Red Blood Cell (RBC):- Part 3 – Interpretations of Peripheral Blood Smear
Interpretations of Peripheral Blood Smear
What sample is needed for the Peripheral Blood Smear?
- The blood sample may be in the EDTA or make a fresh blood smear.
What are the indications for Peripheral Blood Smear?
- Peripheral blood smear gives very significant findings of RBC and white cells.
- To see the effects of drugs on RBC and white cells.
- To find the congenital abnormalities of the cells.
- To find the acquired abnormalities of the cells.
- A peripheral blood smear can give information about acute and chronic infection, infestation, leukemia, etc.
What is the function of Peripheral Blood Smear?
- The differential count on the peripheral blood smears gives us information about anemias, leukemias, and any other abnormality of the blood cells.
- DLC and CBC are less expensive, easy to perform, and can be done in a short time.
- Peripheral blood smears under the expert eye can reveal information about the three cellular components: RBCs, white cells, and platelets.
- All the types of leukocytes can be differentiated, and any abnormality can be found.
What are the RED Blood Cells abnormalities?
RBC size abnormality;
- Microcytes are small in size.
- These are seen in iron deficiency anemia, hereditary spherocytosis, and thalassemia.
- Macrocytes are large and seen in:
- Vit B12 or folic acid deficiency.
- Liver disorders.
- Post Splenectomy anemia.
RBC shape abnormality:
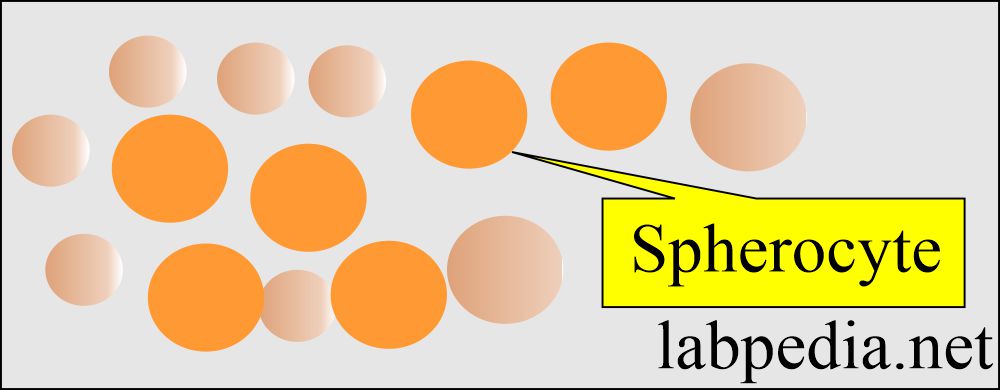
- Spherocytes are small and round. Also, these are thick red blood cells.
- Hereditary spherocytosis.
- Acquired immune hemolytic anemia.
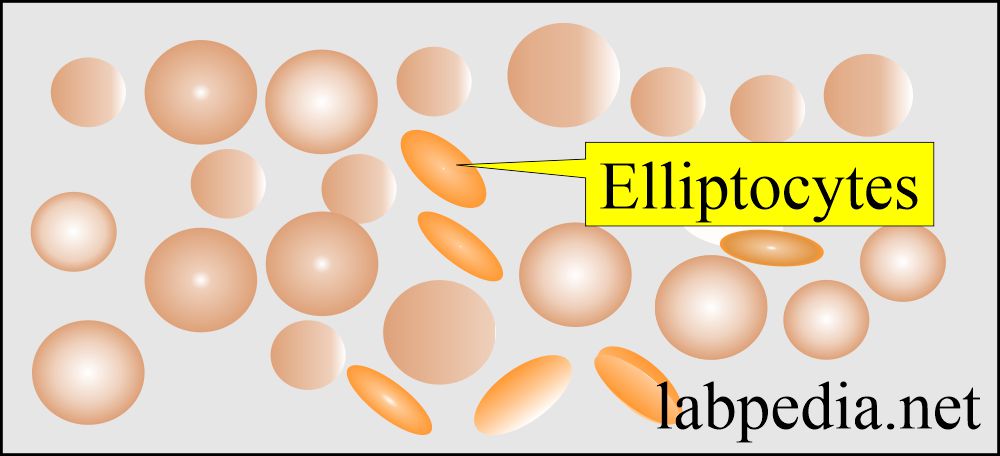
- Elliptocytes: These are sickle-shaped or oval-shaped RBCs, also called pencil-shaped cells; these are seen in:
- Hereditary elliptocytosis.
