Sputum for fungi (Fungus, Yeast and Molds)
Sputum for fungi
What sample is needed for Sputum for fungi?
- The sputum sample is needed to find the presence of the fungus.
- Advise patient to get deep cough sputum.
- The sample can be refrigerated for up to 24 hours.
- Sputum may be stable at room temperature for 72 hours.
- Do not freeze the sample.
- Store it at room temperature.
What are the precautions for Sputum fungi?
- Sputum should be examined as fresh as possible because Histoplasma capsulatum dies rapidly at room temperature.
- Saprophytic fungi, such as candida and commensal bacteria, rapidly multiply if kept at room temperature, interfering with the separation of pathogenic fungi.
- Try to minimize contamination with the saliva.
- Stop aspirin, ibuprofen, naproxen, and warfarin, which will thin the bronchial secretion.
How will you collect a good sample of Sputum for fungi?
- Brush your teeth and rinse your mouth (don’t use antiseptic mouthwash).
- Take a couple of long, deep breaths.
- Breathe in deeply again and cough hard until sputum comes up.
- Spit out the sputum into the sample cup.
- Keep coughing up sputum until there is approximately 1 teaspoon.
What are the indications for Sputum for fungi?
- This is done to diagnose respiratory fungal infection.
- In the case of :
- shortness of breath
- fever
- A cough that is, most of the time, dry.
- Muscle aches and pains.
How will you discuss the microbiology of Fungi?
- Fungi are microorganisms. The majority are nonpathogenic.
- Deep fungi or systemic fungi are characterized by the involvement of the visceral organs or are penetrating types of infection.
- Actinomycetes and Nocardia are bacteria that cause infections resembling fungal infections.
- What are the common types of fungi?
- Dimorphic fungi:
- Blastomyces dermatidis (Blastomycosis).
- Coccidioides immitis (Coccidioidomycosis).
- Cryptococcus neoformans (Cryptococcosis).
- Histoplasma capsulatum (Histoplasmosis).
- Sporothrix schenkii (Sporotrichosis).
- Candida albicans.
- Candida tropicalis.
- Aspergillus fumigatus.
- Aspergillus flavus.
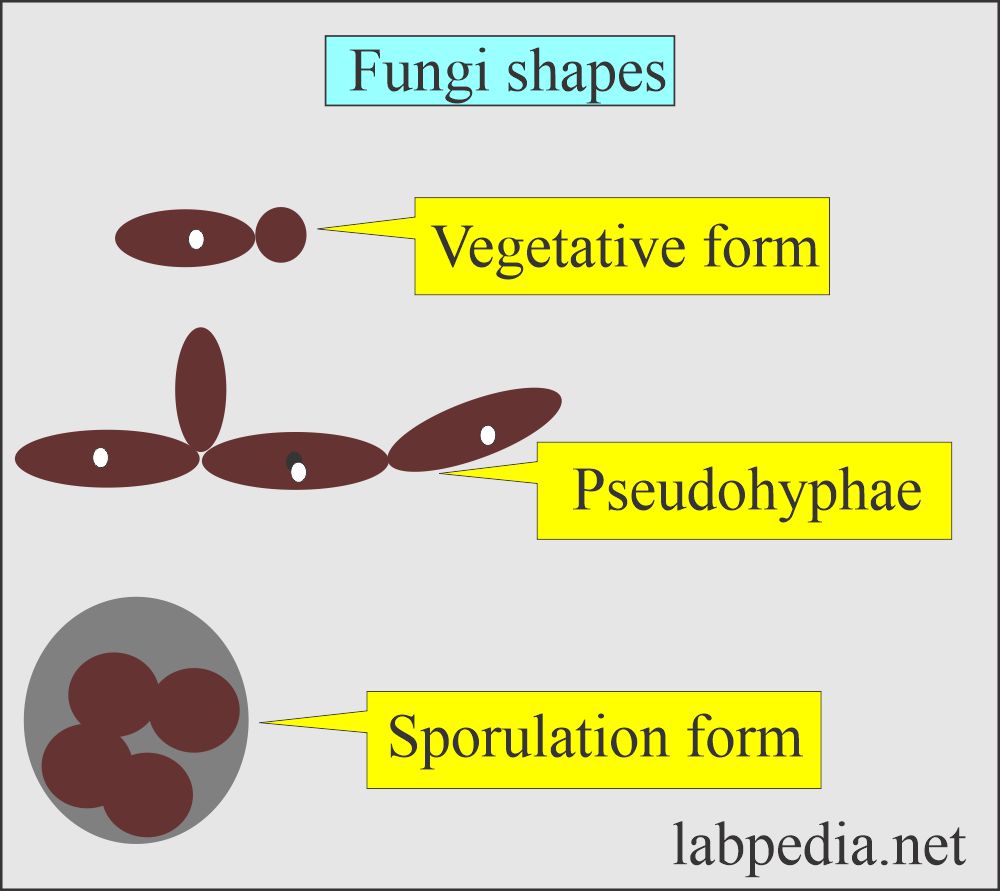
Fungi are eukaryotic organisms and are divided broadly into three main groups:
What are the Yeasts?
