Monoclonal Immunoglobulin (Ig), Monoclonal antibody, Immunofixation Electrophoresis (IFE)
Monoclonal Immunoglobulin (Ig)
What sample is needed for Monoclonal Immunoglobulin (Ig)?
- IFE (Immunofixation electrophoresis) can be done on the patient’s serum.
- Other fluids are CSF, urine, and biological fluids.
- 24 hours of urine is collected according to the instructions.
- Can store the sample at 2 to 8 °C for 5 days.
What are the precautions for Monoclonal Immunoglobulin (Ig)?
- The fresh serum is the sample choice.
- The fasting sample is preferred.
- Avoid anticoagulant use.
- Centrifuge the sample immediately for 15 minutes.
What are the indications for Monoclonal Immunoglobulin (Ig)?
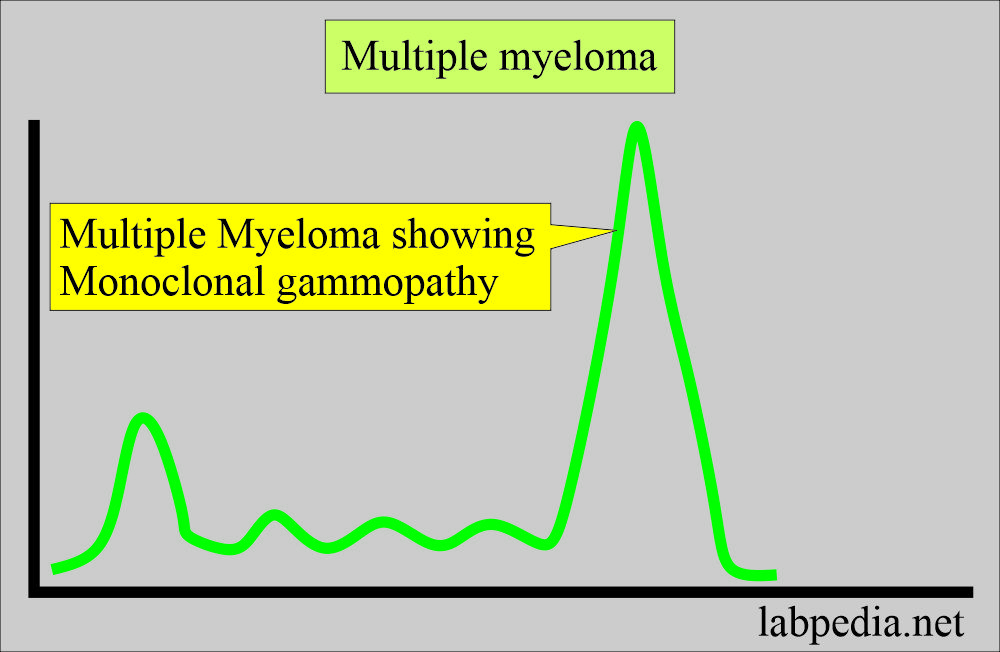
- To identify the monoclonal gammopathy.
- To monitor the treatment with monoclonal gammopathy.
- To find the light chains / heavy chains of immunoglobulin in the urine.
- Monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (MGUS).
- Waldenstrom’s macroglobulinemia.
- Multiple Myeloma (used more than 100 years).
- Amyloidosis.
How will you define monoclonal immunoglobulin(Ig)?
