Tumor Markers:- Part 8 – Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP)
Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP)
What sample is needed for Alpha-Fetoprotein (AFP)?
- The patient’s serum is required.
- Can take a random sample, and no fasting is needed.
What are the Indications for Alpha-Fetoprotein (AFP)?
- For the diagnosis of liver cell carcinoma.
- Patients with chronic active hepatitis.
- Patients with cirrhosis and positive serology (HBV and HCV) should be tested with AFP and ultrasound abdomen.
- AFP is a tumor marker for yolk sac tumors.
- AFP raised in hepatoid gastric carcinoma.
How will you define Alpha-Fetoprotein (AFP)?
- In 1960, the discovery of oncofetal antigens AFP and CEA started the development of tumor markers.
- Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) was found in the serum of mice with liver cell carcinoma and later in the sera of humans with liver cell carcinoma.
- Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) is a tumor marker for liver and germ cell (non-seminoma) carcinoma.
- This is a glycoprotein. This consists of a single polypeptide chain and has a 4% carbohydrate.
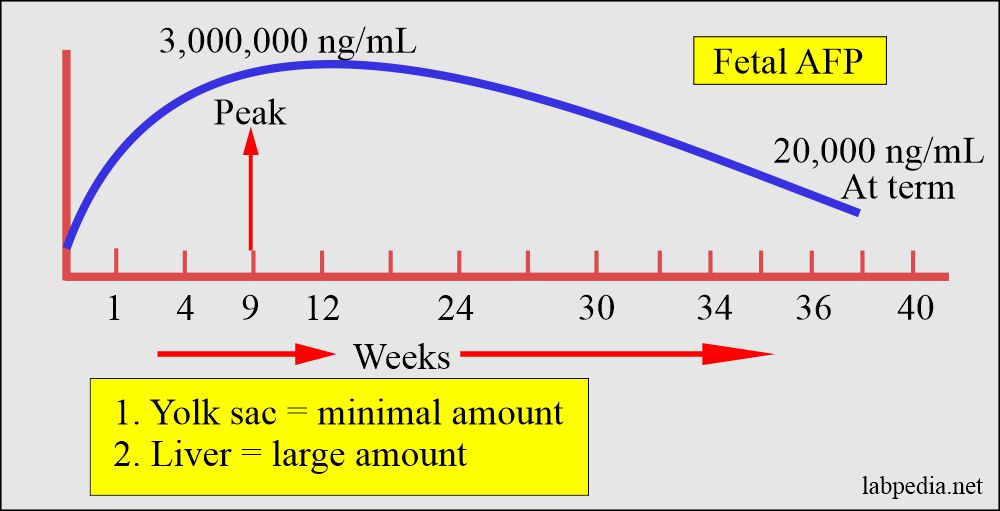
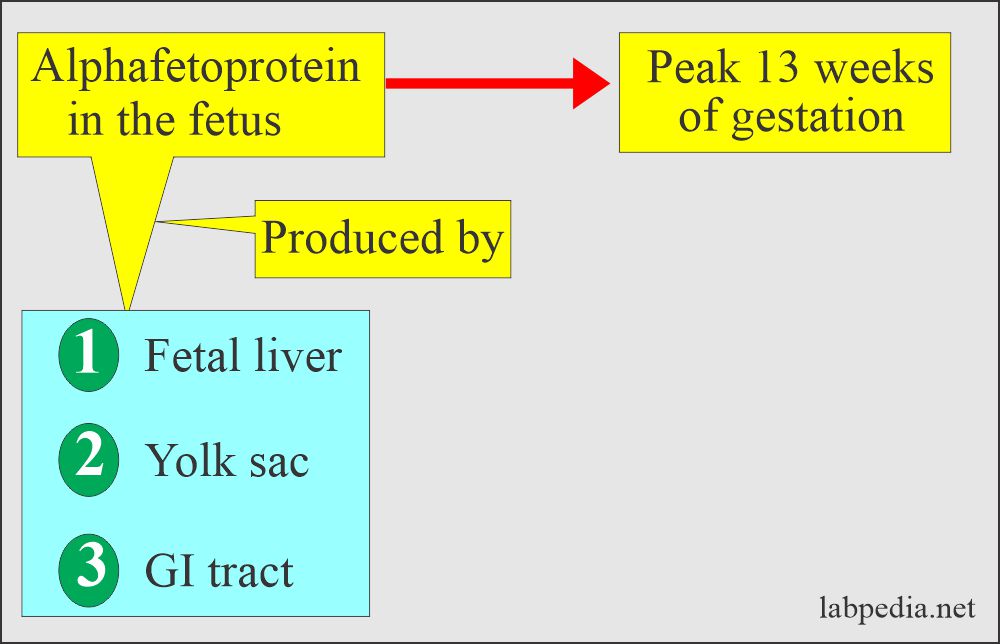
- The yolk sac produces this in small amounts, and the liver produces an abundant amount in the fetus.
