Thyroid:- Part 5 – Thyroxine Total, T4
Thyroxine Total,T4
What sample is needed for T4 Total?
- This test is done on the patient’s serum.
- The sample is stable for 7 days at room temperature, but refrigeration at 4 °C is preferred.
What are the precautions for Thyroxine Total (T4 Total)?
- Avoid lipemic serum.
What are the indications for Thyroxine Total (T4 Total)?
- This is done to assess thyroid function.
- It is advised to diagnose thyroid diseases like hypo or hyperthyroidism.
- This is also done to monitor the therapy.
How will you define Thyroxine Total (T4 Total)?
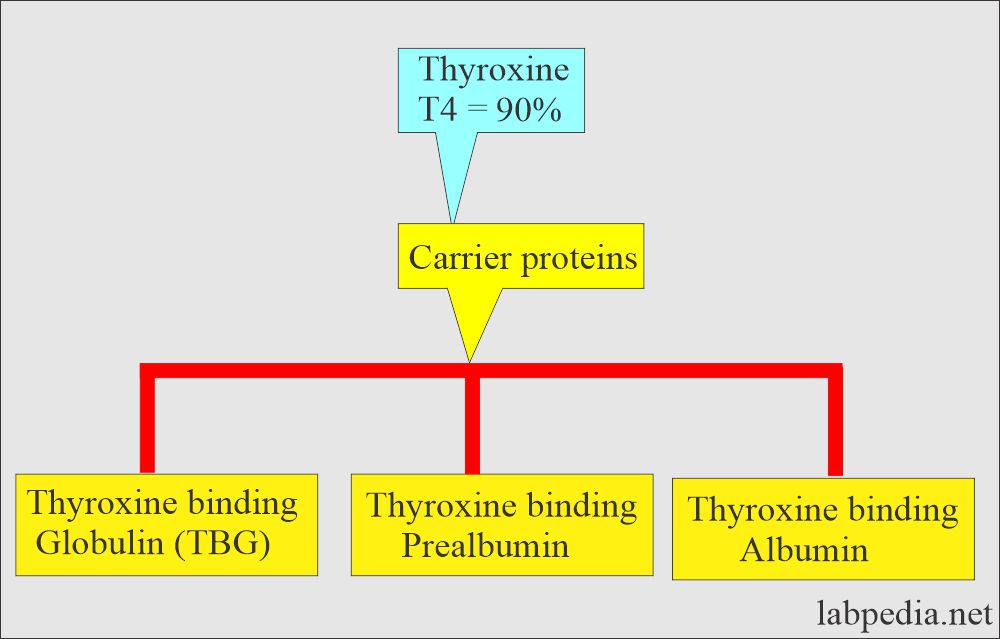
- Thyroxine, also known as T4, is the major secretion of the thyroid gland, bound to thyroid-binding globulin, prealbumin, and albumin.
- Thyroxine is produced in the thyroid gland and is stimulated by the TSH hormone.
- In tissue, thyroxine (T4) is deiodinated into T3, which causes hormonal action.
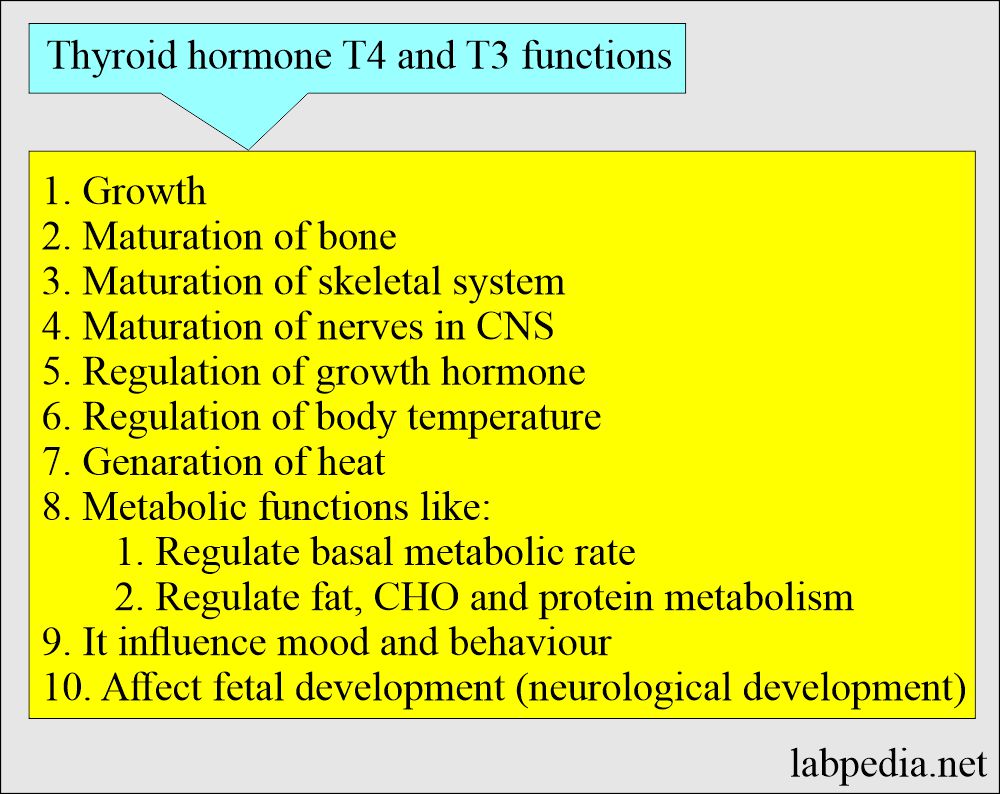
- Thyroxine is needed for the body’s growth, body metabolism, and energy.
