Mycobacterium Tuberculosis:- Part 2 – Mantoux test, TT, Tuberculin skin Test
Mycobacterium Tuberculosis
What sample is needed for the Mantoux test?
- This test is done on the patient’s skin.
What are the indications for the Mantoux test?
- To diagnose a suspected case of tuberculosis.
- Screening of people at risk like:
- Health worker.
- Immigrant to a high-risk area.
- IV drug user.
- Patients at increased risk of developing active TB.
- So, this TT should be targeted to the high-risk group, which is called targeted tuberculin testing, rather than people at low risk, which is called screening testing.
What is the epidemiology of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis?
- Tuberculosis is the second leading cause of od death in the world.
- Nearly 3 million people die each year.
- 7% of all deaths occur worldwide.
- The global epidemic may become worse because of drug-resistant organisms and HIV patients.
- Mycobacteria are widely distributed worldwide. They are referred to as acid-fast bacilli because they resist decolorization after being mordanted with strong acid.
- The staining property is related to the cell wall composition with high lipid contents.
- The acid-fastness results from the formation of complexes between the dye and mycolic acid, one of the cell wall lipids.
What are the laboratory characteristics of Mycobacterium tuberculosis?
- They are weakly gram-positive organisms.
- M. tuberculosis measures 0.2 to x 5.0 µm bacillus.
- These are slender, beaded bacilli and non-sporing organisms.
- It is an obligate aerobe.
- It grows in high O2 tension (pO2) areas like the lung apex tissue.
- It is a slow-growing organism that needs 1 to 2 weeks or more to grow.
- It has high cell-walled lipid content like mycosides and is impervious to gram stains.
- Smears are treated with concentrated carbol fuchsin for 10 to 20 minutes, which acts as a mordant by heating, and then decolorized with 20% sulphuric acid+ alcohol; now, bacilli will have a bright red color.
What are the culture media for Mycobacterium Tuberculosis?
- These bacteria need highly enriched media, Lowenstein-Jensen media. These bacteria do not grow on ordinary media.
- Lowenstein-Jensen media contains whole eggs, aspargine, glycerol, and malachite green, inhibiting contaminants’ growth.
- The specimen is incubated at 37 °C for 2 to 3 weeks, but the culture should be kept for 6 to 8 weeks.
- Nowadays, these bacteria are identified under fluorescent microscopy.
- These are divided into two groups:
- Rapid grower, which forms the colonies in 2 to 3 days.
- A slow grower who takes 2 to 3 weeks.
- The medically important mycobacteria are:
- M. tuberculosis.
- M. bovis.
- M. leprae.
- Atypical mycobacteria.
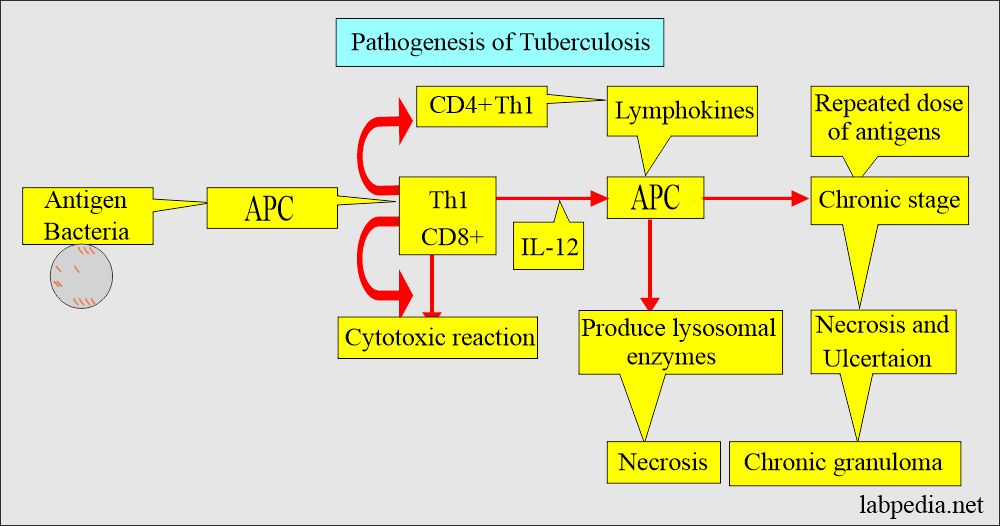
- Mycobacteria tuberculosis causes a slowly progressive chronic infection, usually of the lungs.
- However, other organs are not spared by this disease.
- The primary source is the lung’s secretions, so-called open disease.
Mantoux test:
What is the principle of the Tuberculin sensitivity test (TT) and the Mantoux test?
- The Tuberculin test (TT) is important in diagnosing and preventing tuberculosis.
- This test is more sensitive than the X-ray chest.
- This test is done on the patient, in which purified protein derivatives (PPD) are stabilized by Tween 80 (polysorbate 80-coated nanoparticles) injected into the skin (Intradermal).
- The standard test material is intermediate-strength, 5 tuberculin units, PPD.
