Testosterone Total and Free
Testosterone (Total and Free)
What sample is needed for Testosterone?
- It is done in the serum.
- Can use heparinized plasma.
- 24-hours of the urine sample.
- Separate the serum immediately; if kept for a more extended period (more than 6 hours), you may get false high values.
- The sample is stable at 1 to 4 °C for one week.
- Free Testosterone is stable for 1 to 2 days at 4 °C.
- At -20 °C, the sample is stable for 6 months.
What are the precautions for Testosterone estimation?
- Separate serum from the cells within 6 hours; otherwise, there is a false value elevation.
- The level is high in adults in the morning sample and 25% lower in the evening sample.
- In females, lower values increase 1 to 2 days mid-cycle.
- There are high values after the exercise.
- Value is decreased after the overload with glucose.
- There is a slow progressive decrease after the age of 50 years.
What are the Indications for Testosterone level?
- In males, this test is done to evaluate the following:
- Hypogonadism.
- This stimulation can be done by giving clomiphene and HCG.
- Cryptorchidism.
- Impotence.
- Pituitary gonadotropic function.
- Infertility.
- Precocious puberty.
- Tumor marker for the testicular tumors.
- Hypogonadism.
- In the female, this test is done to assess:
- Hirsutism and virilizing syndrome.
- Ambiguous sex character.
- Precocious puberty.
- Tumor marker for ovarian tumors.
- Maybe it is part of the fertility workup of the chronic anovulatory cycle due to the polycystic ovary.
How will you discuss the Pathophysiology of Testosterone?
