Urea Breath Test for H. Pylori (Helicobacter Pylori)
Urea Breath Test for H. Pylori
What sample is needed for the Urea Breath Test for H. Pylori?
- Two breath samples.
What are the Indications for a Urea Breath Test for H. Pylori?
- This test is used to detect Helicobacter Pylori infection.
- Advised in patients with recurrent:
- Chronic gastritis.
- Duodenal ulceration.
- Duodenal inflammatory process.
- Used for successful therapy.
- It can determine if the infection is active.
- Determining a cure within 4 to 6 weeks is a test of choice.
- It can be used in children.
How will you define Helicobacter Pylori?
- Helicobacter pylori (H.pylori) is a gram-negative bacillus. This was known as Campylobacter pylori.
- It is S-shaped, curved, or gull-winged like Campylobacter.
- This is a gram-negative organism found in the mucus covering the gastric mucosa.
- These organisms are present next to the gastric lining cells of the surface and gastric pits.
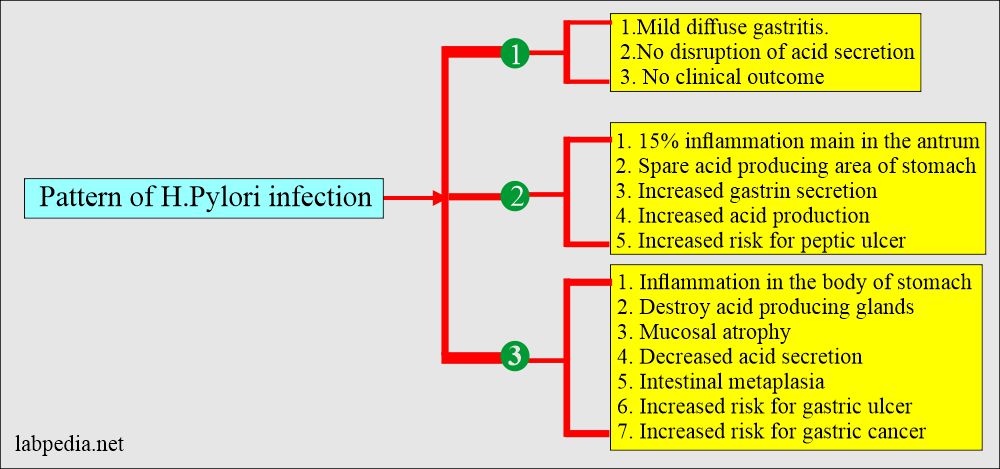
What is the pattern of H. pylori infection?
- H. pylori is associated with the following:
- Acute and chronic gastritis is seen in 90% of cases (70% to 100%).