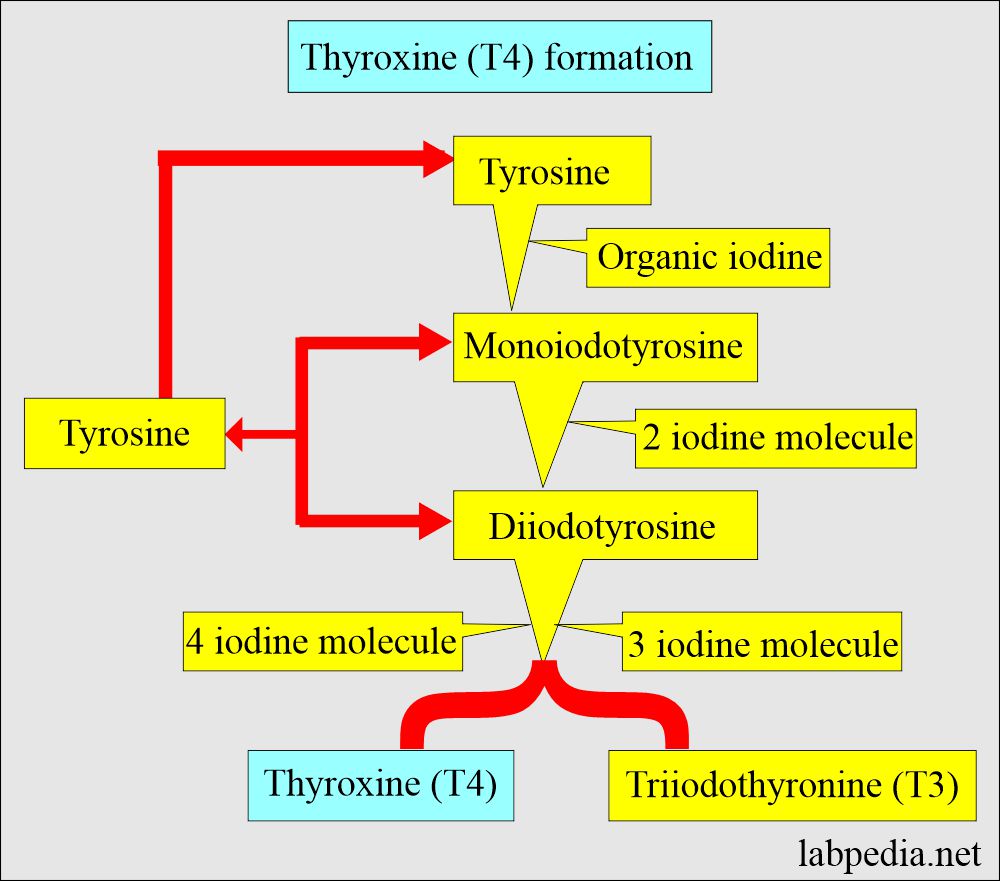
- Thyroxine (T4) is synthesized in the thyroid gland by the amino acid tyrosine and iodine.
How will you discuss the pathophysiology of thyroid hormones?
