Urine For Bile pigments
What sample of urine is needed for the Bile pigments?
- Bile salt can be checked on random urine.
- Bile pigmetns also include bilirubin and biliverdin.
What are the indications of urine for bile pigments?
- This is because bile pigments in the urine indicate liver dysfunction.
- The presence of bile pigments in the urine helps to diagnose the increased production of bilirubin.
What are the precautions for bile pigments?
- There may be a false positive reagent strip.
- In case of increased pH.
- Some drugs, like sulfonamides, procaine, and 5-hydroxy indoleacetic acid, may interfere with the result.
How will you discuss the pathophysiology of the bile and bile pigments?
- Bile acid and bile salts are used as synonyms.
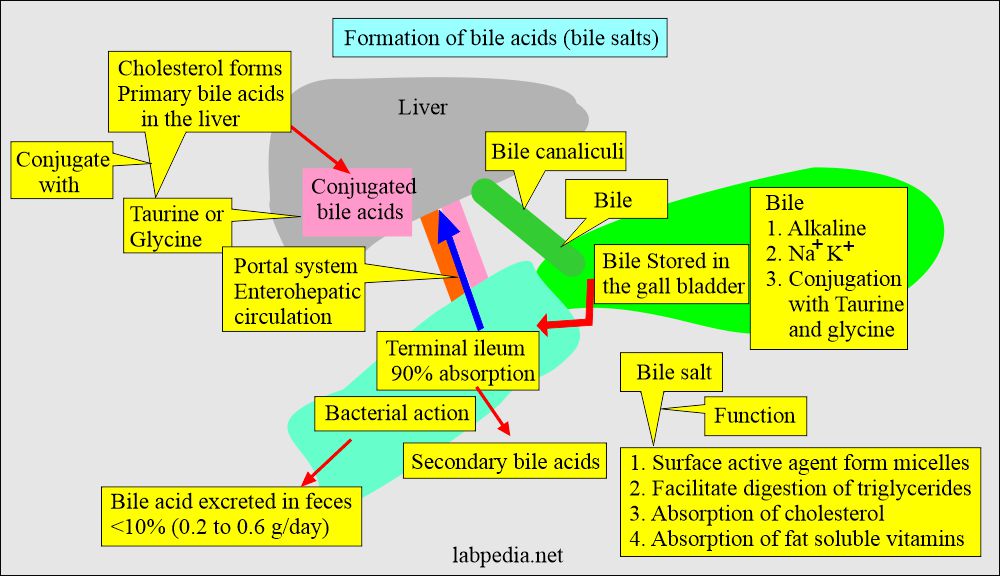
- Bile is a fluid synthesized by the liver and consists of the following:
- Conjugated bile salts.
- Bilirubin diglucuronide.
- Cholesterol.
- Phospholipids.
- Electrolytes.
- Water.
- Bile is alkaline due to the presence of bicarbonate.
- The bile color is golden-brown to greenish-yellow and has a bitter taste.
