Sweat Electrolytes, Cystic Fibrosis and Diagnosis
Cystic Fibrosis
What sample is needed for the diagnosis of cystic fibrosis?
- At Least 100 mg of sweat is collected.
- Sweat is collected by applying the chemical to the skin.
- Sweat may be collected on paper after pilocarpine and low electric current stimulation.
What are the precautions for Cystic Fibrosis?
- The infant should be at least 48 hours of age.
- A proper collection of sweat is tough.
- Take care of evaporation and contamination.
- Use gauze or filter paper, which should be low in electrolyte content.
- Wash and dry the patient’s skin thoroughly after the stimulation and before collection with deionized water.
- A minimum sweat weight or volume is critical to get accurate results.
What are the indications for sweat electrolytes?
- This test is done to confirm the diagnosis of cystic fibrosis.
- Sweat is tested for chloride.
How will you define Cystic Fibrosis?
- This is inherited, an autosomal recessive disease that affects nearly all the exocrine glands in the body.
- Cystic fibrosis transmitted autosomal recessive trait.
- Cystic fibrosis is also called mucoviscidosis of the pancreas.
- Cystic fibrosis is a disorder of mucous secretion with occlusion of exocrine gland function.
- This will produce sweat with very high contents of sodium and chloride.
What is the presentation of the Cystic Fibrosis?
- It is most common in Europe, with a frequency of 1 in 2000 live births.
- In Afro-Americans, its incidence is around 2%.
- It is rare in Asians.
- Cystic fibrosis is present at birth and persists throughout life.
- Cystic fibrosis is a quite common genetic disorder in the Caucasian population.
- Almost all exocrine glands produce abnormal mucus that obstructs the glands and ducts and damages tissue.
- Because of this, abnormal exocrine secretion in cystic fibrosis develops mucous plugs that obstruct the pancreatic ducts.
- The pancreatic enzymes like amylase, lipase, trypsin, and chymotrypsin cannot be expelled into the duodenum.
- These secretions will either be absent or very low in the duodenal aspirate.
- There are abnormal secretions in:
- Lung bronchi.
- Small intestine.
- Pancreatic duct.
- Bile ducts.
- Skin (sweat glands).
Describe the spectrum of cystic fibrosis?
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
- There is recurrent productive cough, dyspnoea, and wheezing.
- There are recurrent airway infections.
- A pancreatic deficiency (pancreatic insufficiency) may occur due to an abnormally viscous fluid, which decreases amylase and lipase activity.
- There are decreased trypsin and chymotrypsin levels.
- There is a decreased bicarbonate level.
- Pancreatic insufficiency also affects glucose metabolism through delayed insulin response.
- There may be recurrent pancreatitis.
- There may be distal intestinal obstruction syndrome.
- There is decreased fat absorption.
- There is nutritional deficiency.
- There are chronic liver diseases.
- The patient may show the effects of the disease through a reduced level of Vitamin A, carotenoids, Vitamin E, cholesterol, and essential fatty acids.
- In the USA, 1/3 of the patients with cystic fibrosis are adults.
- These patients have an increased risk of malignancies of the GI tract, arthropathies, and osteopenia.
- There are electrolytes in the sweat.
What is the mechanism of cystic fibrosis?
- The mucus glands produce abnormal viscid secretions.
- This abnormal secretion may inspissate and plug the ducts of the glands.
- This process will lead to obstructive complications.
- In the lungs, it may lead to recurrent bronchopneumonia, which is a fatal complication.
- The most common pathogens are Pseudomonas and Staphylococcus aureus.
- Next, the most common complication is the destruction of the exocrine portion of the pancreas;
- The pancreatic disease will lead to malabsorption, steatorrhea, digestive abnormalities, and malnutrition.
- Less common abnormalities are biliary liver cirrhosis due to bile duct obstruction.
- In newborns, meconium may lead to paralytic ileus (meconium ileus) and intestinal obstruction.
- There is an increased loss of chloride and sodium in the sweat. This factor is the basis for the diagnosis of cystic fibrosis.