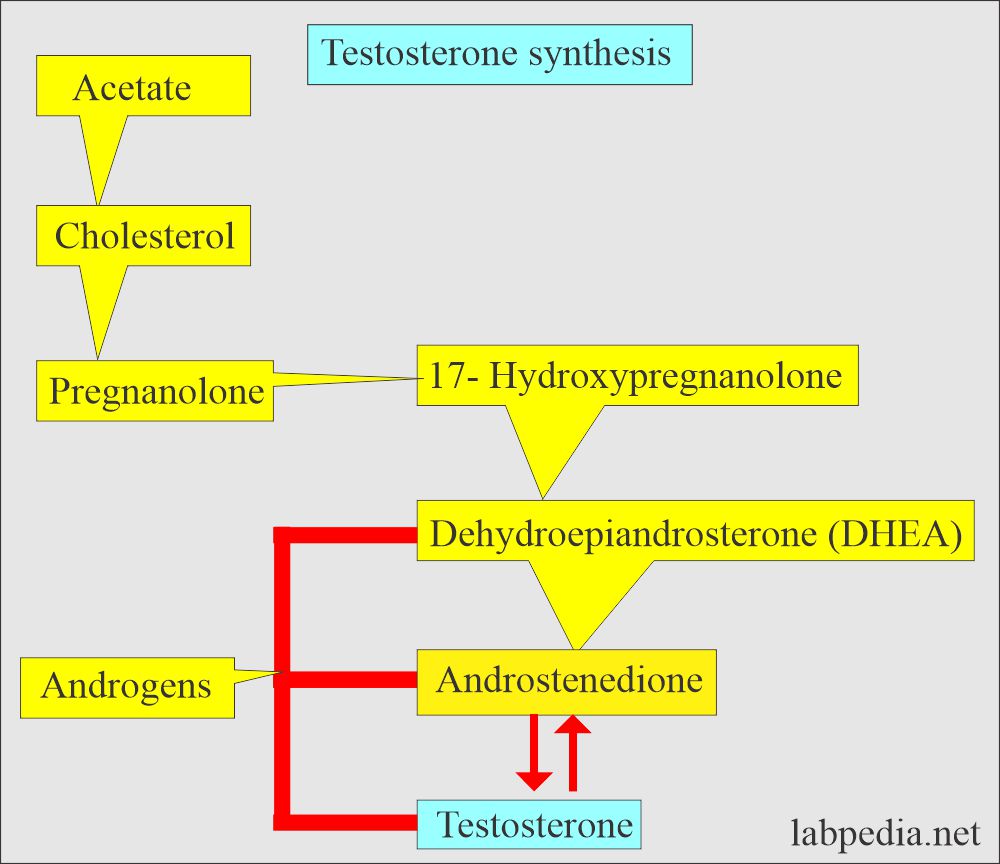
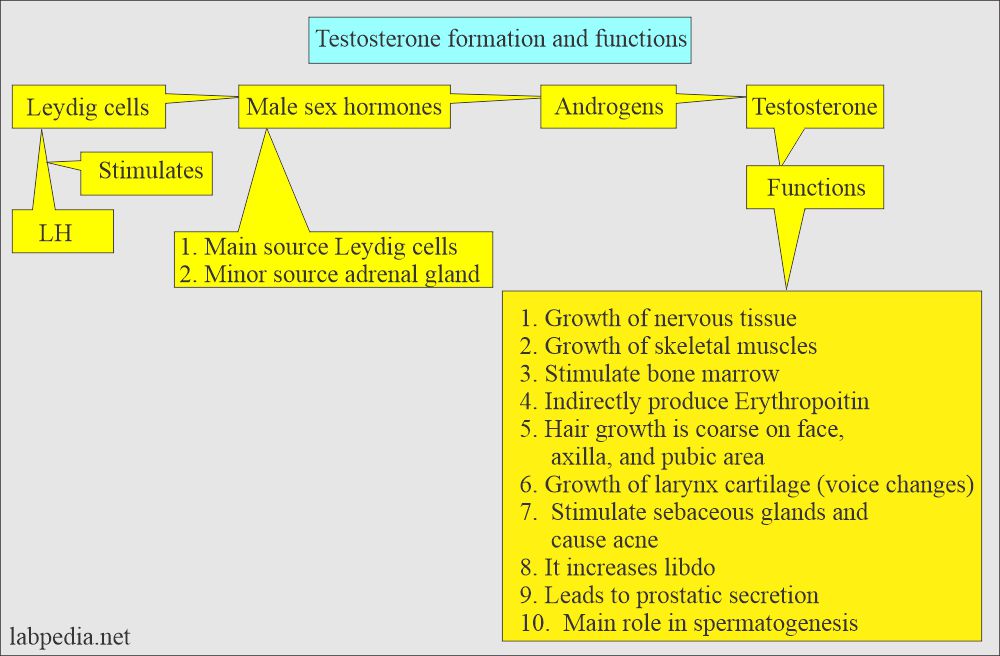
- Testosterone is the main androgen secreted by the testes and its production increases by puberty.
- Women only produce 5% to 10% of the testosterone as much as males.
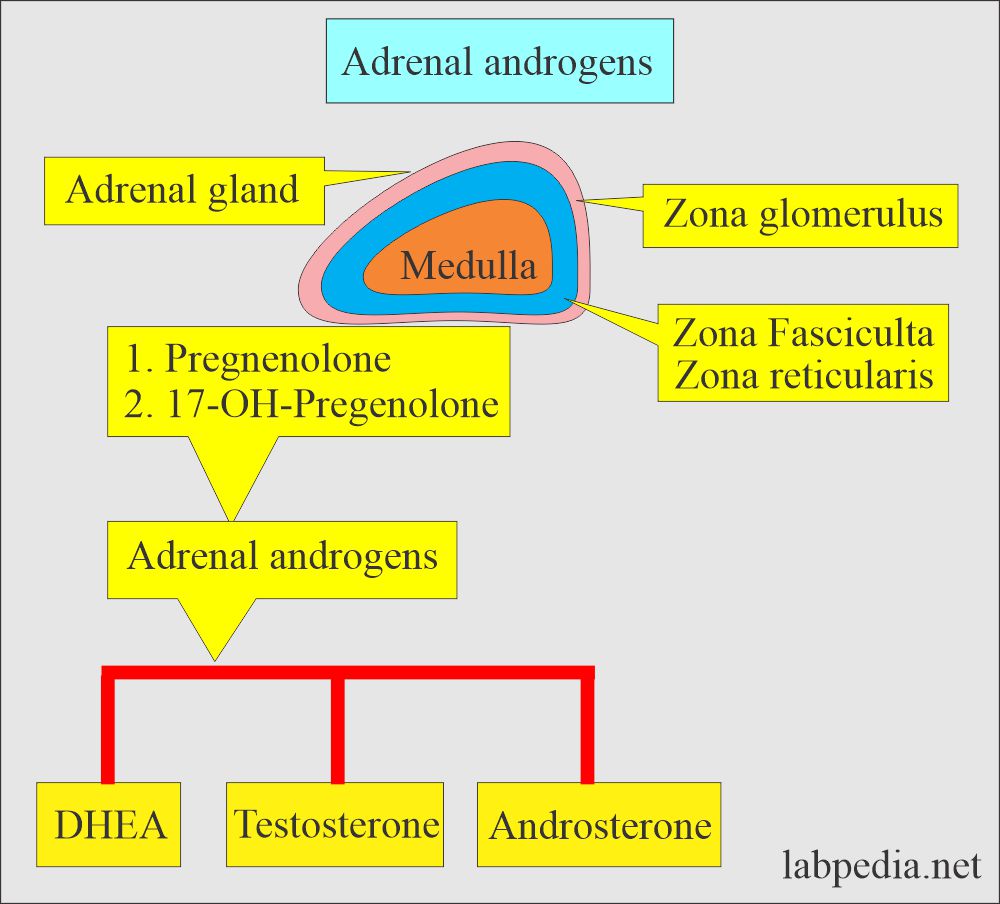
- Androgenic hormone includes:
- Dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA).
- Androsterone.
- Testosterone.
- The adrenal gland produces DHEA, Cortisol, Aldosterone, and Testosterone.
- Testes produce DHEA.
- Ovaries produce DHEA.
- DHEA is a precursor of the Androstenedione precursor of Testosterone and estrogen.
- Testosterone is responsible for the development of male secondary characters.
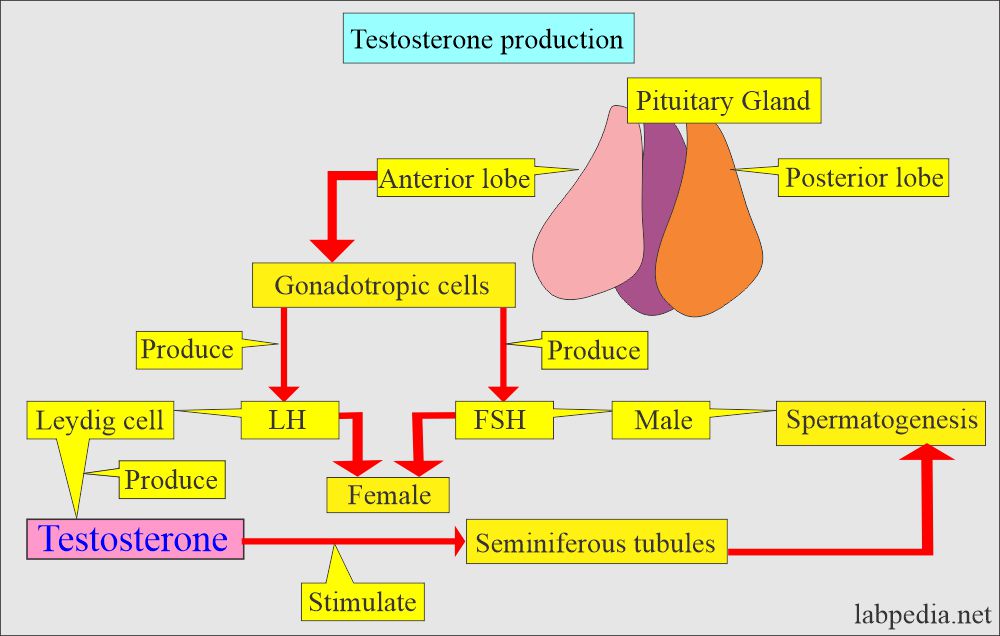
What is the mechanism for the Testosterone secretion?
