Thyroid:- Part 6 – Thyroxine Free T4 (FT4)
Thyroxine Free T4 (FT4)
What sample is needed for Thyroxine Free T4?
- This test is done in the serum.
- Immediately refrigerate the serum.
- The sample is stable at room temperature for seven days, but refrigeration is better.
What are the precautions for Thyroxine Free T4?
- Avoid lipemic serum.
- Neonates have a higher level than older children and adults.
- Some drugs increase T4 levels, like heparin, aspirin, propranolol, and danazol.
- Some of the drugs decrease the T4 level, like furosemide, rifampicin, phenytoin, and methadone.
- If a patient taking exogenous thyroxine has raised the free T4 level.
What are the indications for Thyroxine Free T4?
- The thyroxine-free T4 level evaluates thyroid function in a protein abnormality patient.
- It is used to diagnose thyroid function.
- This is done to monitor replacement and suppressive therapy like levothyroxine. TSH takes 6 to 8 weeks to show changes.
- Free T4 gives corrected values in patients where the total T4 is changed on account of changes in serum proteins or in binding sites like:
- Drugs such as androgens, birth control pills, estrogens, and phenytoin.
- In pregnancy.
- In the case of nephrosis, where serum proteins are altered.
- Usually, it is not helpful unless hypothalamus/pituitary disease is suspected.
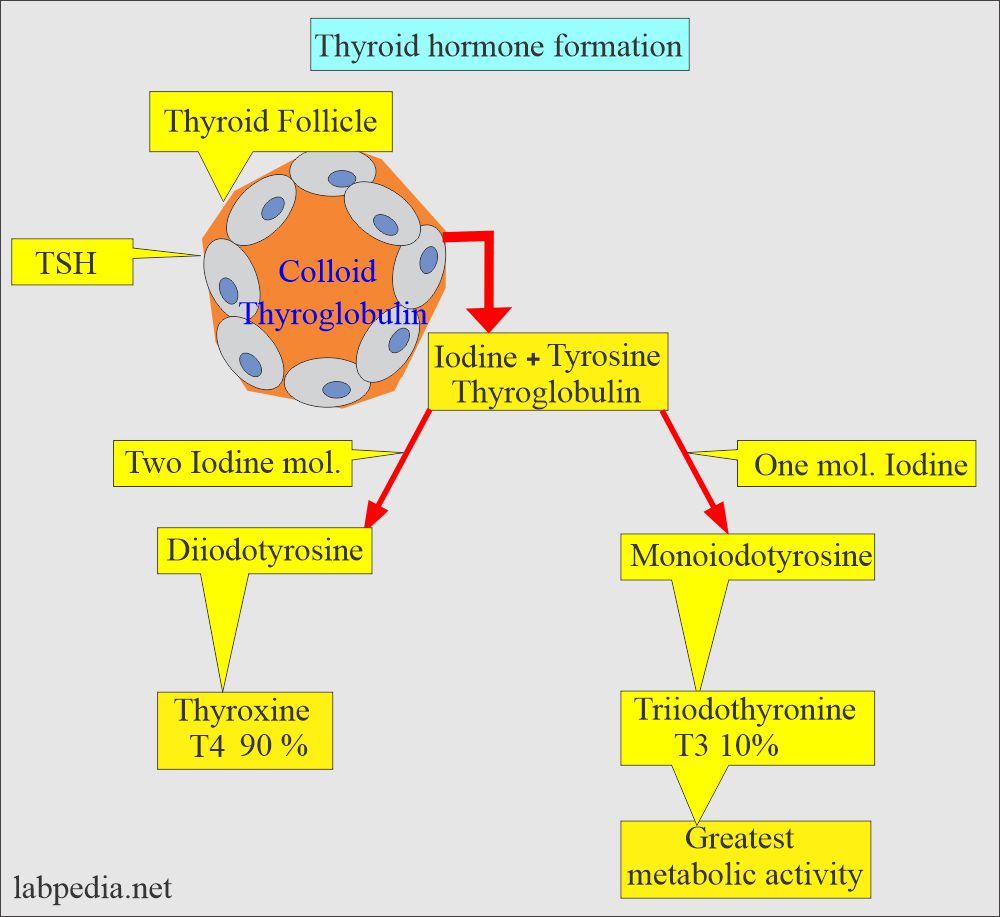
How will you discuss the Pathophysiology of thyroid hormones?
