Plasma Renin-Angiotensin System
Plasma Renin
What sample is needed for Plasma Renin?
- The patient’s venous blood is needed, and EDTA is the anticoagulant.
- EDTA preserve the angiotensin.
- Draw blood in the chilled tubes and keep the sample on ice while transporting.
- A fasting sample is needed.
- 24 – hours of urine sodium is also helpful in making the diagnosis.
What are the precautions for Plasma Renin?
- Stop 2 to 3 weeks before using diuretics, estrogen, and antihypertensive drugs (beta-blockers and ACE- inhibitors).
- Stop taking foods containing caffeine, like tea or coffee, one day before the test.
- Advise a low-sodium diet 3 days before this test.
- There should be a fast for at least 8 hours.
- Renin assay will be affected when the patient is taking:
- Aspirin.
- Taking high doses of corticosteroids.
- There will be a change in pregnancy.
- There will be an effect on the position of the patient.
What are the Indications for Plasma Renin?
- This test is advised in a patient with hypertension.
- This test differentiates hypertension, whether essential, renal, or renovascular.
- This test differentiates primary aldosteronism.
What is the pathophysiology of Plasma Renin?
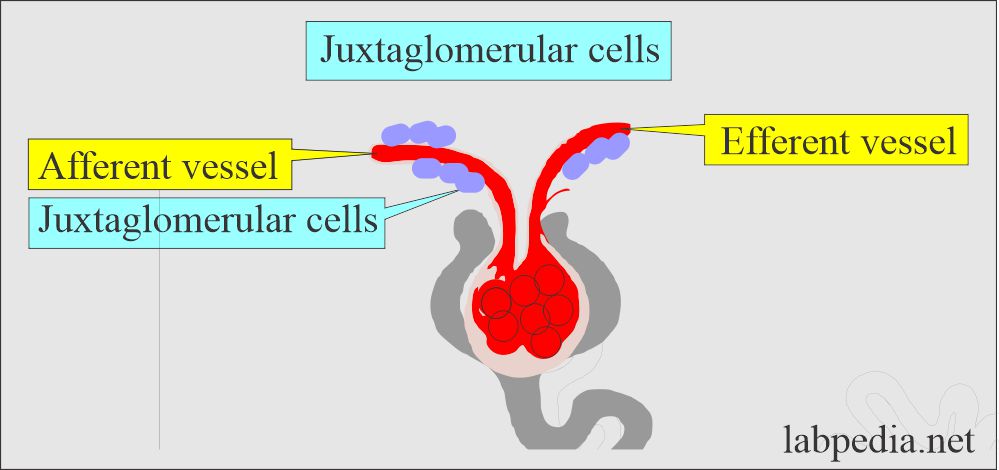
- Renin is an enzyme released by the juxtaglomerular apparatus of the kidneys into the renal vein in response to:
- Hyperkalemia.
- Sodium depletion.
- Hypovolemia.
- Decreased kidney blood perfusion.
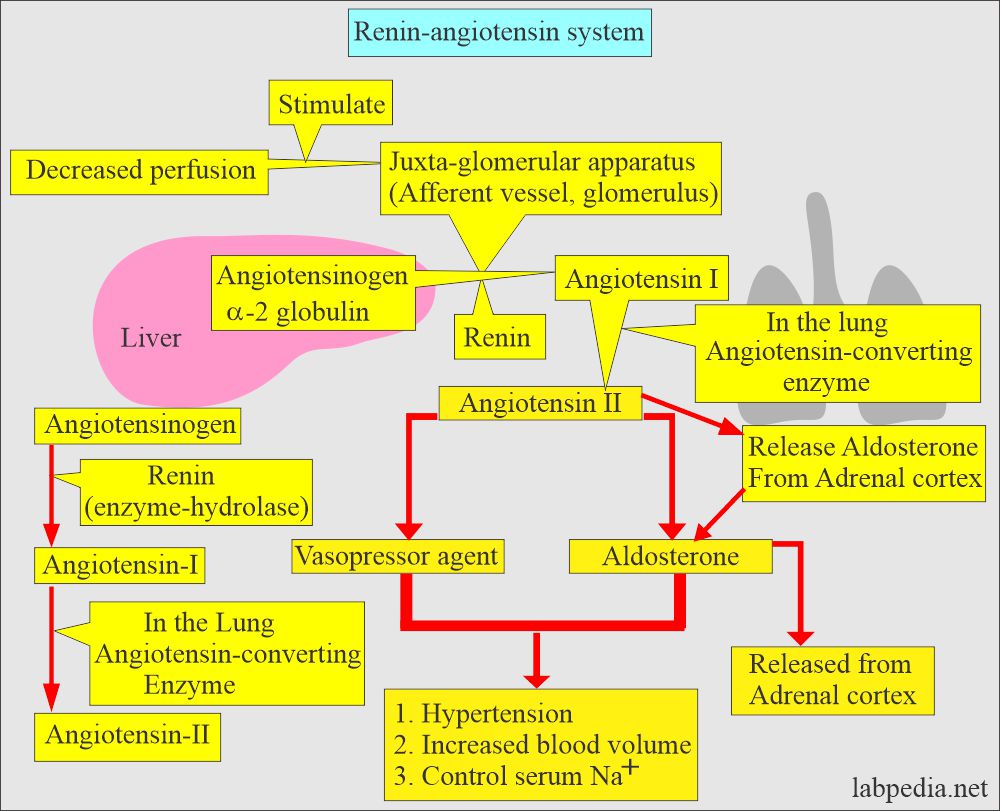
What is the Renin-angiotensin system?