- Sickle cell anemia.
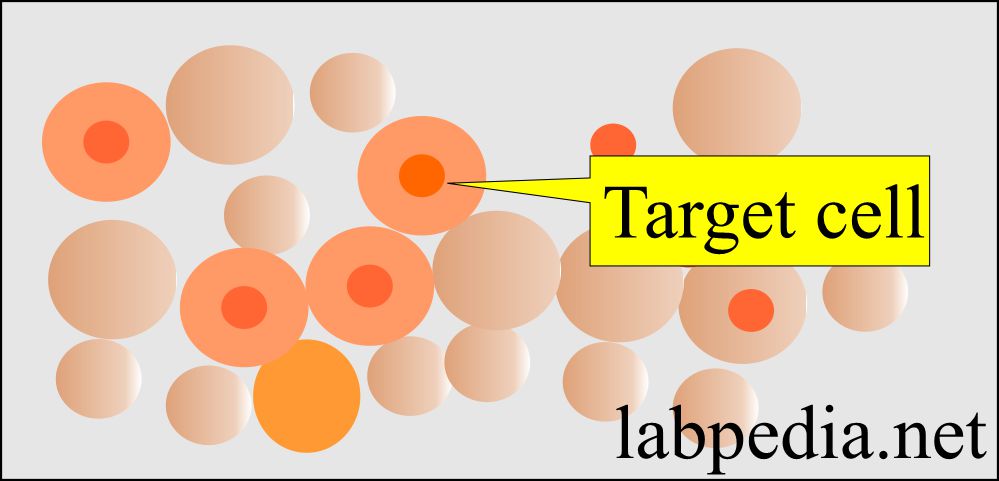
- Target cells have a dark spot in the center, and these are seen in the following:
- Thalassemia.
- Hemoglobinopathies.
- Spiculated RBC has a rough surface or crenated in shape and is seen in:
- Uremia.
- Liver diseases.
- In bleeding ulcers.
- Spur cell is seen in severe liver diseases
- Burr cells These are irregularly contracted red cells. These are seen in :
- Renal diseases.
- Fragmented cells are seen in :
- DIC.
- Post-splenectomy.
- Patient with a heart valve prosthesis.
What are the RBC staining or color abnormalities?
- This will show the staining character of the cells.
- Hypochromasia, when the RBC are pale in color e.g.
- Iron deficiency anemia.
- Thalassemia.
- Hyperchromasia is increased in color intensity, e.g.
- Seen in dehydration.
- The increased concentration of hemoglobin.
What are the Red blood cell intracellular abnormalities?
- Normoblast is not seen normally on peripheral smears. These are seen in the following:
- Normoblast may be seen in the newborn.
- Hemolytic anemias.
- Sickle cell crises.
- Transfusion reaction.
- Erythroblastosis fetalis.
- Marrow space-occupying lesions like Myeloma, leukemia, and fibrosis.
- In physiologic response to hypoxia as in congenital heart disease and congestive heart failure.
