Red Blood Cell (RBC):- Part 2 – Normal Peripheral blood smear, and RBC Morphology
Peripheral blood smear
Sample for Peripheral blood smear
- To assess RBC morphology, make fresh smears and smears from the blood in EDTA.
Precautions for Peripheral blood
- A well-made smear is needed.
- A well-stained smear is also important.
- Otherwise, the analysis of cell morphology may be greatly distorted by poorly made and poorly stained smears.
Indications for Peripheral blood smear
- This is done to see the morphology of RBC as variation and abnormality in size, shape, structure, Hb contents, and staining characteristics.
- Can diagnose the type of Anaemia.
- Can diagnose Thalassemia.
- Also, it can find other abnormalities like hemoglobinopathies.
- This also helps to see the effect of chemotherapy and radiation.
- Special stains can find infections, infestation, leukemia, and other diseases.
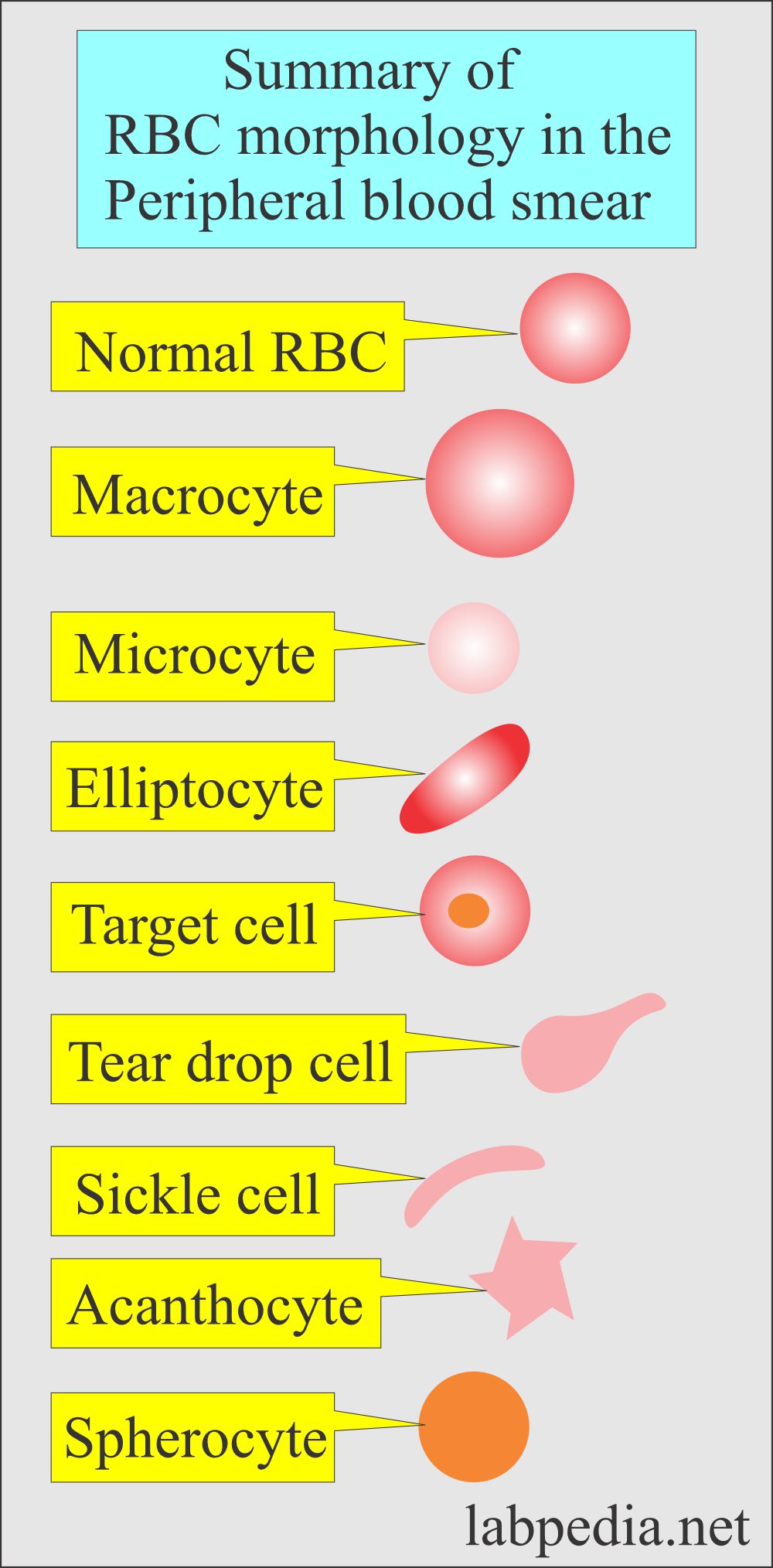
Variation in the morphology of RBCs:
- There are various sizes and shapes of RBC seen in the peripheral blood smear:
- Normocytic when the size is normal (7 to 8 µm).
