Thyroid:- Part 3 – Thyroxine-Binding Globulin (TBG)
Thyroxine-Binding Globulin (TBG)
What sample is needed for Thyroxine Binding Globulin (TBG)?
- Venous blood is needed to prepare the serum.
What are the Indications for Thyroxine-Binding Globulin (TBG)?
- Help to evaluate patients who had abnormal T4 and T3.
- Diagnose hyperthyroidism with raised T4.
- To diagnose hereditary deficiency or increased TBG.
- Also helpful for the diagnosis of hypothyroidism.
- Some times used to detect recurrent or metastatic differentiated thyroid carcinoma, especially follicular carcinoma with an increased level due to carcinoma.
- It is advised to distinguish increased or decreased total T3 or total T4 concentration due to changes in TBG.
How will you define Thyroxine-Binding Globulin (TBG)?
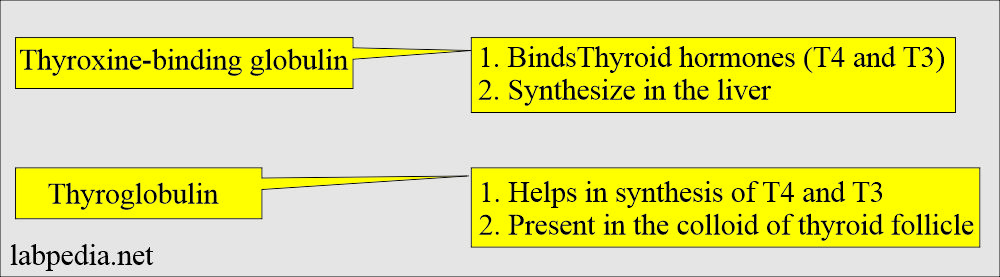
- Thyroxine-binding globulin is a protein synthesized in the liver that binds to thyroid hormones and carries them in the blood.
- Thyroxine-binding globulin and thyroid-binding globulin are the same.
- Thyroxine-binding globulin is the protein that binds with thyroxine, specifically to T4 and, to a lesser extent, T3.
- Thyroxine-binding globulin carries thyroid hormones (Thyroxine T4 and Triiodothyronine T3) to various body parts.
- In summary, Thyroxine-binding globulin protein is a carrier protein.
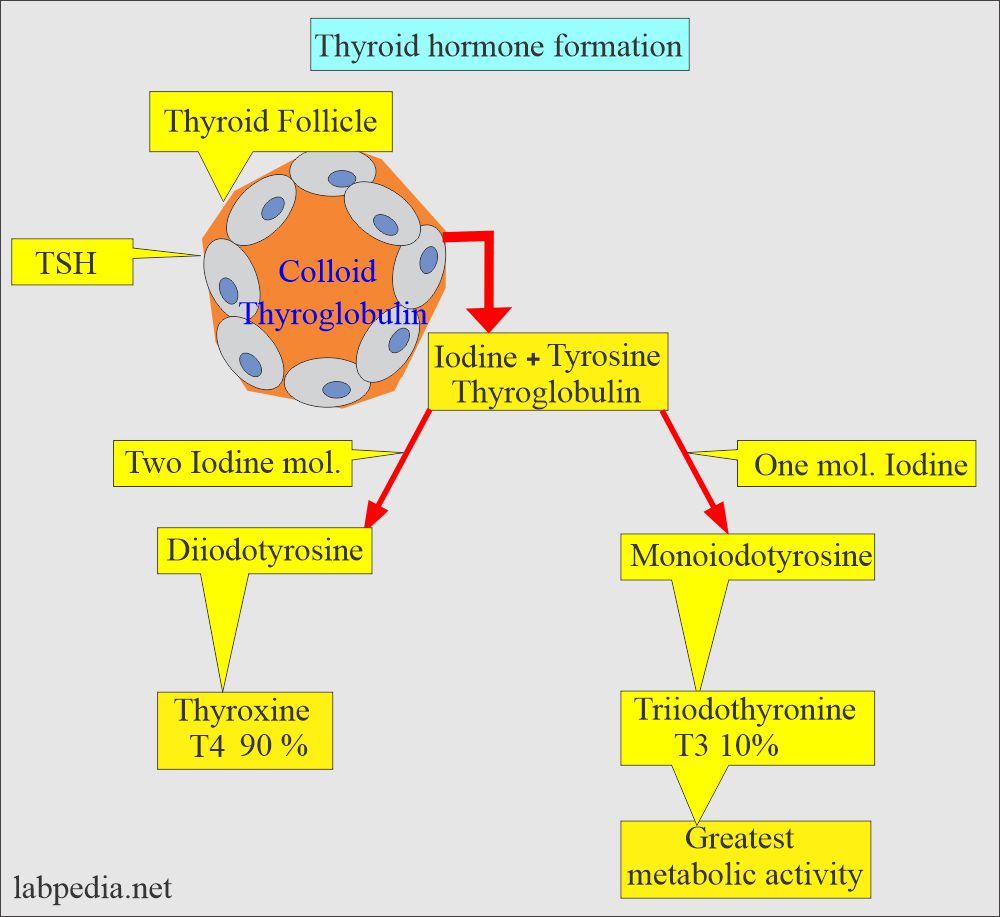
- Thyroglobulin is the protein produced in the thyroid follicles and takes part in the synthesis of thyroxine.
