Urine Albumin 24 hours, Microalbuminuria
Urine Albumin 24 Hours, and Microalbuminuria
What sample is needed for Urine Albumin
- The patient is directed to collect 24 hours of urine as follows.
- Discard the first urine sample.
- Then, he/she will collect all the samples for another 24 hours and collect the last sample.
- Store at 2 to 4 ° C.
- Use no preservatives.
- For microalbuminuria, collect random urine (during a week).
- Stable at room temperature for up to 2 days and 8 °C for up to 14 days.
What are the indications for Urine Albumin and microalbuminuria?
- Patient with renal diseases.
- Patients with diabetes mellitus to rule out diabetic nephropathy.
What are the precautions for Urine Albumin?
- Avoid collection of urine after rigorous exercise.
- Avoid in case of a urinary tract infection.
- Avoid surgery.
- Avoid in the case of acute illness.
- Hematuria may interfere with the result.
- Avoid a high protein or high salt diet.
How will you discuss the pathophysiology of Urine Albumin?
- Details are discussed in urinary proteins.
- Persistent proteinuria detected by routine screening indicates urinary albumin excretion of ≥200 µg/min, which indicates diabetic nephropathy.
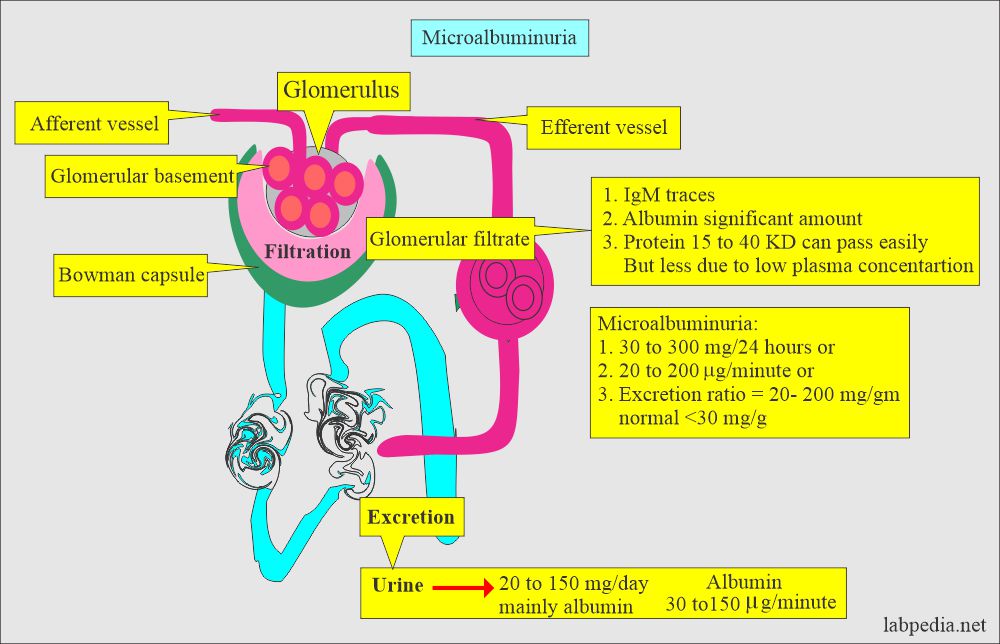
- The routine methods do not detect the albumin level when it is 20 to 200 µg/min or 30 to 300 mg/24 hours.
- Normally, urine contains <10 mg/dL of the protein.
Microalbuminuria:
How will you define microalbuminuria?
- Microalbuminuria is defined as when ordinary methods do not detect proteinuria.
- Microalbuminuria is defined as persistent proteinuria that is below detection by routine reagent strips but greater than normal.
- Urinary protein excretion is 20 to 200 µg/minute or 30 to 300 mg/24 hours is not detected in the urine by ordinary methods.
| Clinical stage | Proteinuria/min | Proteinuria/24 hours |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
How will you discuss the pathophysiology of microalbuminuria?
- Microalbumin in the urine indicates a transcapillary escape of protein in the urine and is a marker of microvascular disease in diabetics.
- The strict control of diabetes prevents diabetic nephropathy and retinopathy.
- Normally, the glomerular membrane allows proteins with a molecular weight of 50,000 to 60,000 or less.
- Albumin has a molecular weight of 67,000, and some albumin may filter through the glomeruli, but the convoluted tubules reabsorb it.
- The presence of proteinuria indicates increased glomerulus permeability or decreased reabsorption by the renal tubules.
- The following diagram explains the kidney’s role in protein excretion.
What is the normal protein and albumin excretion rate?
Total protein/24 hours
- 1 to 14 mg/dL (10 to 140 mg/L).
- At rest = 50 to 80 mg/day
- After intense exercise = <250 mg/day.
Albumin by the RID method:
- 3.9 to 24.4 mg/day
Albumin by By Turbidim:
- 1 to 14 mg/dL (10 to 140 mg/L).
- <150 mg/day.
- At rest = 50 to 80 mg/day
- After strenuous exercise = <250 mg/day
Source 4
24 hours of urine Albumin (protein)
- Adult male = 1 to 14 mg/dL (10 to 140 mg/L).
- Adult female = 3 to 10 mg/dL (30 to 100 mg/L).
- Child <10 years = 1 to 10 mg/dL (10 to 100 mg/L).
Another source
How will you classify the proteinuria/24 hours?
| Severity of proteinuria | Proteinuria gram/day |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Microalbuminuria
- <30 mg/24 hours.
- <20 mg/L (10 hours collection).
What are the causes of microalbuminuria?
- Diabetic nephropathy.
- End-stage renal disease.
- Proliferative retinopathy in type 1 diabetes mellitus.
How would you describe the Albumin/Creatinine ratio?
- A random urine sample is taken. Better take a morning sample.
- What is the significance of the Albumin/Creatinine ratio?
- It detects diabetic nephropathy.
- Advised in hypertension and diabetes mellitus.
- The raised level indicates cardiovascular risk.
- It is advised to see the progression of the kidney disease.
| Albumin excretion | Normal | Microalbuminuria | Clinical albuminuria |
| Albumin excretion | <20 mg/day | 30 to 300 mg/day | >300 mg/day |
| Albumin /(g) creatinine ratio | <30 | 30 to 300 | >300 |
|
|||
Questions and answers:
Question 1: Is there any effect of high protein intake on urinary protein excretion?
Question 2: What is the significance of microalbuminuria?