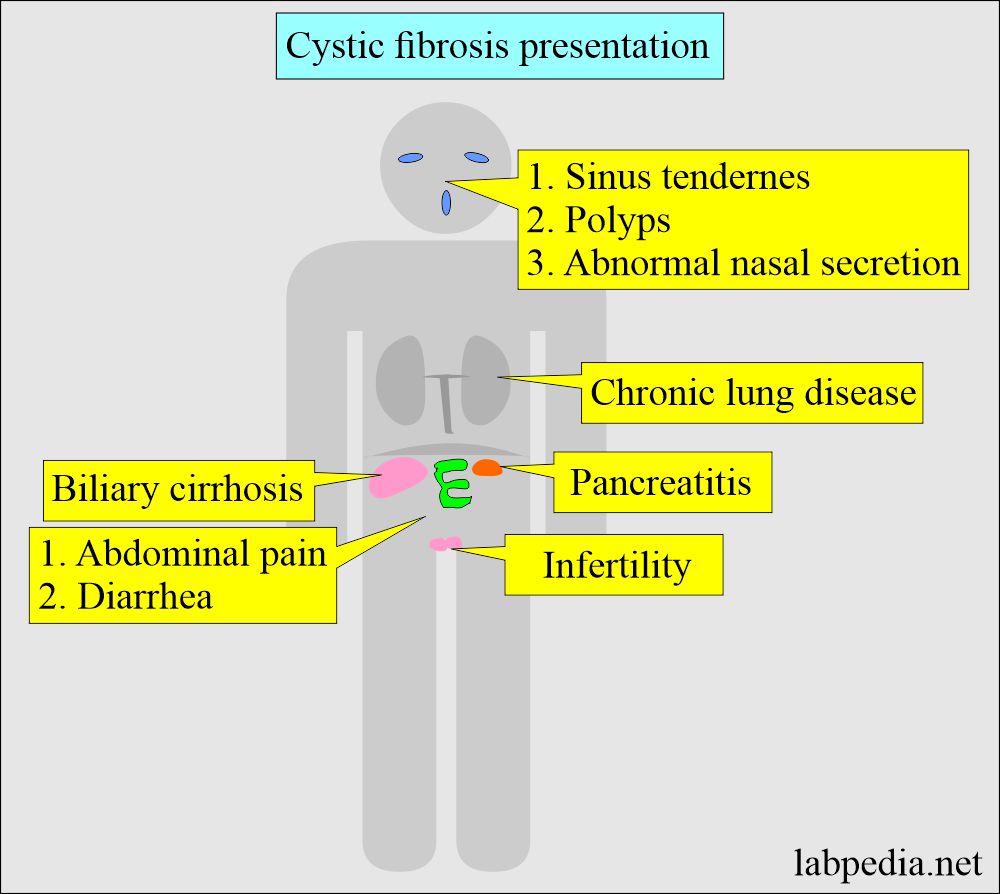
What is the clinical presentation of Cystic Fibrosis?
- Cystic fibrosis is suspected in a young adult if there is a history of:
- Chronic lung disease (Bronchiectasis).
- A chronic cough with sputum production.
- Recurrent hemoptysis.
- There are sinus tenderness, purulent nasal secretion, and nasal polyps.
- Infertility.
- Pancreatitis.
- Chronic lung disease (Bronchiectasis).
- There may be abdominal pain, diarrhea, and steatorrhea.
- Almost all men have a congenital bilateral absence of the vas deferens with azoospermia.
- There may be the occurrence of gallstones.
- There may be biliary cirrhosis.
How will you diagnose Cystic fibrosis?
- It depends upon the following:
- The clinical symptoms.
- Positive sweat test of increased chloride and sodium amount.
- The serum concentration of immunoreactive trypsin is elevated in a newborn with cystic fibrosis.
- The measurement of these enzymes is the basis of the cystic fibrosis newborn screening program.
- Genetic analysis can be used to counsel families on gene carrier status.
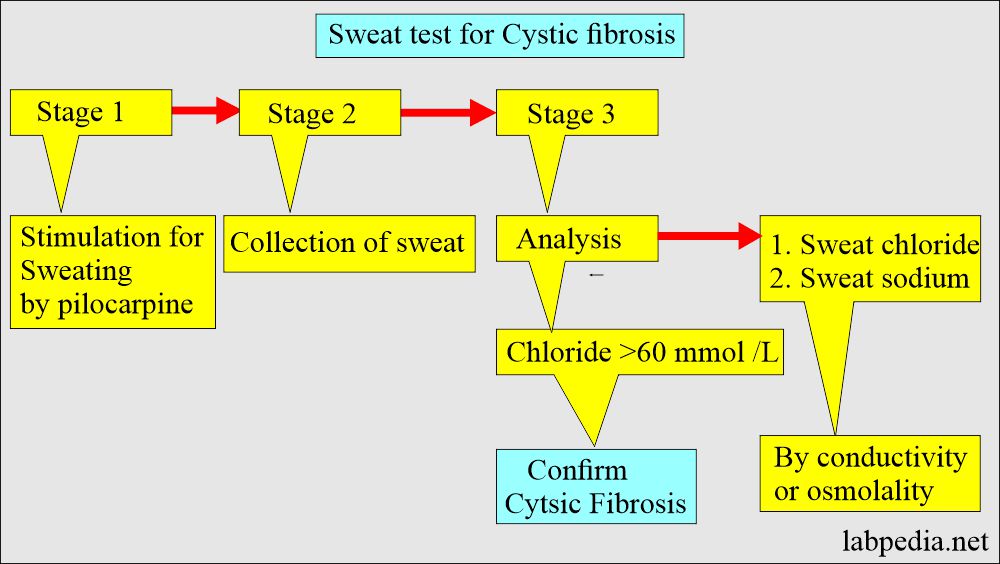
How will you collect sweat to diagnose cystic fibrosis?