- AFP is produced by:
- Yolk sac.
- Then, by the fetal liver.
- It peaks at 10 to 13 weeks of gestation, then declines to <100 µg/L by term. By the age of 2 years, reaches adult levels <5 µg/L.
- It is normal after about 18 months of birth.
- It is close to albumin, genetically and structurally.
- The gene coding for both is chromosome 4q.
- Its concentration is 10% of that of albumin.
What is the structure of Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP)?
- The fetal liver produces an alpha-1 globulin called alpha-fetoprotein. It becomes the dominant fetal serum protein in the first trimester.
- It reaches a peak at 12 weeks, then declines to 1% of the peak at birth.
- By the age of 1 year, there is a marked decrease.
- Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) is a glycoprotein with a molecular weight of 70 kDa.
- It has a single polypeptide chain and around 5% of carbohydrates.
- Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) is synthesized in large quantities by the fetal yolk sac and liver during embryonic development.
- It is the major protein in fetal circulation.
- Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) is genetically and structurally identical to albumin.
What are the functions of the Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP)?
- AFP has increased in pregnancy, usually not >100 ng/mL.
- Its main role is to bind and transport substances that are not water-soluble, such as steroid hormones, lipids, vitamins, and bilirubin.
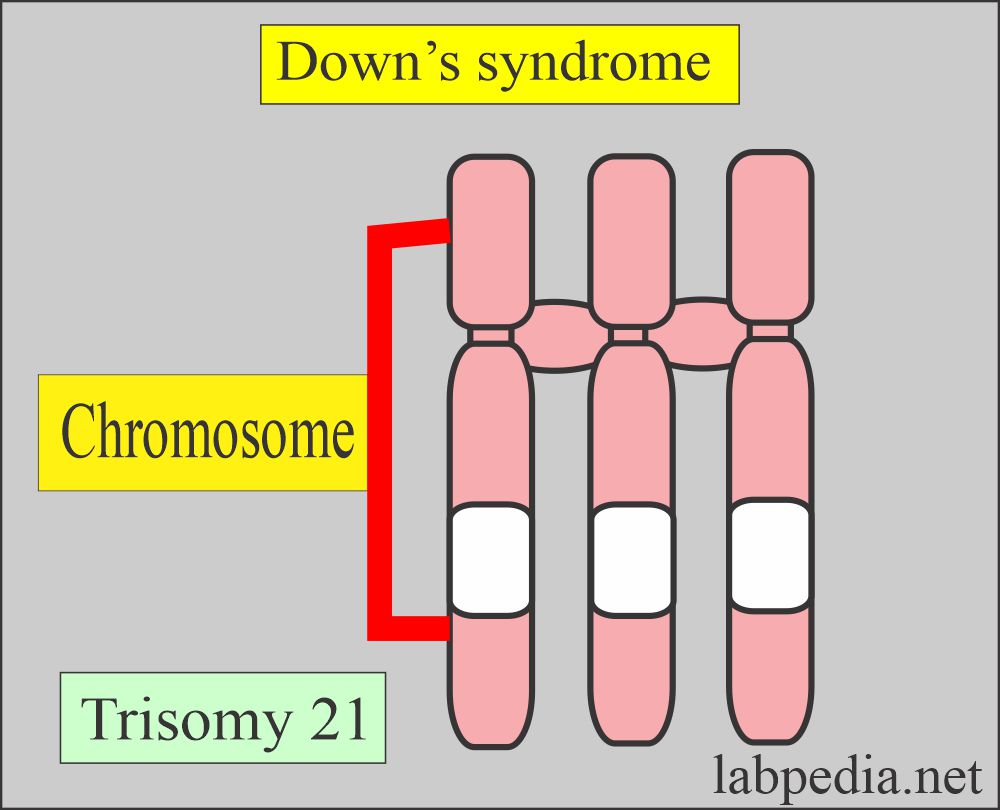
- Maternal serum AFP is lower than expected in Down’s syndrome.