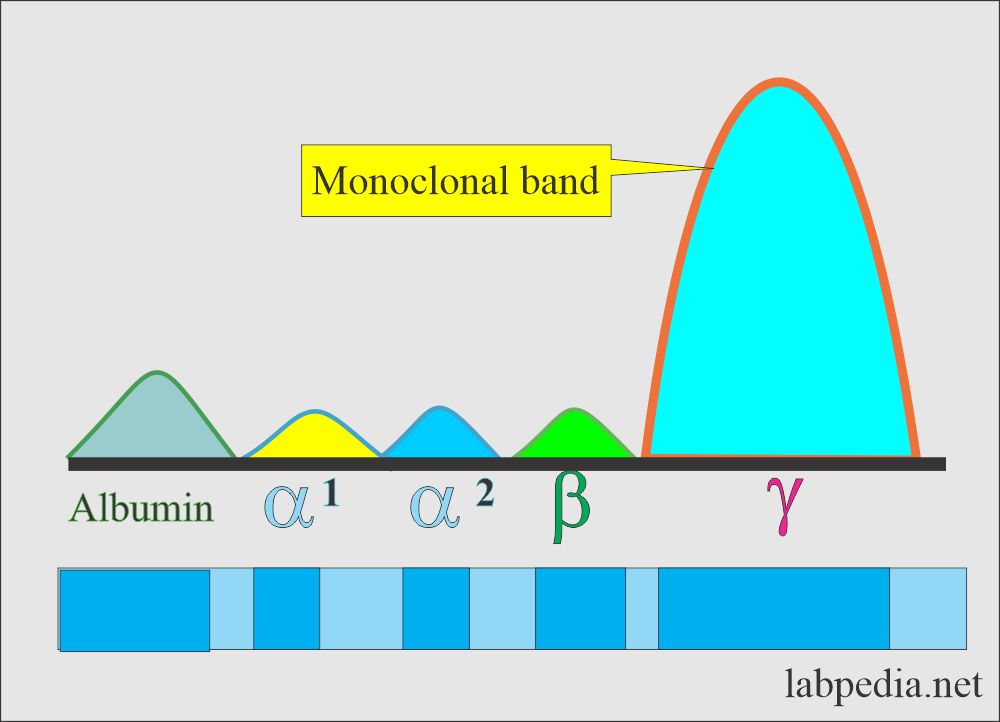
- It is a so-called monoclonal gammopathy spike like M-protein and paraprotein.
- It is located in the γ-region and less frequently in the β-area. Rarely seen in the α2-region.
- The majority of people with monoclonal spikes are myeloma patients.
- Other minorities with monoclonal gammopathy are:
- Walden’s storm macroglobulinemia.
- Secondary monoclonal gammopathy.
- Idiopathic monoclonal gammopathy.
How will you define monoclonal gammopathy?
- Monoclonal gammopathies are clonal disorders of atypical B-lymphocytes. This monoclonal gammopathy is a homogenous product of a single clone of proliferating cells that secretes a single homogenous immunoglobulin (Ig) or its fragments, called monoclonal gammopathy.
- These monoclonal gammopathies are a clonal disorder of B-lymphocyte proliferation.
- These atypical B-lymphocytes are single clones of the proliferating cells that will produce a single immunoglobulin (Ig) or its fragments.
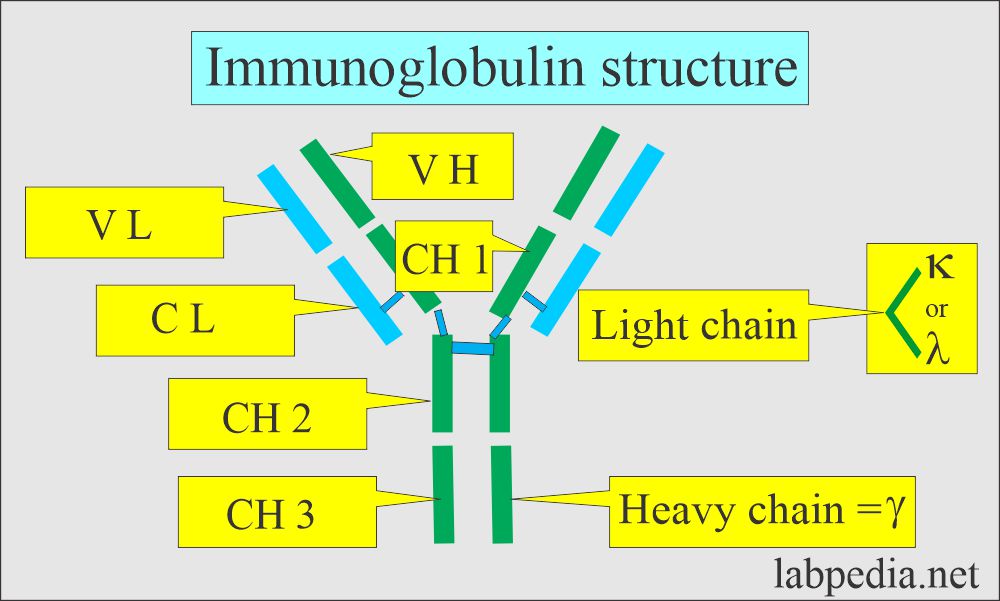
- This abnormal monoclonal immunoglobulin (Ig) has two heavy chains (γ α and μ) in the serum, CSF, and urine. While light chains are either κ or λ are present in the serum, CSF, and urine.
