Pregnancy test:- Part 1 – Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (HCG), Normal Pregnancy
Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (HCG)
What sample is needed for Beta-HCG?
- This is done in the patient’s urine.
- Collect the morning sample, which has the maximum concentration of HCG.
- Try to do the test on a fresh urine sample.
- You can collect the urine at any time of the day.
- Urine specimens should be clear in the case of turbidity or urine sediments requiring filtration or centrifuge.
- Instruct the patient not to drink after 2000 hours (8 PM) until the morning urine sample is collected.
- This test can be done in the serum.
- Perform the test within 48 hours of collection.
- Important: Centrifuge the urine at 900 x g for 10 minutes.
- Can store the sample at 2 to 8 °C for 48 hours.
- Serum for β – HCG is stable for up to 7 days at 2 to 8 °C.
- For longer periods, freeze at -20 °C.
- Avoid hemolyzed, turbid, or samples that contain particulate material.
What are the precautions for Beta-HCG?
- If the test is delayed more than 48 hours, freeze the samples at -20 °C.
- Don’t repeat thawing and freezing again and again.
- Hemolysis and lipemic serum give a false result.
- Hematuria and proteinuria give a false positive test. I will recommend at least centrifuging the urine.
- This test may be negative for diluted urine.
- Drugs like diuretics lead to dilution of the urine and may give a false-negative result.
- Some drugs that give false positive tests are anticonvulsants, hypnotics, tranquilizers, and antiparkinson drugs.
What are the indications for Beta-HCG?
- For the diagnosis of pregnancy.
- It can be used during a high-risk pregnancy.
- It can be used for ectopic pregnancy.
