Types of Blood Samples, Criteria for rejection of the blood sample, Color coding of the blood sample tubes
Blood Samples
What are the types of Blood samples?
- The blood samples from the patients are of various types according to the types of blood tests.
- These blood sample timings are also critical, and some of the tests may need a fasting sample, while some tests may be done on random samples.
How will you discuss the Venous blood sample?
- This is the easiest way to collect the blood sample.
- It is free of complications.
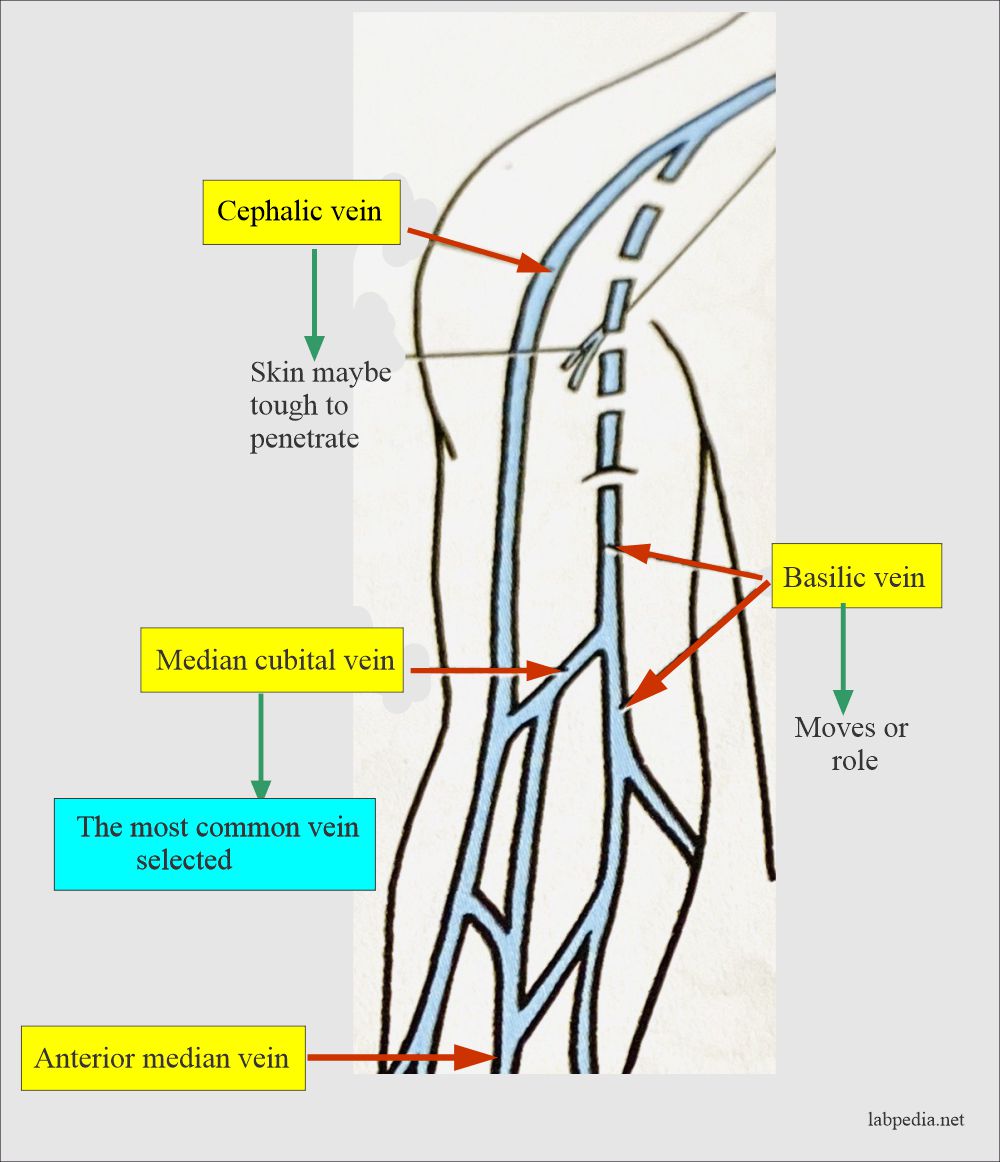
- Blood is taken from the superficial veins.
- The commonest site is the antecubital fossa because of the presence of the basilic vein, cephalic vein, and median cubital veins are the commonest veins.
- Veins of the wrist or hand may be used.
- Another site is the femoral vein.
How will you discuss the Arterial blood sample?
- Arterial blood measures arterial blood gases like oxygen, CO2, and pH.
- Arterial puncture is more difficult than the venous sample.
- The Brachial and radial arteries are often used; the femoral artery is usually avoided because of bleeding.
