Urine 24 hours for VMA (Vanillylmandelic acid), Catecholamines (24 hours urine), Neuroblastoma
Urine 24 hours for VMA
What sample is needed for Urine 24 hours for VMA?
- The test is done in the urine.
- Collect 24-hour urine samples.
- Discard the first urine sample and note the time. Now, collect all urine samples in the container containing 6 mL of HCl. Collect the last sample when 24 hours have passed.
- Or add 20 mL of HCL (6 mol/L)
- Refrigerate the urine during collection, and it is stable for 2 weeks.
- The sample is stable for 2 weeks at 2 to 4 °C.
What are the precautions for Urine 24-hour VMA?
- Following foods and drugs cause the false raised level of VMA.
- Avoid chocolate, coffee, tea, and cocoa for 2 to 3 days before the test is performed.
- Avoid foods like citrus fruits, bananas, and vanilla food.
- Avoid beer and red wine.
- Avoid drugs like aspirin and antihypertensive medicines.
- Vigorous exercise and stress may increase the VMA level.
- Decreased VMA levels may be seen in patients with uremia, alkaline urine, and radiographic contrast media.
- Drugs that may increase the level are levodopa, lithium, nitroglycerine, epinephrine, and caffeine.
- Drugs that may decrease the level are phenothiazine, reserpine, guanethidine, monoamine oxidase inhibitor, and disulfiram.
What are the Indications for Urine 24 hours for VMA?
- To diagnose pheochromocytoma.
- For Tumors of the adrenal medulla.
- To diagnose neuroblastoma.
- In patients with hypertension.
How will you discuss the pathophysiology of Urine 24 hours for VMA?
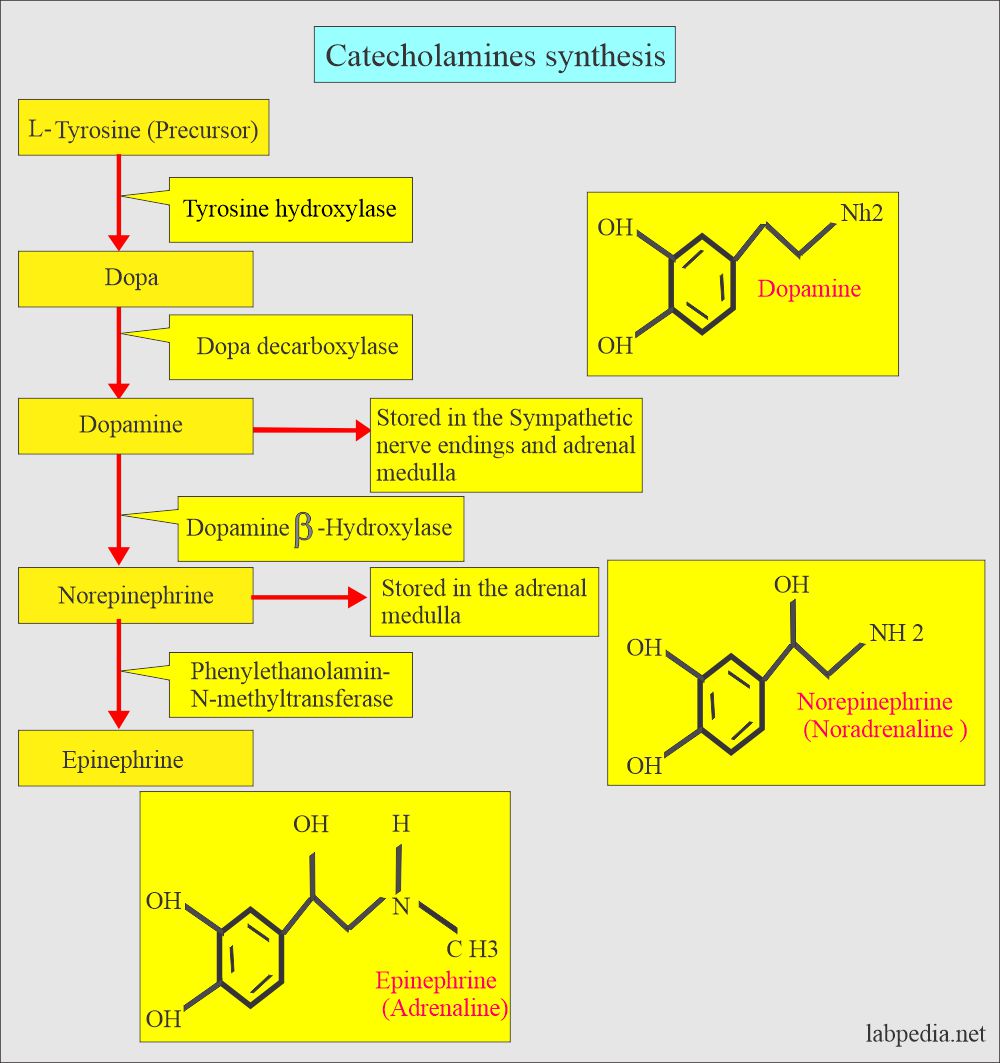
- The catecholamines are formed from the precursor Tyrosine with the action of different enzymes.