What are the bands of monoclonal gammopathy?
- The majority have monoclonal bands due to multiple myeloma.
- Waldenstorm’s macroglobulinemia.
- Secondary monoclonal gammopathies.
- Idiopathic monoclonal gammopathy.
How would you discuss the pathophysiology of Monoclonal Immunoglobulin (Ig)?
- Immunofixation electrophoresis studies will differentiate protein antigens and their split products and the evaluation of myeloma.
- This was described in 1964.
- Immunofixation electrophoresis is replacing electrophoresis because of its rapidity and ease of interpretation.
- The principle is the same in both processes.
- Monoclonal immunoglobulin (Ig) consists of heavy and light chains.
- These are purified antibodies cloned from a single cell.
- These antibodies will bind to surface antigens.
- The production of the monoclonal antibodies in the animals takes 3 to 6 months.
- Only heavy chains are produced in heavy chain diseases, while only light chains are produced in light chain diseases.
- IFE identifies the monoclonal Ig and light chains or heavy chains.
- By electrophoresis, there is a spike of monoclonal Ig (Antibody).
Monoclonal band on electrophoresis:
- Waldenstrom’s macroglobulinemia also shows a monoclonal spike.
- Above both diseases give light chains excretion in the urine.
- IFE can also find that the spike is due to a light chain or heavy chain.
- Chronic diseases give rise to polyclonal bands of these immunoglobulins.
- Non-malignant monoclonal immunoglobulin seen in:
- 5% of people over the age of 75 years of age.
- These are lower in concentration than the malignant bands.
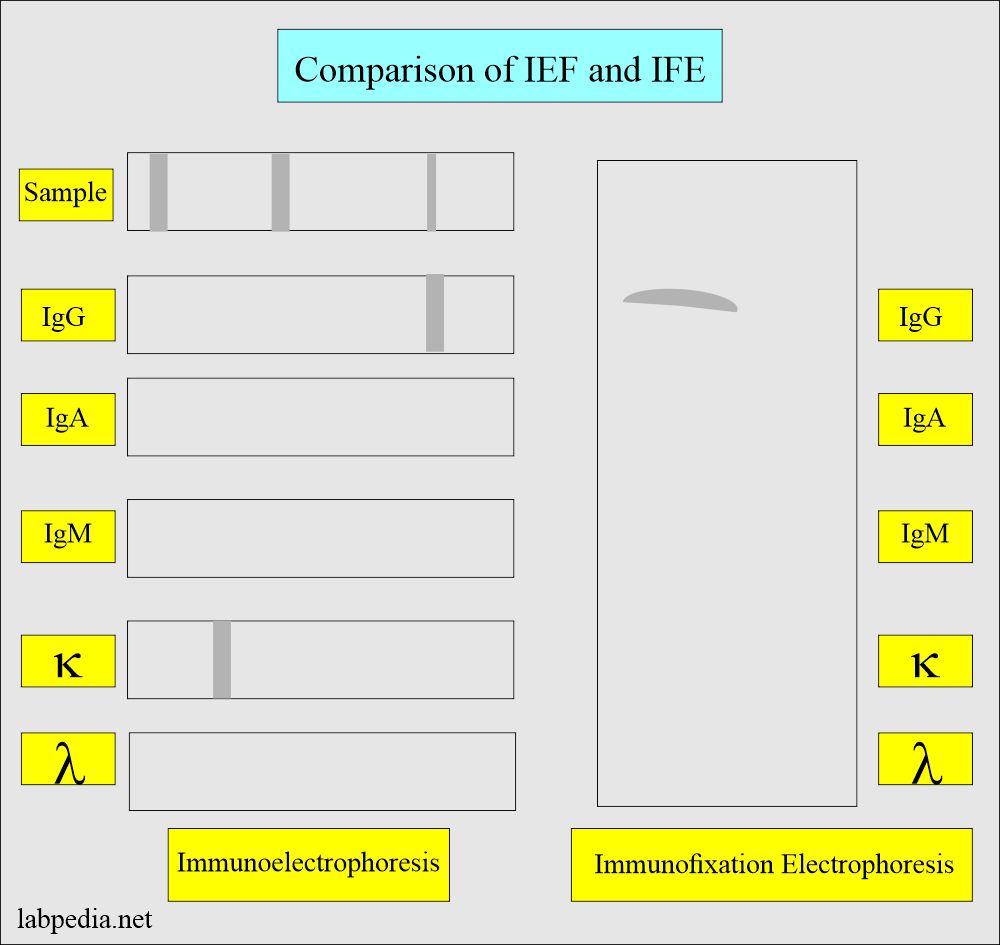
What is the Procedure and Principle of Immunofixation Electrophoresis (IFE)?
- This IFE is a two-stage procedure:
- Agarose gel protein electrophoresis (IEF).
- Immunoprecipitation.
- The patient’s sample is placed in six separate wells on the agarose gel, and their major protein group is separated by electrophoresis.
