Transferrin, Acute Phase Protein
Transferrin, Acute-Phase Protein
What sample is needed for Transferrin?
- The patient’s blood is needed to prepare serum.
- Try to analyze the fresh sample.
- Can store at 4 °C for <72 hours.
- When stored at -20 °C, it is stable for 6 months.
What are the precautions for Transferrin?
- Avoid hemolysis because the RBC contains iron.
- Avoid lipemic serum.
What are the indications for Transferrin?
- Differential diagnosis of anemia.
- Monitoring of treatment of iron deficiency anemia.
- As acute phase protein.
What is the role of Transferrin as an acute-phase protein?
How will you define transferrin as an acute-phase protein?
- During infections or inflammation, transferrin is considered a negative acute-phase protein.
- Its concentration changes in the blood in response to the body’s immune status.
What is the mechanism of transferrin as an acute-phase protein?
- There is the release of inflammatory cytokines:
- Interleukin-6.
- Tumor necrosis factor-alpha.
- It leads to the activation and enhanced functions of the immune cells.
- Stimulate more synthesis of transferrin.
- Iron is needed for the host defense.
- It can bind to bacteria and viruses and prevent their growth.
- It helps in clearance by the immune system.
What is the role of Transferrin as an acute-phase protein?
- This is decreased in acute inflammation and raised in chronic conditions.
- This acts as an acute-phase protein.
- Its high level relates to the ability of the body to fight against the infection.
Pathophysiology of Transferrin
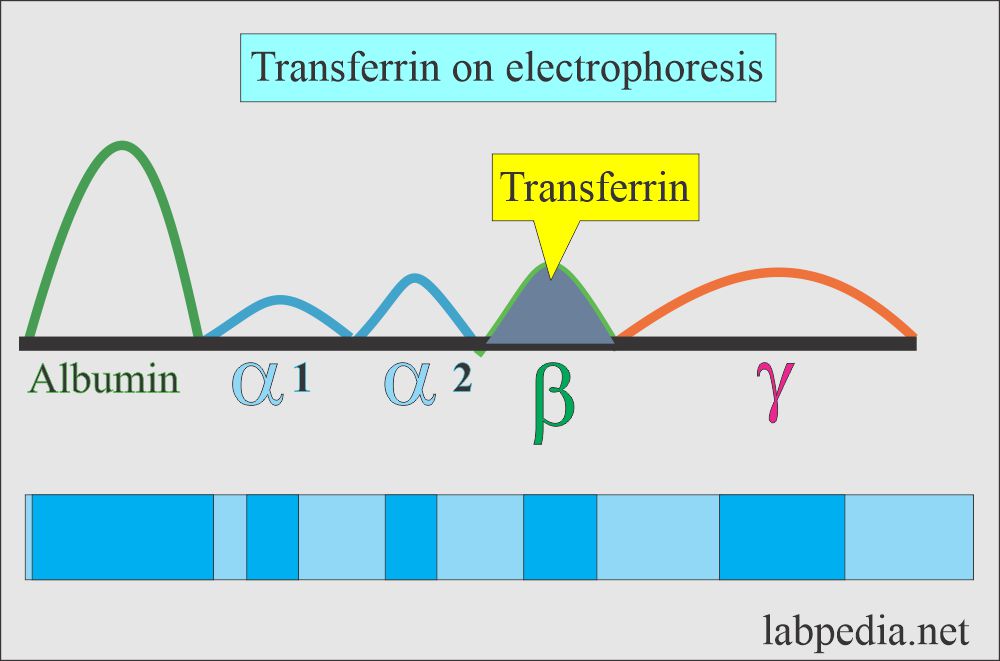
- Transferrin is a major beta-globulin (glycoprotein). This is an iron-carrying protein.
- This is also called siderophilin.
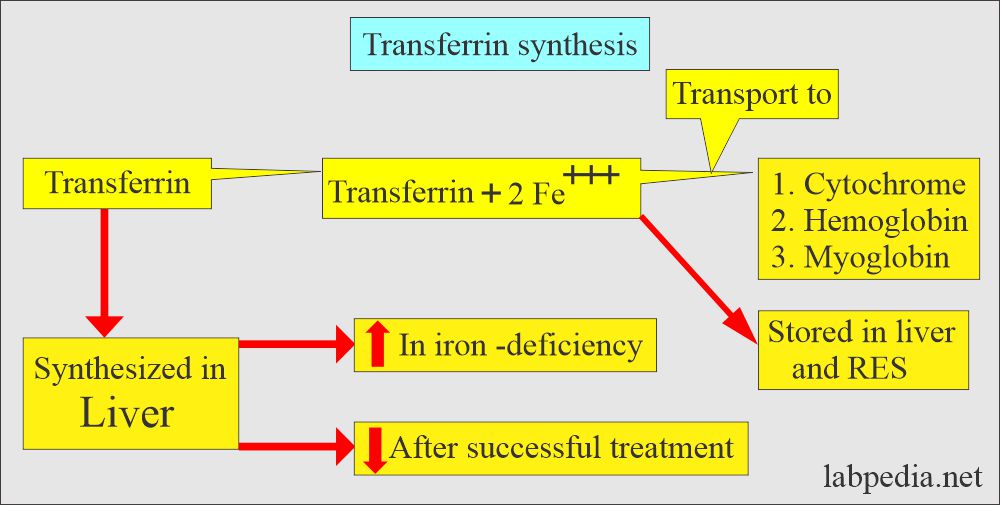
- The transferrin transports the Ferric ion (Fe+++); normally, there is 20% to 30% saturation, increasing in iron-deficiency anemia.