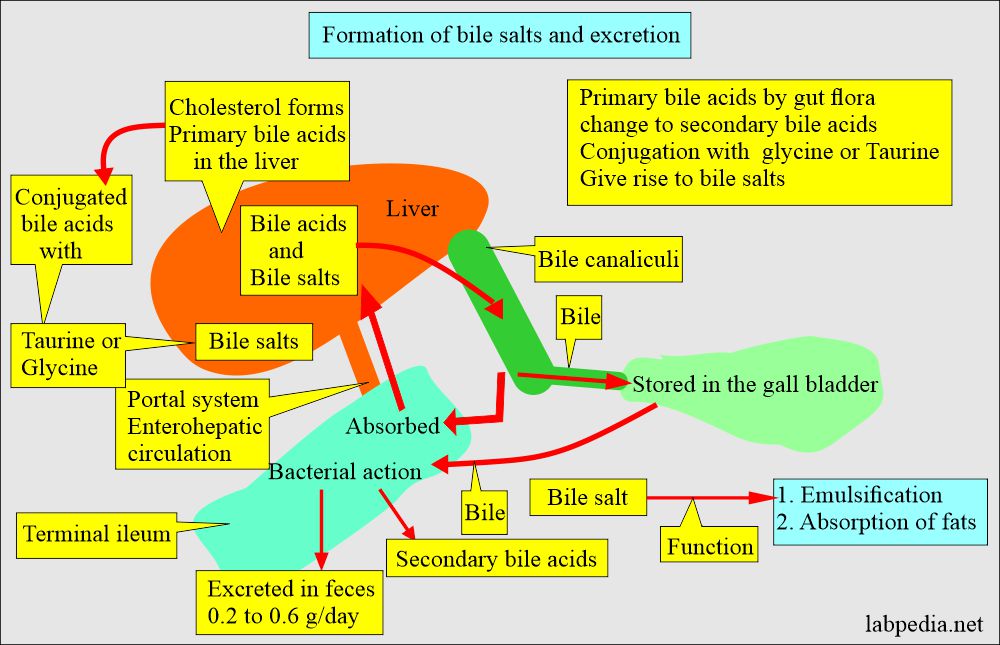
How will you discuss the biosynthesis of Bile acids and Bile salts?
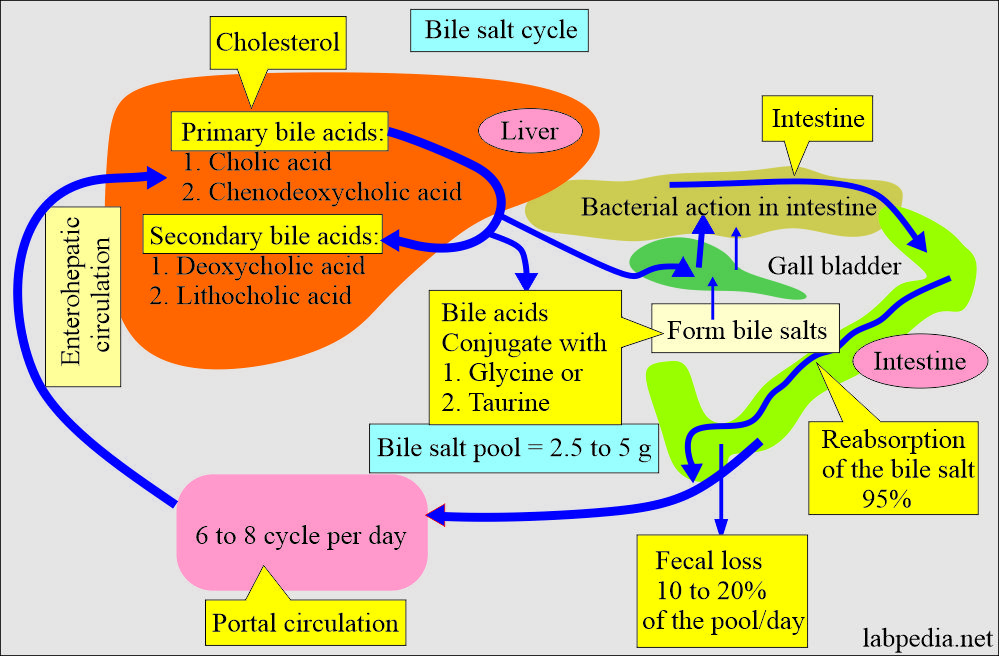
- Bile acids are synthesized in the hepatocytes from cholesterol. These are excreted into the bile and then pass into the duodenum.
- The primary bile acids are:
- Cholic acid.
- Chenodeoxycholic acid.
- These primary bile acids pass into the duodenum (intestine), and the bacterial action converts to secondary bile acids.
- Secondary bile acids are:
- Deoxycholic acid.
- Lithocholic acid.
- The bile acid can conjugate with glycine and taurine and form bile salts.
- The primary bile acids are:
- Bile salts help stimulate the bile flow and are a potent antibacterial.
- The primary bile pigments due to catabolism of the hemoglobin are:
- Bilirubin. is orange or yellow in color.