- The Adrenal Gland makes a lot of catecholamines as a reaction to stress.
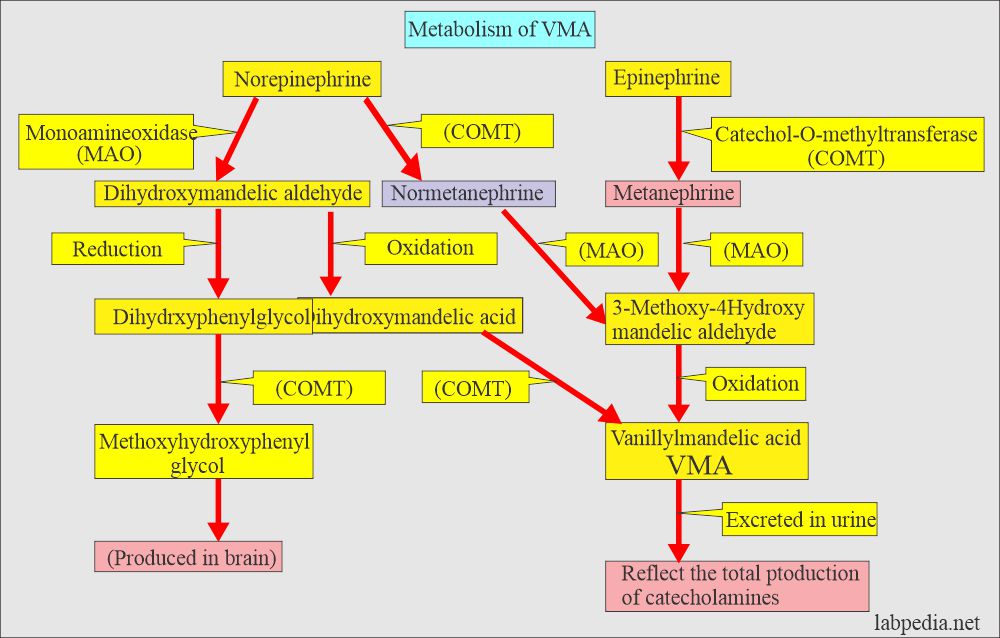
- The end product of catecholamines is VMA excreted in the urine.
- 3-methoxy-4-hydroxymandelic acid is also called VMA.
- The main catecholamines are:
- Epinephrine.
- Adrenaline.
- Norepinephrine (Noradrenaline).
- Dopamine.
- Catecholamines break down into VMA + Metanephrine, which is excreted in the urine.
- VMA is 10 to 100 times more concentrated in the urine than other amines.
- Increased catecholamine is found in the patient with:
- Fall in blood pressure (Decreased blood volume).
- Thyroid hormone deficiency.
- Congestive heart failure.
- Arrhythmias.
- Decreased level of catecholamines seen in a patient with idiopathic postural hypotension.
What are the normal values of the VMA?
