Urine Calcium (Ca), (Quantitative 24 hrs urine calcium)
Urine Calcium (Ca)
What sample is needed for Urine Calcium (Ca)?
- 24- hours of urine is collected in the acid wash bottle.
- Add 10 to 20 mL of 6M/L HCl.
- A random urine sample of 1 to 2 mL can also be evaluated.
- Refrigerate the urine during collection.
- Or acidify the urine to pH <2.0 to dissolve the calcium salts.
What are the precautions for Urine Calcium (Ca)?
- Wash the bottle with diluted HCl and then rinse it with water.
- Avoid contamination with calcium.
- Don’t use cork because it may contaminate the urine.
- If this test is done for metabolic disorders, advise the patient to have a low-calcium diet and stop calcium medications 1 to 3 days before the urine collection.
- For patients with renal stones, the formation should have the same routine diet for the last three days before collecting the urine. Can continue medications.
What are the indications for Urine Calcium (Ca)?
- This is done to evaluate calcium intake (hypercalcemia).
- This also tells the rate of :
- Absorption of calcium from the GI tract.
- Bone Resorption.
- Renal loss.
- Measurement of calcium levels in urine and serum levels is used to diagnose and monitor calcium metabolism disorders.
- This test is also used in renal stone evaluation and follow-up.
- Urine calcium is also advised for the calcium intake or rate of intestinal absorption, bone resorption, and renal loss.
How would you discuss the pathophysiology of Calcium (Ca)?
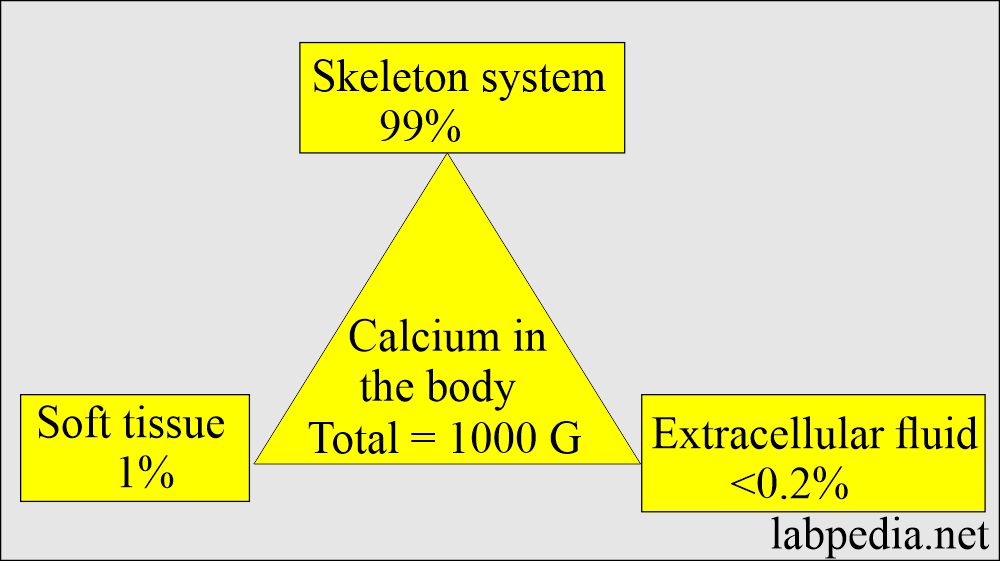
- Calcium is the fifth most common element in the body.
- The average human body contains 1 kg of calcium.
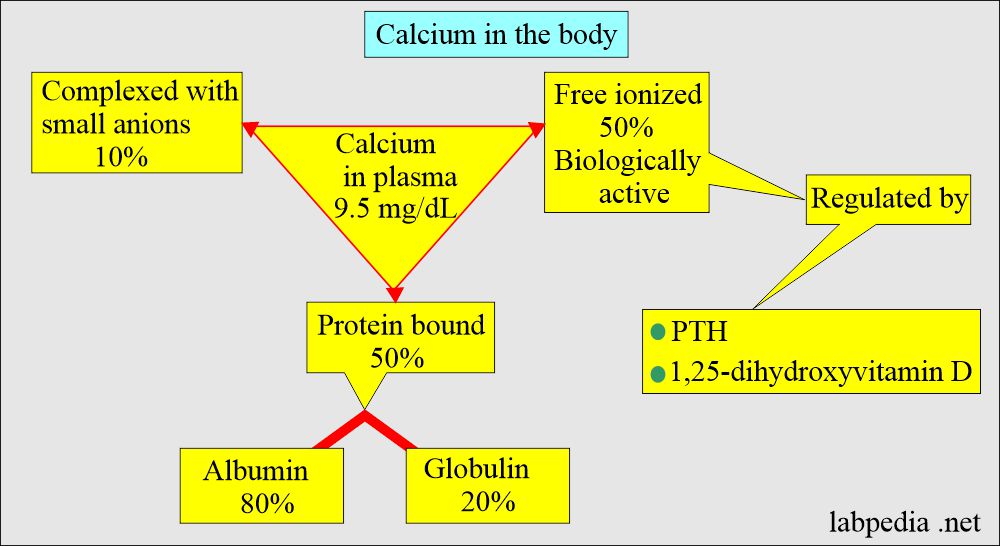
- Calcium exists in three forms in the blood.