- These are single-celled. These are facultative anaerobes.
- Candida e.g. C.albicans
- Cryptococcus, e.g., C. neoformans.
- Torulopsis.
- Trichosporum.
- Malassezia.
- Rhodotorula.
What are the Molds?
- These are filamentous fungi (hyphae). These are aerobic.
- These fungal hyphae form mycelium.
- Mycelium has two functions:
- The vegetative mycelium penetrates into the medium and absorbs nutrients.
- Aerial mycelium has reproductive structures for the spread of molds.
What are the Dimorphic fungi?
- This exists in both the above forms.
-
- Blastomyces dermatidis, causing North American blastomycosis.
- Histoplasma capsulatum, causing Histoplasmosis.
- Histoplasma duboisii, causing African histoplasmosis.
- Sporothrix schenckii, causing Sporotrichosis.
- Some of the fungi that exist in either form are called dimorphic fungi.
- The cell wall of the fungi is thick and composed of polysaccharides.
- Fungi are not motile.
What are the factors leading to fungal infections?
- Most of these fungal diseases are opportunistic and need some predisposing factor leading to Mycosis.
- Predisposing factors are:
- Cancers.
- Radiation.
- Chemotherapy.
- Antibiotics.
- Immune deficiency syndrome.
- A sputum fungal smear is one of the best ways to determine whether your respiratory illness is caused by fungus.
- A positive smear for fungus indicates a fungal infection.
What are the fungal infections seen in the respiratory system?
- The following types of fungal infections may be seen in the respiratory system:
- Aspergillosis.
- Blastomycosis.
- Coccidioidomycosis.
- Histoplasmosis.
- Cryptococcus.
- Pneumocystis carinii.
What is the normal for Sputum fungi?
- A normal (negative) result means no fungus was seen in the test sample.
Abnormal Results
- When sputum is positive for fungal infection.
What is the procedure for Sputum fungi identification?
- The smear can be stained.
- Wet preparation:
- Take skin scraping, hair, nail clipping, vaginal swab, sputum, or body fluids.
- Make a thin sputum smear and mix it with KOH (10%).
- Then, the smear is examined under the microscope.
- Advantages of wet preparation:
- Same day result.
- In some cases, accurate diagnosis.
- Disadvantages:
- Good with the expert person.
- False positive and false negative cases are seen.
- Gram stain (invented by Hans Christian Gram).
- Make a sputum smear on the slide.
- Fix it with heat.
- Stain with Gram’s stain.
- See under the microscope.
- Wright stain or Giemsa:
- It is used for histoplasmosis.
- Papincolaou stain:
- It can be used like gram stain and has the same advantages and disadvantages.
- Indian ink or nigrosin:
- This preparation is used for Cryptococcus.
- Tissue biopsy:
- Tissue biopsy may be stained with PAS (periodic acid-Schiff) or methenamine silver stain.
- It is dependent upon the number of organisms present in the biopsy tissue.
- Culture:
- It is done on the Saubourads dextrose agar medium (SDAM).
- It gives a definite diagnosis.
- It depends upon the number of organisms present in the culture specimen.
- It also depends upon the specific media used for the culture.
- Candida albicans show raised creamy smooth colonies after 72 hours on SDAM.
- Another media used is nutrient agar media.
- Fungi grow slowly, and it may take several weeks to grow fungi.
- C. neoformans form white, granular, or wrinkled first and later on moist, shiny, and mucoid colonies on SDAM.
- Serology:
- It may be helpful in some fungal infections like histoplasmosis, coccidioidomycosis, and South American blastomycosis.
- Two samples are needed: one to find the cause of fungal disease and one to repeat for rising titer after 1 to 2 weeks.
- So, the confirmation is delayed for 2 to 3 weeks.
- There may be a false negative result or false positive results, and nondiagnostic results as well.
- Skin test:
- The advantage is the results in 24 to 48 hours.
- The disadvantage is that antibodies need time to develop.
Questions and answers:
Question 1: What are the yeast?
Question 2: What are the most important precautions?