- The thyroid hormone comprises Triiodothyronine (T3) and Thyroxine (T4).
- Over 90 % of thyroid hormone is made of Thyroxine T4.
- As much as 99% of T4 is bound to protein (Thyroid-binding globulin and albumin).
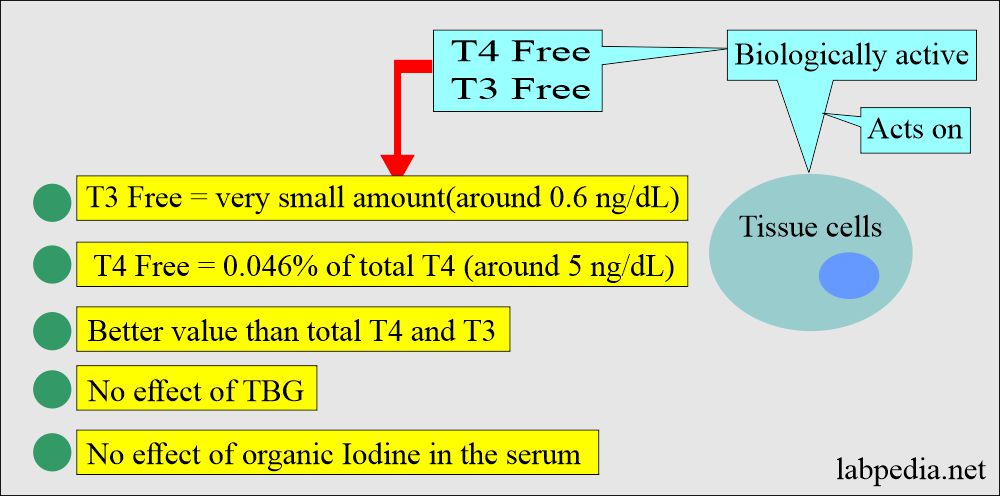
- Only 0.04% is Thyroxine free T4, and this is biologically active.
- Only 1 to 5% of T4 is unbound or free T4 (source 2).
- Free thyroxine FT4 comprises a small fraction of total thyroxine.
- When measuring total T4 = unbound T4 + bound T4.
- The protein level influences the T4 level.
- FT4 is unbound to protein and is available to the tissue.
- FT4 is a metabolically active hormone.
- Pregnancy and hormone replacement therapy increase the TBG and lead to false increases at the T4 level.
- In that case, suggest hyperthyroidism when actually the patient is euthyroid.
- In such cases, when you measure Free T4, it will be normal, indicating the measurement of the Free T4 is more accurate than the total T4.
- In the case of hypoproteinemia, TBG is low, so total T4 will also be low, suggesting hypothyroidism.
- Now, if you measure Free T4, it will be the normal level and negate the abnormal level of total T4, which is due to a low level of TBG and not a result of hypothyroidism.
- Total T4 is a good indicator of thyroid function if the TBG is normal.
What is Normal Thyroxine T4 Free (FT4)?