- Lymphocytes will recognize PPD as an antigen and give rise to type IV, cell-mediated reaction.
- There will be a local inflammatory reaction in a person who has TB or has past exposure to TB.
- This test will give a severe reaction in the case of active TB or patients with vaccination. The skin may slough.
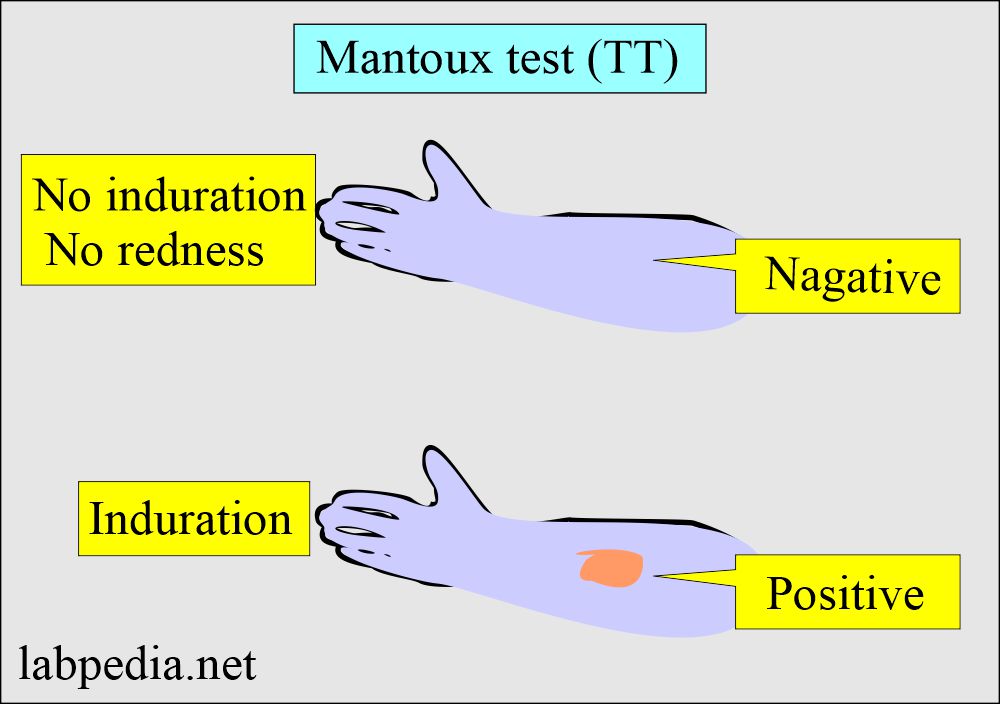
How would you read the Tuberculin test (TT) or Mantoux test:
- Read the test area after 48 to 72 hours of the injection.
- The negative case is when there is no induration.
- In positive cases, there will be induration at the site of injection appearing in 48 to 72 hours.
What are the criteria of the American Thoracic Society and CDC?
- They suggest the following criteria for different population groups:
- Induration <5 mm Diameter is seen in:
- HIV patients or immunodeficiency state.
- Or a patient with a CMI defect.
- Close contact with active TB case.
- The patient had an X-ray finding of old TB.
- Patients with fibrosis or calcification in the lung suggest previous pulmonary tuberculosis.
- Induration >10 mm in Diameter seen in:
- I/V drug users.
- Nursing home residents.
- The traveler from the endemic or high-risk area of Tuberculosis, prisoners, homeless, I/V drug abusers, and other chronically ill patients.
- A worker in the home care facility.
- Malnutrition, postgastrectomy, steroid use, and Diabetes.
- Induration >15 mm in diameter seen in:
- Patient with active TB.
- All patients who don’t fulfill the above criteria.
- A booster reaction may be mistaken for conversion among hospital workers or other people where repeated testing is needed.
- In cases where the primary reaction is negative, or the result is in doubt, give the second dose after one week.
- If the size of the induration is increased by more than 6 mm next year, a new tuberculous infection may be suggested.
What are the contraindications for the Tuberculin and Mantoux skin tests (T T)?
- A patient who has active TB will have a very severe reaction.
- A patient who has a vaccination with Bacillus Calmette Guerin (BCG).
- No use in a malnourished patient.
Where will you see the positive Tuberculin and Mantoux skin tests (TT)?
- An active case of TB.
- Other types of Mycobacterial infection.
Where will you see a negative Tuberculin or Mantoux skin test (TT)?
- Immune incompetent chronically ill patient.
- The patient was not exposed to TB.
- It is found that 20% of the HIV-negative and 40% of HIV-positive cases have tuberculosis.
- Viral infections, including measles and rubella, can suppress tuberculin reactivity. However, this effect is transient.
- Because the tuberculin skin test is limited in sensitivity and specificity, new methods, such as a sandwich-capture enzyme-linked immunoabsorbent assay, are being developed to diagnose Mycobacterium tuberculous infection.
Questions and answers:
Question 1: Where will you see manteaux test positive when induration is >15 mm?
Question 2: Why Tuberculous bacilli acid-fast?