- AFP detects ≤25% of the cases.
- Ultrasound is used to calculate the gestational stage, which is important to calculate the risk of Down’s syndrome.
- AFP is 25% to 30% lower in Down’s syndrome.
- Down syndrome = Trisomy 21 and Mongolism. It is the most common autosomal trisomy.
Maternal serum AFP is raised or higher in the neural tube defect:
- A level> 1000 µg/L indicate malignancy:
- At this level, 50% of liver cell carcinomas are diagnosed.
- It is ideal for diagnosing a liver tumor below the size of 5 cm.
- To find these small tumors, the cut-off value has to be set at a lower level between 200 to 1000 µg/L.
- In healthy individuals, it is 10 µg/L.
What is the normal Alpha-Fetoprotein (AFP)?
- Adult = <40 ng/mL (<40 µg/L)
- Child <1 year = <30 ng/mL
- Mid-trimester = 10 to 15 ng/mL.
Another source
- 0 to 15 ng/mL
What is the role of Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) as a tumor marker?
What are the values in Liver cell carcinoma?
- AFP is raised in 80% of liver cell carcinoma.
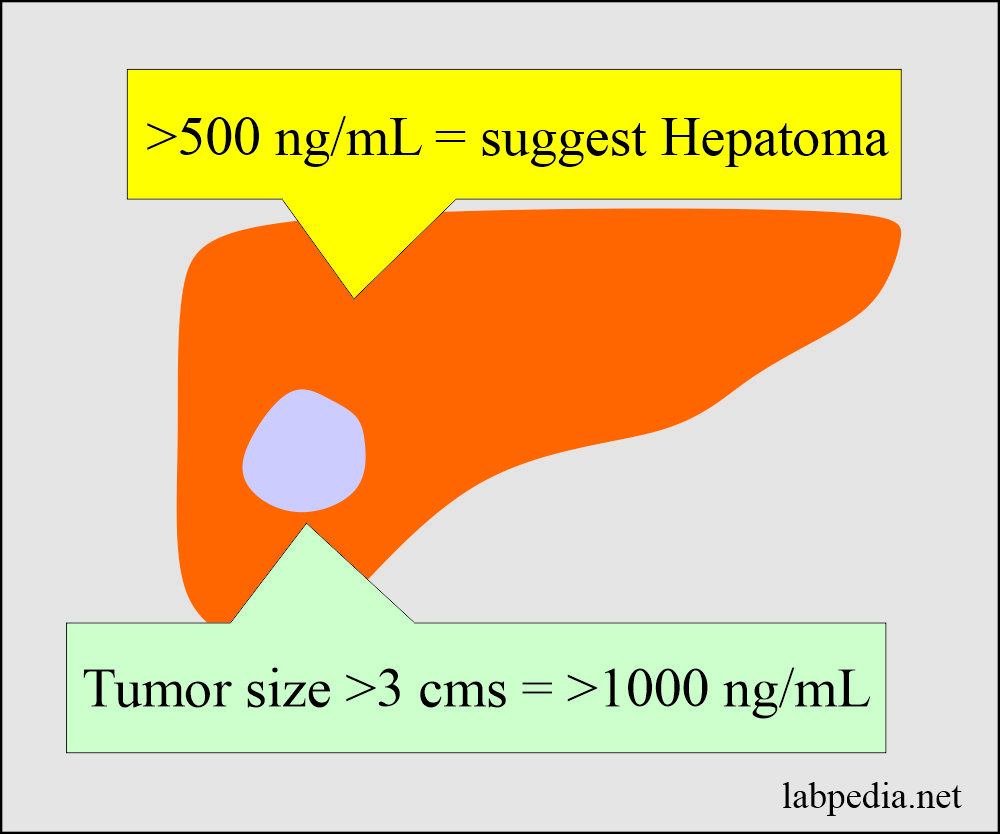
- >500 ng/mL is diagnostic of liver cell carcinoma.