- Normochromic when the color is normal.
- Microcytic when the size is smaller than normal RBC, and these are less than 6 µm.
- In iron deficiency anemia and thalassemia, and hemoglobinopathies.
- Macrocytic when the size is larger than > 8 µm.
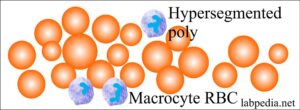
- Found in liver diseases, alcoholism, and oval in megaloblastic anemia.
- Anisocytosis is an abnormal variation in size from the normal diameter of 6 to 8 µm, seen in severe anemia like iron deficiency, hemolytic anemia, and hypersplenism.
- Hypochromasia when the RBCs are pale with decreased Hb concentration.
- Poikilocytes, when RBCs have variation in shapes.
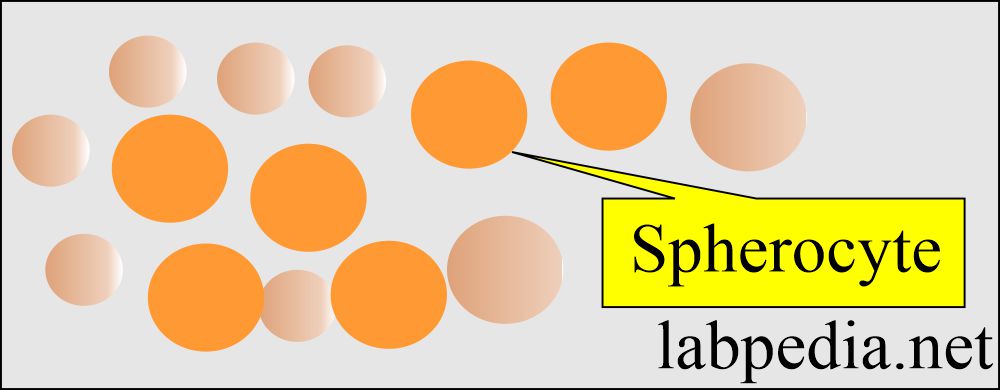
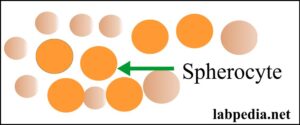
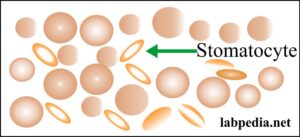
- Spherocytes when RBCs are round without the central pale area.
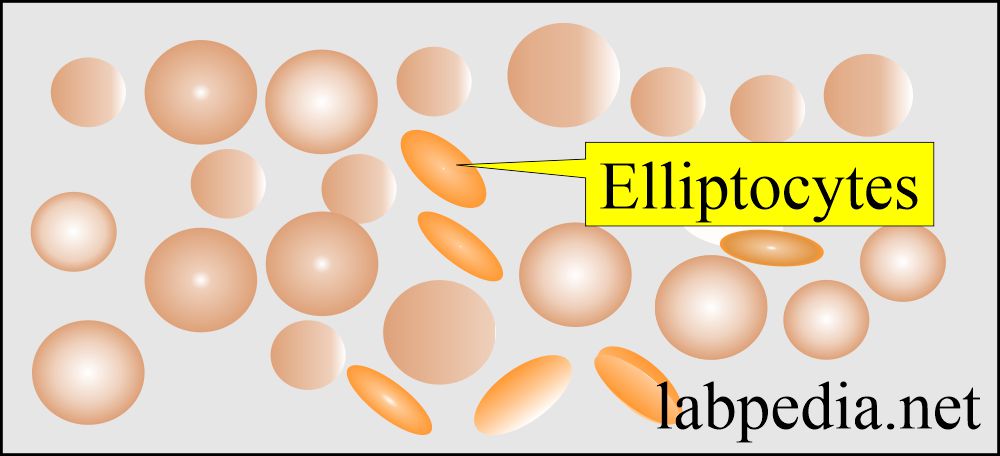
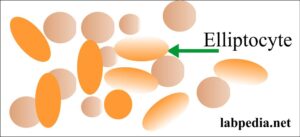
- Elliptocytes when RBCs are oval or elongated.
