Red Blood Cell (RBC):- Part 5 – Summary of RBC Morphology Interpretations and Diagnosis (Table)
Summary of RBC Morphology Interpretations
What sample is needed for RBC Morphology Interpretations?
- Direct blood smear or blood in EDTA can be used.
What are the indications for RBC Morphology Interpretations?
- To diagnose anemia.
- For typing of the anemia.
How will you Summarize RBC Morphology and Interpretations?
| RBC morphology | Lab findings | Causes |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

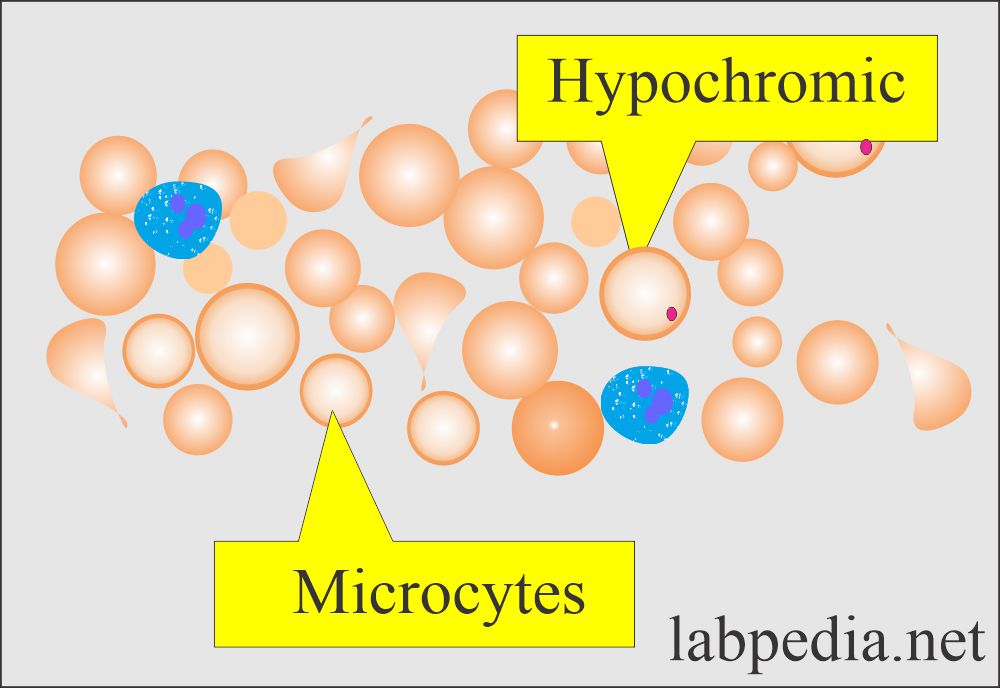
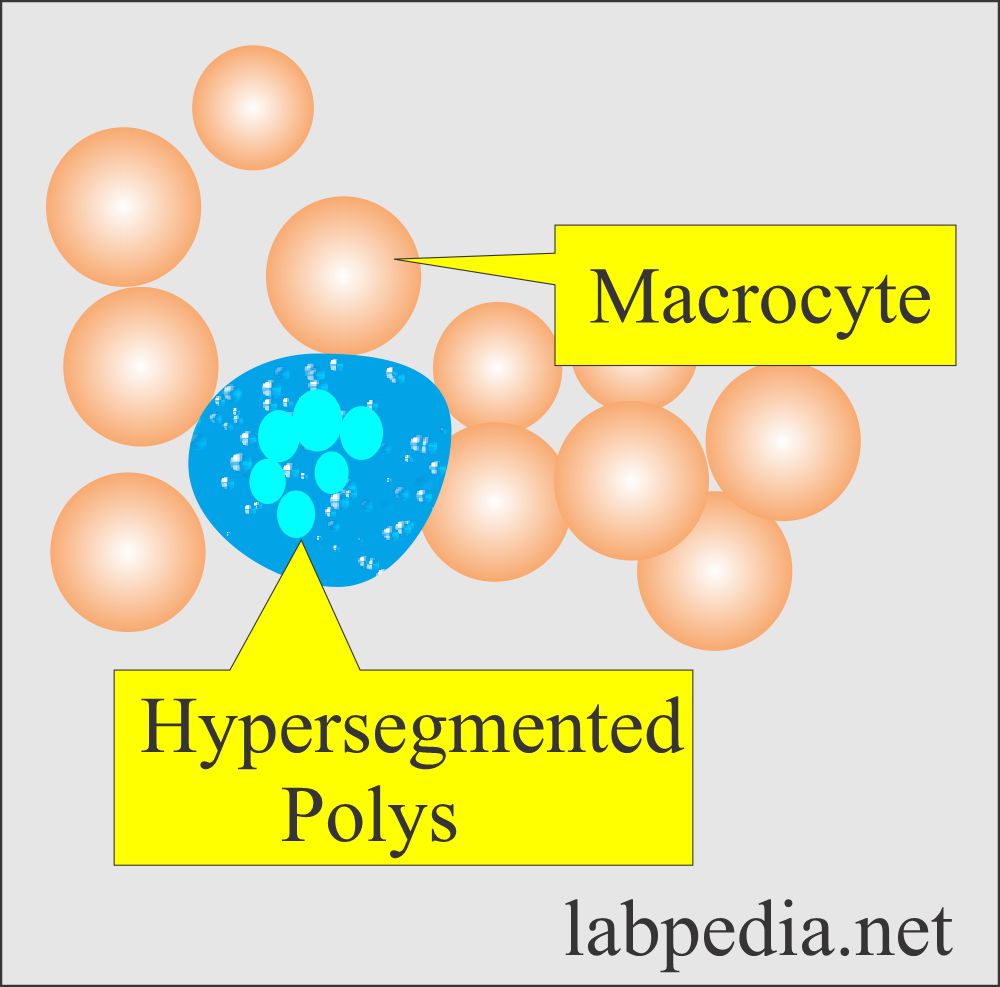
