Tumor Markers:- Part 6 – BRCA1, BRCA2, Significance in Breast Cancer
Tumor Markers
BRCA1 and BRCA2
How will you define BRCA1 and BRCA2?
- BRCA stands for the breast cancer gene (BReast CAncer gene).
- The most important dominant genes are breast cancer susceptibility genes BRCA1 and BRCA2.
- What is the location of the BRCA gene?
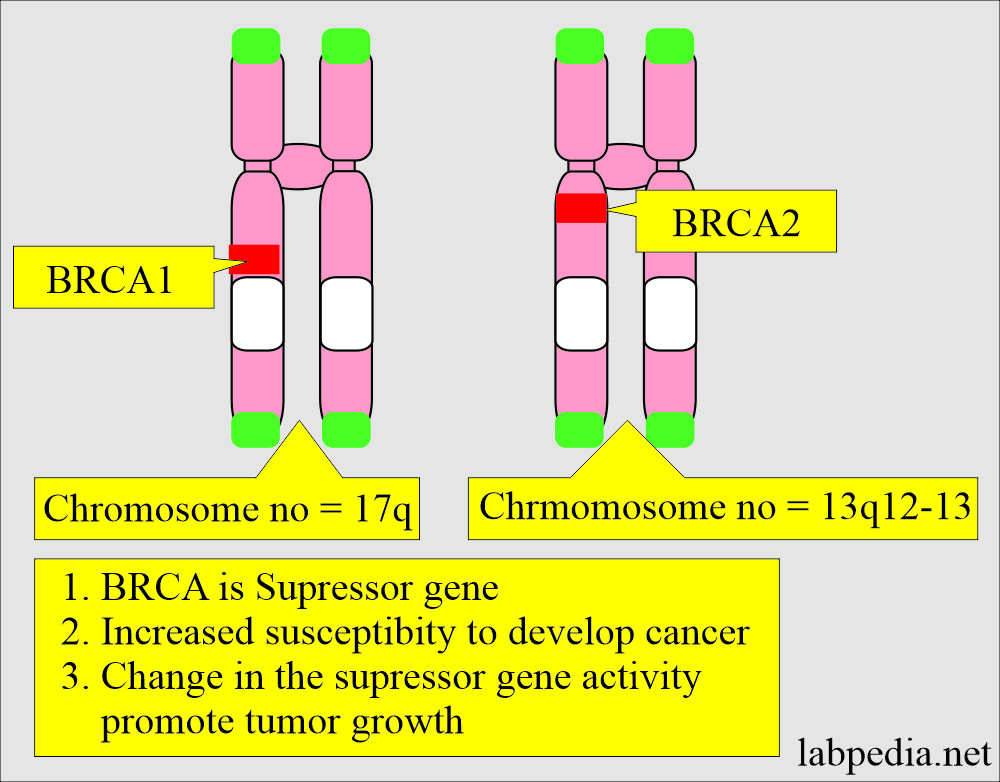
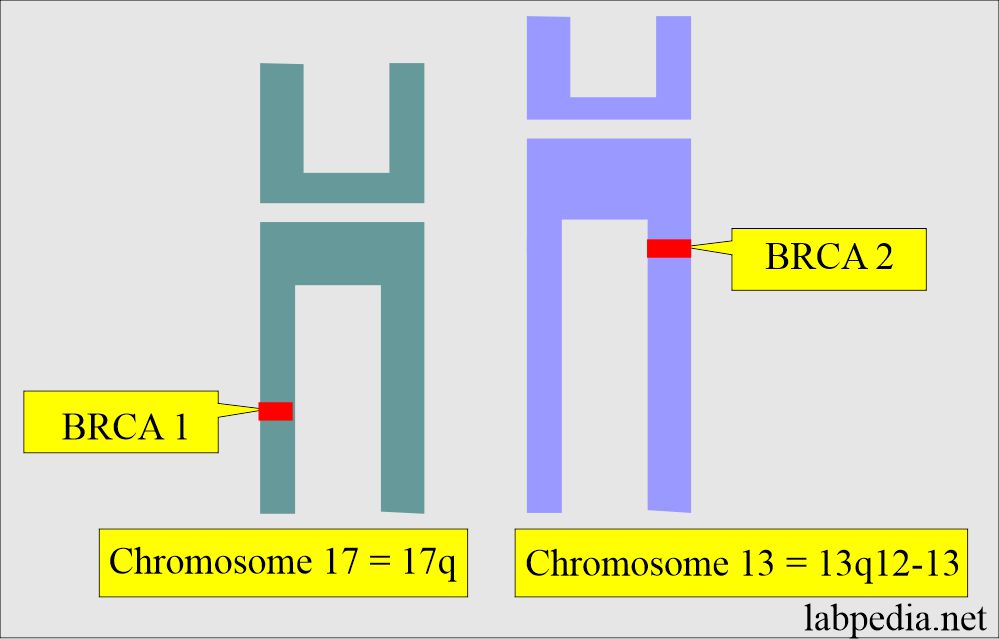
- The BRCA1 gene is present on chromosome 17q. It is a breast cancer type 1 susceptibility protein.