Source 1
T4 Free (FT4)
| Age | ng/dL |
| Newborn 1 to 4 days | 2.2 to 5.3 |
| Child (2 weeks to 20 Years | 0.8 to 2.0 |
| Adults 21 to 87 years | 0.8 to 2.7 |
| Pregnancy | |
| 1st trimester | 0.7 to 2.0 |
| 2nd and 3rd trimester | 0.5 to 1.6 |
- To converts SI unit x 12.9 = nmol/L
T4 Total (T4)
| Age | µg/dL |
| Cord blood | 7.4 to 13.0 |
| 1 to 3 days | 11.8 to 22.6 |
| 1 to 2 weeks | 9.8 to 16.6 |
| 1 to 4 month | 7.2 to 14.4 |
| 4 to 12 month | 7.8 to 16.5 |
| 1 to 5 year | 7.3 to 15.0 |
| 5 to 10 year | 6.4 to 13.3 |
| 10 to 15 year | 5.6 to 11.7 |
| Adult | Male = 4.6 to 10.5 Female = 5.5 to 11.0 |
| >60 year | 5.0 to 10.7 |
| Maternal serum 15 to 40 weeks | 9.1 to 14.0 |
Another source 2
T4 Free
- Newborn (0 to 4 days) = 2 to 6 ng/dL (26 to 77 pmol/L)
- Child 2 weeks to 20 years = 0.8 to 2.0 ng//dL
- Adult = 0.8 to 2.8 ng/dL (10 to 36 pmol/L)
Newborn FT4 index
- Newborn FT4 index = 9.9 to 7.5 ng/dL
- pubertal child and adult FT4 index = 4.2 to 13.0 ng/dL
T4 Total (T4)
| Age | µg/dL |
| 1 to 3 days | 11.22 |
| 1 to 2 weeks | 10 to 16 |
| 1 to 12 months | 8 to 16 |
| 1 to 5 years | 7 to 15 |
| 5 to 10 years | 6 to 13 |
| 10 to 15 years | 5 to 12 |
| Adult | Male 4 to 12 Female 5 to 12 |
| >60 years | 5 to 11 |
What are the causes of increased Thyroxine-Free T4 (FT4)?
- Hyperthyroidism.
- Grave’s disease.
- Hypothyroidism is treated with thyroxine.
- Euthyroid sick syndrome.
- Toxic thyroid adenoma.
- Acute thyroiditis.
- Struma ovarii.
- Patients with hydatidiform mole or choriocarcinoma where the HCG level is raised will show:
- Increased Free T4.
- Suppressed TSH.
- Blunted response of TSH response to TRH stimulation.
What are the causes of decreased Thyroxine-Free T4?
- Primary hypothyroidism.
- Hypothyroidism is treated with triiodothyronine.
- Secondary hypothyroidism (pituitary).
- Congenital TBG deficiency.
- Tertiary hypothyroidism (Hypothalamic).
- Cushing’s disease.
- Cirrhosis.
- Renal failure.
- Iodine insufficiency.
- Myxedema.
- Advanced cancer.
How will you differentiate different thyroid diseases?
| Clinical disease | Free T4 | Total T4 | T3 | TSH | Thyroglobulin |
| Hyperthyroidism primary clinical | Increased | Increased | Increased | Decreased | Normal |
| Hyperthyroidism subclinical | Normal | Normal | Normal | Decreased | Normal |
| Hypothyroidism primary clinical | Decreased | Decreased | Decreased | Increased | Normal/Increased |
| Hypothyroidism primary subclinical | Normal | Normal | Normal | Increased | Normal |
| Hypothyroidism Secondary | Decreased | Decreased | Decreased | Normal/Decreased | |
| T3 thyrotoxicosis | Normal | Normal | Increased | Decreased | Normal |
| TSH-secreting tumors | Increased | Increased | Increased | Increased | Normal |
| Pregnancy with hyperthyroidism | Increased | Increased | Increased | Normal | Increased |
| Pregnancy with hypothyroidism | Decreased | Increased | Increased | Increased | Increased |
| Goiter | Normal | Normal | Normal | Normal | Normal |
| Thyroid carcinoma | Normal | Normal | Normal | Normal | Increased |
| Hashimoto’s thyroiditis | Variable | Variable | Variable | Variable | |
| Nephrosis | Decreased | Decreased | Normal | Decreased |
Questions and answers:
Question 1: What is the value of Free T4?
Question 2: What will happen to Free T4 in the Grave's disease?
- Please see more details on Thyroid function.