Mean Corpuscular Volume (MCV), Mean Cell Volume
Mean Corpuscular Volume (MCV)
What sample is needed for Mean Corpuscular Volume (MCV)?
- The best sample is EDTA blood.
- Stable for 6 hours at 25 °C and 24 hours at 4 °C.
- Fetal blood is collected percutaneously from the umbilical area.
What are the indications for Mean Corpuscular Volume (MCV)?
- This is one of the blood indices.
- This is done to classify and diagnose anemia.
- It is a useful screening test for occult alcoholism.
How would you define Mean Corpuscular Volume (MCV)?
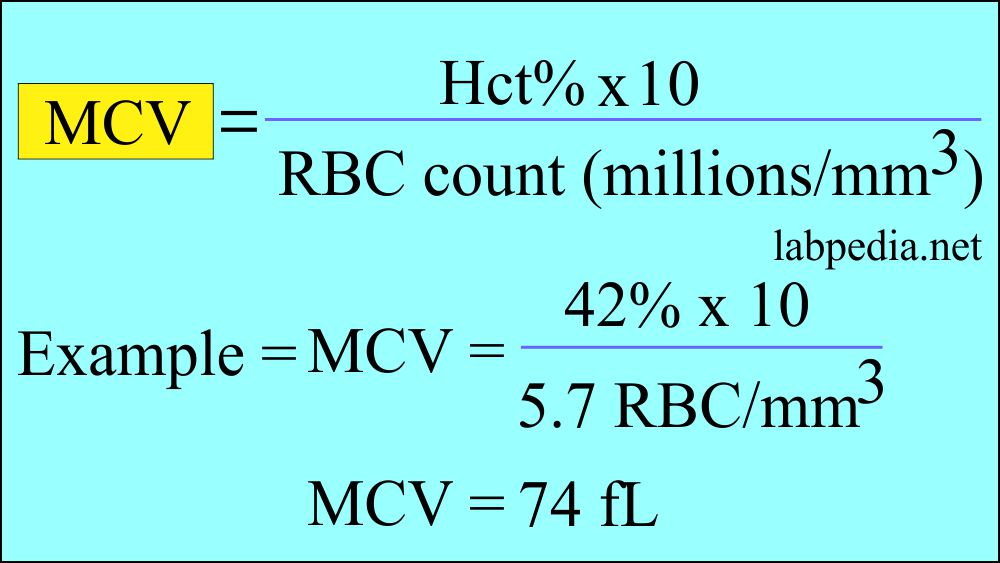
- It represents an average measurement of RBC volume varying from 82 to 98 fL.
- Mean Corpuscular Volume (MCV) is manually calculated as hematocrit divided by RBC count.
- It can be measured directly by the automated instrument.
What are the facts about Mean Corpuscular Volume (MCV)?
- MCV measures the effect of average RBC size on hematocrit.
- Mean Corpuscular Volume (MCV) measures a single RBC’s average volume or size.
- If the average size of RBCs increases, the same number of RBCs will have a slightly larger cell mass and a slightly increased hematocrit value. The opposite happens if the average size of RBCs is smaller than normal.
- MCV indicates the volume occupied by a single RBC and is measured in a cubic micrometer of the mean volume.
- Cubic micrometer = femtoliter ( fL ).
- MCV helps to classify various anemias.
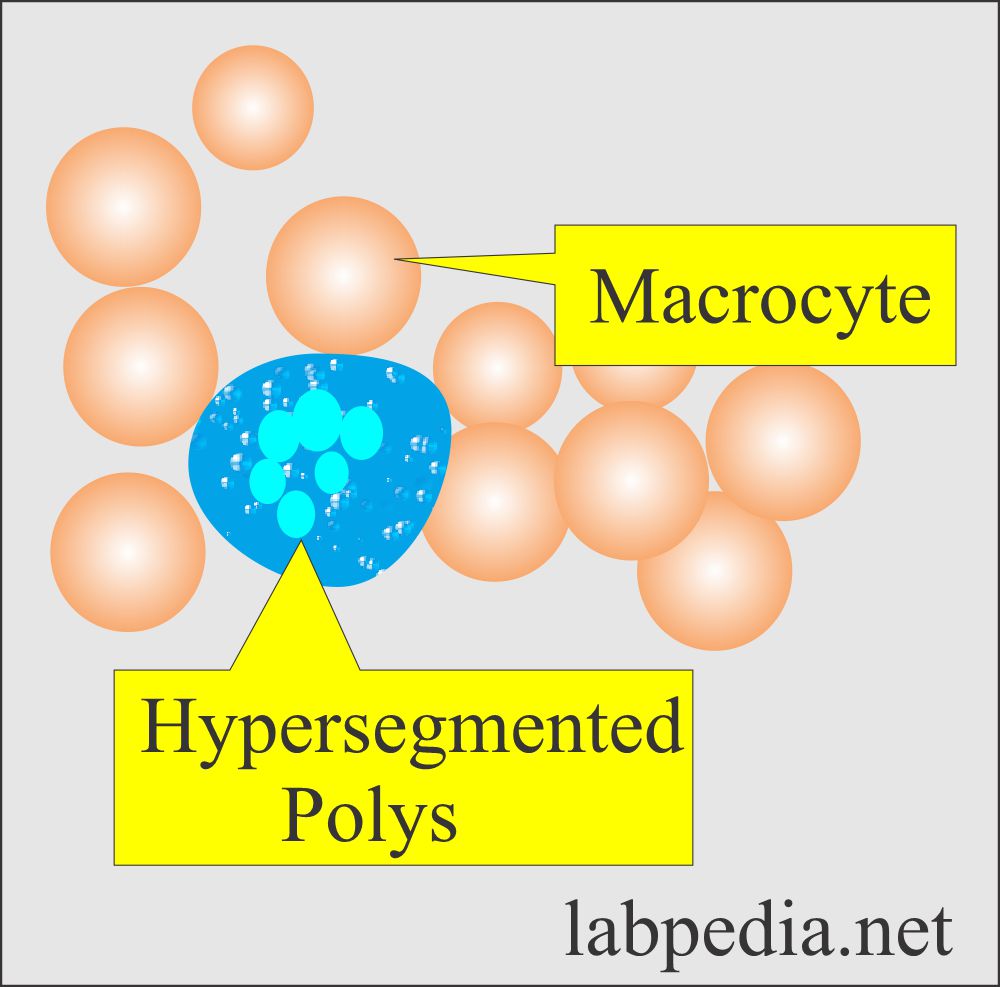
- Macrocytic RBC:
- When the RBC size is larger than normal, more than 100 fL.