- For screening of Down’s syndrome.
- This may be used as a tumor marker in some malignancies.
What is the pathophysiology of Human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG)?
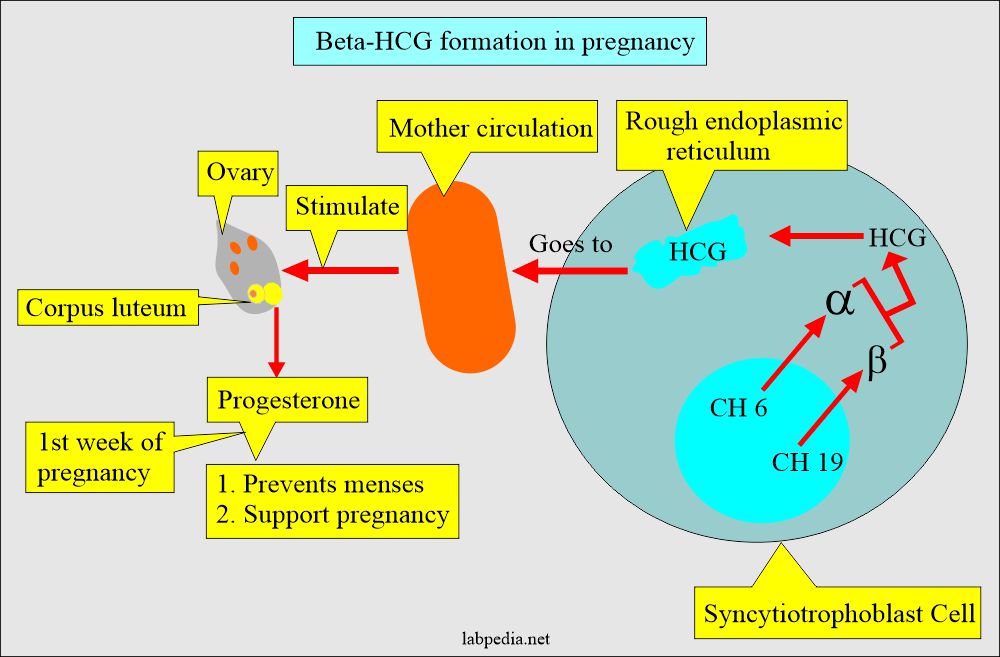
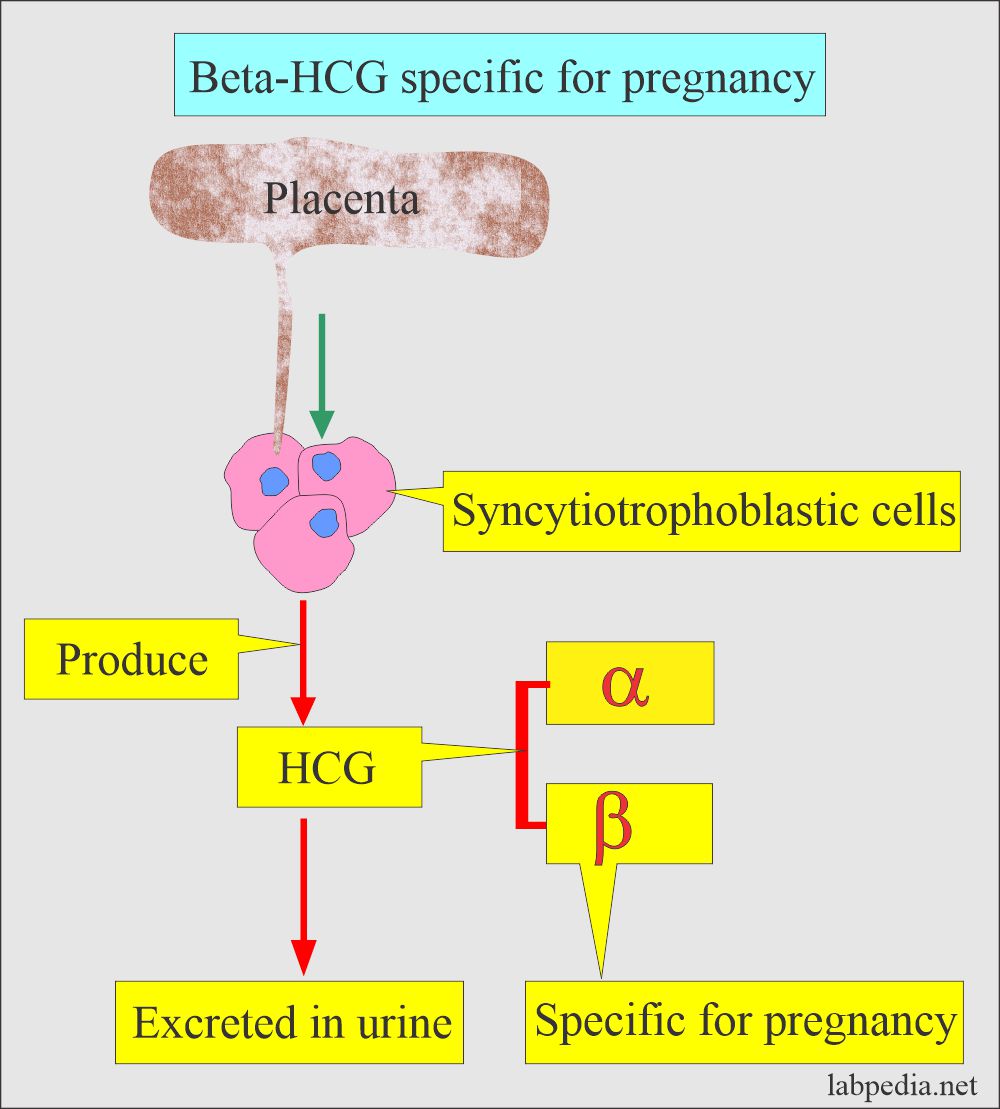
- The placental trophoblastic cells produce an appreciable amount of hormone, human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG).
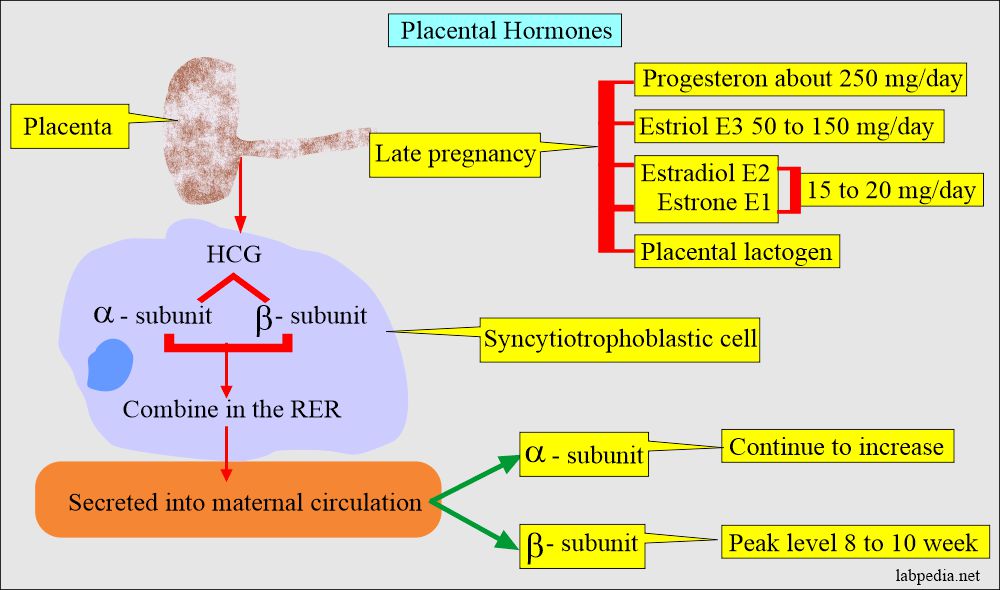
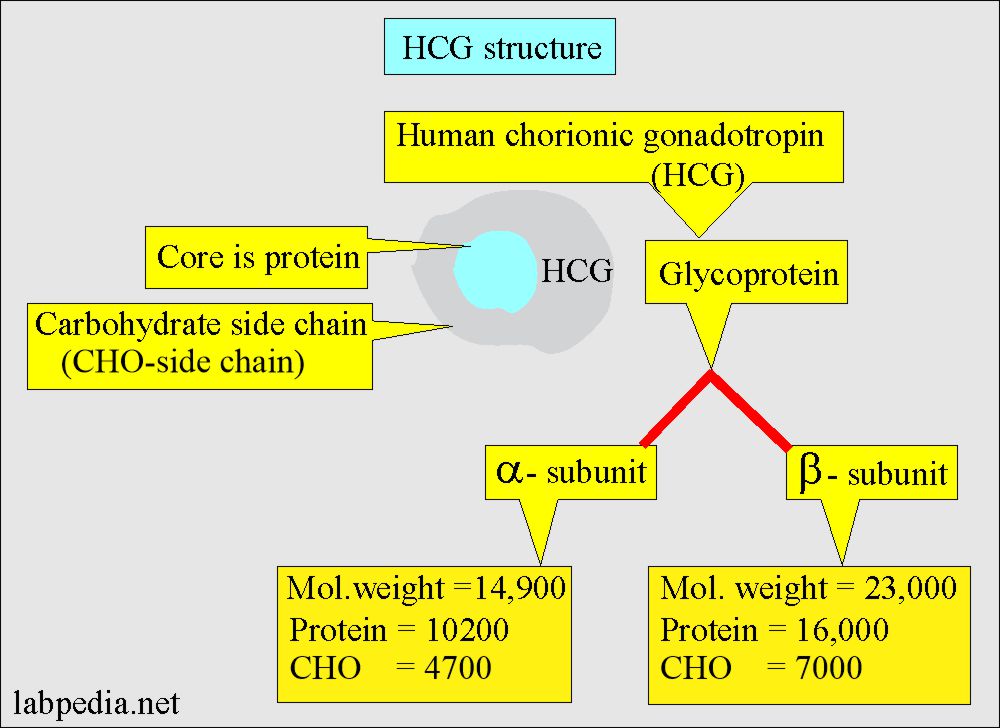
- HCG is a glycoprotein with alpha (α) and beta (β) subunits.
- Molecular weight is 37,900 D and has a higher carbohydrate proportion than any other hormone.
- This is synthesized in the syncytiotrophoblast of the placenta.
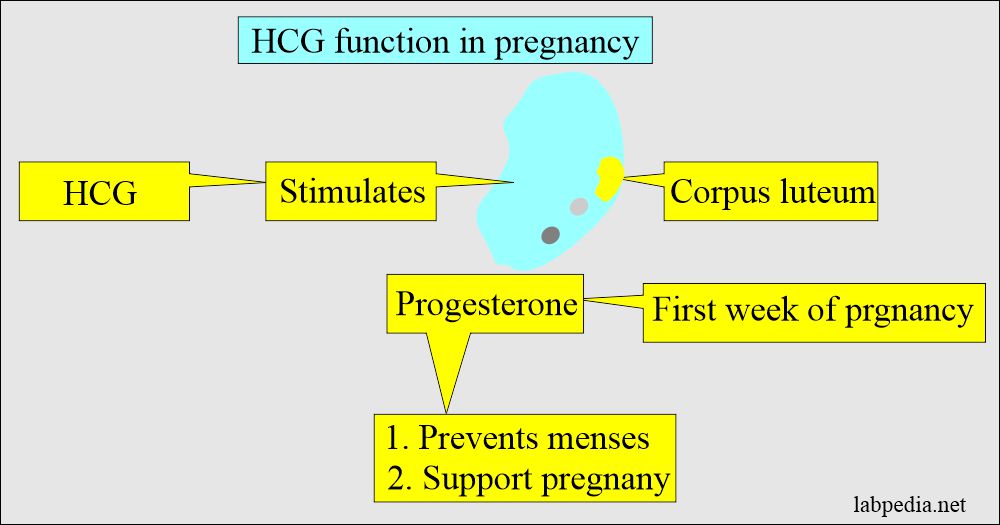
- HCG stimulates the corpus luteum to produce progesterone, which maintains the pregnancy.