- Duodenal ulcer is seen in 70% to 75% of the cases.
- Gastric ulcer is seen in 30% to 50% of the cases.
- Gastric carcinoma is seen in 20% to 25% of the cases.
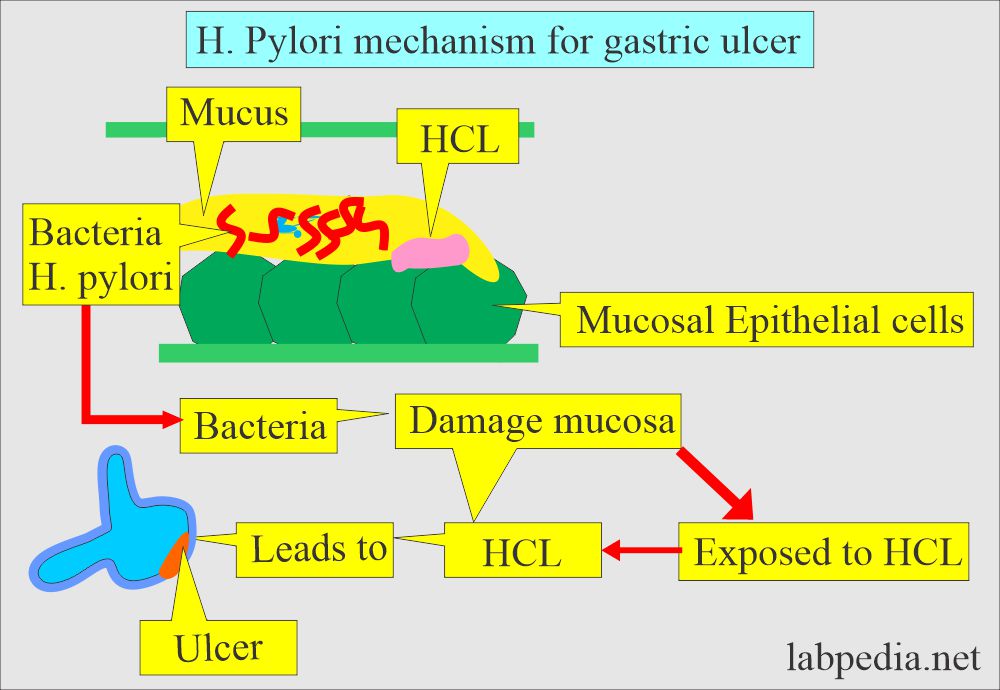
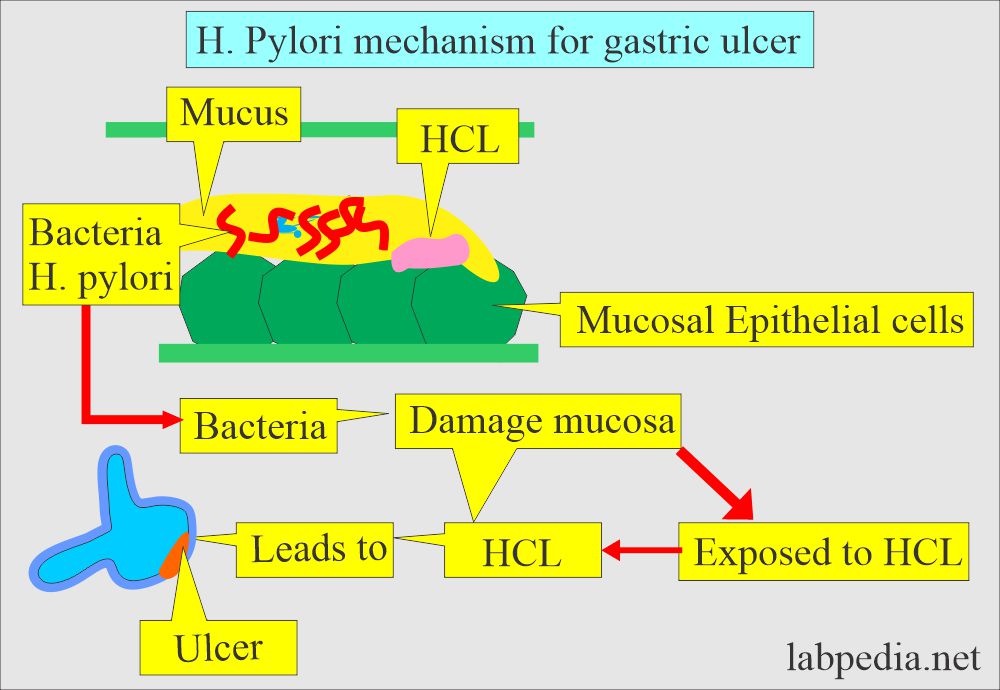
What is the mechanism of damage to gastric mucosa by H. pylori?
- H. pylori inhabit the mucus of the gastric mucosa.
- These bacteria are found in the mucus of the gastric mucosa.
- These bacteria cause damage to the mucosa, where HCL leads to ulcer formation.
- H. pylori is also considered carcinogenic (class 1 gastric carcinogen).
- The colonies of H.Pylori are seen in:
- Duodenal ulcer = 90% to 95% .
- Gastric ulcer = 60% to 70%.
- Gastric cancers = 20% to 25%.
- Around 10% of the young, healthy people <30 years of age have the colonies of H. pylori.
- Gastric colonization by H. pylori increases with age.
- Most of these patients remain asymptomatic and never develop an ulcer.
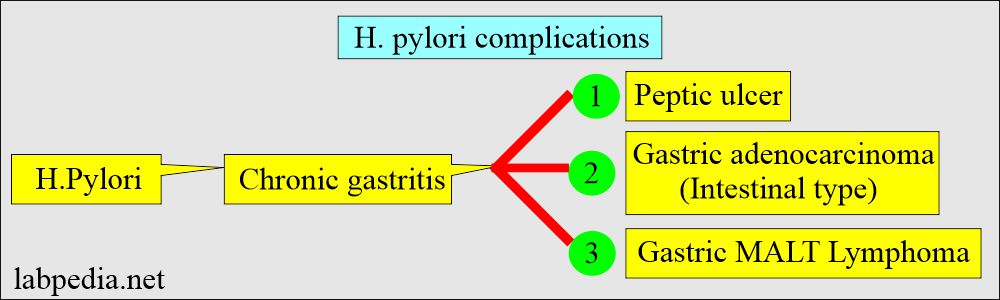
What are the complications of H. pylori infection?
- There is a risk of H. pylori infection leading to:
- Gastric ulcer.
- Chronic gastritis.
- Duodenal Ulcer.
- Ulcerative esophagitis.