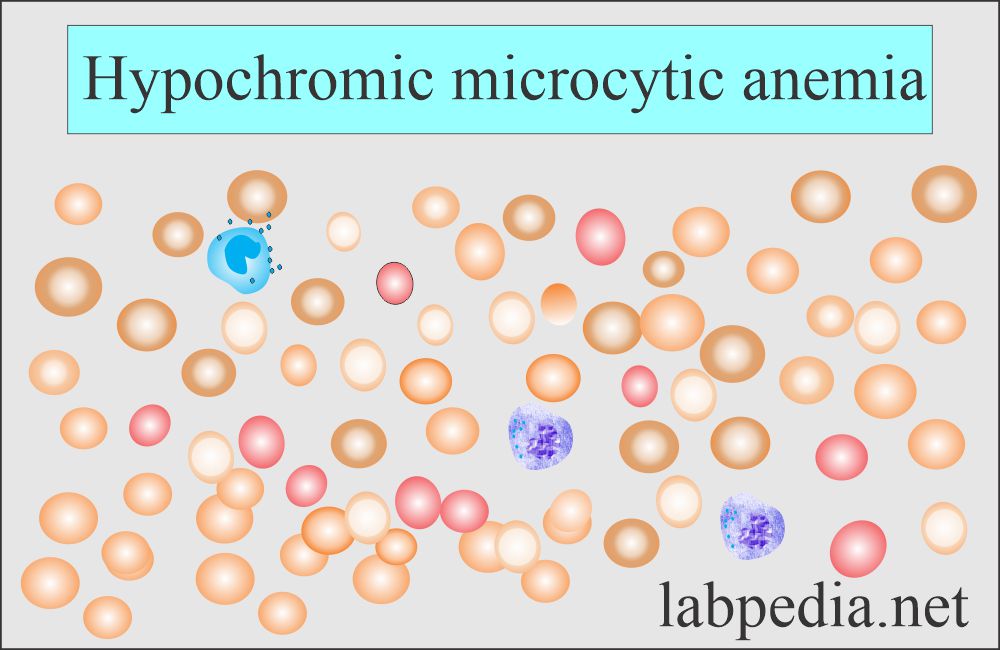
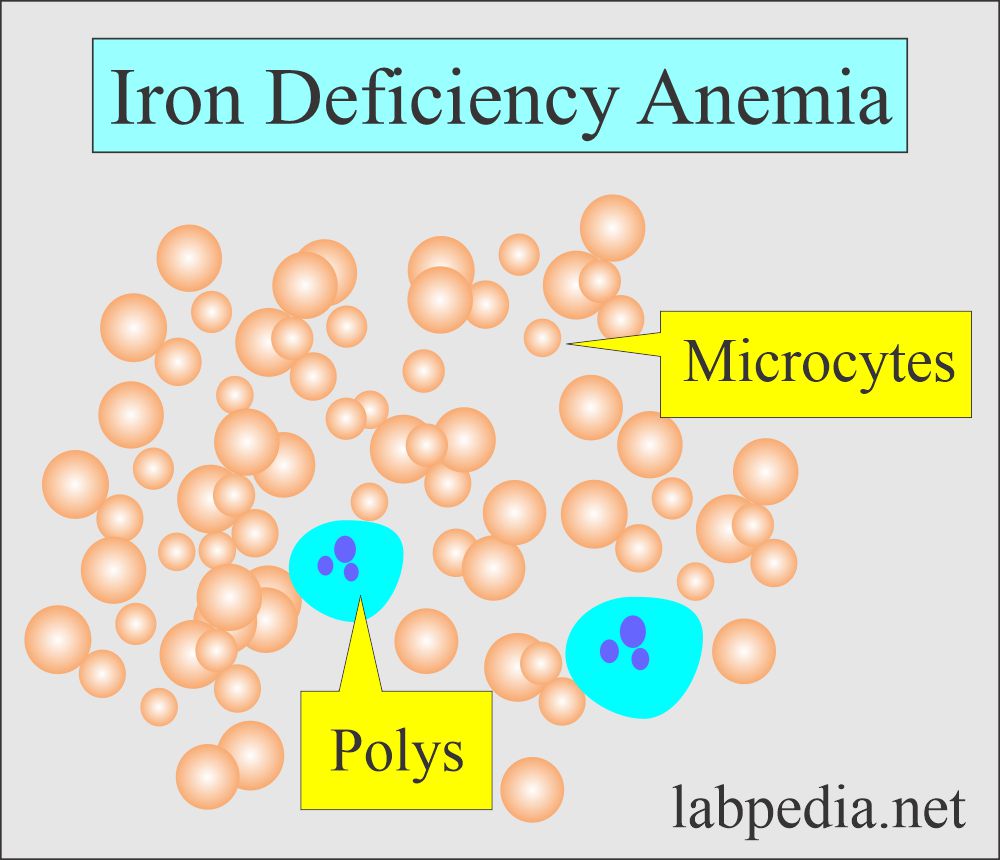
- Microcytic RBC:
- When the RBC size is smaller than normal, it is less than 82 fL.