Source 1
VMA
| Age | mg/day |
| 0 to 10 day | <1.0 |
| 10 days to 24 months | <2.0 |
| 24 months to 18 years | <5.0 |
| Adult | 2.1 to 7.6 |
Source 2
- Adult/elderly = <6.8 mg/24 hours
- Adolescent = 1 to 5 mg/24 hours
- Child = 1 to 3 mg/24 hours
- Infants = <2 mg/24 hours
- Newborn = <1 mg/24 hours
Other sources
| Test | Urine sample | Plasma |
| VMA | up to 9 mg/24 hours | |
| VMA Some reference says | 2.1 to 7.6 mg/24 hours | |
| Catecholamines total | <100 µg/ 24 hours | |
| Epinephrine | 0 to 20 µg/ 24 hours | <50 pg/mL |
| Metanephrine | 74 to 297 µg/ 24 hours | |
| Norepinephrine | 15 to 80 µg/ 24 hours | 110 to 410 pg/mL |
| Dopamine | 65 to 400 µg/ 24 hours | <87 pg/mL |
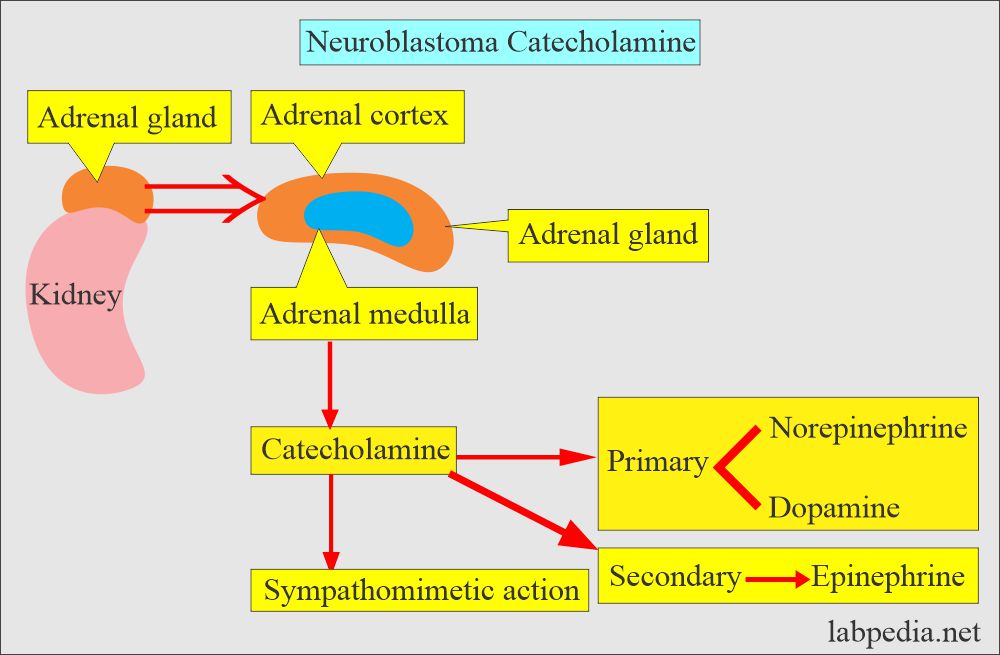
Neuroblastoma
How will you define Neuroblastoma?
- Neuroblastoma is a neural crest tumor like pheochromocytoma arising from the adrenal gland or sympathetic chain.
- Neuroblastoma is the second most common extracranial, nonhematological neoplasm of childhood between the ages of 1 to 4 years.
- Neuroblastoma is the most common abdominal malignant mass except Wilm’s tumor.
- Catecholamines include norepinephrine, normetanephrine, dopamine, VMA, and HVA (all are increased).
What are the signs and symptoms of Neuroblastoma?
- Most common tumors of children under the age of 5 years.
- It arises anywhere along with the sympathetic nervous system.
- A common site is the adrenal medulla.
- Neuroblastoma diagnosed in the first year of life has a better prognosis.
- Due to increased catecholamines from the adrenal medulla, there are:
- Hypertension.
- Rapid heartbeat.
- Diarrhea.
- Before the tumor is diagnosed, there is already spread to lymph nodes, liver, lungs, bone, and bone marrow.
- 70% of the cases have metastasis at the time of diagnosis.
How will you diagnose Neuroblastoma?
- Biopsy with immunocytochemistry.
- Bone marrow for the presence of cancer cells.
