Surgical Pathology:- Part 2 – Types of Biopsies
Types of biopsies
How do you send the biopsy?
- Always send the biopsies in the formalin.
- The commercially available formalin is diluted to 10 % with distal water.
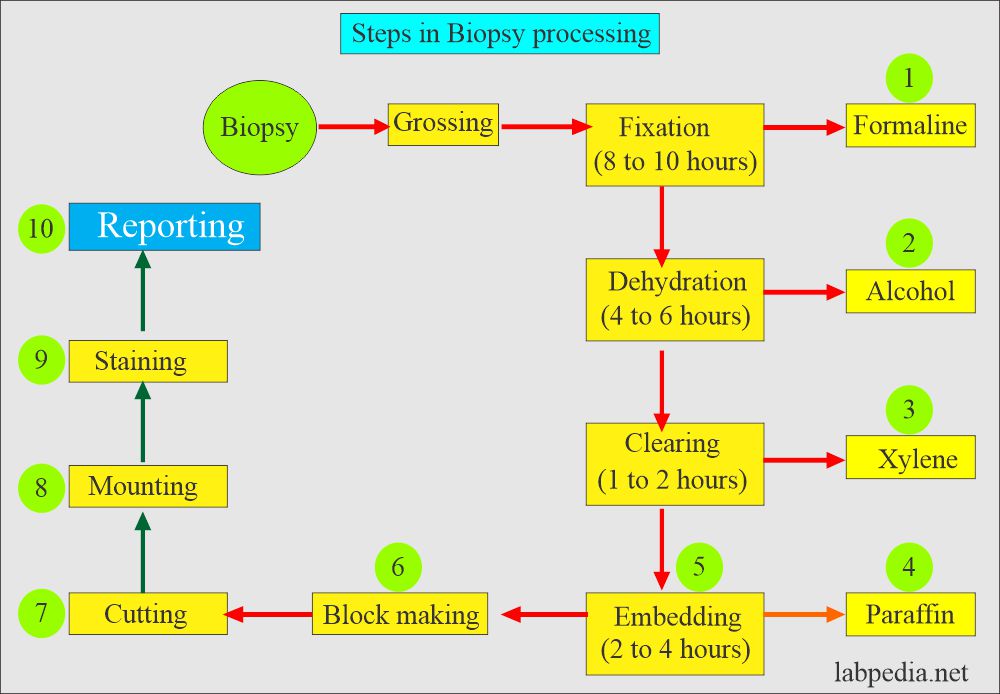
What are the steps for fixing surgical pathology?
- Formalin aims to fix the tissue to stop the autolytic changes in the biopsies.
- All specimens should be placed immediately following excision into 10% neutral buffered formalin to allow them to “fix.”
- Ideally, the amount of fixative should be at least ten times the volume of the specimen.
- However, this might not be practical for very large specimens (which should be transported to the laboratory as soon as possible).
- Squeezing small biopsies must be avoided, as this can cause cells to become distorted and unidentifiable when examined microscopically.
- Large specimens must not be ‘squeezed’ into too small containers as this compromises fixation and may adversely affect the final report.
- The proper fixation time needed is between 10 to 24 hours.
What are the precautions for sending the biopsy?
- Never send the biopsy in distal water or saline. The tissue will be autolyzed in these liquids, and proper histopathologic changes will not be seen.
How would you report surgical pathology?
- 80% of Diagnostic Biopsies were reported within 7 Calendar Days.
- In urgent cases, a biopsy can be reported in 3 days.
What are the special biopsies types?
What Biopsy Specimens are needed for Bacteriological Examination?
- Suppose the biopsy requires bacteriological investigation (for example, a lymph node that may be infected with tuberculosis). In that case, part of the biopsy should be sent separately without fixative in an appropriate sterile container to the laboratory with a Microbiology request form.
- The Cellular and Anatomical Pathology and Microbiology request forms should be identified with the ‘Danger of Infection’ labels and double-bagged if a high-risk pathogen is suspected (see below).
- Whenever there is suspicion about the possibility of tuberculosis, it must always be sent in formalin.
What are the possibilities of the biopsy from various sites?
- Bone marrow for hematological diseases.
- Breast tissue for benign and malignant diseases.
- Endometrial tissue.
- Esophageal tissue for gastroesophageal reflux disease.
- Small intestine for gluten-sensitive enteropathy.
- Kidney for glomerular disease and lupus nephritis.
- Liver for cirrhosis, hemochromatosis, and fever of undetermined origin.
- Lung biopsy.
- Pleural biopsy.
How will you do a liver biopsy to determine dry copper and iron weight?
- Specimens for dry copper or dry iron weight must be sent dry. Please do not place the specimen in formalin, which will invalidate the result.
How would you take a skin biopsy for Hansen’s disease?
- Select the most active margin of the most active lesion.
- Obtain a full-thickness biopsy, including the subcutaneous fat.
- Either elliptical or punch biopsy is OK (a 4 mm punch is sufficient).
- Send in 10% neutral buffered formalin.
How will you take Muscle biopsy?
- The muscle biopsy sample is immediately divided.
- One portion remains unfixed.
- Meanwhile, smaller portions are placed into formalin and glutaraldehyde fixatives.
- Fix the tissue on the card so that the muscles should remain straight.
- The specimens are then sent to the laboratory for specialized processing and interpretation.
- Routine evaluation of the muscle biopsy sample involves the examination of formalin-fixed, paraffin-processed sections.
- Unfixed frozen sections with standard histological and enzyme histochemical stains at the light microscopic level.
- Immunohistochemical stains are utilized to diagnose various muscular dystrophies.
- Electron microscopic examination of the glutaraldehyde-fixed portion of the biopsy is performed when the light microscopic studies are inconclusive.
How will you have a Kidney biopsy?
- These are done with the help of a needle.
- The material is sent in formalin.
- Special stains and immunochemistry are done to diagnose various types of renal diseases.
How will you do Bone marrow biopsy?
- Aspiration of bone marrow is done with a wide-bore needle.
- Trephine biopsy is the real bone tissue that is taken.
How will you do a Testicular biopsy?
- This may be:
- An open biopsy is to take surgical tissue from the testes.
- A punch biopsy may be taken when small tissue is needed.
- FNA is done with a fine needle of 23 or 25 gauge.
How will you do the Spleen biopsy?
- This can be taken:
- FNA can be done.
- Also, you can take a biopsy with a wide-bore needle, but there are chances for the possibility of bleeding.
How will you do Lymph node biopsy?
- This can be done by:
- FNA can be done.
- Open lymph node biopsy gives better appreciation.
How will you do a Cervical biopsy?
- Cervical tissue is taken by curettage or scraping and making the smear.
Questions and answers:
Question 1: What is the purpose of a testicular biopsy?
Question 2: What is the purpose of a kidney biopsy?
- Note that more details are provided in surgical pathology part 1.