- It is considered that the most common cause of macrocytosis is alcoholism with or without cirrhosis.
What is the normal Mean Corpuscular Volume (MCV)?
Source 1
| Age | fL | |
| Fetal blood | ||
| 18 to 20 weeks | 133.9 ± 8.8 | |
| 21 to 22 weeks | 130.1 ± 6.2 | |
| 23 to 25 weeks | 126.2 ± 6.2 | |
| 26 to 30 weeks | 118.2 ± 5.8 | |
| Infants and Child | ||
| Cord blood | 98 to 118 | |
| 0.5 month | 88 to 140 | |
| 0ne month | 91 to 112 | |
| 2 month | 84 to 106 | |
| 4 month | 76 to 97 | |
| 6 month | 68 to 85 | |
| 9 month | 70 to 85 | |
| 12 month | 71 to 84 | |
| 0.5 to 2 year | 70 to 84 | |
| 2 to 5 year | 73 to 85 | |
| 5 to 9 year | 75 to 87 | |
| 9 to 12 year | 76 to 90 | |
| Male | Female | |
| 12 to 14 year | 77 to 94 | 73 to 95 |
| 15 to 17 year | 79 to 95 | 78 to 98 |
| 18 to 44 year | 80 to 99 | 81 to 100 |
| 45 to 64 year | 81 to 101 | 81 to 101 |
| 65 to 74 year | 81to 103 | 81 to 102 |
Source 2
- Adult = 80 to 95 fL.
- Newborn = 96 to 108 fL
Another source
- Both sexes = 80 to 100 fL
- Heavy smoking increases the MCV as much as 3 fL
What are the causes of increased Mean Corpuscular Volume (MCV)?
Macrocytic anemia causes are:
- B12 or folic acid deficiency :
- Decreased ingestion.
- Laking animal protein.
- Vegetarians.
- Impaired absorption.
- Intrinsic factor deficiency.
- Abnormal intrinsic factor molecule.
- Patient with partial or total gastrectomy.
- Ileal resection.
- Sprue.
- Celiac disease.
- Intestinal lymphoma.
- Drug-induced malabsorption.
- Decreased ingestion.
- Parasitic infestation.
- Diphyllobothrium latum.
- Infected diverticula.
- Blind loop.
- Increased requirement.
- Pregnancy.
- Malignancies.
- Hyperthyroidism.
- Chronic pancreatic disease.
What are the causes of decreased Mean Corpuscular Volume (MCV)?
Microcytic anemias are seen in:
- Iron metabolism-related.
- Iron deficiency anemia.
- Decreased dietary intake.
- Malabsorption.
- Increased iron loss.
- Increased body requirements for iron.
- Congenital hypochromic microcytic anemia.
- Anemias of chronic diseases.
- A defect in heme synthesis.
- Idiopathic refractory sideroblastic anemia.
- Acquired sideroblastic anemia.
- Hereditary sideroblastic anemia.
- Autosomal anemia ( X chromosome-linked ).
- Disorder of globin synthesis.
- Thalassemia.
- Hemoglobinopathies.
What are the causes when the Mean Corpuscular Volume (MCV) is increased?
Macrocytic anemias are seen in:
- Pernicious anemia (vit.B12 deficiency).
- Folic acid deficiency.
- Liver diseases.
- Alcoholism.
- Antimetabolic therapy.
What is the differential diagnosis of anemias based on MCV?
| MCV (Macrocytosis) | MCV (Microcytosis) |
Common causes are:
Less common causes are:
|
Common causes are:
Less common causes are:
|
Questions and answers:
Question 1: What is the MCV for microcytes?
Question 2: What is MCV of the macrocytes?