- The BRCA2 gene is present on chromosome 13q12-13.
- BRCA1 and BRCA2 are human genes that produce tumor suppressor proteins.
- These proteins help repair damaged DNA, ensuring the stability of a cell’s genetic material.
- Mutations in these genes can lead to a higher risk of developing certain cancers, particularly breast and ovarian cancer.
How is the inheritance of the BRCA gene?
- Breast cancer patients have an inherited predisposition to develop breast and ovarian cancer that is inherited as an autosomal dominant trait.
- In these patients, two genetic loci have been identified and labeled as BRCA1 and BRCA2.
- BRCA1 encodes 1863 amino acids protein that may act as a transcription factor.
- Finding mutated BRCA1 and BRCAS2 genes in somatic cells helps to find the females who carry this mutated gene.
- It is documented that ladies carrying one of these mutated genes are prone to developing breast or ovarian cancer.
- BRCA1 gene mutation ladies have an 85% chance of developing breast cancer and a 45% chance of developing ovarian cancer by the age of 65 years.
What is the role of the BRCA gene as a tumor marker?
- BRCA1 and BRCA2 are suppressor genes.
- The BRCA gene indicates an increased susceptibility to the development of breast cancer.
- In the case of a lady having breast cancer on one side, if she has a BRCA gene mutation-positive, then have a 65% chance of developing breast cancer on the other side, compared to the BRCA gene negative, where only 15% develop cancer.
- The BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations show 50% and 30%, respectively, breast cancer inheritance.
- The BRCA1 mutation is estimated to have a 20 times greater risk by the age of 40 years compared to the general population.
- Lifetime risk is 60% to 85%.
- The White population is more prone to the BRCA1 mutation, which affects 3.3% of women.
- BRCA1 mutation is less common in the black population.
- The ladies who show BRCA1 gene mutation are at greater risk of developing ovarian cancer,
- The ladies <2% develop ovarian cancer by the age of 70 years when there is no BRCA gene mutation.
- However, in women with BRCA gene mutation, 44% develop ovarian cancer by the same age of 70 years.
- The BRCA gene mutation also increases susceptibility to ovarian cancer.
What is the mechanism of the BRCA gene?
- These genes encode tumor suppressor proteins.
- So any change or mutation in the gene may inhibit or retard its suppressor function leading to uncontrolled cell proliferation.
- BRCA1 gene mutation also has increased the incidence of ovarian cancer.
- Women with BRCA1 gene mutation develop:
- Ovarian cancer in 44% of the ladies by the age of 85 years.
- Breast cancer in 85% of the ladies by the age of 85 years.
- Women with BRCA 2 have a 20% chance of developing breast cancer.
- Another source: Women by the age of 70 years, the chances for breast cancer are 45%.
- Another source:
- By the age of 70 years:
- In 100 women without BRCA 1/2, around 7 women will get breast cancer.
- Of 100 women with positive BRCA 1/2, around 45 to 65 years of age will get breast cancer.
- By the age of 70 years:
How will you screen the ladies with BRCA gene mutation?
- Ladies need transvaginal ultrasounds at 6 to 12 months.
- The CA-125 blood test should be done every 6 to 12 months.
- Some BRCA 1/2 positive women never develop breast cancer.
How will you Summarize BRCA antigen?
BRCA1
- This is called the breast cancer gene.
- This gene is located on chromosome 17q.
- BRCA1 encodes for a protein that consists of 1863 amino acids.
- Breast cancer with BRCA1 has an exceptionally high proliferation rate.
- Breast cancer with BRCA1 has overexpression of p53.
- Mutation of the BRCA1 gene, an individual has an 85 % risk of developing breast cancer and 45 % of ovarian cancer by the age of 85 years.
BRCA2
- This is called the breast cancer gene.
- BRCA2 is located on chromosome 13q12-13.
- BRCA2 also has a higher proliferation than BRCA-negative cases.
- Mutation of BRCA1 and BRCA2 was found in individuals with a family history of breast cancer.
- Mutation in one of these genes carrying women may develop breast cancer or ovarian cancer.
| Parameters | BRCA1 | BRCA2 |
| Location | Chromosome 17q | Chromosome 13q12-13 |
| Mutation | Changes in BRCA1 lead to breast cancer | Less chances for breast cancer (6%) |
| ER/PR and Her-2 | Negative | Positive |
| Treatment response |
|
More responsive to hormone therapy |
| Detection of BRCA gene mutation |
|
The lifetime risk for breast cancer is 40% to 70% |
| Risk for ovarian tumor | Ovarian tumor risk is 40% to 60% | Ovarian tumor risk is <10% to 20% |
| Other cancers | Low risk of prostate | High risk of male breast, prostate, and pancreas |
Questions and answers:
Question 1: What should be done if the female is positive for BRCA1 and 2 gene mutation?
Question 2: Which mutated gene is worse BRCA1 or BRCA2?