- Found in hereditary elliptocytosis.
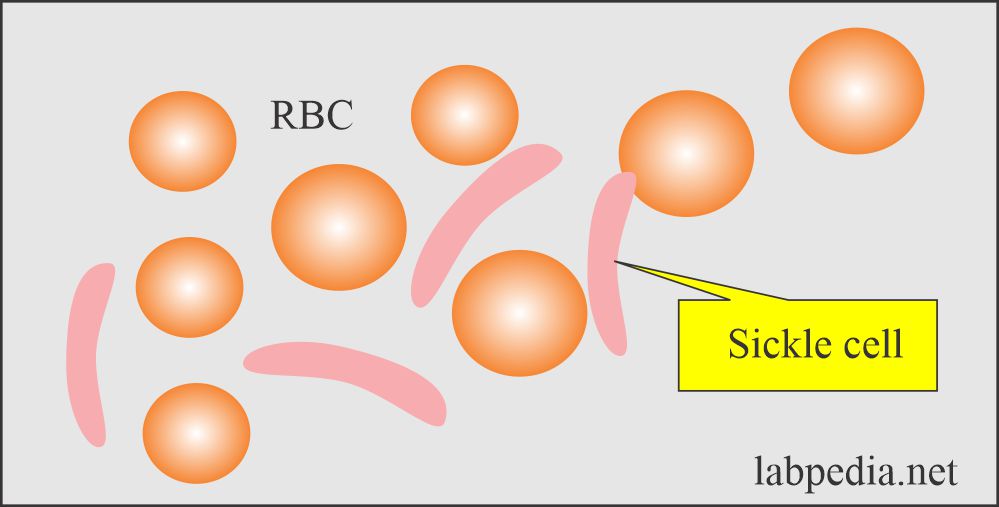
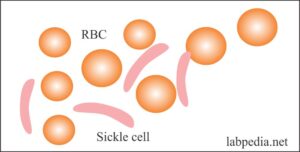
- Sickle cell is a crescent-shaped RBC seen in sickle cell anemia.
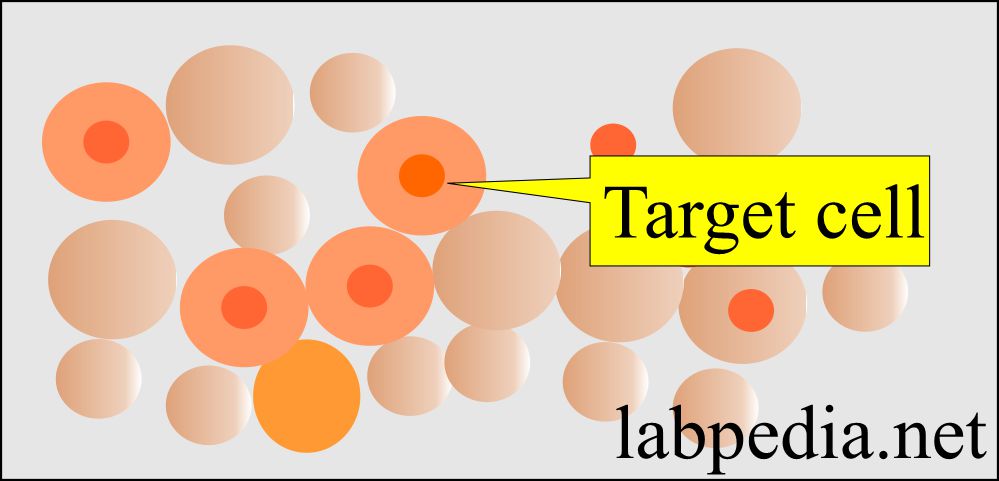
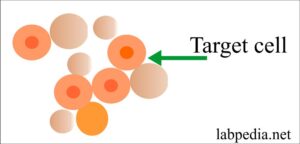
- The target cell is RBC, with a dark central area and clear space between this dark area and the periphery.
