Renal Functions:- Part 2 – Renal Functions Assessment
Renal Functions Assessment
What sample is needed for Renal Function Tests?
- A fresh serum is needed.
- Fresh urine is also needed.
How will you assess renal functions?
- For concentration and Dilution, advise Specific gravity (Sp. Gr).
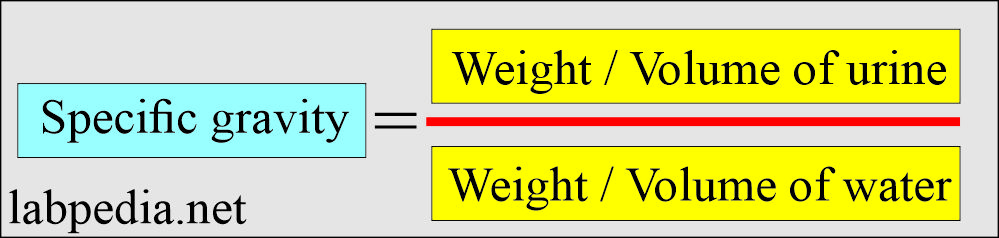
Specific gravity
How will you explain the Specific gravity?
- It measures the concentration of particles, including waste products and electrolytes, in the urine.
- Specific gravity is the weight of urine compared to that of distal water (water’s specific gravity is 1.000).
- Particles in the urine give it weight or Sp.Gr.
- Specific Gravity evaluates the concentrating and excretory power of the kidneys.
- The renal diseases will decrease the concentrating power, leading to low Sp.Gr.
- When reporting Sp. Gr keep in mind the presence of glucose and proteinuria.
- An Overhydrated person will have diluted urine and low Sp.Gr.
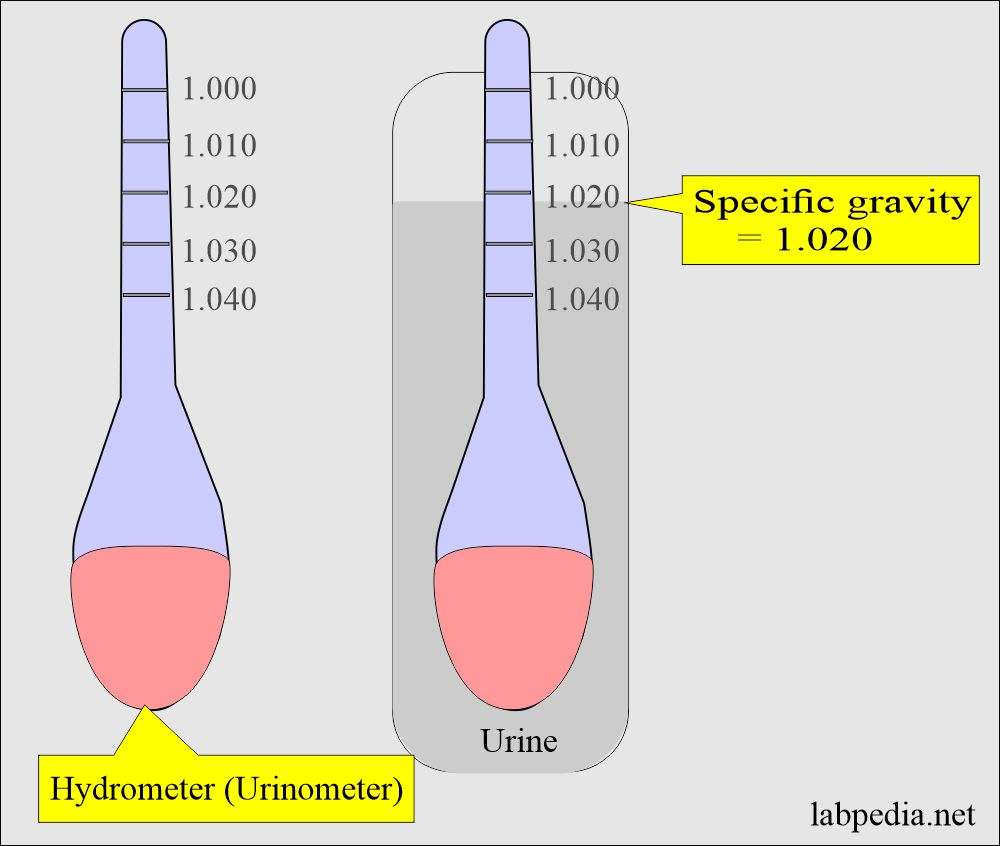
- High specific gravity indicates concentrated urine and low specific gravity indicates diluted urine.
- To find the renal function as concentration and dilution:
- Concentration = Specific Gravity > 1.025
- Dilution = < 1.003
What is the Phenolsulfonphthalein (PSP) secretion test?
- PSP is an exogenous material given to the patient to assess the tubular excretory function of the kidney.