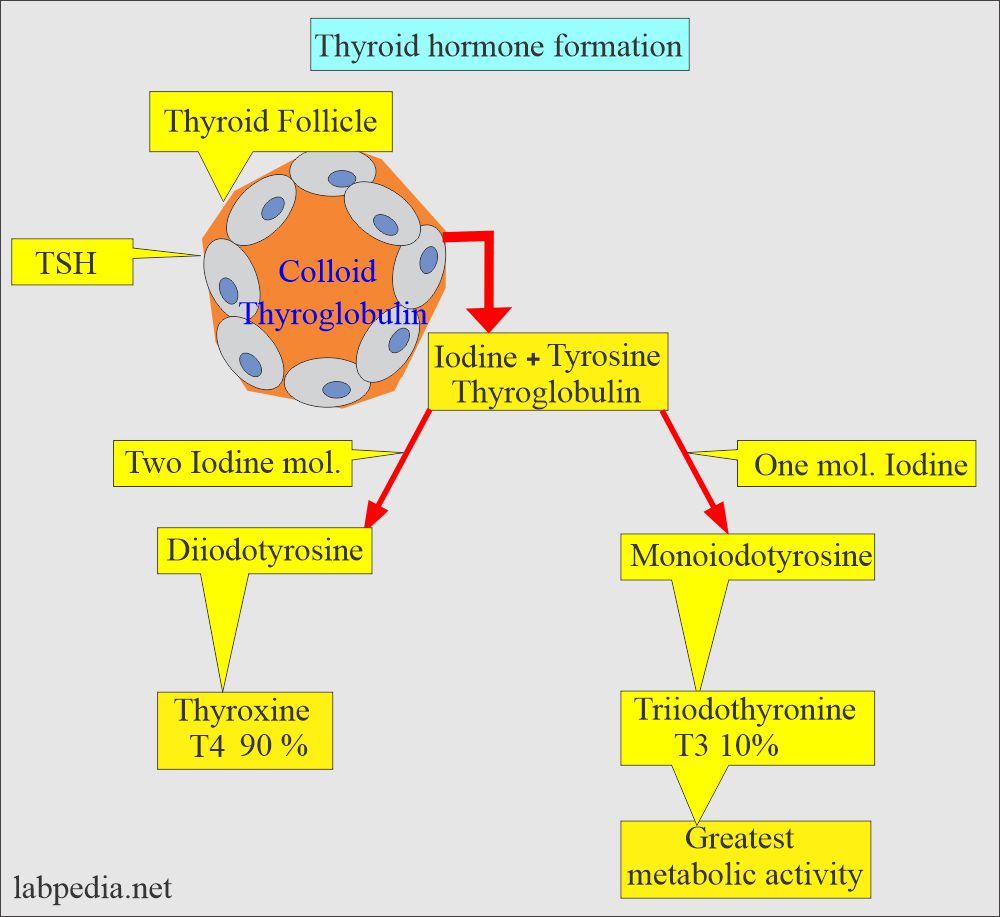
- Thyroid hormone formation is basically intrathyroidal iodine metabolism.
- This process consists of the following stages:
- Iodine trapping is an uptake of iodine by the follicular cells.
- Oganification or iodination is the process where iodine is incorporated into thyroid hormones.
- Normally thyroid organifies about 75 µg of iodine per day.
- Coupling.
- Storage.
- Secretion.
- Thyroxine T4 forms by the combination of:
- diiodotyrosine + diiodotyrosine = Tetra-Iodo-Tyrosine (Thyroxine or T4).
How will you interpret Thyroxine (T4)?
- T4 makes most of the thyroid hormone because T3 is only 10%.
- 80% of the T4 is metabolized into:
- T3 = 35%
- rT3 (reverse T3) = 45%
- rT3 is a biologically inactive isomer.
- 80% of the T4 is metabolized into:
- Most of the T4 is bound to thyroglobulin, prealbumin, and albumin.
- T4 is pro-hormone with thyroglobulin binding (TBG).
- There is a very small fraction of free T4.
- Serum Total T4 = Bound T4 + Free T4
- When T4 converts into T3, then hormonal action starts.
What are Thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3) functions?
- Thyroid glands play a major role in body function. T4 and T3 are involved in the growth and maturation of bone and skeletal systems.
- T3 is 3 to 8 times more metabolically active than T4 and is considered the active form of the thyroid hormone.
- It regulates body temperature.
- It plays a role in the body’s metabolism of fats, carbohydrates, and proteins.
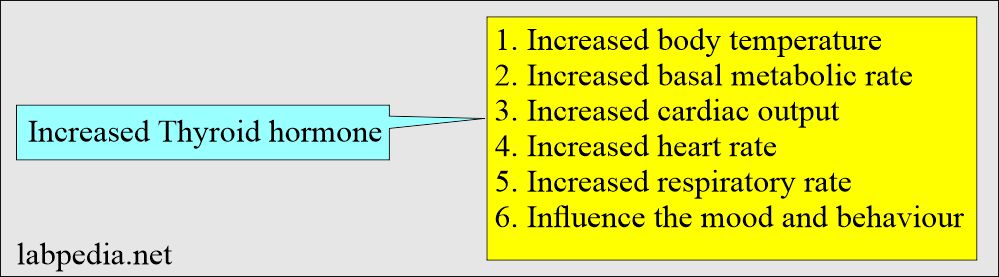
What is the effect of raised thyroid hormones, T4 and T3?