- In men, testosterone is secreted by:
- Adrenal glands produce 2/3 of the total testosterone.
- Testes produce 1/3 of the total testosterone.
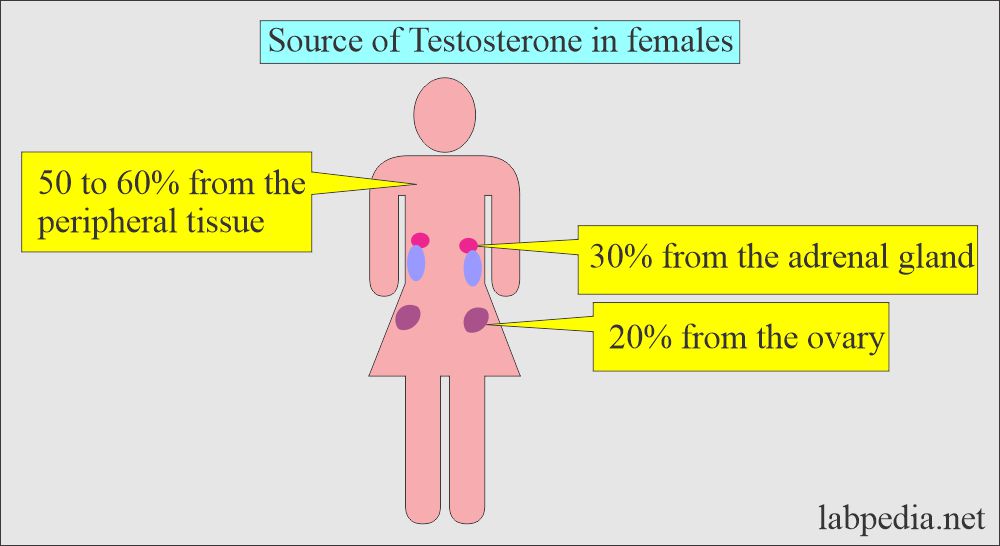
- In females, testosterone is secreted by:
- The adrenal gland is the source of all testosterone in females.
- Ovaries also produce some testosterone.
- Testosterone fluctuation in the level.:
- In the male, there is a peak level early in the morning.
- The female has cyclic elevation for 1 to 2 days around mid-cycle.
- Testosterone is made by:
- In males:
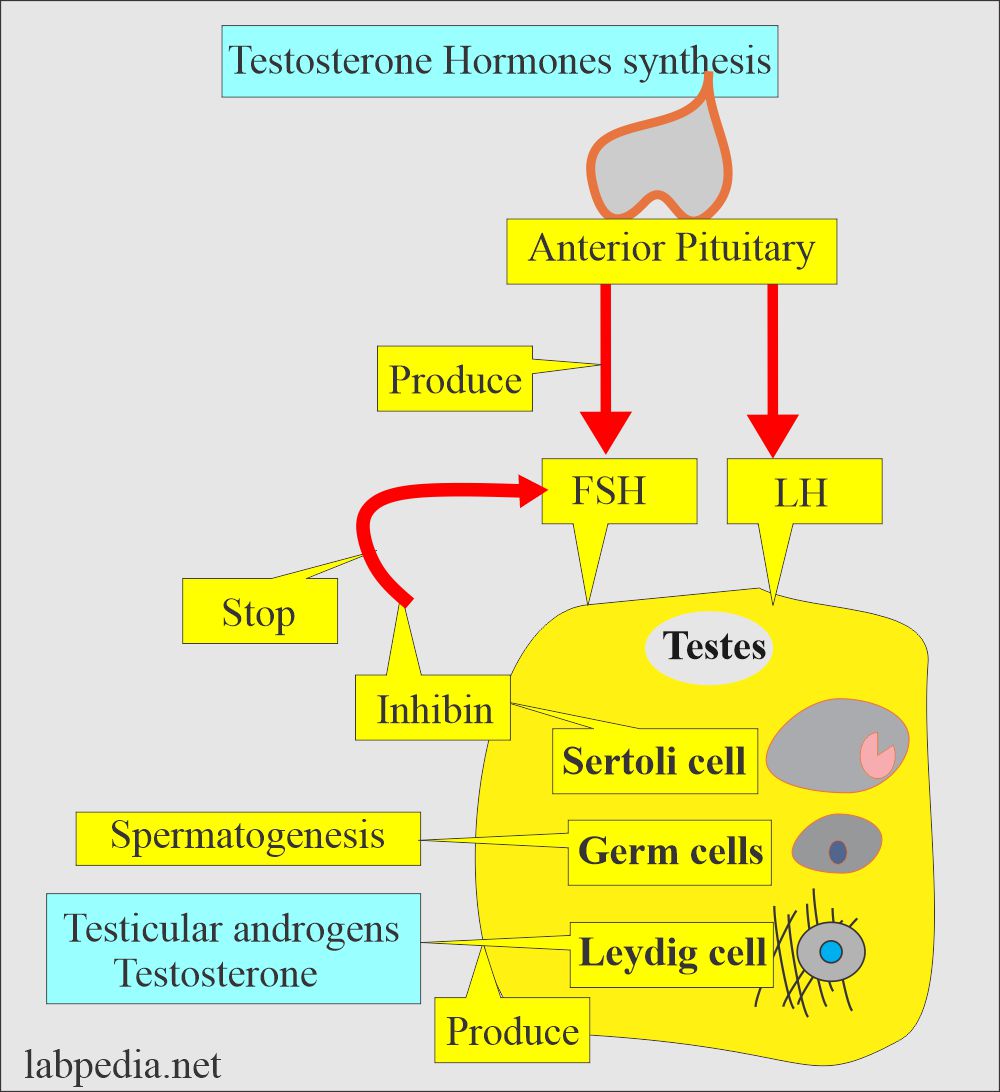
- In males, it is produced mainly by the Leydig cells, which comprise almost 95% of the total.
- In female:
- About 50% is made by converting DHEA into fatty tissue.
- 30% conversion of DHEA in the adrenal glands.
- 20% is made directly by the ovaries.
What is the role of the pituitary gland in Testosterone?
- The pituitary gland produces LH in males and FSH in females.
- LH stimulates the Leydig cells to produce Testosterone.
- FSH Stimulates Sertoli cell to help in spermatogenesis.
What are the functions of Testosterone?
- Testosterone stimulates spermatogenesis and secondary sex character.
- Testosterone Increased production is seen in:
- In Male produces premature puberty.
- Females produce masculinity (manifested by amenorrhea and excessive growth of body hair).
- Testosterone exists in two forms in the serum:
- In males:
- Circulating testosterone is bound to:
- 60% to 65% strongly bound to sex hormone-binding globulin (beta-globulin).
- 20% to 40% is bound to serum albumin.
- 1% to 2% testosterone is free or unbound testosterone. This is the only biologically active testosterone.
- In females:
- Testosterone fractions consist of:
- 1% is free testosterone.
- 80% bound to sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBD).
- 19% bound to albumin.
- The free fraction is 2% unbound to the sex hormone globulin and albumin.
Total testosterone = Bound fraction + Free fraction.
-
- Free Testosterone fraction is the Active form.
How will you discuss Testosterone metabolism?
- Testosterone is metabolized in the liver, and the main metabolites are:
- Androsterone.
- DHT (dihydrotestosterone).
- These are further metabolized into androstenedione and etiocholanelone.
- End metabolites are excreted through the kidneys.
- The main metabolites of adrenal, testicular, and ovarian hormones are secreted through the kidneys as 17-ketosteroids.
What is the normal value of Testosterone?
