Thyroid:- Part 8 – Free Triiodothyronine, Free T3
Free Triiodothyronine (Free T3)
What sample is needed for Free Triiodothyronine (Free T3)?
- This is done on the patient’s serum.
- A non-fasting blood sample can be taken.
- Plasma (heparin or EDTA) can be used.
- The sample is stable for 7 to 14 days at room temperature or 2 to 8 °C.
What are the precautions for Triiodothyronine Free T3?
- Avoid hemolyzed or lipemic samples.
- Centrifuge turbid sample before performing the test.
What are the indications for Free T3?
- Used to evaluate thyroid function.
- It is done to rule out T3 toxicosis.
- This is done to clarify the protein binding abnormalities.
- This is also done to monitor the therapy.
How will you interpret Free Triiodothyronine (Free T3)?
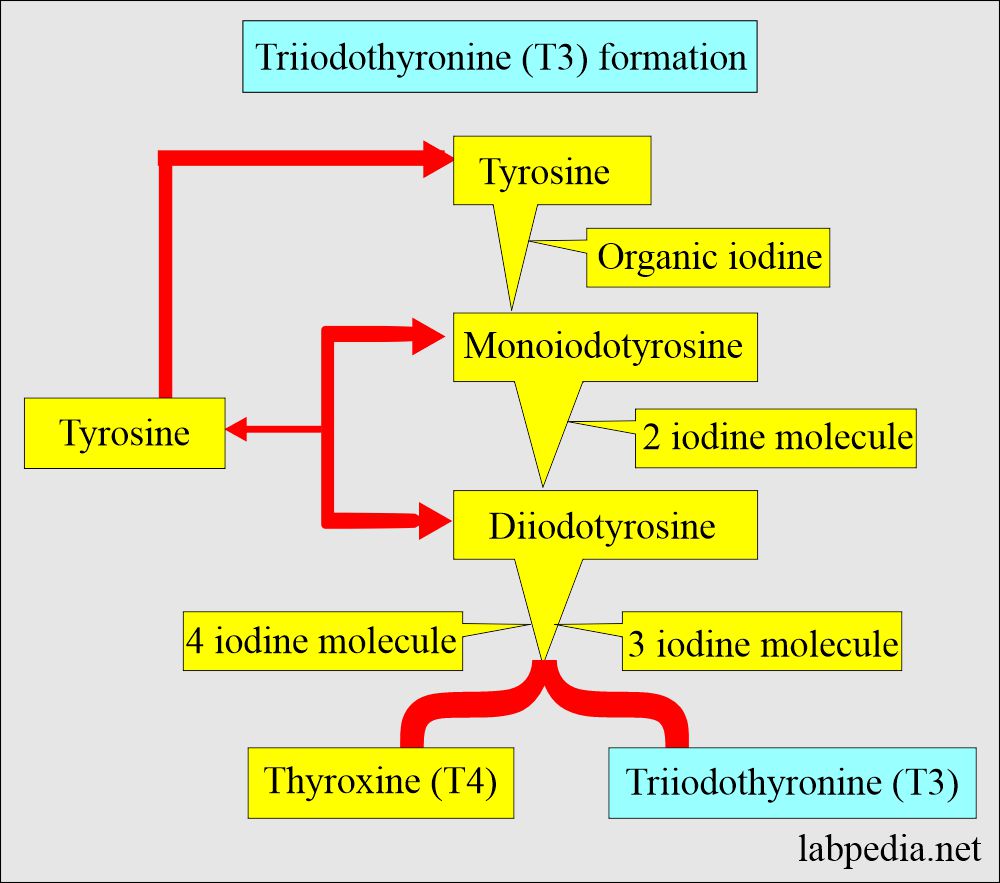
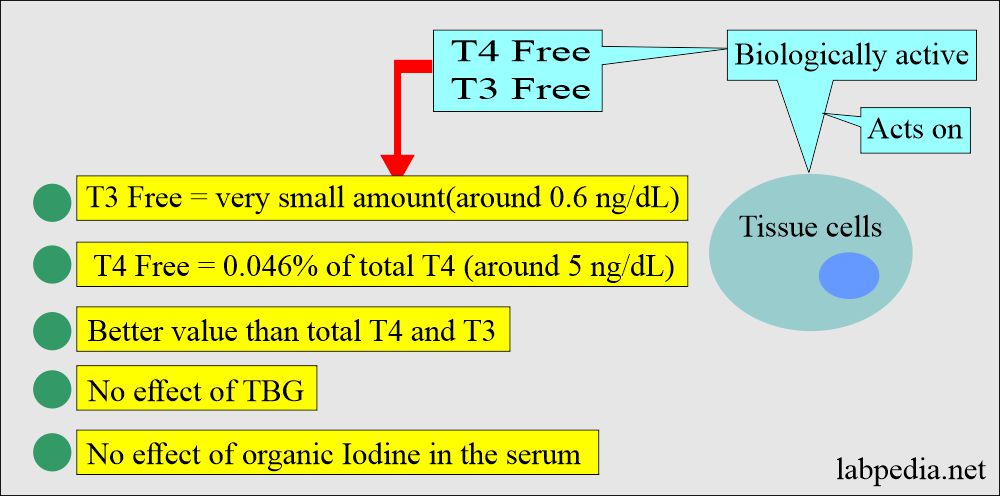
- This is the free T3, which is unbound to the protein.