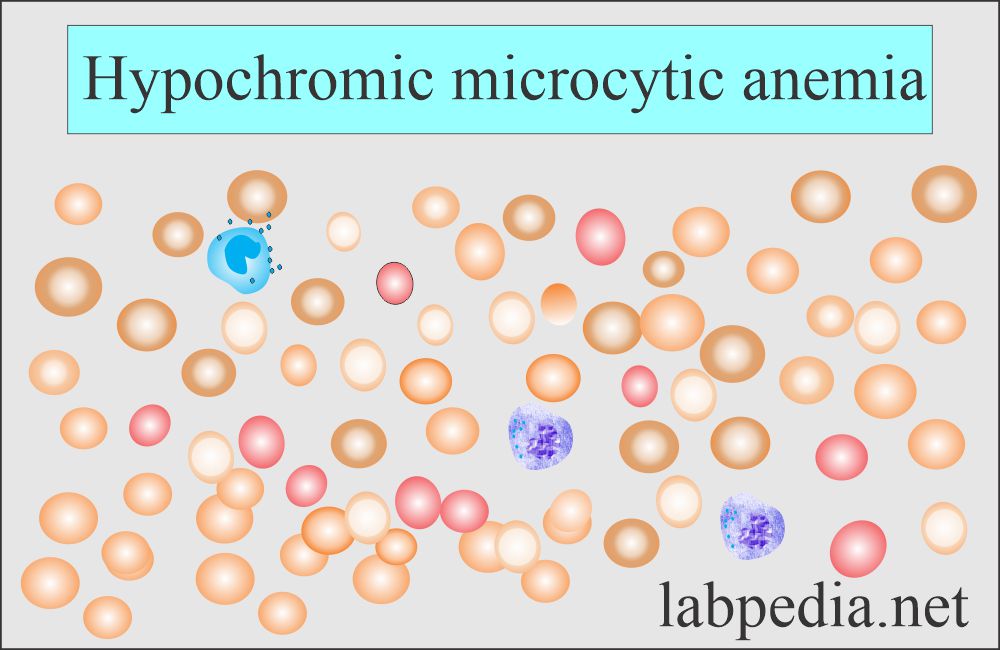
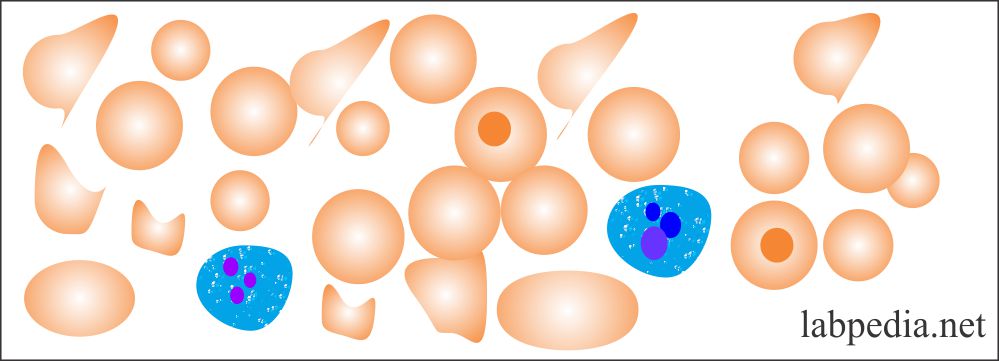
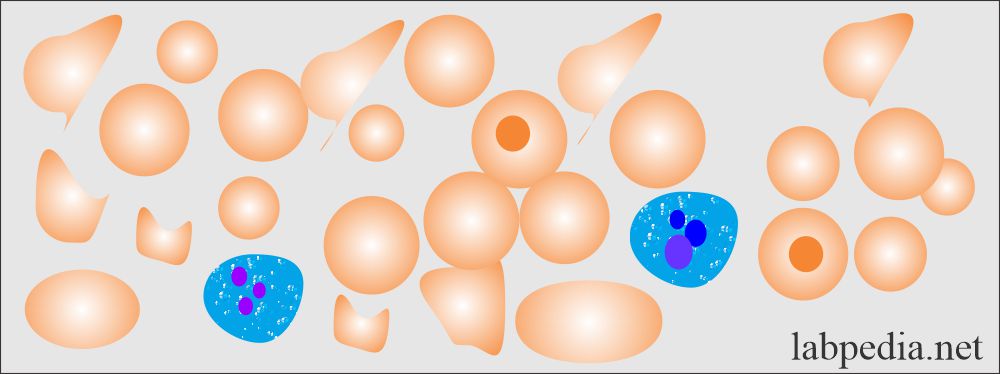
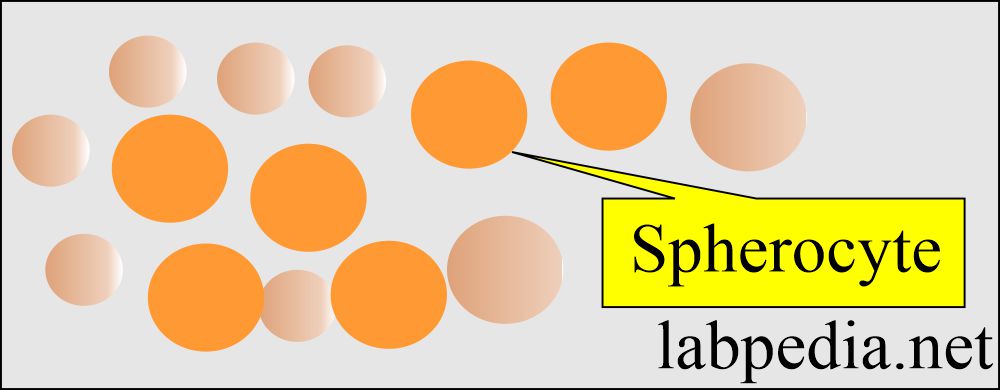
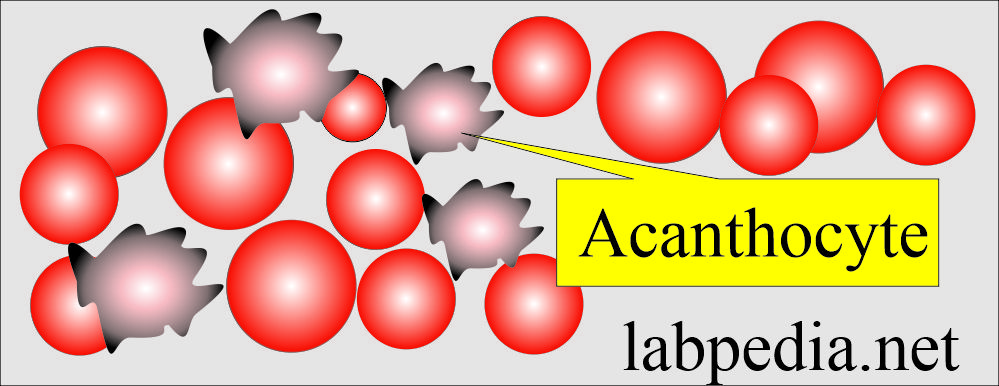
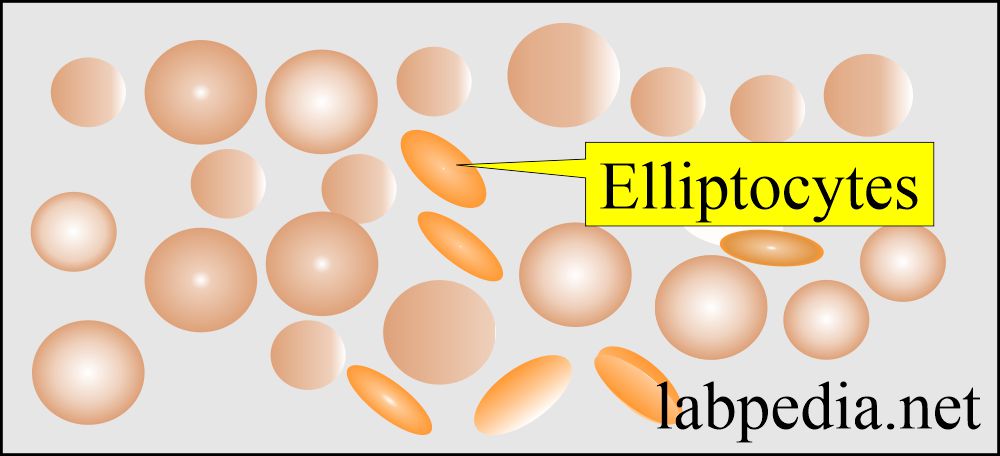
Nice more and more know this subject
Thanks.
Thankyou for your information
Thanks.