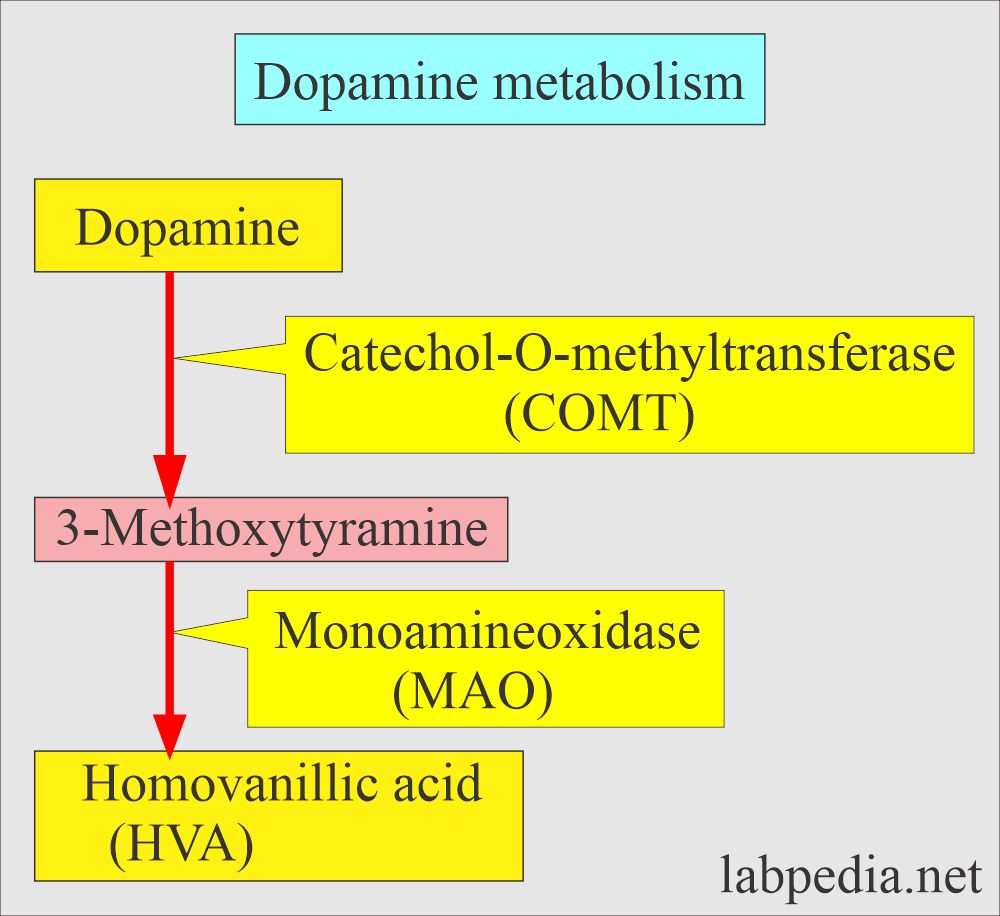
- Increased blood or urine levels of catecholamine metabolites like:
- VMA.
- HVA (homovanilic acid).
- Urinary measurement is preferred.
- At diagnosis, 90% have increased HVA, and 75% have increased VMA.
- Screening for catecholamines at 6 months can diagnose Neuroblastoma.
- Radiology like CT or MRI.
How will you summarize the diagnostic tests for Neuroblastoma?
| Type of the test | Value of the test |
|
Increased |
|
Increased |
|
Increased |
|
Increased |
|
Increased |
How will you treat Neuroblastoma?
- Surgery.
- Radiation.
- Chemotherapy.
- Bone marrow transplantation.
- Treatment by a combination of radiation and chemotherapy gives good results.
What are the causes of increased VMA levels?
- Adrenal gland tumor (Pheochromocytoma)
- It May be seen in any major stress like:
- Burns.
- Body infections ( sepsis).
- Surgery or traumatic injury.
- Many blood pressure drugs.
- Neuroblastoma.
- Ganglioblastoma.
- Ganglioneuroma.
- Carcinoid tumors.
What are the causes of decreased VMA levels?
- In Diabetes
- Parkinsonism.
What are the causes of increased Catecholamine?
- Pheochromocytoma.
- Neuroblastoma.
- Ganglioneuroma.
- Diabetic acidosis.
- Hypothyroidism.
- Myocardial infarction.
What are the causes of decreased Catecholamine?
- Parkinsonism.
- Diabetic neuropathy.
What is the difference between Neuroblastoma and Pheochromocytoma?
| Urine levels of the parameters | Neuroblastoma | Pheochromocytoma benign | Pheochromocytoma malignant |
| VMA | Increased | Increased | |
| Homovanillic acid | Increased | Normal | Increased |
| Dopamine | Increased | Normal | Increased |
| Metanephrines | Increased | Increased |
Questions and answers?
Question 1: What is the significance of VMA in 24-hour urine sample?
Question 2: What are the catecholamines?

test procedure
Writing procedures for every test is beyond my reach. I will write and send you soon.
It is beyond our scope. But I will write to you and send it.
Hi, do you consider conditions where a deficit of NE is seen?
Norepinephrine deficiency may also be seen in:
1. stress and anxiety.
2. Medicines like antidepressants, hypertension medication,