- Biliverdin is green in color.
- Urobilinogen (Urobilin).
- The leading site of the formation of bile pigments is the liver.
- Ultimately, these leave the body in feces and a small amount in the urine.
- Human bile contains:
- Cholate conjugate = 38%.
- Chenodeoxycholate conjugate = 34%.
- Deoxycholate conjugate = 28%.
- Lithocholate = 1 to 2%.
- The hepatic bile contains 5% to 15% of the solids; the major components are bile acids.
How Bilirubin in the urine is excreted?
- Normally, conjugated bilirubin in the urine is not detected.
- Bilirubin in the urine appears in:
- Biliary tract obstruction is like extrahepatic obstruction of the common bile duct.
- Biliary tract obstruction may be intrahepatic, like cholestatic liver cell injury in active cirrhosis and viral hepatitis.
How is Urobilinogen in the urine excreted?
- Urobilinogen is produced from conjugated bilirubin by the metabolic activity of the bacteria in the intestine, followed by absorption into the blood circulation.
How will you detect Bile salt and bilirubin?
- Bile pigments (Bilirubin) give the urine a greenish-yellow, yellow, or brown color.
- The Fouchet test:
- It detects bile pigments (Bilirubin).
- Sulfur granules test:
- It detects bile salts.
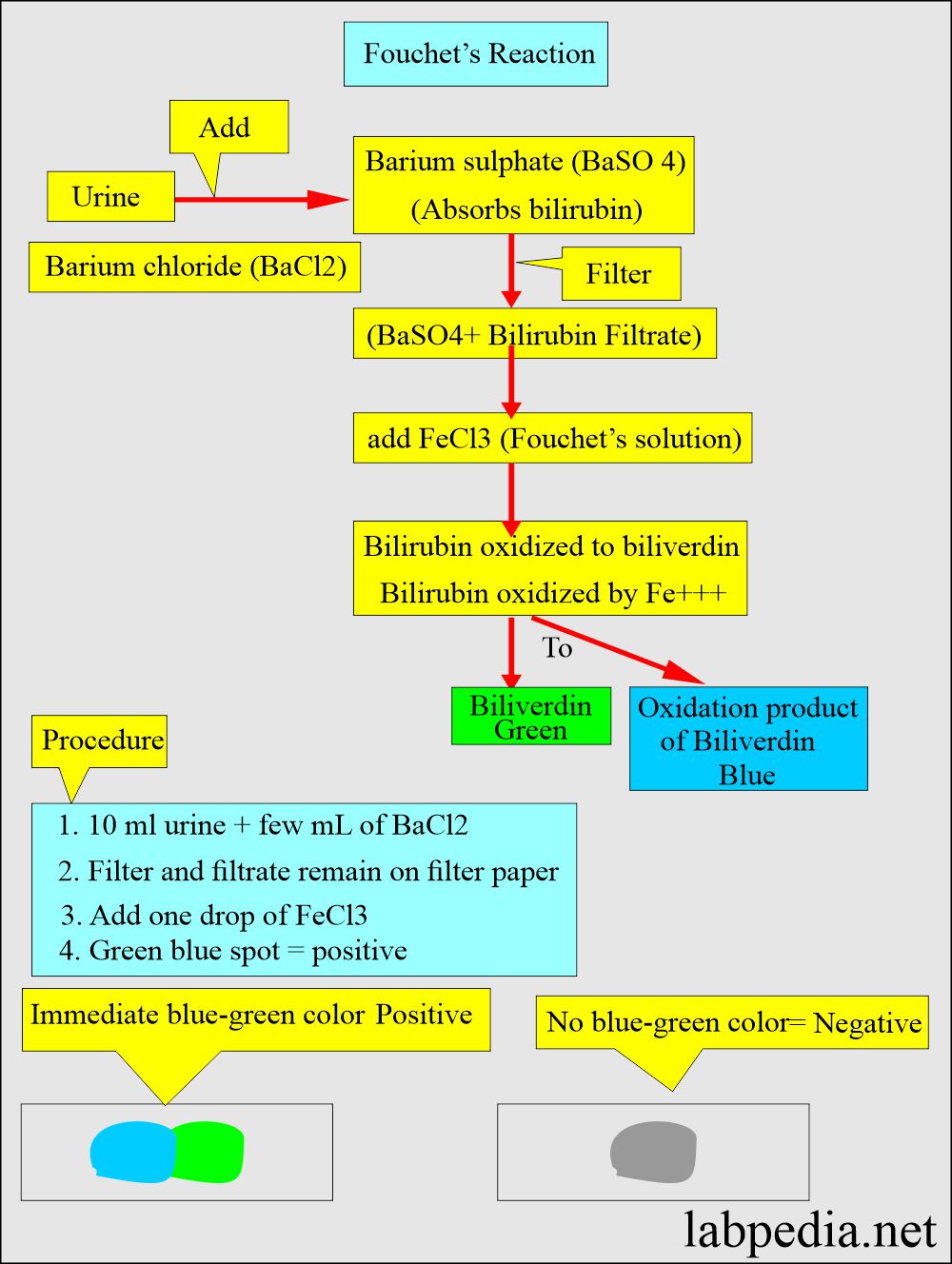
How will you perform Fouchet’s test?