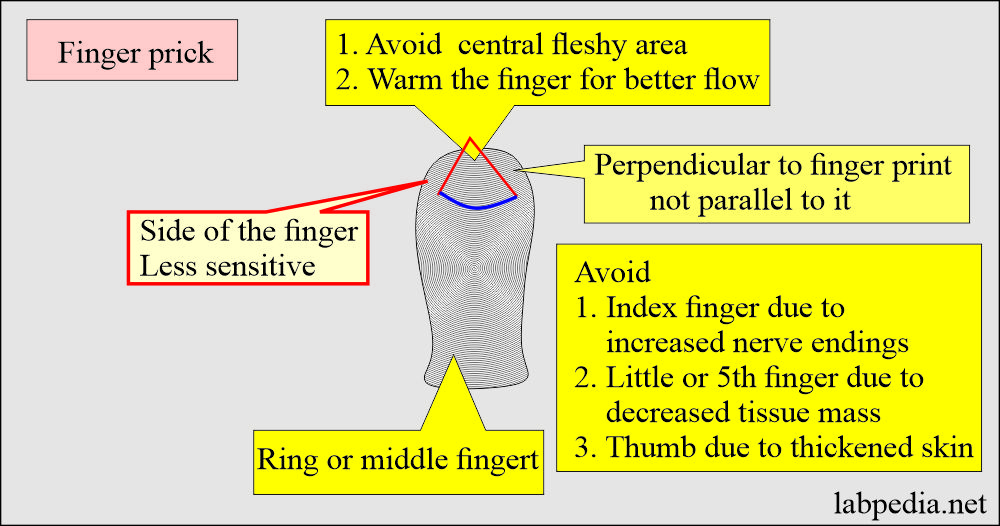
How will you discuss the Capillary blood sample?
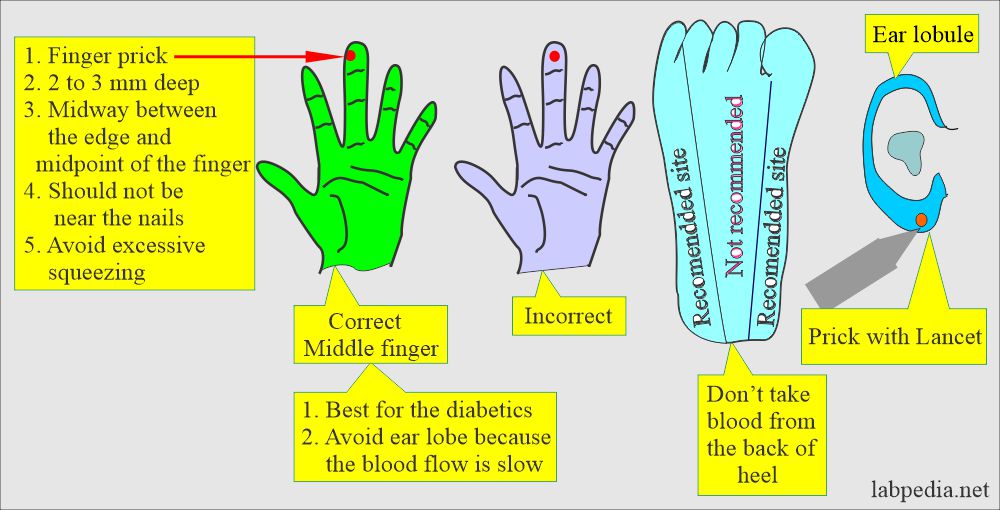
- It is mostly used in the pediatric patient group where there is no need for a large amount of blood.
- The common sites are the fingertips, heel, and ear lobes. The heel is most commonly used in infants.
What are the Criteria for the rejection of the blood samples?
- Blood samples are not labeled or not properly labeled.
- Insufficient blood quantity.
- Blood sample showing hemolysis.
- A wrong collection tube is used.
- Insufficient quantity of anticoagulants.
- Improper transport of the sample.
What are the Blood sample’s commercially color-coded tubes?
| Stopper tube | Additives | Outcome of additive | Purpose of use | Test tubes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Na+polyanetholesulfate |
|
Blood culture | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Potassium determination | |
|
|
|
Westgreen ESR determination |
How will you summarize color-coded blood collection tubes?
- Red top tube = No additives for chemistry tests.
- Blue top = Coagulation studies.
- Green top = For general purpose, blood gases, chemistry.
- Lavender top = For CBC and hematology.
- Gray top = For chemistry and glucose.
- Yellow top = For blood culture.
What is the difference between plasma and Red blood cells?
| Contents | Plasma | Red Blood Cells |
| Glucose mg/dL | 90 | 74 |
| Uric acid | 4.6 | 2.5 |
| Nonprotein nitrogen mg/dL | 8.0 | 40 |
| Cholesterol mg/dL | 194 | 139 |
| K+ meq/L | 4.4 | 100 |
| Na+ meq/L | 140 | 16 |
| Ca2+ meq/L | 5.0 | 0.5 |
| Cl– meq/L | 104 | 52 |
| HCO3– mmol/L | 26 | 19 |
| LDH units | 360 | 58000 |
| Transaminase | 25 | 500 |
Questions and answers:
Question 1: What is the role of a gold-colored test tube?
Question 2: What colored tube will you use for chemistry, serology, and blood banking?

Good
Thanks
Marvellous
Thanks.