Tumor Markers:- Part 5 – M-band, NMP 22, BTA, Oncogenes (Genetic Markers)
Tumor Markers
- Tumor markers in the diagnosis and monitoring of tumors are some more examples.
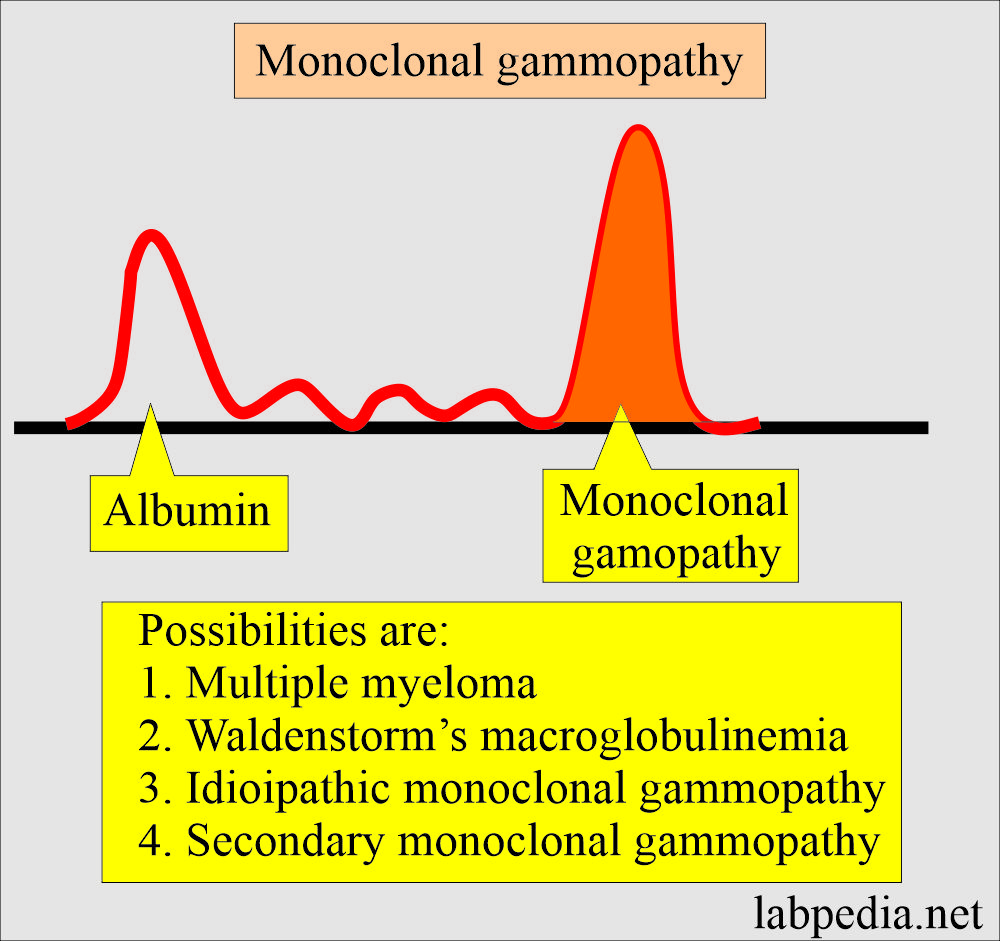
M-Band of Multiple Myeloma
What sample is needed for the M-Band of Multiple myeloma?
- Venous blood is needed to prepare the serum for electrophoresis.
- The urine sample is needed for Bence-Jones proteinuria.
How will you define M-band for Multiple myeloma?
- The monoclonal immunoglobulin band is a tumor marker for diagnosing Multiple myeloma.
What are the Multiple Myeloma components?
- M-band or monoclonal paraprotein is used to diagnose multiple myeloma.
- Myeloma protein is an abnormal immunoglobulin fragment, such as an immunoglobulin light chain, that is produced in excess by an abnormal monoclonal proliferation of plasma cells, typically in multiple myeloma.
- Other terms used are M-protein, M-component, M-spike, or paraprotein.
- This M-protein is found in serum and urine electrophoresis.
