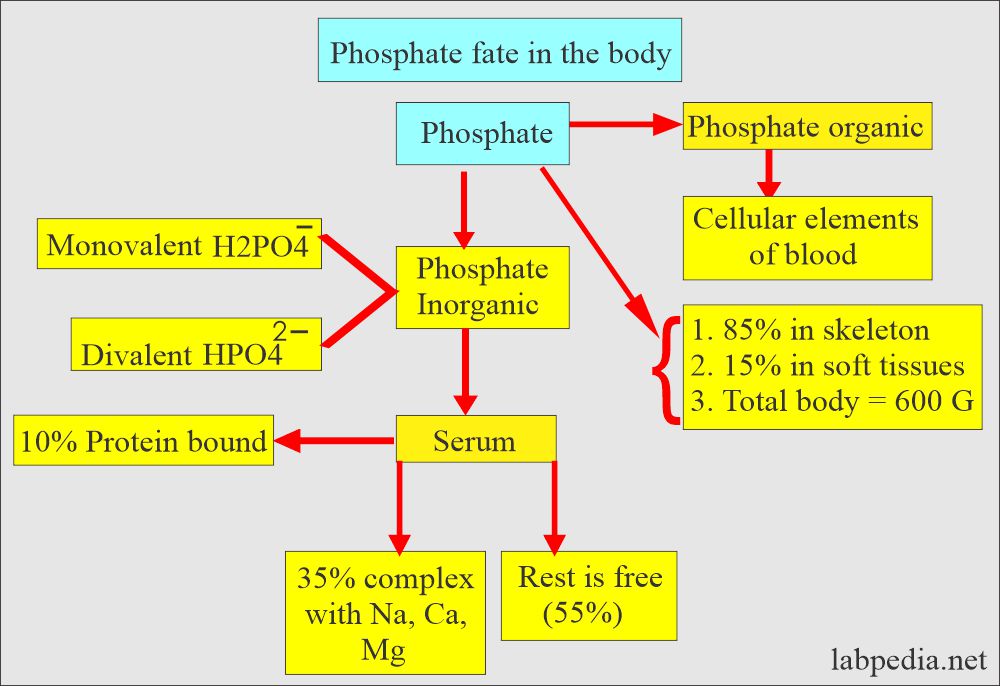
- Phosphorus in the body is in the form of phosphate, so phosphorus and phosphate are used interchangeably.
- The urine phosphate test measures the amount of mineral phosphate in the urine sample collected over 24 hours.
What are the Phosphorus functions?
- The body needs phosphate:
- To build and repair the bones and teeth.
- To help nerves function (phosphorus signaling).
- To help in muscle contraction.
- To produce energy.
- It helps in the synthesis of DNA and RNA.
- It is one of the acid-base buffers.
How is phosphorus distributed in the body?
- 85% of the phosphate is in the bones.
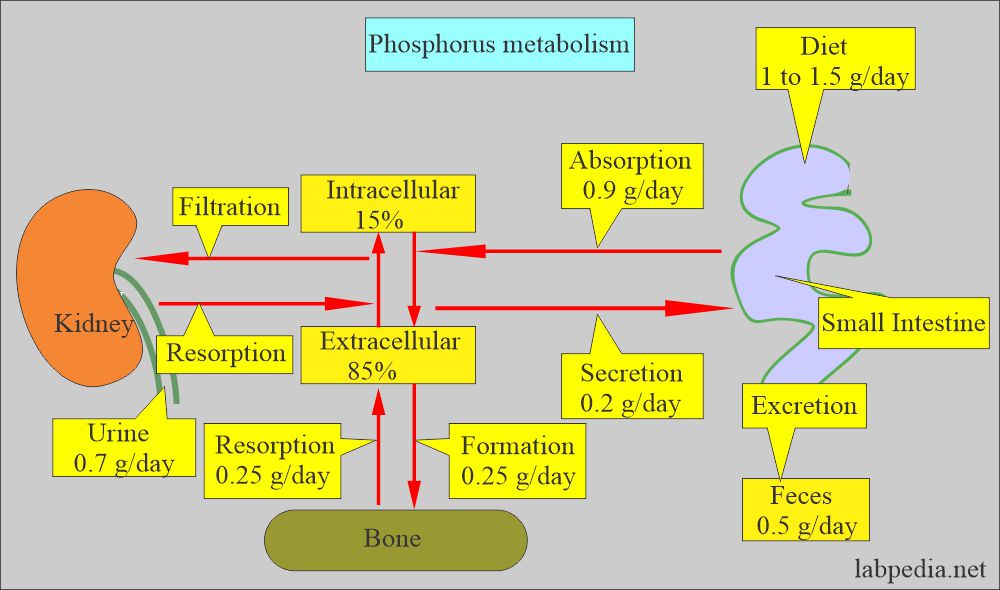
What is phosphorus metabolism, and how is it controlled in the body?
- The kidneys help control the amount of phosphate in the blood.
- The extra amount of phosphate is excreted by the kidneys in urine.
- Kidneys filter phosphorus easily by the glomeruli.
- The proximal tubules reabsorb 85% to 90% filtered phosphorus.
- The parathyroid gland inhibits reabsorption, increasing phosphorus excretion.
- Fibroblast growth factor also increases phosphorus excretion.
- Phosphate is a charged particle (ion) that contains the mineral phosphorus.
- The kidneys filter the extra phosphate, passing out the body in the urine.
- Kidney diseases can affect the phosphate level in the urine.
- If the blood has less phosphate, it is less in the urine.
- Eating a meal high in phosphorus will increase the phosphate level.
- High vitamin D levels and an overactive parathyroid gland increase the phosphorus level.
What is the normal phosphorus in urine?
Source 1
Phosphorus, inorganic in the urine:
- Constant daily diet = <1.0 g/day (<32.3 mmol/day).
- Nonrestricted diet = 0.4 to 1.31 g/day (12.9 to 42.0 mmol/day).
- Constant daily diet = 0.9 to 1.5 g (29 to 48 mmol) phosphorus and calcium 10 mg/kg (0.25 mmol/Kg)
Another source
- Adult = 0.4 to 1.3 grams / 24-hour urine sample.
- Calcium- and phosphate-restricted diet = < 1.0 g per 24-hour urine sample.
What are the causes of increased urine phosphate (Hyperphosphturia)?
- Kidney diseases.
- Hyperparathyroidism.
- Excessive intake of vitamin D.
- Dietary intake.
What causes decreased phosphate levels in the blood and urine (Hypophosphaturia)?
- When the level is <2.5 mg/dL in the blood.
- Hypoparathyroidism.
- Kidney diseases.
- Liver diseases.
- Severe malnutrition.
- In hospitalized patients.
Questions and answers:
Question 1: What is the value of phosphorus estimation in the urine?
Question 2: What is the role of the kidney in phosphorus metabolism?