- Found in iron deficiency anemia, liver disease, post-splenectomy, and hemoglobinopathies.
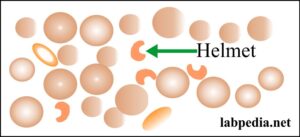
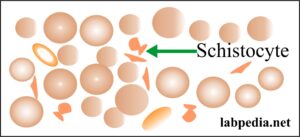
- Schistocytes or helmet shape RBCs. These are irregularly contracted cells or fragmented RBCs.
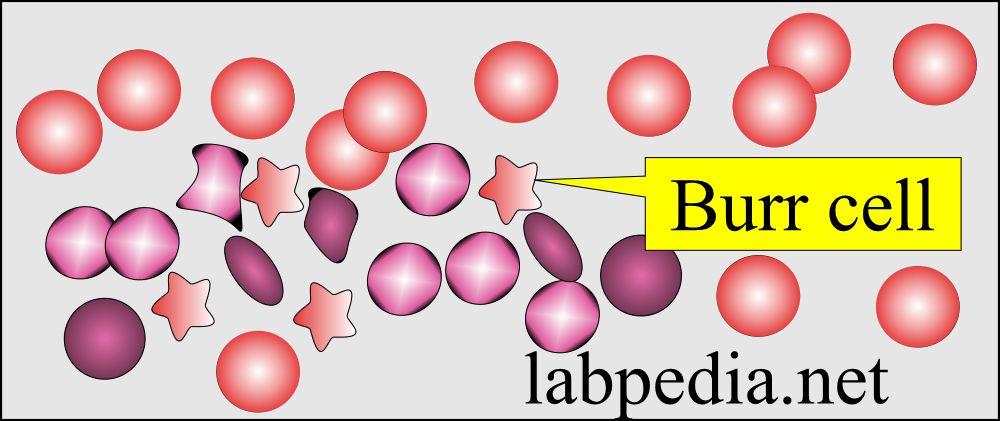
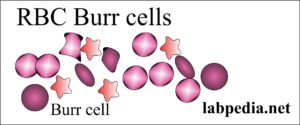
- Burr cells are RBCs with spinous processes.
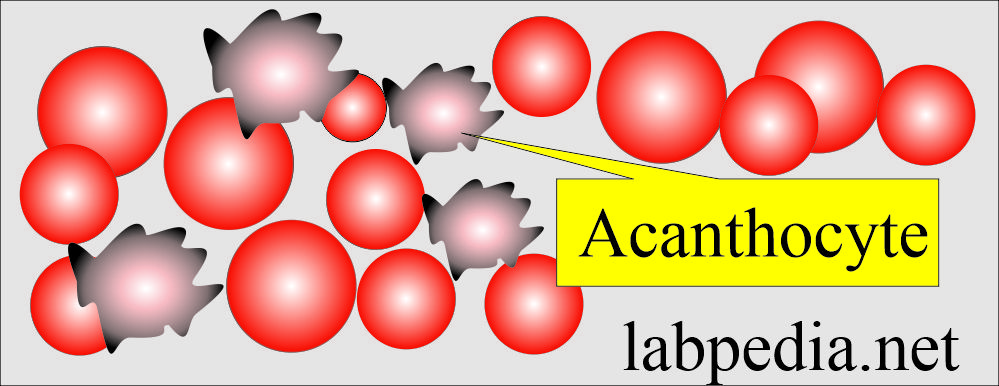
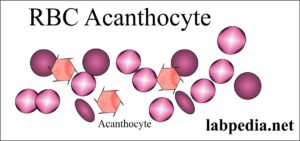
- Acanthocytes are RBCs with small cells with thorny projections.
