Prostatic Acid Phosphatase (PAP), Acid Phosphatase
Prostatic Acid Phosphatase (PAP)
What sample is needed to estimate Prostatic Acid Phosphatase (PAP)?
- It is done on the patient’s serum.
- Separate the serum immediately to decrease the contact with RBCs.
- The sample can be stabilized by adding 10 mg/mL of disodium citrate monohydrate to the serum.
- Or add the 50 µL of acetic acid (5 mol/L) per mL of the serum to lower the pH to 5.4.
- Separate serum immediately and perform the test.
What are the precautions for a Prostatic Acid Phosphatase (PAP) sample?
- If there is a delay, add citrate buffer or acetic acid to reach a pH of 5.4 to 6.2. Otherwise, enzyme activity will rapidly lose its ability to function.
- If the sample is kept at room temperature for more than one hour, 50% of the activity is lost.
- Avoid hemolysis. The hemolysed sample is contaminated with isoenzyme and should be discarded.
- The lipemic serum also interferes with the reading of the final result because of turbidity.
- It can be stored at 4 C° or -20 °C.
- The sample is unstable at a temperature of >37 °C.
- The sample is also unstable at a pH of >7.0.
What are the indications for Prostatic Acid Phosphatase (PAP)?
- For the diagnosis of prostatic carcinoma.
- This is raised in prostatic carcinoma and metastasis due to prostatic carcinoma.
How would you discuss the pathophysiology of Prostatic Acid Phosphatase (PAP) and Acid Phosphatase?
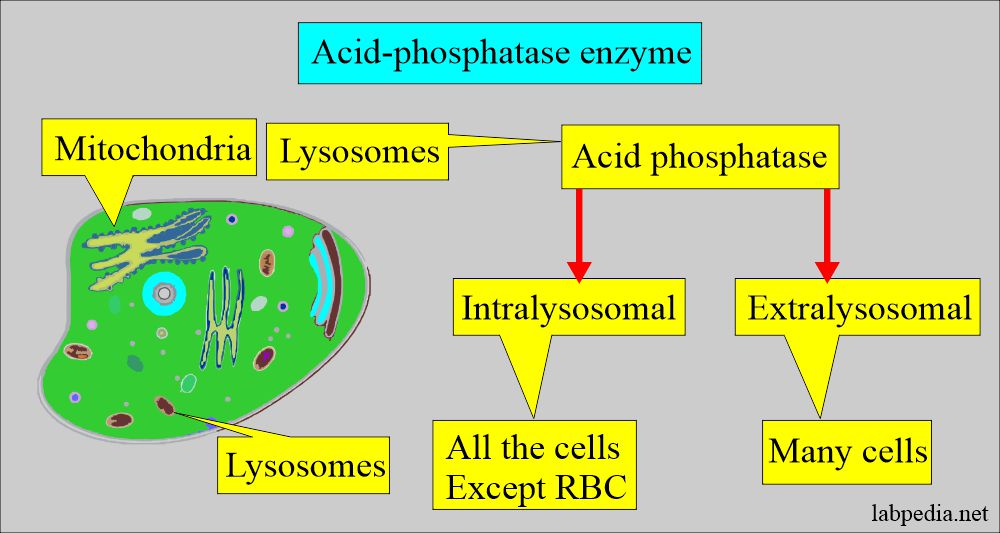
- Acid phosphatase is a lysosomal enzyme.
- Prostatic acid phosphatase is a subtype of total Acid phosphatase.
- The prostatic component is found in the lysosomes of the prostatic epithelium.
- This glycoprotein has a molecular weight of 100,000 and a biological half-life of 1.1 to 2.6 hours.