- It will detect the bilirubin in the urine.
- Reagents are:
- Barium chloride 10%.
- Fouchet’s reagents consist of:
- Trichloracetic acid = 25 grams.
- Ferric chloride (FeCl3) 10% = 10 mL
- Distle water = 100 mL
- The procedure of Fouchet’s test:
- Take 5 ml of the urine; if the urine is alkaline, then add one to 2 drops of glacial acetic acid (concentrated).
- Take 5 mL of urine and add barium chloride (BaCl2 10%) 2.5 mL.
- Mix well.
- The sample will become cloudy.
- Filter or centrifuge to obtain the precipitate, which contains bilirubin.
- A precipitate of sulfates appears to which bilirubin is bound (barium-sulfate-bilirubin complex).
- To the filtrate on the paper (precipitate), add one drop of Fouchet’s reagent (Ferric chloride).
- When ferric chloride is added to urine in trichloroacetic acid, it oxidizes bilirubin to green color biliverdin.
- Immediately, a blue-green color develops, indicating a positive for bilirubin.
| Test result | Positive for bile contents |
|
|
|
|
How will you perform the Foam test for bilirubin?
Urine is kept in a small vial and vigorously shaken. The bile pigments will stain the resulting foam.
- There is yellowish foam in the case of urine bilirubin.
- In normal urine, the foam will be white.
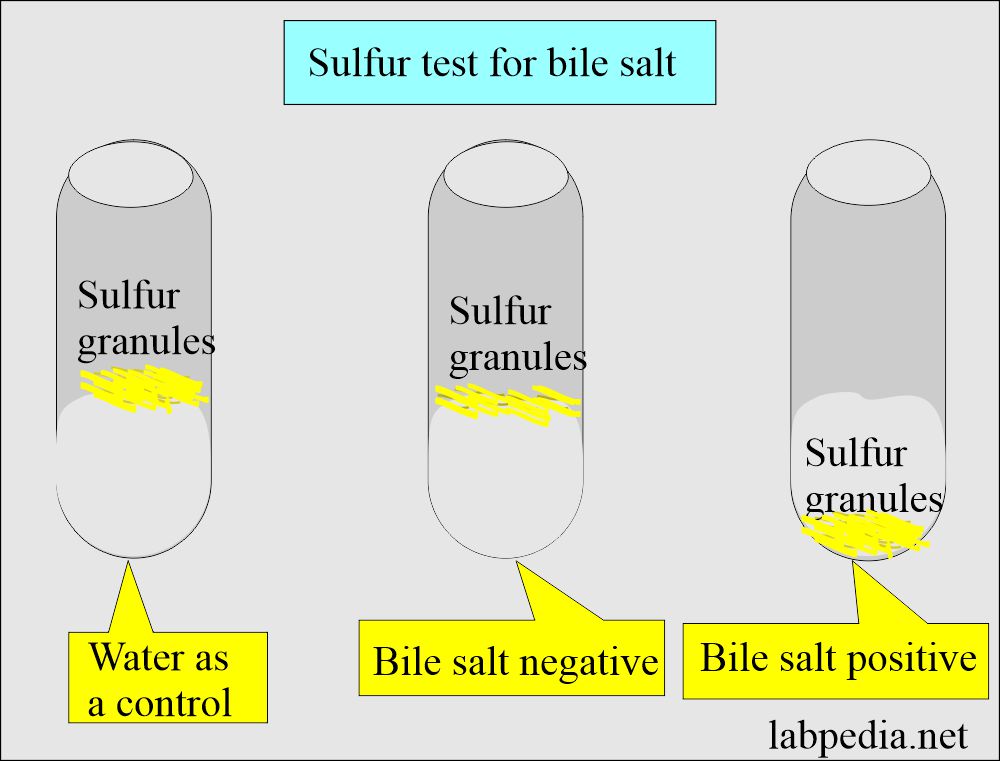
How will you perform the Sulfur granule test for bile salts:?