- >90% of patients with Multiple myelomas show M-band in electrophoresis.
- The M band (protein) is a paraprotein visible on electrophoresis. It gives a tall peak on a densitometer, which is also called an M-spike.
- M-band in the myeloma patients on electrophoresis, when total protein is 8.8 g/dL.
What is Bence-Jones proteinuria?
- It is a protein that is a light chain excreted in the urine of Multiple myeloma cases.
- Decreasing the level of Bence-Jones protein in the treatment shows a good response to treatment.
What is the pattern of serum electrophoresis?
| Protein fractions | Result in % | The result of myeloma patient g/dL | Normal range g/dL |
| Albumin | 35.2 | 3.1 | 3.5 to 5.2 |
| α1 – globulin | 3.4 | 0.3 | 0.2 to 0.4 |
| α2 – globulin | 6.8 | 0.6 | 0.4 to 0.8 |
| β – globulin | 8.0 | 0.7 | 0.5 to 1.1 |
| γ – globulin (M-band) | 46.6 | 4.1 | 0.6 to 1.3 |
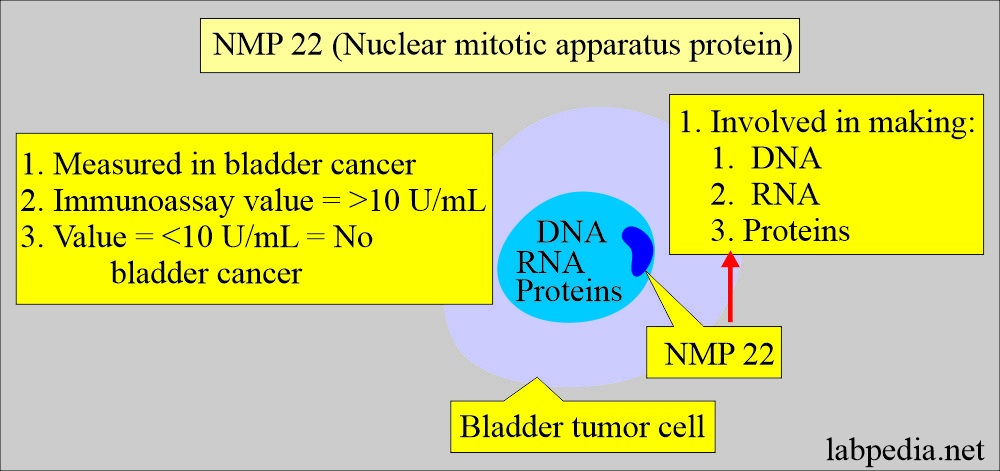
NMP 22 (Nuclear matrix apparatus protein 22)
How will you define NMP 22?
- Other names are Bladder cancer marker or bladder tumor antigen.
- NMP 22 detects a nuclear protein called NuMA (Nuclear mitotic apparatus) released from the nuclei of tumor cells when they die.
- A protein is found inside the nucleus of a cell. It is involved in making DNA, RNA, and proteins and helps control how certain genes are expressed in a cell.
- NMP 22 may be found in higher than normal amounts in the urine of patients with some types of cancer, e.g., bladder cancer.
- Measuring the amount of NMP 22 in the urine may help diagnose cancer or determine how well treatment is working. NMP 22 is a type of tumor marker, also called nuclear matrix protein 22.
- This is recommended for the follow-up of Transitional cell carcinoma of the urinary tract.
- This is a cheaper marker for the recurrence of bladder cancer.
- This is elevated in bladder cancer.
- NMP22 is a good screening test for a patient who is at greater risk of developing bladder cancer.
- NMP22 may be raised in the tumor involving the ureter and renal pelvis.
What is the mechanism of NMP 22 formation?
- Nuclear matrix proteins make the internal structure of the nucleus.
- This bladder tumor antigen is a factor H-related protein produced by the bladder tumor.
- NMP 22 is a nuclear matrix protein deposited in the urine during the apoptosis of bladder cancer cells.
- Their role is the regulation of DNA replication and synthesis of RNA.
- This protein is excreted in the urine.
- Normally, no or very little amount of this protein is found in the urine.
How will you interpret NMP 22?