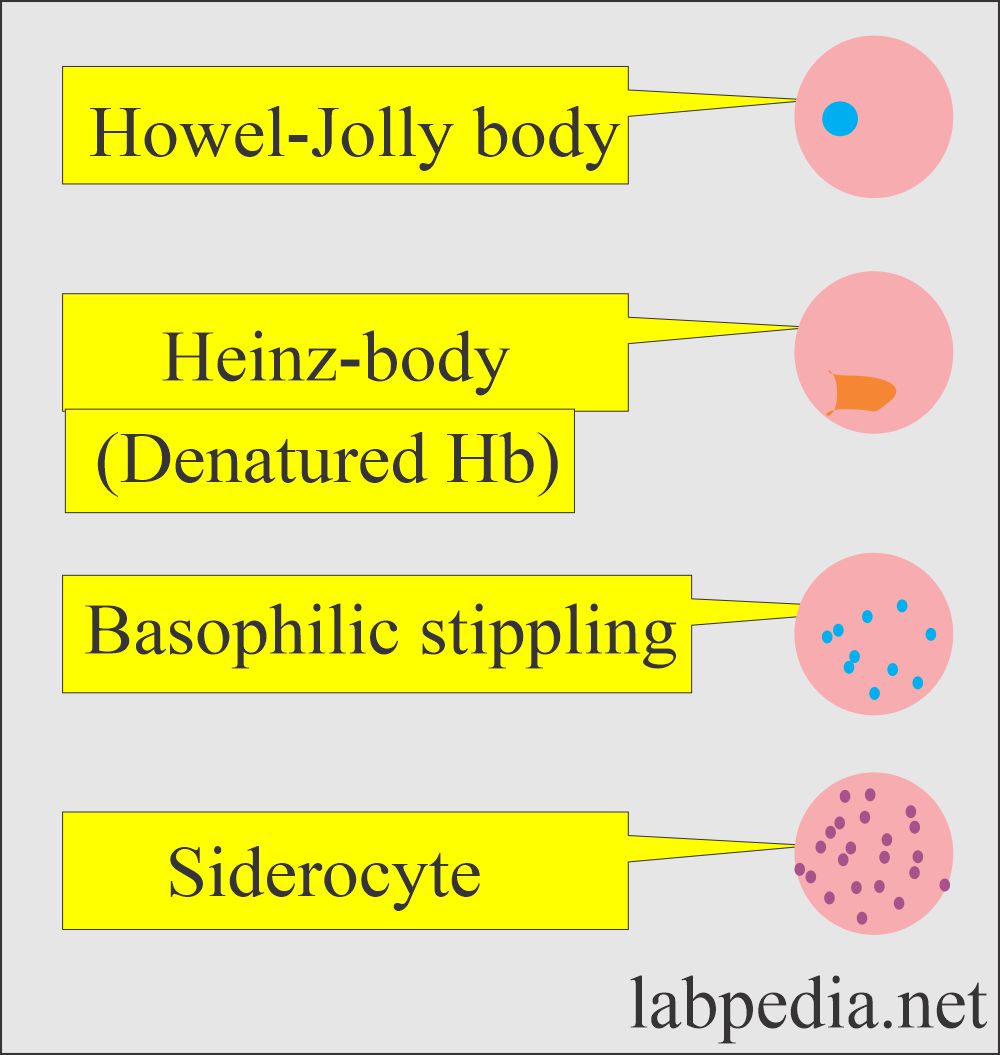
- Basophilic stippling: These are the inclusion in the cytoplasm of RBC seen in the following:
- Lead poisoning.
- Reticulocytosis.
- Howell-Jolly bodies: These are remnants of nuclear material in the RBC and are seen in the following:
- In patients with splenectomy.
- Hemolytic anemia.
- Megaloblastic anemia.
- Heinz bodies are small irregular parts of hemoglobin seen in the following:
- Hemoglobinopathies.
- Hemolytic anemia.
- G 6 PD deficiency.
- Drug-induced injury to RBC.
- Dimorphic red cells This is a feature of sideroblastic anemia.
- Also seen in a patient with post-transfusion.
How will you evaluate White blood cells?
- It can be estimated in number, differential count, and any abnormality of the maturity can be evaluated.
- For leukemia, one will see more immature cells.
- The decreased count will indicate bone marrow depression.
- This may be due to drugs.
- Fibrosis of the marrow.
- Neoplasm.
How will you evaluate Platelet count?
- This can also be estimated from the smear.
- Thrombocytopenia is when the platelets are seen in less number on the smear.
- Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura ( ITP ).
- Hypersplenism.
- Hemorrhage.
- Leukemia.
- Myelofibrosis.
- Cancer chemotherapy.
- Inherited disorders like Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome.
- D I C.
- Systemic lupus erythematosus.
- Infections may be bacterial or viral.
- Thrombocytosis when there is an increased number of platelets on smears.
- This may be seen in the following:
- Infection.
- Some leukemias and lymphomas.
- In splenectomy.
- Polycythemia vera.
- Rheumatoid arthritis.
- Please see the differential count ( CBC ) and RBC morphology for more details.
Questions and answers:
Question 1: Can you evaluate platelets from the peripheral blood smear.
Question 2: What is the cause of Heinz bodies in RBCs?

Hank you