What are the interpretations of Thyroxine-binding globulin (TBG)?
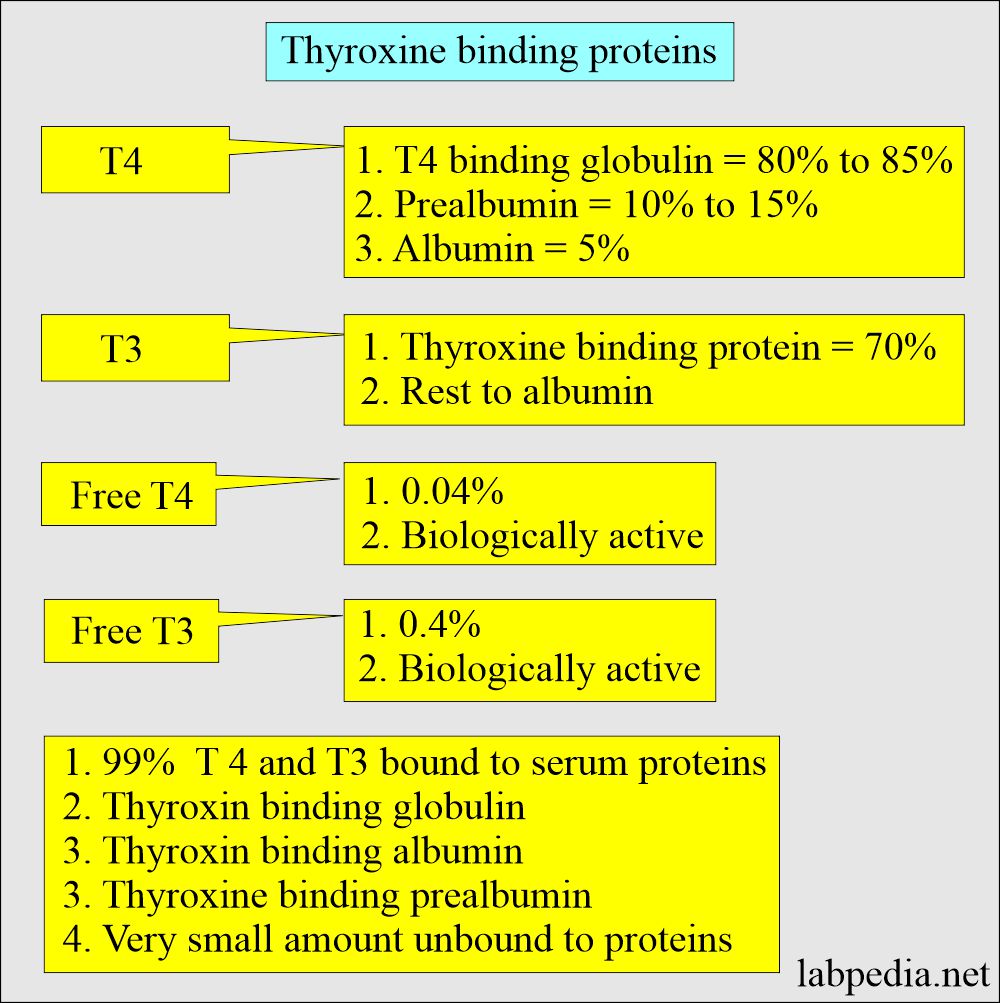
- Almost all thyroid hormones are protein-bound.
- Thyroid hormones are bound to:
- Albumin.
- Prealbumin (Thyroid-binding prealbumin).
- Thyroxine-binding globulin is the most important.
- T4-binding protein is alpha-1- globulin
- TBG effect free and bound T4 and T3.
- T4 + T3 assay = total T4 and T3 = These measures bound and free thyroid hormone.
- Most of these hormones are bound to TBG.
- Free T3/T4 are metabolically active hormones.