- One of these tracks is treated with a chemical fixation solution to fix all the proteins in agarose and create an electrophoresis reference pattern for the specimen.
- The other five tracks are treated with heavy and light chains antisera, which react with individual immunoglobulins in the specimen, causing them to Immuno-precipitation.
- Fix in the agarose.
- All unreacted proteins are washed from those five tracks out of the gel.
- Now, all 6 tracks are stained to visualize the fixed protein bands.
What is the normal Monoclonal Immunoglobulin (Ig)?
- No monoclonal band is identified.
What are the causes of seeing monoclonal bands?
- Multiple myelomas show in 99% of the patients in serum and urine.
- Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia always shows a serum IgM-type monoclonal band.
- Monoclonal light chains, also called κ or Bence Jones protein, are seen in the urine of Multiple myeloma cases in 75 % of the patients.
- Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia also shows light chains in the urine in 75 % of the patients.
- Amyloidosis can be seen in the urine through the light or heavy chain.
What are the signs and symptoms of Multiple Myeloma?
- Weakness and fatigue.
- Weakness in the legs.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Recurrent infections.
- Bone pain in the back or ribs.
- H/O fracture
What are the conditions where you will see Polyclonal bands?
- Chronic infections.
- Autoimmune diseases.
- Chronic liver diseases.
- Amyloidosis.
What are the causes of the Monoclonal Ig band in the urine?
- Multiple myelomas.
- Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia.
How will you diagnose monoclonal gammopathy?
- Bone marrow plasma cells are >10% of the total cells.
- Monoclonal protein in the serum or urine.
- Evidence of end-organ diseases like:
- Anemia.
- Bone lesions.
- Hypercalcemia.
- Renal diseases.
Questions and answers:
Question 1: Do you normally see monoclonal immunoglobulin?
Question 2: What is the indication of monoclonal gammopathy?