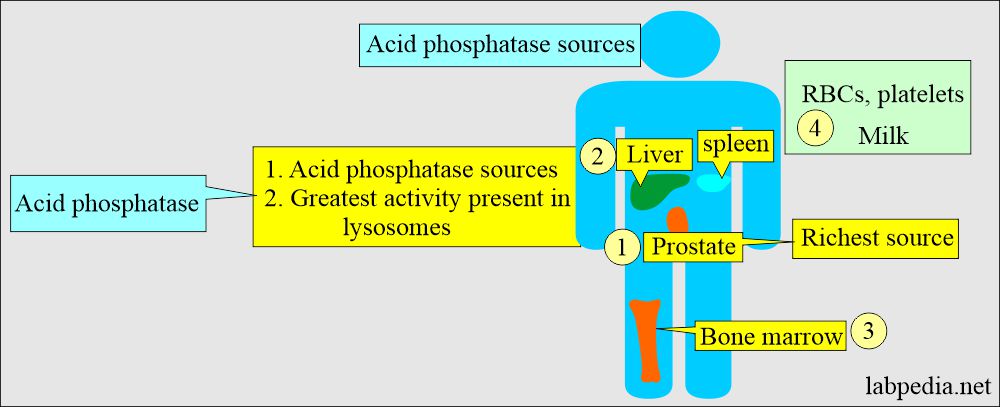
- Very small amounts of Acid phosphatase are found in the liver, RBCs, Spleen, Platelets, and bone marrow, with a negligible quantity of Prostatic acid phosphatase.
- The greatest activity is present in the prostate, the richest source. It gives a small amount in the blood of a healthy person.
- AP is raised in 50% to 75% of the cases with local invasion of prostatic carcinoma.
- AP is raised in >90 % of cases of metastatic disease.
- Acid phosphatase has an optimal activity below a pH of 7.0.
- AP is unstable, especially at room temperature at 37 °C and a pH of >7.0.
- AP activity is lost >50% in one hour at room temperature.
- Acidification of the serum to a pH of <6.5 will stabilize the enzyme.
- Erythrocyte AP is inhibited by formaldehyde and cupric ions, which make Prostatic AP resistant.
- Tartrate-resistant phosphatase is very helpful in the diagnosis of hairy cell leukemia.
- Prostatic acid phosphatase (PAP) is replaced by:
- The PSA (Prostatic specific antigen).
- Digital rectal examination.
- Transrectal ultrasonography.
- Surgical biopsy of the prostate for histopathology.
- Total body bone scan.
What is the normal Prostatic Acid Phosphatase (PAP)?
Source 1
- Total Acid phosphatase= 0 to 5.5 U/L
- Prostatic acid phosphatase level = 0 to 0.6 U/L (<2.8 ng/ml)
Source 2
- Adult / Elderly = 0.13 to 0.63 units/L
- Children = 8.6 to 12.6 units/L
- Newborn = 10.4 to 16.4 units/L
Source 3
- Prostatic acid phosphatase = <2.5 ng/mL (immunoassay)
- Tartarate inhibition method = 0 to 0.6 U/L
Source 4
- 2.5 to 3.7 ng/mL (2.5 to 3.7 µg/L)
What causes increased Prostatic Acid Phosphatase (PAP) and acid phosphatase?
- Prostatic carcinoma.
- Prostatic massage.
- TUR.
- Leukemia (Myeloid leukemia and hairy cell leukemia).
- Bone disorder, e.g., Paget’s disease, metastatic carcinoma from breast and lung.
- This is raised in osteoclastoma (Giant cell tumor), Osteoclastic tumors, and osteopetrosis.
- Storage disorder, e.g., Gaucher’s disease, Niemann picks disease.
- Hyperparathyroidism with bone involvement.
What is the medicolegal importance of acid phosphatase?
- The importance of Acid phosphatase (AP) in the semen is very important to rule out the case of rape because AP has a high concentration in the semen.
- The swab from the victim is kept in 2.5 ml of broth.
- Or store in normal saline. Freeze and thaw the sample at 2 to 4 °C before performing the test.
- Store at room temperature or 4 °C.
- Specimen retains Acid phosphatase (AP) activity for one month.
NOTE: Please see more details in the Acid phosphatase total.
Questions and answers:
Question 1: What is the significance of prostatic acid phosphatase?
Question 2: What is the medicolegal value of acid phosphatase?