- This hormone is excreted in the urine.
- HCG is present in the blood and urine.
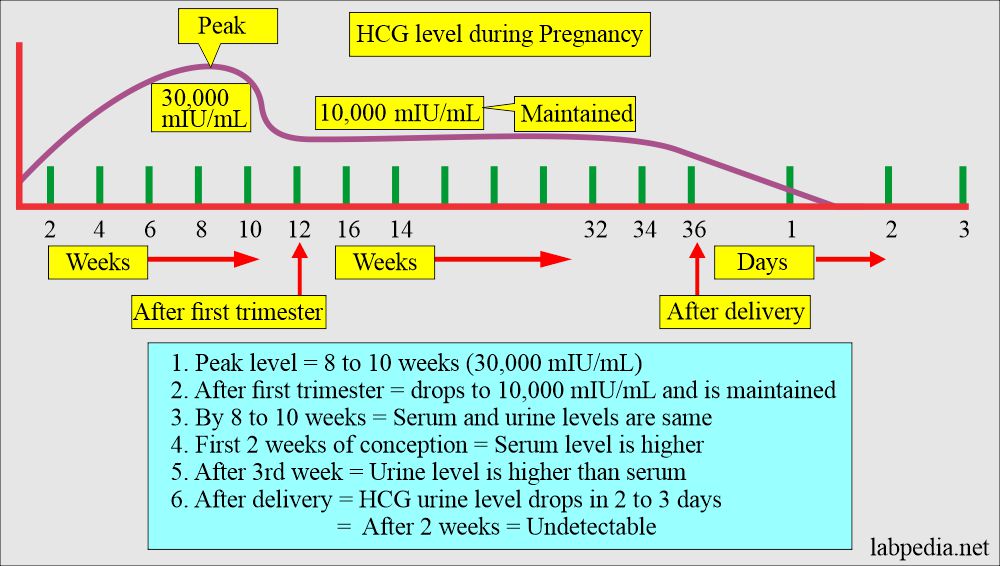
- HCG appears as early as the 10th day of fertilization or conception.
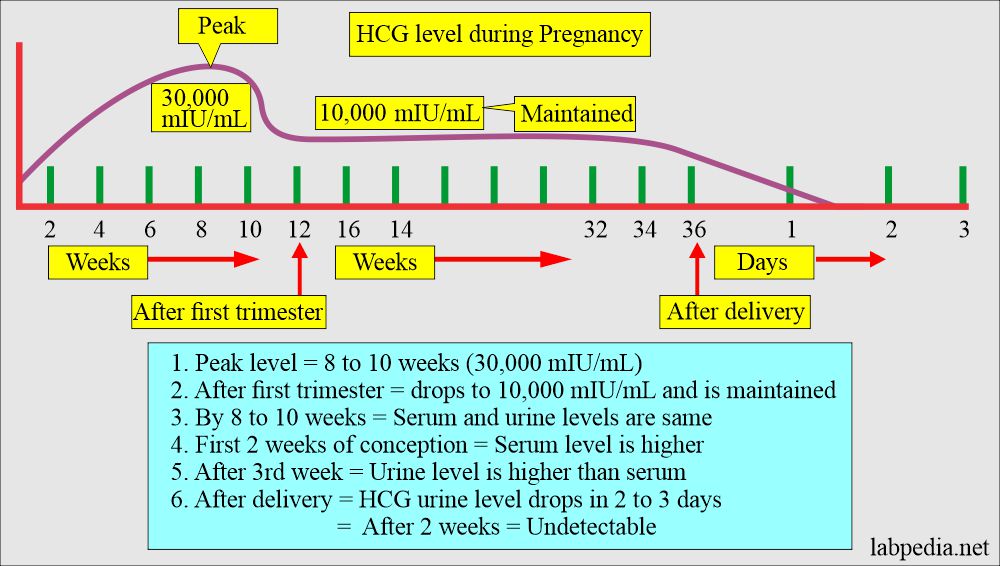
- In the first few weeks of the pregnancy, HCG rises markedly, and the serum levels are higher than the urine.
- After about one month, the HCG levels are the same in the serum and urine.
- This hormone is negative in the urine of men and nonpregnant women.