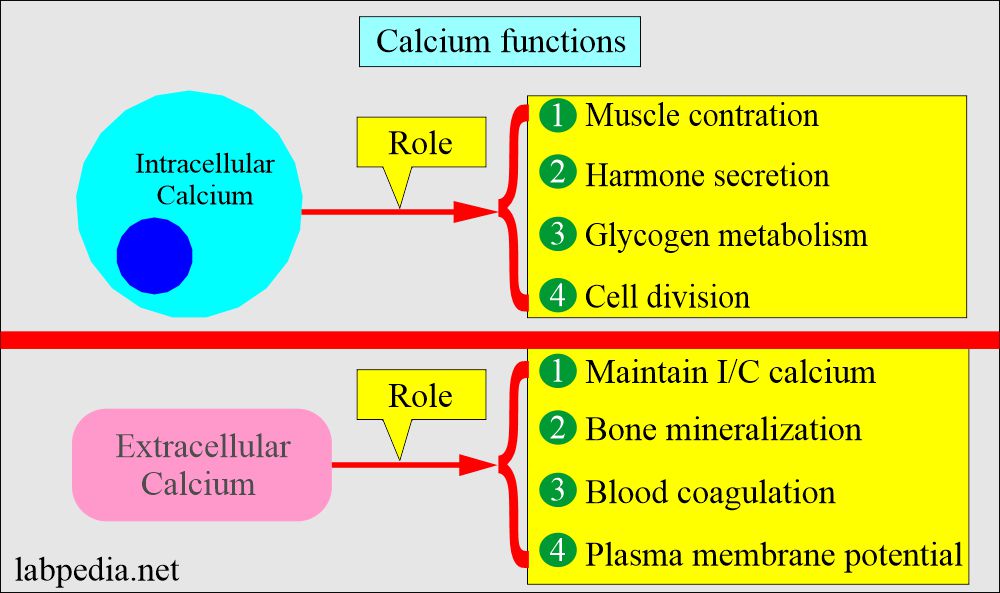
- What are the functions of Calcium in the body?
- Calcium in the body exists as intracellular and extracellular, and both have different functions.
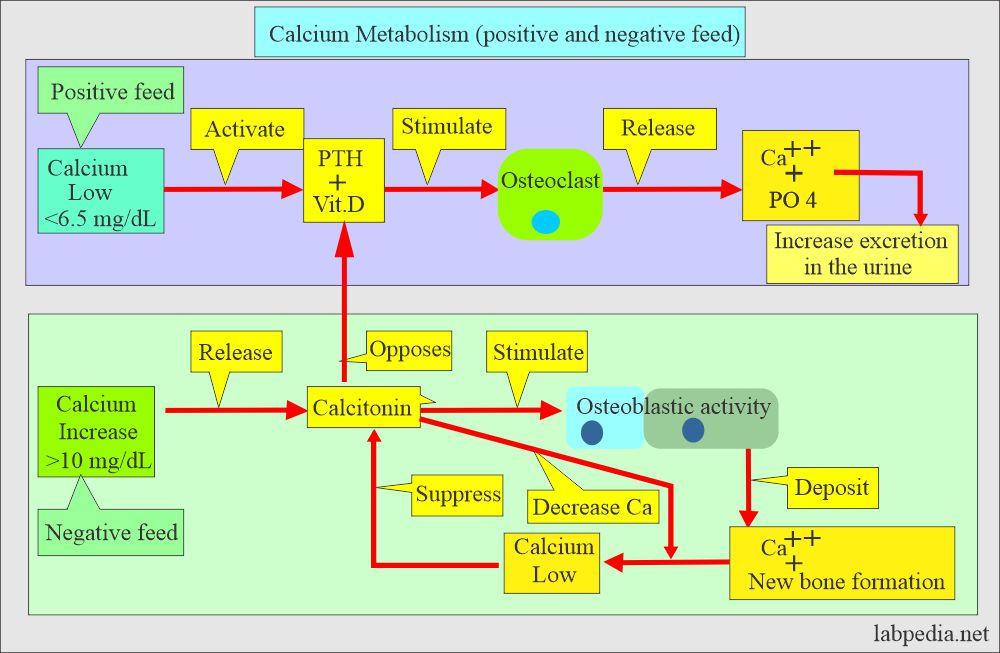
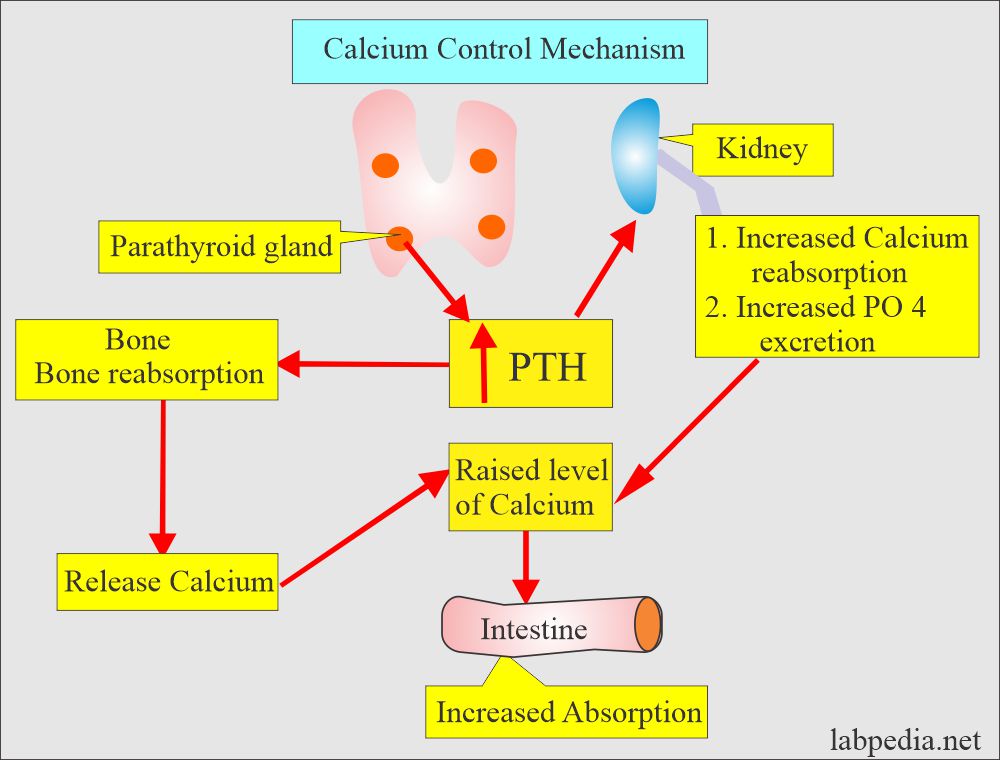
- The parathyroid hormone maintains blood calcium levels.
- PTH indirectly increases the absorption of calcium from the gastrointestinal tract by producing the vit. D.
- PTH increases the serum calcium level by increasing bone resorption and mobilizing Calcium.
- Urine calcium is high in 30% to 80% of primary hyperparathyroidism cases, but it is not diagnostic.
What is the mechanism of Calcium excretion?
- Mostly, calcium is lost in the stool.
- A minimal amount is excreted in the urine.
- In hypercalcemia, there is increased secretion of calcium in the urine.
- In hypocalcemia, there is decreased secretion of calcium in the urine.
- Urinary calcium excretion is dependent upon the dietary intake of calcium.
- Drugs like Thiazide and oral contraceptives lead to decreased levels.
What are the causes of increased urinary calcium?
- Increased intestinal calcium absorption.
- The defect in the renal tubular reabsorption.
- Loss or reabsorption from the bone.
- Or a combination of the above possibilities.
- In primary hyperparathyroid disease, 30% to 80% of the patients have high urinary calcium.
- Urine calcium does not have much value in the differential diagnosis.
What are the values of normal urinary calcium?
Source 1
| Diet | mg/day | mmol/Kg/day |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- The average Calcium diet is 800 mg/day.