- Sample collected in three stages:
- Stimulation for sweating by pilocarpine (This is a muscarinic alkaloid drug that can induce sweating). There is a local injection into the skin to produce sweat, which is collected.
- This is the iontophoresis procedure.
- Collection of the sweat.
- Sweat can be collected on gauze or filter paper.
- Qualitative or quantitative analysis of sweat.
- Electrode method: The electrode is applied to the skin, where the colorless chemical produces sweat. It may take 5 minutes to collect the sweat.
- Electrodes are stimulated, and sweat is put on the gauze or paper.
- This collected sample is sent to the lab.
- The sweat, considered a good collection, should weigh 50 mg. If this is <50 mg, that is not a good sweat collection.
- A new method does not require a blood sample; instead, a sweat-analyzing skin patch can be used.
- Sweat chloride >60 meq/L (>60 mmol/L) and sodium >70 meq/L (>70 mmom/L) are considered abnormal.
What are the critical issues with sweat electrolyte tests?
- The proper collection of sweat is very difficult.
- Avoid evaporation and contamination of the sample.
- Collect a sufficient amount and minimize skin reactions.
- The minimum weight or volume of the sweat is critical for the sweat test.
- In newborns, sodium and chloride levels are higher in the first three days of life, and they come down after the fourth day.
What are the normals for Cystic fibrosis?
Source 1
Sweat Chloride (iontophoresis)
- Normal = 5 to35 meq/L
- Marginal = 30 to 70 meq/L
- Cystic fibrosis = 60 200 meq/L
Sweat Sodium ((iontophoresis)
- Child and adult = 10 to 40 meq/L
- Child, X: = 27 meq/L
- Adult, X: = 33 meq/L
- Cystic fibrosis = 70 to 190 meq/L
- To convert into SI unit x 1.0 = mmol/L
Source 2
Sodium values in children
- Normal = <70 meq/L
- Abnormal = >90 meq/L
- Equivocal = 70 to 90 meq/L
Chloride values in children
- Normal = <50 meq/L
- Abnormal = >60 meq/L
- Equivocal = 50 to 60 meq/L
Another source
- Normal Chloride = 5 to 35 mmol/L (<50 meq/L)
- Cystic fibrosis evidence:
- Sweat Chloride = 40 to 59 mmol/L (does not confirm the diagnosis of cystic fibrosis).
- Sweat chloride less than or equal to 39 mmol/L in an infant over 6 months old is an unlikely diagnosis of cystic fibrosis.
- Sweat Chloride 60 or >60 mmol/L is diagnostic of cystic fibrosis.
- Normal Sodium = <70 mmol/L (<70 meq/L)
- Cystic fibrosis = >90 mmol/L (>90 meq/L)
What are the causes of increased Sweat electrolytes?
- Cystic fibrosis of the pancreas.
- Sodium
- 50 to 140 meq / L and mean maybe 103 meq / L.
- Chloride
- Normal = 4 to 60 meq / L.
- In diseases, it is 50 to 120 meq / L.
- Potassium
- Normal mean = 9 meq / L.
- In the disease = mean 15 meq / L.
- Sodium
- Other causes than cystic fibrosis are:
- Addison disease (Untreated adrenal insufficiency).
- Pseudohypoaldosteronism.
- Some unusual diseases like Glucose–6 phosphate deficiency, glycogen storage disease, and diabetes insipidus.
- Anorexia nervosa
- Atopic dermatitis.
- Familial cholestasis.
- Klinefelter syndrome.
- Nephrosis.
- Untreated hypothyroidism.
- Protein-calorie malnutrition.
- Ectodermal Dysplasia.
- Environmental deprivation.
- Nephrosis and nephrogenic diabetes inspidus.
- Psychosocial failure to thrive.
Questions and answers:
Question 1: Can you see sweat test positive in some diseases?
Question 2: What is difficulty in sweat test?