- <5% of the female may show a minute amount of HCG.
What is the structure of Beta-HCG, Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (HCG)?
- Alpha subunit (α-HCG):
- This is the same for all the glycoprotein hormones. This is also part of pituitary hormones.
- α-HCG has a molecular weight of 14,900, where protein is 10200 and carbohydrates are 47,000.
- Beta subunit (β-HCG):
- This is specific to the HCG. This gives immunologic and biologic specificity. The β-HCG has antigenic individuality.
- β-HCG has a molecular weight of 23,000, where the protein portion is 16,000 and carbohydrates are 7000.
- Free β-subunit and intact β-subunit HCG are measured in most of the current methodologies.
- The β-HCG unit is specific for a pregnancy test.
- This test becomes negative after delivery in 3 to 5 days.
- β-HCG in blood detects pregnancy as early as 6 to 10 days after the oocyte implantation.
- This will be positive after 14 days of the last cycle in the urine.
- In a normal pregnancy, one can find 25 mIU/mL after 2 to 3 days of implantation and after 8 to 10 days of fertilization.
- The qualitative test detects pregnancy.
- This has less sensitivity (20 to 50 IU/L) than the quantitative test.
- This will be negative in the first week of the menstrual cycle.
Normal pregnancy
- A normal pregnancy lasts approximately 40 weeks, measured from the first day of the last normal menstrual cycle.
- Normal pregnancy is divided into three trimesters. Each trimester is slightly longer than 13 weeks.
- The first trimester:
- o to 13 weeks, begins on the first day of the last menses.
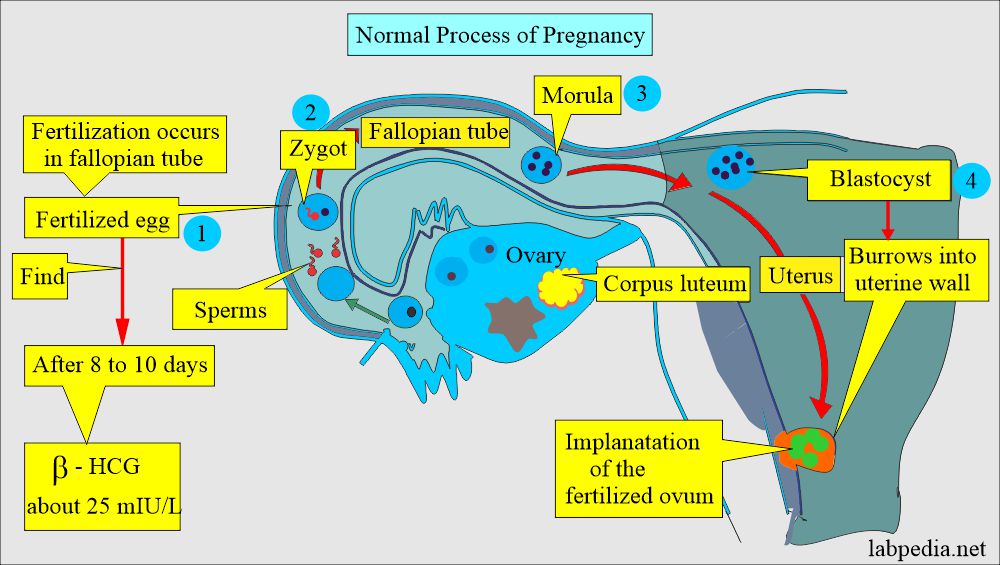
- Ovulation occurs on approximately the 14th day of the regular menstrual cycle.
- The fertilization occurs in the fallopian tubes and becomes a zygote carried down the tube into the uterus.
- The zygote divides and becomes morula.
- The morula develops a cavity, the primitive yolk sac, and becomes a blastocyst, which implants in the uterine wall about 5 days after fertilization.
- The cells on the exterior wall of the blastocyst become trophoblasts, which invade the uterine endometrium and develop into chorionic villi, creating the placenta.
- Now, these products of conception are referred to as an embryo.
- A cavity called the amnion forms within the embryo and enlarges with the accumulation of liquor amnii, usually called as amniotic fluid.
- From the combination of three primary cells named:
- Endoderm.
- Mesoderm.
- Ectoderm.
- The organs will start to develop; this process is called organogenesis.
- In the 10th week, the embryo is formed, where most major organs are developed, and now it is called a fetus.
- In the 13th week, the fetus weighs approximately 13 grams and is 8 cm long.
- Second trimester:
- During the second trimester, 13 to 26 weeks, the growth of the fetus is rapid.