Source 4
- Normal diet = 100 to 300 mg/ 24 hours or 2.50 to 7.50 mmol/day.
- Low calcium diet = 100 to 150 mg /24 hours or 1.25 to 3.75 mmol/day.
Another source
- 50 to 250 mg/24 hours.
What are the causes of false raised values of urinary calcium?
- Some drugs like calcitonin, vitamins A, K, and C.
- Corticosteroids.
- Urine is taken after meals with a high calcium intake, e.g., milk.
- Increased exposure to sunlight.
- Immobilization, especially in children.
What are the causes of false decreased values of urinary calcium?
- Increased ingestion of PO4, HCO3–, and antacid.
- Thiazide diuretics.
- Lithium therapy.
- Alkaline urine.
- Oral contraceptives and estrogens.
What are the causes of increased urinary calcium?
- In hyperparathyroidism, 30% to 80% of the cases.
- Paget’s diseases.
- Renal diseases.
- Sarcoidosis.
- Breast cancer.
- Urinary bladder cancers.
- Multiple Myeloma.
- Bone metastasis (osteolytic).
- Vit.D intoxication.
- Thyrotoxicosis.
- Osteoporosis.
- Fanconi’s syndrome.
- Idiopathic hypercalciuria.
- Prolonged immobilization.
What are the causes of decreased urinary calcium?
- Renal osteodystrophy.
- Rickets
- Hypoparathyroidism.
- Pre-eclampsia.
- Vit.D deficiency.
- Metastatic carcinoma of the prostate.
- Preeclampsia.
- Acute renal failure, nephritis, and nephrosis.
- Malabsorption conditions like :
- Celiac disease.
- Sprue disease.
- Steatorrhea.
Questions and answers:
Question 1: How much body contains calcium?
Question 2: What is the role of calcitonin in our body?

Urine calcium spot normal values
That is good for you that spot test for calcium is negative.