- One molecule of transferrin binds two ions of iron.
- Ferrous ions bind more rapidly than ferric ions.
- It changes in color from colorless to pink.

- The liver synthesizes the transferrin, and this will bind the iron.
- This is synthesized in the liver and depends on its demands in anemia.
- Transferrin can be lost in the urine because of its small molecular size.
- More loss in severe proteinuria.
- CSF also contains a small amount of transferrin.
- Its function in the CSF is not known.
- This can be used as a marker in the case of CSF leakage.
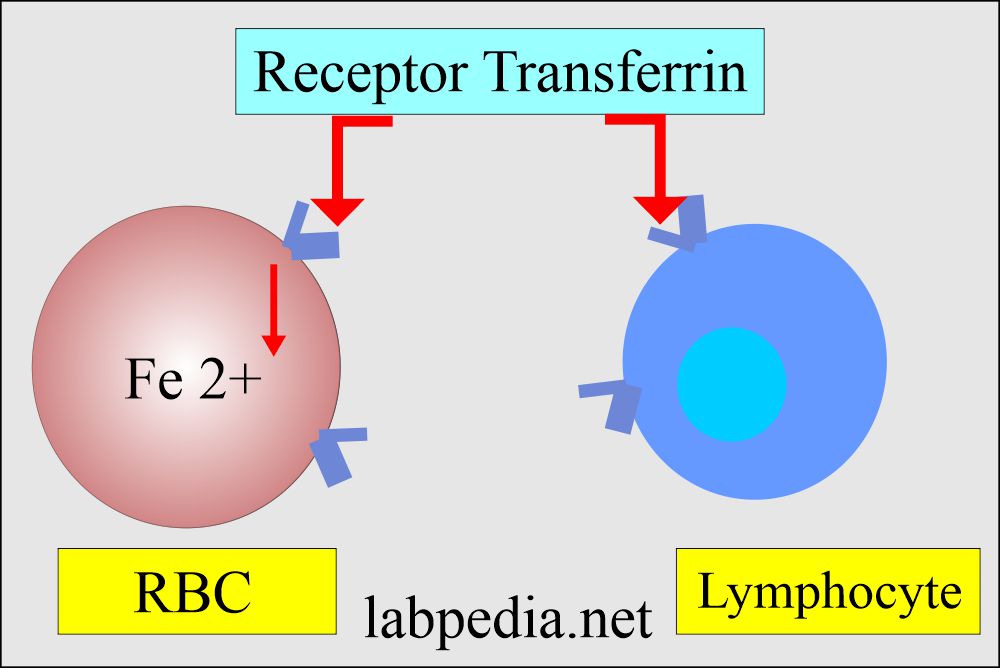
- RBC has a receptor for transferrin. These receptors are also present in the lymphocytes.
What is the effect of Transferrin in various conditions?
- In the case of iron deficiency anemia, the transferrin level increases.
- There is a low level of transferrin in the case of malignancy and inflammation.
What is the function of Transferrin?
- This transports iron.
- It regulates the absorption of iron.
- It protects against the toxic effects of iron.
Transferrin saturation is a better index of iron saturation.
-
- Transferrin saturation % = serum iron x 100 / TIBC
Normal Transferrin level
- o to 4 days = 130 to 275 mg/dL
- 3 months to 16 years = 203 to 360 mg/dL
- 16 to 60 years =
- male = 215 to 365 mg/dL
- female = 250 to 380 mg/dL
- 60 to 90 years = 190 to 375 mg/dL
- >90 years = 186 to 347 mg/dL
- Another source
- Male = 215 to 365 mg/dL
- Female = 250 to 380 mg/dL
- Newborn = 130 to 275 mg/dL
- Child = 203 to 360 mg/dL
- Source 4
- Adult = 250 to 425 mg/dL (2.5 to 4.2 g/L)
- Children = 203 to 360 mg/dL (2.0 to 3.6 g/L)
- Newborn = 130 to 275 mg/dL (1.3 to 2.7 g/L)
- Transferrin saturation:
- Male = 20% to 50%.
- Female = 15% to 50%
What causes an increase in the Transferrin level?
- Iron deficiency anemia.
- In pregnancy.
- Use of oral contraceptives or estrogen therapy.
What causes a decrease in the Transferrin level?
- In protein malnutrition.
- In protein loss from burns.
- In iron overload diseases (hemochromatosis).
- In acute and chronic diseases.
- Acute liver diseases.
- Renal diseases like nephrosis.
- The absence of transferrin is seen in the genetic disorder called Atransferrinemia.
- It is characterized by anemia and hemosiderosis.
- Hemosiderosis is seen in the liver and heart.
Value for the layman:
- Transferrin is advised when the patient has anemia (decreased hemoglobin).
- This is a better test for evaluating anemia, iron deficiency, thalassemia, sideroblastic anemia, and hemochromatosis.
Questions and answers:
Question 1: What is the role of Transferrin as an acute-phase protein?
Question 2: What is the role of transferrin in the body?