- The fetus weighs around 700 grams, is 30 cm long, and many organs begin to mature.
- Third trimester:
- During the third trimester, 27 to 40 weeks, the maturation of the organs is complete, the weight is 3200 grams, and the fetus is about 50 cm long.
- Full term:
- Now, the term is 37 to 40 weeks; normal labor starts with the rhythmic contraction of the uterus.
Stages of normal pregnancy and development of fetus:
| Clinical features | First trimester | Second trimester | Third trimester |
| Time period | 0 to 13 weeks | 13 to 26 weeks | 26 to 40 weeks |
| Weight | 13 grams | 700 grams | 3200 grams |
| Length | 8 cms | 30 cms | 50 cms |
| Organs development | Embryo (Fetus), three epithelial layers | Organs start maturing | Maturation of organs is complete |
What are the possible complications of the pregnancy?
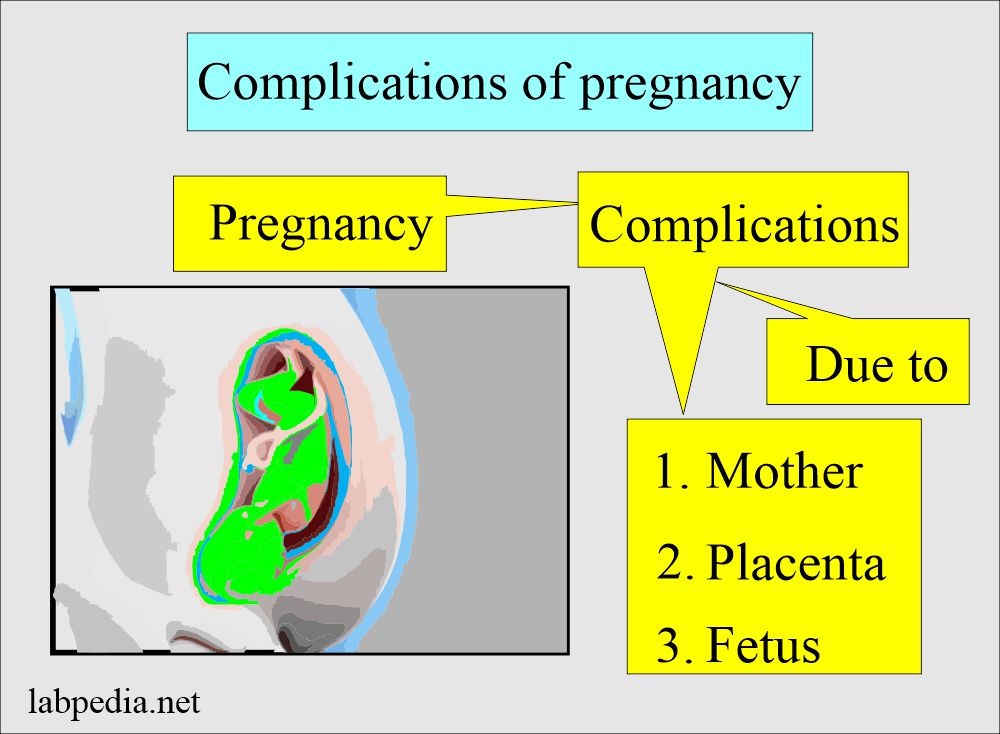
- Most of the pregnancy progresses without any complications.
- The most common causes can arise from:
- Mother.
- Placenta.
- Fetus.
Mother:
What are the complications arising from the mother?
- Ectopic pregnancy.
- Hyperemesis graviderum.
- Preeclampsia.
- Liver diseases.
- Isoimmunization by the blood groups is a hemolytic disorder.
- Grave’s disease.
- HELLP syndrome (H =hemolysis, EL = elevated liver enzymes, LP = low platelets count).
Placenta:
What are the abnormalities of the placenta?
- Molar pregnancy (Hydatidiform mole).
- 5% of the partial mole transforms into choriocarcinoma.
- 20% of the complete mole transforms into choriocarcinoma.
- Rarely choriocarcinoma.
Fetus:
What are the complications due to the fetus?
- Neural tube defect.
- Down’s syndrome.
- Trisomy 18.Preterm delivery.
- Preterm delivery.
- Presence of fetal fibronectin.
- Fetal respiratory distress syndrome.
What is the Normal value of HCG During Pregnancy?
- Negative in nonpregnant women.
- Positive in pregnant women.
- The blood test is positive after 11 days of conception.
- This test may become positive as early as 4 days after the expected date of menstruation.