-
- Found in liver disease, renal failure, and abetalipoproteinemia.
-
- Teardrop cell is RBCs with a tear-like appearance.
- The nucleated cell is RBC with the presence of a nucleus. These are normoblast or megaloblastic cells.
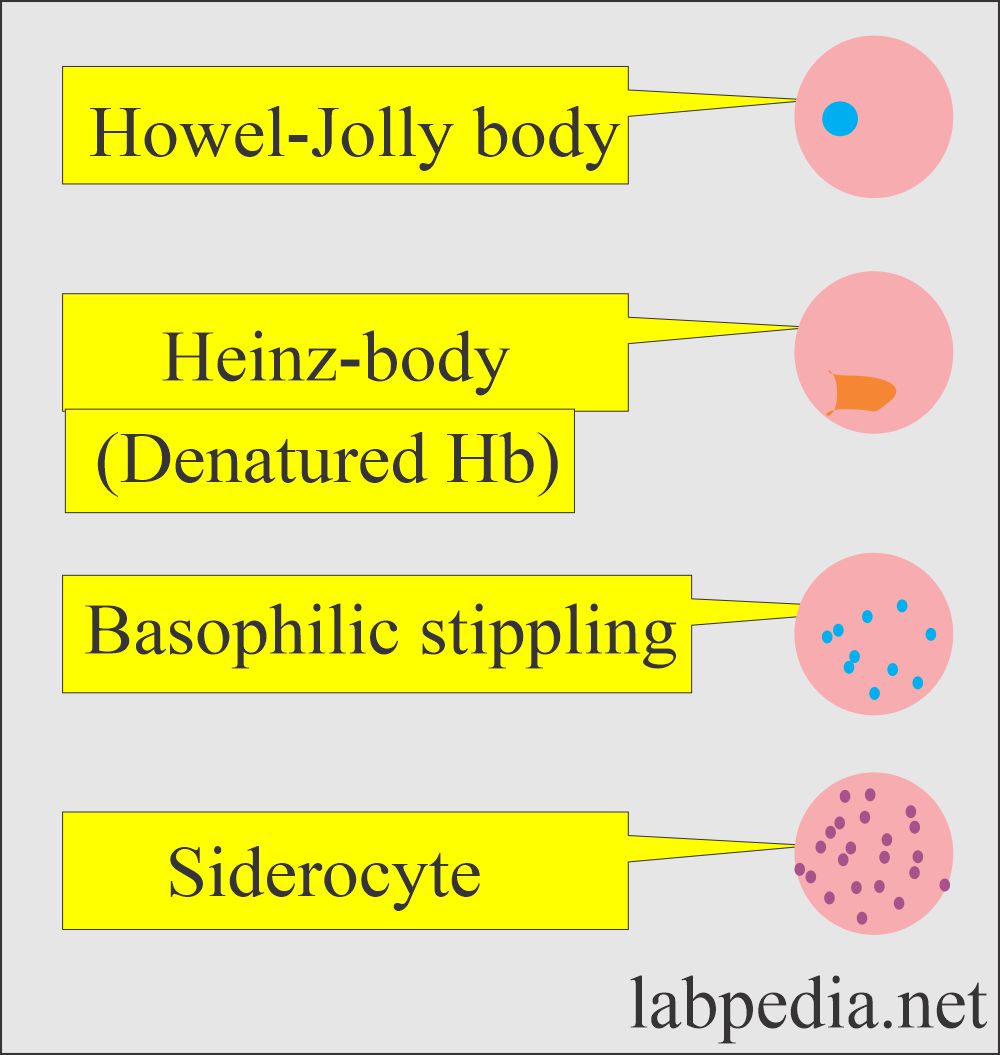
Red blood cells inclusion In the peripheral blood smears:
- Howell-Jolly bodies. These are spherical purple bodies within RBCs; these are nuclear debris.
- Heinz inclusion bodies. These are small round inclusion of denatured hemoglobin, seen with supravital stain or under phase microscopy.
- Siderocytes are the RBCs containing siderotic granules which stain blue with Prussian blue stain.
- Basophilic stippling is the presence of punctate stippling seen with the Wright stain.