- Carefully sprinkle the sulfur granules over the surface of the urine.
- Also, it can run water as the control.
- In the case of bile salts, sulfur will settle in the bottom.
- In the case of negative urine, sulfur granules will remain on the surface.
What is normal urine Bile pigments?
- Normally, bile pigments and bile salt are absent in normal urine.
What are the causes of increased urine urobilinogen?
- It is increased in hemolytic anemia with absent urine bilirubin.
- In case of hemorrhage into the tissue, like pulmonary infarction and severe bruises.
- In case of severe hepatic cell damage in acute viral hepatitis, drugs and toxins.
- In patients with cholangitis.
What are the causes for absent urine urobilinogen?
- When there is complete biliary obstruction and stool is pale or clay-colored.
Questions and answers:
Question 1: What is the difference between bile acid and bile salts?
Question 2: What is the end result of Fouchet's reaction?


In my urine report bili pigment level negative and also acetone level is negative
So have any problem with my urine
I don’t think so.
Thanks you really appreciated for the explanation.
Welcome.
It’s very helpful to read for me…thank u❤️
Thanks.
Sir my kft report show 9 uric level and all test report is normal in liver bilrubin direct and sgpt increse slightly means 4 points from normal range and in urinalysis my uribilinogen is postive normal written .but still my urine is frothy why
Your uric acid level is too high, you need treatment for hyperuricemia. But your LFT (liver function test) is not clear to me.
Sir, Bile salts and bi le pigment are present in my report.. What does that mean?
It indicates biliary tract obstruction. For the layman, it suggests liver disease. Please get an ultrasound to find the cause of the obstruction.
Very Helpful Sir
Thanks.
Dr.Riaz
Information is so helpful…
May allah bless you ameen
Thanks.
Hi sir,
In my urine report
Bile salt -present
Bile pigment – positive
I had also abdomen ULtra sound .. that all normal.. my question is when I search Internet its showing positive bile pigment cause liver dysfunction. Is that true?
Normally bile salts and bile pigments are absent. Their presence indicates liver dysfunction. Please consult a hepatologist to find out the cause.
Thnks
You are welcome.
Thank u sir I’m a pharmacy student and recently we are discussing all that urea cycle and urine excretion processes and definitely this article clear my 99% concepts more☺️
I have a question if the appearance of urine is turbid what does that mean?
And if ketones and glucose is nill in urinary report so it’s okay like their excretion is not allowed in urine like this question is for general concept .
Ketones and glucose should be negative when positive indicate pathology. Turbid urine may be due to some crystalluria or infection.
During the pregnancy if Bile pigment report is negative. can we ignore this or its serious problem, because so much itching in hand and leg.
Bile salts negative is good for you. Please consult dermatologist and your gynecologist for itching of hand and leg.
very useful information Sir
i hope you will provide more informations regarding lab tests
Dr Khalid DUHS Karachi
Thanks.