- Pregnancy is detected 8 to 14 days after the first missed menstrual cycle, and the positivity is 95%.
- The urine test is positive after 12 to 14 days of conception (fertilization).
- The peak level is 8 to 11 weeks of pregnancy, and in another reference peak level, it is at the 60th to 70th day of pregnancy, then it starts to drop progressively.
- The peak level in serum and urine at the 8th to 10th week of gestation is around 30,000m IU/mL.
What are the normal values of HCG during pregnancy?
| Detectable level | HCG mIU/mL |
| 6 to 8 days of conception | level around 10 to 15 |
| Double every 3 days | 1200 to 6000 |
| Double every 4 days | 6000 to peak level |
| 10 to 12 weeks | 150,000 to 200,000 |
| At the end first trimester | around 100,000 |
| By the early second trimester | the peak level is 10,000 (800ng/mL) |
| 2n trimester | 10,000 to 50,000 |
| 3rd trimester | 10,000 to 50,000 |
| After delivery until 2 weeks | detectable |
| Ectopic pregnancy | no normal dynamics of HCG (Abnormal) |
- To convert into SI units x 1.0 = IU/L
Source 2
HCG
- Qualitative = Negative
- Pregnancy = Positive
- Male and nonpregnant females = <5 mIU/mL
Quantitation of HCG
| Gestation week | Whole HCG mIU/mL |
| <1 | 5 to 50 |
| 2 | 50 to 500 |
| 3 | 100 to 10,000 |
| 4 | 1000 to 30,000 |
| 5 | 3500 to 115,000 |
| 6 to 8 | 12,000 to 270,000 |
| 12 | 15,000 to 220,000 |
β-HCG Normal
- <2 ng/mL
- Or <5 mIU/mL
What are the types of pregnancy diagnostic tests?
Biologic test on urine.
- These tests are not used now. These are of historical importance.
- In this test, the urine of the suspected lady is injected into an animal like a rabbit, mouse, or frog. These animals develop the corpus luteum.
- Then, these animals were sacrificed, and a search was done for the corpus luteum.
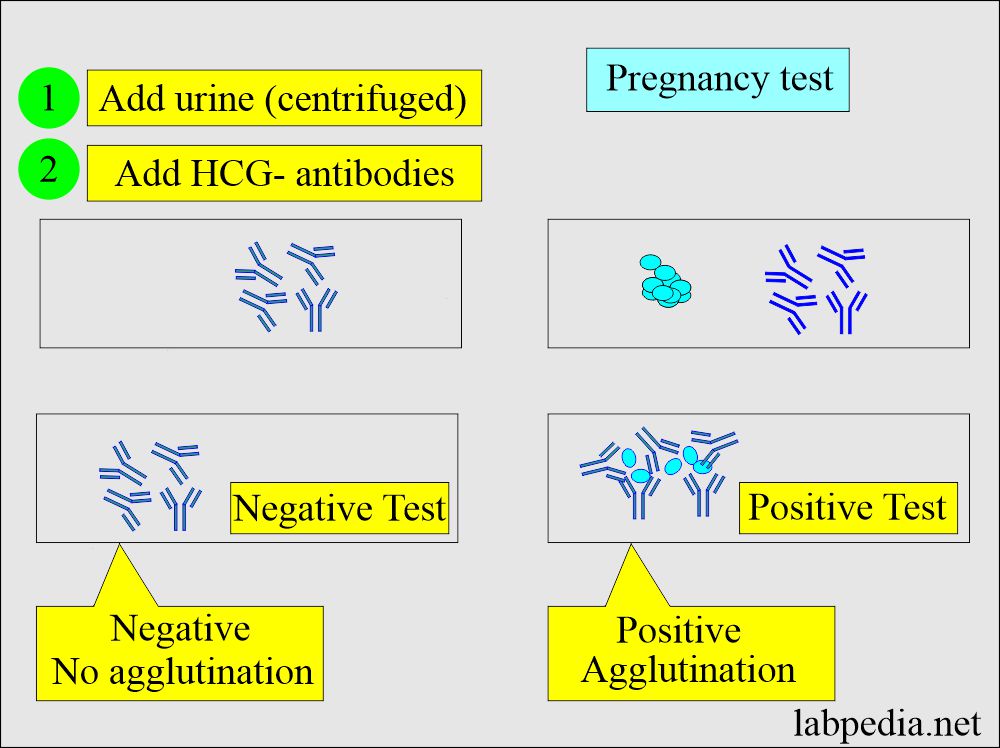
Immunologic tests.
- These are agglutination inhibition tests done on urine and blood.