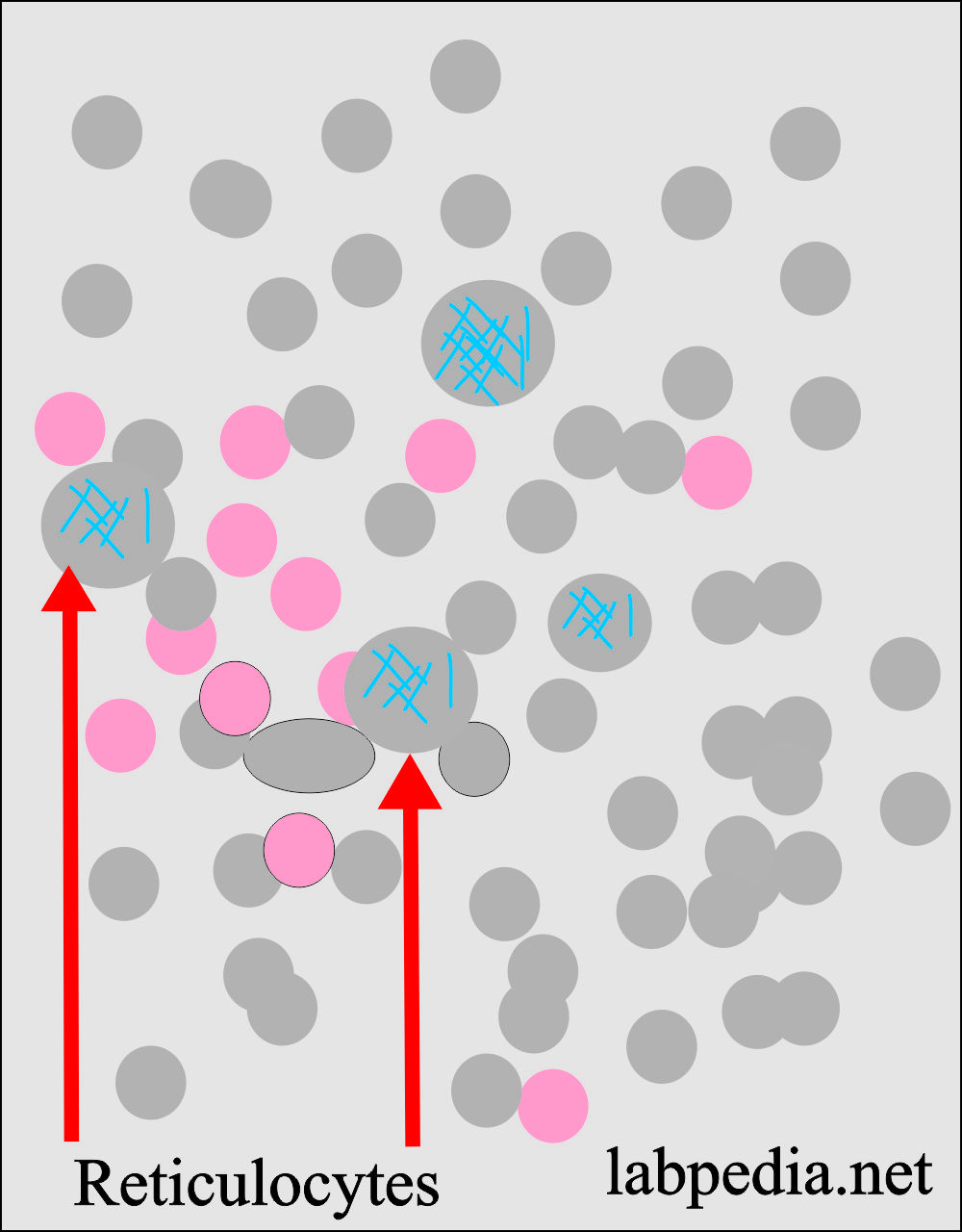
Reticulocytes:
- Reticulocytes may also be seen in the peripheral blood smear.
- These are RBCs containing RNA and stained pinkish-blue in color. Methylene blue show a reticular network.