- This will reflect the renal plasma flow and tubular secretory function.
- It is injected into the patient and measured every 15 minutes.
- 94% of the PSP is secreted with very little filtered by the glomeruli, and it binds albumin in the blood.
- This test PSP is difficult; now, p-aminohippuric acid is used to find tubular secretion and renal blood flow.
- Normal
- >25% in urine in 15 minutes (25% to 50% PSP should be secreted in the first 15 minutes).
- 10% to 15% additional secreted in the next 15 minutes.
- 55% to 75% in 2 hours.
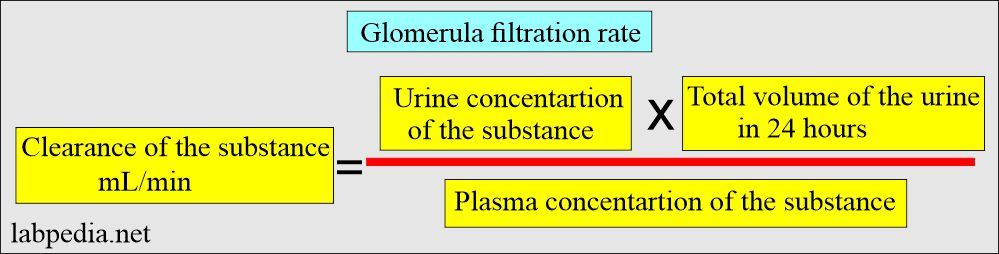
Glomerular filtration rate (GFR)
How will you define the Glomerular filtration rate (GFR)?
- This is the quantity of blood cleared of substances like creatinine and urea per unit of time.
- Substances like creatinine and urea filter through the kidney glomeruli at the rate of milliliters (mL) per minute.
- GFR depends upon the following:
- Plasma concentration of the substance.
- The excretion rate of the kidney will reflect the following:
- Renal plasma flow.
- Glomerular filtration rate.
- The substance should not be reabsorbed, secreted, synthesized, or degraded in the nephron.
- GFR is the most reliable measure of kidney function.
- GFR may be measured by obtaining clearance for exogenous substances like inulin.
- Endogenous substances like creatinine and urea nitrogen may measure GFR.
What is normal GFR?
- Creatinine clearance:
- Male = 97 to 137 ml/minute.
- Female = 88 to 128 mL/minute.
- Inulin clearance:
- Male = 110 to 150 ml/minute.
- Female = 105 to 132 ml/minute.
- Urea clearance:
- Maximum = 60 to 100 ml/minute.
Serum Creatinine
What are the details about Serum Creatinine?
- Creatinine is the end product of the catabolism of creatine phosphate.
- Free creatinine, a waste product of creatine metabolism, is present in all body fluids and secretions.
- Creatinine is freely filtered by the glomerulus.
- There is diurnal variation when it is low at 7 AM and high at 7 PM.
- There is a slight increase after the meal, especially after the meat in the diet, because a small amount is present in the meat.
- There is minimal effect on liver function.
- This is the measure of kidney function.
What is the normal serum creatinine?
- serum creatinine = 1.0 to 1.5 mg/dL
Creatinine clearance (GFR = Creatinine clearance)
- It estimates the renal excretion or filtering capacity of the kidney.
- Normal creatinine clearance
- Male = 97 to 137 ml/minute
- Female = 88 to 128 ml/minute.
Urine albumin
What is the role of serum albumin in kidney function?
- Evaluation of the protein is a sensitive indicator of kidney function.
- Normally, proteins are not present in the urine because the spaces in the glomerulus are too small to allow the protein to filter out.
- In the case of glomerulus membrane damage due to diseases, spaces become larger and allow the passage of protein in the urine.
- Protein (albumin) in the urine can indicate kidney disease.
- Proteinuria in pregnant women is an indicator of pre-eclampsia.
- Albumin levels can increase with heavy exercise, poor blood sugar control, urinary tract infections, and other illnesses.
- What is normal urine albumin?
- The level in a 24-hour urine sample is less than 30 mg/day.
Microalbuminuria
How will you define microalbuminuria?
- This is an early sign of kidney disease, especially in people with diabetes.
- This is basically albumin in minute amounts, indicating glomerular membrane damage.
- Diabetic patients should have this test for microalbuminuria at least yearly.
- What is normal microalbuminuria?
- Urine normally in healthy people contains from 30 mg/L to 300 mg/L of albumin.
Blood urea nitrogen (BUN)
- Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN) is another measure of waste (urea) in the blood.
- BUN is used to measure whether a person is receiving the correct amount of dialysis.
- What is the normal BUN level?
- For a healthy adult is 7 to 20 mg/dL
- In children is 5 to 18 mg/dL.
- Patients on dialysis have higher BUN levels, usually 40 to 60 mg/dL.
Questions and answers:
Question 1: What is the importance of microalbuminuria?
Question 2: What is the difference between urea and BUN?