- 99 % of T3 is bound to carrier proteins.
- The main transport protein is thyroxine-binding globulin (TBG).
- Also, this is bound to albumin and prealbumin.
- Only the free (unbound) portion of triiodothyronine (free T3) is believed to be responsible for the biological action.
- The concentrations of the carrier proteins are altered in many clinical conditions, such as pregnancy, etc.
- However, the free T3 concentration remains constant even in the abnormal thyroid gland.
- Measurements of free T3 concentrations, therefore, correlate more reliably with your clinical status than total T3 levels.
- The total T3 level may be increased in the:
- Pregnancy.
- Oral contraceptives.
- Estrogen therapy.
- In the above conditions, the free T3 level remains normal.
- T3 half-life is only one day compared to one week of thyroxine (T4).
What is normal Free Triiodothyronine (Free T3 )?
Source 1
Free Triiodothyronine T3 (Free T3)
- Cord blood (>37 weeks ) = 15 to 391 pg/dL
- Child and adult = 260 to 480 pg/dL (4.0 to 7.4 pmol/L)
- Pregnancy
- First trimester = 211 to 383 pg/dL
- Second and third trimesters = 196 to 338 pg/dL
Source 2
Total Triiodothyronine T3 (T3 total)
- 1 to 3 days = 100 to 740 ng/dL
- 1 to 11 months = 105 to 245 ng/dL
- 1 to 5 years = 105 to 270 ng/dL
- 6 to 10 years = 95 to 240 ng/dL
- 11 to 15 years = 80 to 215 ng/dL
- 16 to 20 years = 80 to 210 ng/dL
- 20 to 50 years = 75 to 220 ng/dL
- >50 years = 40 to 180 ng/dL
- Adult = 260 to 480 pg/dL
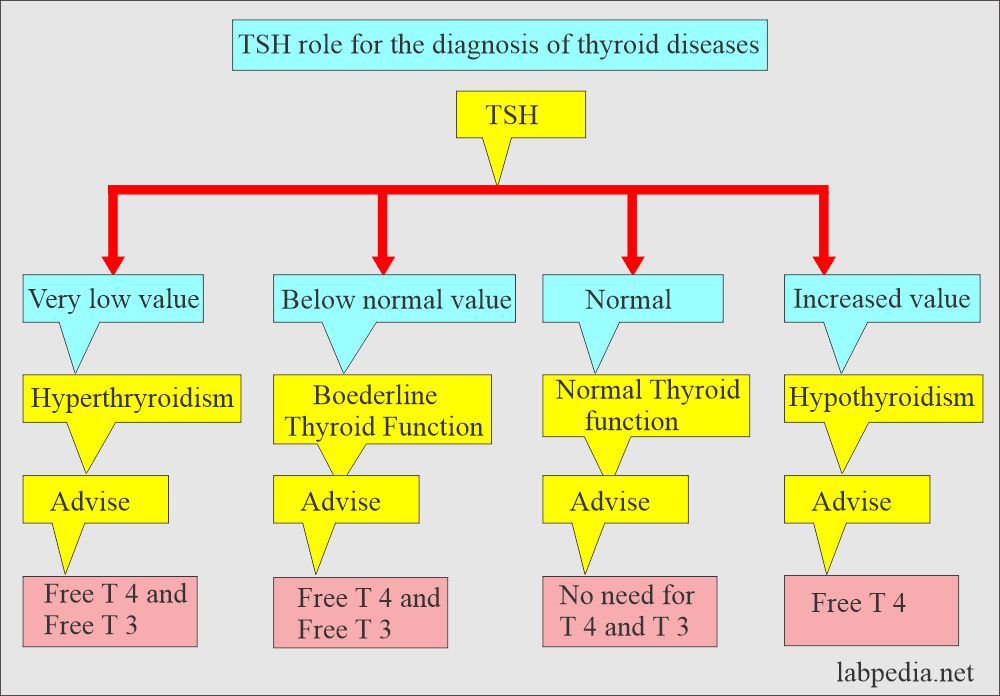
What is the role of Free T3 and TSH in diagnosing thyroid diseases?
What are the causes of increased Free T3 values?
- T3 toxicosis.
- Hyperthyroidism.
- Peripheral resistance syndrome.
What are the causes of decreased Free T3 values?
- Hypothyroidism.
- Pregnancy in the third trimester.
Questions and answers:
Question 1: What is the role of Free T3?
Question 2: What will happen to Free T3 in pregmancy?
Please see more details on Total T3 and Thyroid functions.