- NMP 22 is advised in patients who have urinary bladder cancer.
- It is quite sensitive but nonspecific.
- When NMP 22 is performed after 1 to 6 weeks of the urinary bladder tumor surgery, it is raised, indicating recurrence of the tumor.
- NMP 22 results are normal in 80% of the patients with no disease.
- Infection may give false positive results due to the inflammatory cells (WBCs). WBCs are the source of false positive results.
How will you perform NMP 22 in the Urine sample?
- This protein is unstable in the urine. If urine is not stabilized immediately, they can get a false result.
What is the normal NMP22?
-
- <10 units/mL.
Bladder tumor-associated Antigen (BTA)
- BTA are high molecular weight polypeptides.
- BTA presence in the urine may be due to the following:
- Involvement of the basement membrane in the tumor. OR
- Produced by the cancer. OR
- Combination of both.
- BTA represents 70% sensitivity and 70% specificity.
- BTA test was positive in 40% of the cases on cystoscopy, proving bladder tumor.
- While cytology gives only 17% positivity.
- BTA is a marker of a bladder tumor.
- But BTA is not a good screening test because this may be raised in other conditions like:
- Recent urologic surgery.
- Calculi.
- Urinary tract infection.
- FDA approved only for the recurrence of the bladder tumor along with cystoscopy.
What is the normal BTA?
Source 2:
-
- <14 units/mL
Genetic markers
How will you define genetic markers?
- Genetic abnormalities, also known as genetic disorders, are health problems caused by changes to genes or chromosomes.
- The genetic disorder may be:
- Genetic when occurring during fetal life or not seen at birth.
- Familial when present in the extended family members or sporadic.
- It is considered that multiple genetic alterations may lead to uncontrolled proliferation of the cells and result in cancers.
- This gene abnormality also gives rise to metastases.
- Evaluation of chromosomal changes may help to diagnose cancers.
- c-erb B-2 is also called an HER-2/neu gene.
- Genetic tests are available for >940 diseases, of which 400 are only research tests.
What are the indications for genetic testing?
- It is advised for the diagnosis of carrier identification, such as sickle cell trait and Tay-Sach disease.
- It is advised for prenatal diagnosis of an abnormality like Down’s syndrome.
- It is advised for screening of newborns for congenital hypothyroidism and PKU.
What are the types of genes?
- Oncogene :
- These are the cell activation genes. Promote tumor formation.
- Suppressor gene:
- These genes are involved in recognizing and repairing damaged DNA.
What are the possibilities of the genetic abnormalities?
- Some of the genetic abnormalities involve chromosomes.
- Chromosomal abnormalities may be autosomal and not involving sex chromosomes.
- Others are sex-linked, and these are inherited through the sex chromosomes.
- What are the possible genetic abnormalities?
- Total or partial deletion of chromosomes.
- The presence of an extra chromosome is when an extra chromosome attaches to a pair of chromosomes. (Trisomy).
- Translocation is when a portion of a chromosome breaks off and attaches to another chromosome.
- Gene abnormality, which is not seen by routine chromosomal analysis. These are diagnosed by nucleic acid probes.
- Other genetic abnormalities are due to a defective or missing enzyme.
- These abnormalities require chromosomal analysis.
What are the types of Oncogenes?
| Oncogene | Type of cancer |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
How will you discuss the Suppressor gene?
- A study shows that normal cells contain a gene that suppresses the expression of malignancy.
- The loss of the chromosome 5 gene leads to increased cell growth.
- Metastasis occurs with the loss of genes.
- Detecting a mutation in the tumor suppressor gene is important for diagnosing and prognosing tumors.
- This mutation of the suppressor gene also helps to predict susceptibility when the mutation is carried in the germline, e.g., breast cancer genes BRCA1 and BRCA2.
What are the types of Suppressor genes?
| Suppressor gene | Tumor |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
What are the examples of tumor markers?
| Test | Marker of tumor |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
What is the significance of various enzymes in different tumors?
| Enzymes | Organs involved in tumor |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Questions and answers:
Question 1: What is BTA?
Question 2: What are the oncogene?
- Please see in Tumor marker parts 1, 2, and 3.