- When TBG increases, more T4/T3 is bound, and less active free T4/T3 is available, leading to the Stimulation of TSH that will produce more T4/T3. However, there is no hypothyroidism because this is compensation for increasing TBG. This is seen in pregnant women and patients taking exogenous estrogen.
- In the case of raised T4, evaluate that:
- Is it due to hyperthyroidism?
- Or due to increased TBG.
- Estrogen increases the TBG in the serum, whereas androgens and glucocorticoids decrease TBG synthesis.
What is the normal Thyroxine-binding globulin (TBG)?
Source 1
| Age | mg/dL |
| Cord blood | 3.6 to 9.6 |
| 4 to 12 months | 3.1 to 5.6 |
| 1 to 5 years | 2.9 to 5.4 |
| 5 to 10 years | 2.5 to 5.0 |
| 10 to 15 years | 2.1 to 4.6 |
| Adult |
Male = 1.2 to 2.5 Female = 1.4 to 3.0 |
| Pregnancy 3rd trimester | 5.3 ± 0.6 |
- To convert into SI unit x 10 = mg/L
Source 2
Thyroxine-binding globulin
| Age | Male mg/dL | Female mg/dL |
| 1 to 5 days | 2.2 to 4.2 | 2.2 to 4.2 |
| 1 to 11 months | 1.6 to 3.6 | 1.7 to 3.7 |
| 1 to 9 years | 1.2 to 2.8 | 1.5 to 2.7 |
| 10 to 19 years | 1.4 to 2.6 | 1.4 to 3.0 |
| >20 years | 1.7 to 3.6 | 1.7 to 3.6 |
| Oral contraceptive | 1.5 to 5.5 | |
| Pregnancy (third trimester) | 4.7 to 5.9 |
Source 4
Thyroxine-binding globulins :
- Infants = 3 to 6 mg/dL.
- Men = 1.2 to 2.5 mg/dL.
- Women = 1.4 to 3.0 mg/dL.
- Female on Oral contraceptives = 1.5 to 5.5 mg/dL.
- Female Pregnancy (3rd trimester) = 4.7 to 5.9 mg/dL.
- Thyroxine binding globulin for T 4 = 10 to 25 mg/dL
- Prealbumin for T 4 = 49 to 70 mg/dL.
- Albumin for T 4 = 12 to 34 mg/dL
What are the causes of increased Thyroxine-binding globulin (TBG)?
- In some cases of hypothyroidism.
- Genetic abnormality.
- Neonates.
- Inherited.
- Idiopathic
- Lymphocytic painless subacute thyroiditis.
- Hepatitis (Infectious type)
- Porphyria (acute intermittent).
- Estrogen-producing tumors.
- Late HIV infection.
- Pregnancy.
- Certain drugs like estrogen, birth control tablets, clofibrate, heroin, perphenazine, and methadone.
What are the causes of decreased Thyroxine-binding globulin (TBG)?
- Genetic deficiency.
- Nephrotic syndrome.
- Protein-losing enteropathy.
- Malnutrition.
- Testosterone-producing tumors where testosterone decreases TBG.
- Ovarian failure.
- Stress illness and surgical stress.
- Chronic liver disease.
- Acromegaly.
How will you differentiate different thyroid diseases?
| Clinical disease | Free T4 | Total T4 | T3 | TSH | Thyroglobulin |
| Hyperthyroidism primary clinical | Increased | Increased | Increased | Decreased | Normal |
| Hyperthyroidism subclinical | Normal | Normal | Normal | Decreased | Normal |
| Hypothyroidism primary clinical | Decreased | Decreased | Decreased | Increased | Normal/Increased |
| Hypothyroidism primary subclinical | Normal | Normal | Normal | Increased | Normal |
| Hypothyroidism Secondary | Decreased | Decreased | Decreased | Normal/Decreased | |
| T3 thyrotoxicosis | Normal | Normal | Increased | Decreased | Normal |
| TSH-secreting tumors | Increased | Increased | Increased | Increased | Normal |
| Pregnancy with hyperthyroidism | Increased | Increased | Increased | Normal | Increased |
| Pregnancy with hypothyroidism | Decreased | Increased | Increased | Increased | Increased |
| Goiter | Normal | Normal | Normal | Normal | Normal |
| Thyroid carcinoma | Normal | Normal | Normal | Normal | Increased |
| Hashimoto’s thyroiditis | Variable | Variable | Variable | Variable | |
| Nephrosis | Decreased | Decreased | Normal | Decreased |
Questions and answers:
Question 1: What is the difference between thyroxine-binding globulin and thyroglobulin?
Question 2: What is the effect of estrogen on thyroxine-binding globulin?