- Renin is the hydrolase class enzyme that catalyzes the angiotensinogen cleavage to create angiotensin I.
- Angiotensinogen is derived from the liver and is alpha-2 globulin.
- Angiotensin I is converted to angiotensin II in the lung, where the angiotensin-converting enzyme is abundant.
- Angiotensin II is the potent vasopressor agent responsible for the renal type of hypertension.
- Angiotensin II also releases aldosterone from the adrenal cortex.
- Angiotensin II + aldosterone both leads to :
- Hypertension.
- Increase in the blood volume.
- Control serum sodium.
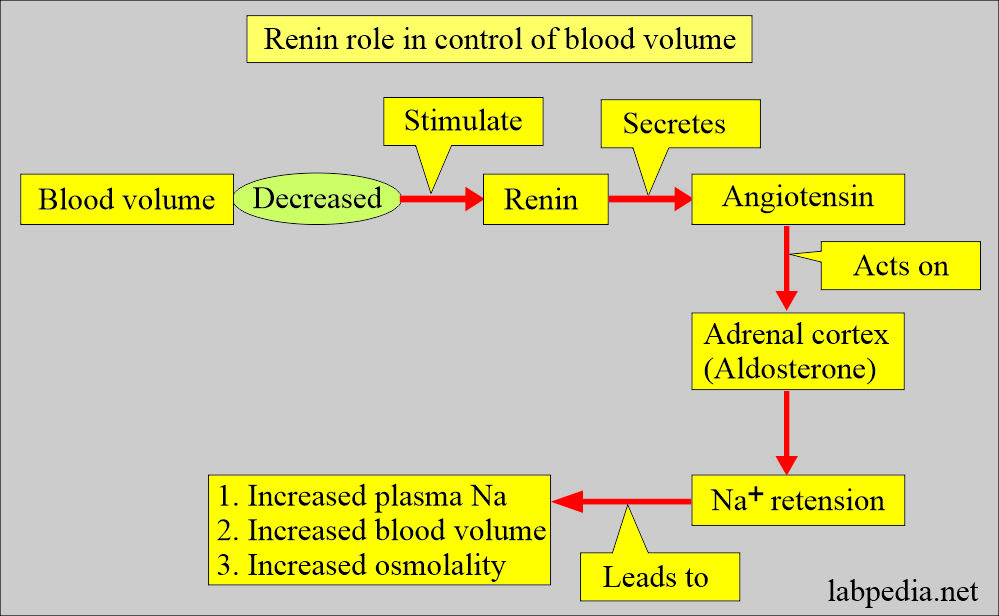
- The Renin+aldosterone regulate:
- Sodium and potassium balance.
- Blood pressure.
- Blood volume.
- Renin is released when there are:
- Low plasma volume.
- Low blood pressure.
- Low sodium.
- Increased Potassium.
- Renin release is suppressed when there are:
- Loss of potassium.
- Increased blood volume.
- An acute increase in blood pressure.
- Renin value increases when the position changes from recumbent to upright.
- High sodium intake decreases the renin level.