Source 1
Testosterone Free
| Age | pg/mL | |
| Male | Female | |
| Cord | 5 to 22 | 4 to 16 |
| Newborn (1 to 15 days) | 1.5 to 31.0 | 0.5 to 2.5 |
| 1 to 3 month | 3.3 to 8.0 | 0.1 to 1.3 |
| 3 to5 month | 0.7 to 14.0 | 0.3 to 1.1 |
| 5 to 7 month | 0.4 to 4.8 | 0.2 to 0.6 |
| Children | ||
| 6 to 9 year | 0.1 to 3.2 | 0.1 to 0.9 |
| 10 to 11 year | 0.6 to 5.7 | 1.0 to 5.2 |
| 12 to 14 year | 1.4 to 156 | 1.0 to 5.2 |
| 15 to 17 year | 80 to 159 | 1.0 to 5.2 |
| Adult | 50 to 110 | 1.0 to 8.5 |
- To convert into SI units x 3.47 = pmol/L
Testosterone Total (blood)
| Age | ng/dL | |
| Male | Female | |
| Cord | 13 to 55 | 5 to 45 |
| Premature | 37 to 198 | 5 to 22 |
| Newborn | 75 to 400 | 20 to 64 |
| 1 to 5 month | 1 to 177 | 1 to 5 |
| 6 to 11 month | 2 to 7 | 2 to 5 |
| Children | ||
| 1 to 5 year | 2 to 25 | 2 to 10 |
| 6 to 9 year | 3 to 30 | 2 to 20 |
| Puberty Tanner stage | ||
| 1 | 2 to 23 | 2 to 10 |
| 2 | 5 to 70 | 5 to 30 |
| 3 | 15 to 280 | 10 to 30 |
| 4 | 105 to545 | 15 to 40 |
| 5 | 265 to 800 | 10 to 40 |
| Adult | 280 to 1100 | 15 to 70 |
| Pregnancy | 3 to 4 x adult level | |
| Postmenopausal | 8 to 35 | |
- To convert into SI unit x 0.0347 = nmol/L
Urine
- 20 to 50 years
- Male = 50 to 135 µg/day
- Female = 2 to 12 µg/day
- >50 years
- Male = 40 to 60 µg/day
- Female = 2 to 8 µg/day
- >50 years
Source 2
Total testosterone
- Men = 3 to 10 ng/mL
- Women = <1 ng/mL
- Prepubertal boys and girls = 0.05 to 0.2 ng/mL
Source 4
Free testosterone
- Men = 50 to 210 pg/mL.
- Women = 1.0 to 8.5 pg/mL.
- Children:
- Boy = 0.1 to 3.2 pg/mL.
- Children Girl = 0.1 to 0.9 pg/mL.
- Puberty:
- Boy = 1.4 to 156 pg/mL.
- Puberty Girls = 1.0 to 5.2 pg/ml.
Total testosterone
- Men = 270 to 1070 ng/dL.
- Women = 15 to 70 ng/dL.
- Postmenopausal women = 8 to 35 ng/dL.
- Pregnant women = 3 to 4 ng/dL
Testosterone by age:
- Serum level of testosterone :
- In male infants :
- By 2 weeks = around 25 ng/dL.
- BY 2 months = around 275 ng/dL.
- In female infants :
- By 2 weeks = around 25 ng/dL.
- By 2 months = Value decreases and remains low throughout early childhood.
What are the causes of Increased values of Total Testosterone?
- Male
- hyperthyroidism.
- Adrenal tumors.
- Adrenal Hyperplasia.
- Hypothalamic tumor, Pinealoma.
- Viral encephalitis.
- Testicular or extragonadal tumors where Leydig cells produce testosterone.
- Testosterone resistance syndrome.
- Female
- Adrenal neoplasm.
- Hilar cell tumor.
- Idiopathic Hirsutism.
- Trophoblastic disease during pregnancy
- Ovarian tumors
- Polycystic ovary.
What are the causes of decreased Total testosterone value in Males?
- Klinefelter syndrome.
- Pituitary failure leading to hypogonadism.
- Hypopituitarism may be primary or secondary.
- Orchiectomy.
- Delayed puberty.
- Down syndrome (trisomy 21).
- Cirrhosis.
- Cryptorchidism due to undescended testes.
What are the causes of increased Free Testosterone in Females?
- Hirsutism.
- Virilization.
- Polycystic ovaries.
What are the causes of decreased Free Testosterone in Males?
- Hypogonadism.
- Old age.
Questions and answers:
Question 1: What type of cell is the source of testosterone?
Question 2: Total testosterone is biologically active?