- This test produces antibodies against HCG, which can be detected in 2 min or, in some kits, 2 hours.
- These have a high false-positive rate, so the test should be done after 28 days of the last menstrual cycle.
- The false-negative test may be seen when the HCG level is less than 25 to 50 IU/L.
- The false-negative test may be seen if the urine contains the following:
- Protein.
- Drugs.
- Bacteria contamination.
- White blood cells or RBCs.
- The false-negative result may be seen if the reagents:
- Kept at the extreme of the temperature.
- Extreme urine pH.
- Expired reagents.
- Now, some of the improved kits can detect after 18 days.
What are the Monoclonal antibody-based tests?
- The monoclonal antibody against HCG can detect a small amount of the HCG even 3 to 7 days after conception.
- Limitations of monoclonal antibody-based tests:
- These are not quantitative tests and may miss, not find early pregnancy or any other abnormality.
- Always run a positive control. The standard usually contains a small amount of HCG.
- Routine tests needed in a normal pregnancy for the evaluation of the fetus’s survival and abnormality:
What tests are required before the pregnancy?
| Test needed in pregnancy | Value in pregnancy | Interpretations/Complications |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
To assess for:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
What are the effects of Pregnancy on different biochemical parameters?
| Lab tests | Effect of pregnancy | Explanation |
|
It is decreased | It is due to an increase in the plasma volume |
|
|
|
|
It has a mild decrease | There is an increase in the glomerular filtration rate |
|
There is a mild decrease | There is an increase in the glomerular filtration rate |
|
It is increased | It is due to an increase in the production of placental heat-stable ALK |
|
It is increased | |
|
It is increased | |
|
It is increased | It is due to increased calcium and transfer of Ca++ to the fetus |
|
It is increased | In this case, ionized Ca++ remains normal |
|
These are increased | But the patient is euthyroid |
|
it is increased | Patient is euthyroid |
How will you interpret the differential diagnosis of positive pregnancy tests?
- HCG is present in the pregnancy.
- HCG may also be seen in 65% of the Ectopic pregnancy.
- A level of 20 IU/L or less subunit within the first week of pregnancy indicates ectopic pregnancy because there are insufficient trophoblastic cells.
- Hydatidiform mole.
- Choriocarcinoma.
- Germ cell tumors of the ovary and testes.
- HCG may be produced in primary liver cell carcinoma.
What are the causes of the False-positive pregnancy test?
- This can happen in 2% to 5% of the cases.
- This may be seen due to interfering substances like:
- Proteins (proteinuria).
- Drugs like chlorpromazine, phenothiazine, and methadone.
- Bacteria infection.
- RBCs or WBCs (hematuria and pyuria).
- Cross-reactivity with pituitary gonadotropins, e.g., a high level of LH in postmenopausal women.
What are the causes of the Negative pregnancy test?
- Dead fetus.
- Threatened Abortion.
- There is a sudden drop in the level of the plateau.
- Incomplete abortion.
What are the causes of False-negative pregnancy tests?
- These are common because the kits usually detect HCG levels at 1000 to 2000 mIU/L concentrations.
- Therefore, these qualitative tests will not be positive until 8 to 14 days after the first missed menstrual cycle.
- These qualitative tests may not detect normal pregnancy even after the second trimester (when HCG levels are low).
- These tests may be negative in an ectopic pregnancy (when HCG levels are low).
- Use of the old reagents.
- In case the temperature or change in the pH denatures the antiserum-HCG.
- It may be negative in the diluted urine with low specific gravity.
- The sample was taken too early in the pregnancy.
What are the causes of Low HCG levels?
- There may be a miscarriage.
- Maybe blighted ovum.
When will you see Positive HCG tests?
- Pregnancy.
- Ectopic pregnancy (it is positive in 65% of the cases).
- Hydatidiform mole.
- In males with testicular germ cell tumors (choriocarcinoma and embryonal cell carcinoma).
- In a female with ovarian germ cell tumors (choriocarcinoma and embryonal cell carcinoma).
- Liver cell carcinoma (hepatoma) can also make HCG.
How will you explain the Pregnancy test to the layman?
- Remember if there are missed menstruation cycles that are more than one week delayed. Then, ask for the morning sample for a pregnancy test.
- If it is negative and there is no menstruation, repeat the pregnancy test after 6 to 7 days.
- If still negative, then advise for the ultrasound of the abdomen, including the uterus.
NOTE: Please see more details on the beta-HCG level.
Questions and answers:
Question 1: When will you see a negative pregnancy test?
Question 2: When you will see postive pregnancy test other than pregnancy?