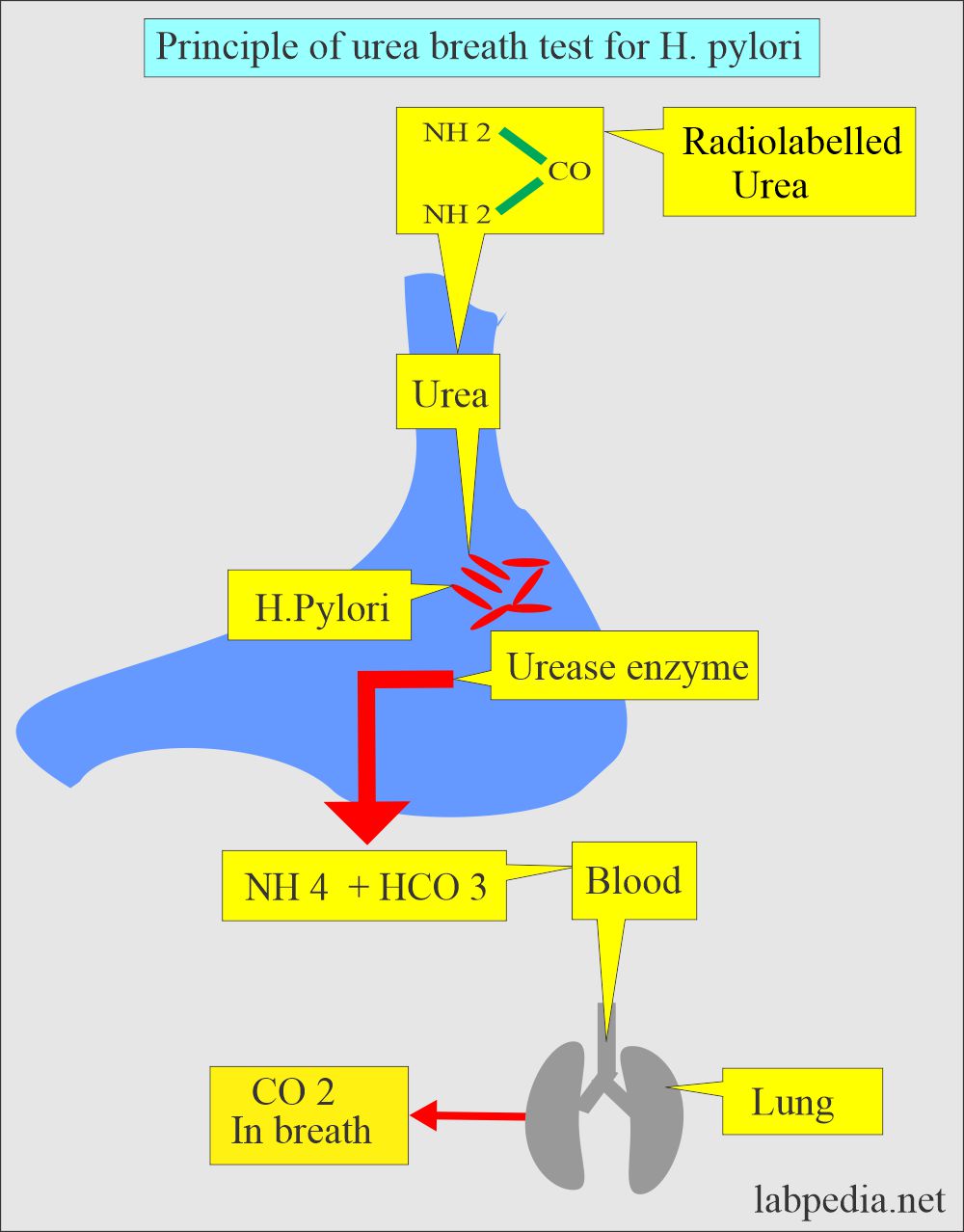
What is the principle of the Urea Breath test for H. pylori?
- H. pylori converts urea into CO2 due to the presence of the urease enzyme.
- Urea breath test uses oral 14C or 13C- labeled urea.
- Radio-labeled CO2 was measured in breath before and after ingestion of labeled urea carbon in the presence of urease enzyme.
- Give orally radiolabelled urea (containing nonradioactive isotope 13C).
- In gastric mucosa, if H. Pylori present then it will convert urea into CO2 (13C).
- This CO2 (13C) label passes through blood and goes to the lungs.
- Now measure CO2 (13C) by:
- Gas chromatography.
- Mass spectrometer.
How will you perform Two breath samples?
- First, take a sample before giving the isotope-labeled (13C) urea.
- Second, after 30 minutes of a dose of isotope-labeled (13C) urea.
- Specificity and sensitivity are 95%, and the test is cheaper to diagnose than invasive procedures.
What are the normal values of the urea breath test for H. pylori?
Breath test (Source 4)
- <50 DPM for H. pylori.
- 50 to 199 DPM for H. pylori
- >200 DPM positive for H. pylori.
- < 3 %.
- A positive test means H. Pylori infection.
- Source 1
Serology:
- IgG and IgA antibodies are present in 81% to 100% of the patients with gastritis.
- However, only 25% of the patients had no histological evidence of H. pylori.
- The testing of IgM is not helpful.
What are the possibilities of a False-negative test?
- You can get a false negative test if the patient uses antacids within a week before the test.
- The patient should not use any antibiotics and bismuth for one month.
- No proton pump inhibitors and sucralfate for two weeks before the test.
- The patient should be at rest during the collection of breath.
How will you diagnose the H. pylori infection?
The following tests can diagnose it:
- Positive breath test.
- Presence of specific antibody. Sensitivity is 94%, and specificity is 78%.
- Positive culture.
- A positive biopsy is done by endoscopy. Sensitivity is 93%, and specificity is 99%.
- The stool is examined for the H. pylori antigen.
Questions and answers:
Question 1: What are the complications of H. pylori?
Question 2: What is the principle of the urea breath test?