- The measurement of plasma renin activity is used in the differential diagnosis of hypertension.
- Renin stimulation test is advised to diagnose and differentiate between primary and secondary hyperaldosteronism.
What is the normal level of Angiotensin 1 and Plasma Renin?
Source 1
Normal Plasma Angiotensin I level
Angiotensin1
| Age | ng /mL/hour |
| Cord blood | 4.0 to 32.0 |
| Newborn 1 to 7 days | 2.0 to 35.0 |
| The child’s Normal sodium diet, supine | |
| 1 to 12 month | 24.0 to 37.0 |
| 1 to 3 years | 1.7 to 11.2 |
| 3 to 5 years | 1.0 to 6.5 |
| 5 to 10 years | 0.5 to 5.9 |
| 10 to 15 years | 0.5 to 3.3 |
| Adult Normal, sodium diet | |
| Supine | 0.2 to 1.6 |
| Standing (4 hours) | 0.7 to 3.3 |
- To convert into SI unit x, 1.0 = µg x hour -1 x L-1
Renin direct
- Adult =
- Supine = 12 to 79 mU/L
- Upright = 13 to 114 mU/L
Source 2
Plasma Renin assay
- Adult/elder:
- Upright position + sodium depletion (sodium-restricted diet)
- 20 to 39 years = 2.9 to 24 ng/mL/hour.
- >40 years = 2.9 to 10.8 ng/mL/ hours.
- Upright position + normal sodium intake
- 20 to 39 years = 0.1 to 4.3 ng/mL/hour.
- >40 years = 0.1 to 3 ng/mL/hour.
- Upright position + sodium depletion (sodium-restricted diet)
- Children:
- o to 3 years= <16.6 ng/ mL/ hour.
- 3 to 6 years = <6.7 ng/ mL/ hour.
- 6 to 9 years = <4.4 ng / mL/hour.
- 9 to 12 years = <5.9 ng /mL/hour.
- 12 to 15 years = <4.2 ng / mL/hour.
- 15 to 18 years = <4.3 ng / mL/hour.
Source 5
Plasma renin assay
Normal sodium diet
- Adult
- supine = 0.2 to 1.6 ng/mL
- Standing = 0.7 to 3.3 ng/mL
Low sodium diet
- Adult
- Supine = Level increases 2 times the normal
- Standing = Level increases 6 times the normal
Another source
- Adults on a normal sodium diet.
| Patient age | Normal Angiotensin 1 ng/mL /hour |
| Supine (adult) | 0.2 to 1.6 |
| Standing for 4 hours (adult) | 0.7 to 3.3 |
| Neonates cord blood | 4 to 2 |
| Neonates 1 to 7 days | 2 to 35 |
| Infants 1 to 12 months | 2.4 to 37 |
| Children 1 to 3 years | 1.7 to 11.2 |
| Children 3 to 5 years | 1 to 6.5 |
| Children 5 to 10 years | 0.5 to 5.9 |
| Children 10 to 15 years | 0.5 to 3.3 |
- (Note. These are from two different sources. Values vary depending on diet, health, age, and sex).
What are the causes of Increased Renin levels?
- Secondary aldosteronism with malignant hypertension.
- Chronic renal failure.
- Renovascular hypertension.
- Salt losing status due to GI diseases.
- Renin-producing tumor of the kidney.
- Pheochromocytoma.
- Few patients with essential hypertension, around 15%.
- Reduced plasma volume due to low sodium.
- Drugs like diuretics.
- Addison disease.
- Cirrhosis.
- Hyperkalemia.
- Hemorrhage.
What are the causes of Decreased Renin levels?
- Unilateral renal artery stenosis.
- Primary aldosteronism (98%).
- Congenital adrenal hyperplasia with 17-hydroxy deficiency.
- Administration of salt-retaining steroids.
Questions and answers:
Question 1: What is the role of angiotensin II?
Question 2: What is the role of juxtaglomerular cells?

very informative
thank you
please share how do u perform
captopril challenge test
Thanks for the comments.
I am sending a few references for the captopril challenge test:
https://bmcendocrdisord.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12902-019-0390-3
1. In this test, patients need to be seated throughout the test. Take EDTA plasma for renin activity.
2. Now give 50 mg of captopril by oral route.
3. Take second EDTA plasma sample for renin after one hour of the captopril dose.
Thats great
Thank you so much professor.