- AFP may be raised for 18 months before the S/S appears.
- AFP is a sensitive indicator of recurrence.
- AFP >1000 ng/mL in 50% of the cases indicates tumor size >3 cm in diameter.
- In 90% of the cases, AFP >200 ng/mL, and 70% have a concentration of AFP >400 ng/mL.
- In 90% of cases of liver cell carcinoma, Alpha-Fetoprotein (AFP) is raised >200 ng/mL.
- In 70% of the cases, liver cell carcinoma Alpha-Fetoprotein (AFP) is raised >400 ng/mL.
- In benign liver diseases, alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) rarely is >400 ng/mL.
- This is more likely raised in immature carcinoma than the mature type of carcinoma.
- An initial high level indicates a poor prognosis.
- Failure to come to normal indicates a problem with surgery where there is incomplete resection or metastasis.
- The postoperative decrease followed by an increase in the AFP indicates recurrence.
- If there is a short doubling in the AFP value, suggest metastasis at the time of surgery.
- AFP is useful for liver cell carcinoma:
- Diagnosing.
- Prognosis.
- Monitor therapy.
What is the role of AFP as a tumor marker for the Germ cell tumor (nonseminomatous tumor)?
- Yolk sac tumors lead to an increase in AFP, which correlates with the tumor prognosis; e.g., >1000 ng/mL is associated with a poor prognosis.
- Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) is raised in Embryonic cell carcinoma in 27% of the cases.
- Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) is raised in Malignant teratoma in 60% of the cases.
- Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) is increased in Testicular teratocarcinoma in 75% of the cases.
- Choriocarcinoma element is seen in seminoma, yolk sac, teratoma, and embryonal cell carcinoma.
- Pancreatic carcinoma AFP is positive in 23% of the cases.
- Gastric carcinoma is AFP 18% positive.
- Bronchogenic carcinoma is 7% positive.
- Colon carcinoma is 5% positive.
What are the causes of increased AFP (Maternal AFP)?
- Multiple pregnancy.
- Race (10% to 15%), higher level in blacks.
- Open neural tube defects like:
- Open spina bifida.
- Encephalocele.
- Anencephaly.
- Myelocele.
- Hydrops fetalis.
- Intrauterine death.
- Feto-metrnal haemorrage.
- Cystic hygroma.
- Renal disorders like polycystic kidneys, renal agenesis, and urethral obstruction.
- Sacrococcygeal sarcoma.
- Tetralogy of Fallot.
- Turner syndrome.
- Oligohydramnios.
- Placental infarction, thrombosis, inflammation, very large placenta, and cystic changes.
- Cystic hygroma.
- Oloigohydroamnios.
What are the causes of decreased AFP?
- Down’s syndrome.
- Long-standing death of the fetus.
- Hydatidiform mole.
- Choriocarcinoma.
- Increased maternal weight.
- Females with diabetes mellitus.
- Pseudopregnancy and no pregnancy.
Questions and answers:
Question 1: What is the level of Alpha-Fetoprotein (AFP) for the diagnosis of liver cell carcinoma?
Question 2: What is the relation of Alpha-Fetoprotein (AFP) to albumin?
- Note: In some books on the same page, the values are given in ng/mL and ng/dL. It is difficult for me to decide which one I can follow.