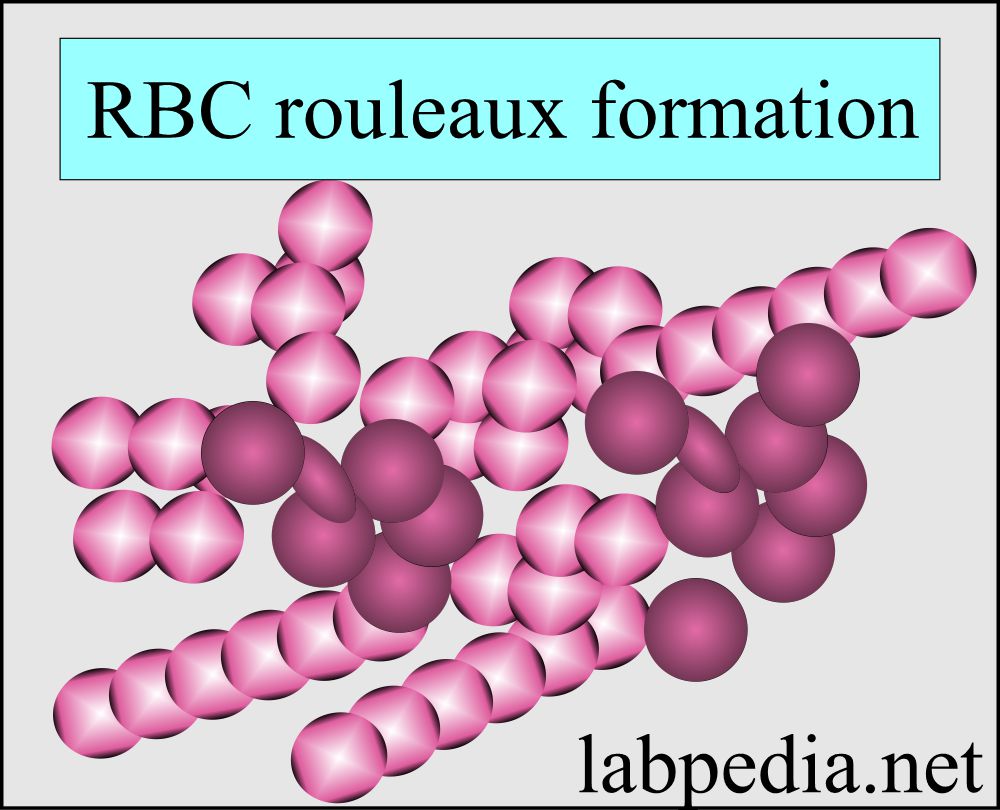
Rouleaux formation:
- This typical formation is the pilling of RBCs on each other or aggregated RBCs.
Normal cells in the Peripheral blood:
- Band form neutrophils = 2% to 6%
- Neutrophils = 50% to 70%
- Eosinophils = 1% to 5%
- Basophils = 0% to 2%
- Lymphocytes = 20% to 44%
- Monocytes = 2% to 10%
Interpretation of the peripheral blood smear:
- Screen the slide and note any abnormalities present in the smear regarding RBCs.
- It can evaluate the number or any abnormality of white cells.
- It can evaluate the number of platelets.
- So the peripheral smear gives the following information.
- Any abnormality of RBCs.
- Any abnormality in white cells.
- Can assess the number of platelets.
Various pictures of anemias:
- In hemolysis, hemorrhage, or in increased erythropoiesis. There are basophilic or polychromatophilic macrocytes
- Megaloblastic anemia shows oval macrocytes with increased lobules in the neutrophils.
- In hemoglobinopathies anemia, there are target cells, e.g., in thalassemia and Hb C.
- Target cells are also seen in iron- deficiency anemia and liver diseases.
- Thalassemia and lead poisoning show microcytes with stippling.
Red blood cells morphology and their etiology:
- Note please see more information on CBC and peripheral blood smear.
Questions and answers:
Question 1: What is the peripheral blood picture of thalassemia?
Question 2: What are the burr cells?


very informative. thank you
✌️✌️
Good article. Shapes of some abnormal RBC type are missing that must be added.
Please, thanks for the comments. Can you specify missing abnormal cells?
very well
Thanks.