What are the normal values of thyroxine (T4)?
Source 1
T4 Total (T4)
| Age | µg/dL |
| Cord blood | 7.4 to 13.0 |
| 1 to 3 days | 11.8 to 22.6 |
| 1 to 2 weeks | 9.8 to 16.6 |
| 1 to 4 month | 7.2 to 14.4 |
| 4 to 12 month | 7.8 to 16.5 |
| 1 to 5 year | 7.3 to 15.0 |
| 5 to 10 year | 6.4 to 13.3 |
| 10 to 15 year | 5.6 to 11.7 |
| Adult | Male = 4.6 to 10.5 Female = 5.5 to 11.0 |
| >60 year | 5.0 to 10.7 |
| Maternal serum 15 to 40 weeks | 9.1 to 14.0 |
Source 1
T4 Free (FT4)
| Age | ng/dL |
| Newborn 1 to 4 days | 2.2 to 5.3 |
| Child (2 weeks to 20 Years | 0.8 to 2.0 |
| Adults 21 to 87 years | 0.8 to 2.7 |
| Pregnancy | |
| 1st trimester | 0.7 to 2.0 |
| 2nd and 3rd trimester | 0.5 to 1.6 |
- To converts SI unit x 12.9 = nmol/L
Another source 2
T4 Total (T4)
| Age | µg/dL |
| 1 to 3 days | 11.22 |
| 1 to 2 weeks | 10 to 16 |
| One o 12 months | 8 to 16 |
| 1 to 5 years | 7 to 15 |
| 5 to ten years | 6 to 13 |
| 10 to 15 years | 5 to 12 |
| Adult | Male 4 to 12 Female 5 to 12 |
| >60 years | 5 to 11 |
Another Source 2
T4 Free
- Newborn (0 to 4 days) = 2 to 6 ng/dL (26 to 77 pmol/L)
- Child 2 weeks to 20 years = 0.8 to 2.0 ng//dL
- Adult = 0.8 to 2.8 ng/dL (10 to 36 pmol/L)
- Infants 1 to 3 days = 11 to 22 µg/dL.
- Infants 1 to 4 months = 8 to 16 .µg/dL
- Child 1 to 5 years = 7 to 15 .µg/dL
- Child 10 to 15 years = 5 to 12 µg/dL.
- Adult Male = 4 to 12 µg/dL.
- Adult female = 5 to 12 µg/dL.
- Adult > 60 years = 5 to 11 µg/dL.
What are the causes of increased T4 levels?
- Grave’s disease.
- Toxic thyroid adenoma.
- Struma ovarii.
- Acute thyroiditis.
What are the causes of decreased T4 levels?
- Hypothyroidism like:
- Cretinism.
- Myxedema.
- Surgical ablation.
- Failure of the hypothalamus.
- Protein-losing conditions like :
- Nephrotic syndrome.
- Renal failure.
- Iodine insufficiency.
- Cirrhosis.
- Cushing’s syndrome.
- Advanced cancers.
- Pituitary insufficiency.
The critical value of T4 Total:
- Newborn = <7 µg/dL
- Adult = <2 µg/dL
How will you differentiate different thyroid diseases?
| Clinical disease | Free T4 | Total T4 | T3 | TSH | Thyroglobulin |
| Hyperthyroidism primary clinical | Increased | Increased | Increased | Decreased | Normal |
| Hyperthyroidism subclinical | Normal | Normal | Normal | Decreased | Normal |
| Hypothyroidism primary clinical | Decreased | Decreased | Decreased | Increased | Normal/Increased |
| Hypothyroidism primary subclinical | Normal | Normal | Normal | Increased | Normal |
| Hypothyroidism Secondary | Decreased | Decreased | Decreased | Normal/Decreased | |
| T3 thyrotoxicosis | Normal | Normal | Increased | Decreased | Normal |
| TSH-secreting tumors | Increased | Increased | Increased | Increased | Normal |
| Pregnancy with hyperthyroidism | Increased | Increased | Increased | Normal | Increased |
| Pregnancy with hypothyroidism | Decreased | Increased | Increased | Increased | Increased |
| Goiter | Normal | Normal | Normal | Normal | Normal |
| Thyroid carcinoma | Normal | Normal | Normal | Normal | Increased |
| Hashimoto’s thyroiditis | Variable | Variable | Variable | Variable | |
| Nephrosis | Decreased | Decreased | Normal | Decreased |
Questions and answers:
Question 1: What is thyroxine?
Question 2: Which thyroid hormone is biologically active?
Please see more details on Free T4 and thyroid function.