Liver:- Part 3 – Differential Diagnosis of Jaundice
Differential diagnosis of jaundice
What sample is needed for the liver function test?
- The serum of the patient is needed.
- Don’t expose the sample to light.
- The liver function tests can differentiate various types of jaundice due to liver diseases.
What is the differential diagnosis of jaundice and LFT?
| Disease | Urine | Stool | Serum Bilirubin | Serum cholesterol | |
| Tests | Bilirubin | Urobilinogen | Bilirubin Urobilinogen | Direct Indirect | Cholesterol |
|
Increased | Normal or Increased | Decreased Decreased | Increased Increased | Normal or Increased |
| Hepatitis due to drugs | Inc | N or Inc | Decreased Decreased | Increased Increased | Normal |
| Cholestatic Hepatitis | Inc | N or Dec | Decreased Decreased | Increased Slight Inc | Increased |
| Jaundice due to Cirrhosis | Inc | N or Inc | <1 indirect >1 direct | Increased Increased | |
| Extrabiliary obstruction | Increased | Decreased | Decreased +++ Dec +++ | Increased N or Inc | Inc mild to moderate |
Inc = increased N = Normal Dec = Decreased
What are the diagnostic tests for various liver diseases?
| Disease | Lab Tests | Interpretation |
| Acute Viral Hepatitis | Bilirubin | raised (variable level) |
| SGOT | raised 10 to 100 times the normal value | |
| SGPT | raised 10 to 100 times the normal value | |
| Gamma GT | raised 5 times the normal value | |
| Viral markers | positive | |
| Chronic hepatitis | SGPT | mildly raised |
| SGOT | mildly raised | |
| Bilirubin | persistently raised | |
| Cirrhosis | SGPT | slightly raised |
| SGOT | Slightly raised | |
| Bilirubin | mildly raised | |
| Alkaline phosphatase | mildly raised | |
| Gamma GT | mildly raise | |
| Prothrombin time | prolonged | |
| Alcoholic liver | SGPT / SGOT | mildly raised |
| Gamma GT | raised 2 to 3 times the normal value | |
| Albumin | decreased | |
| Globulin | raised | |
| Primary biliary cirrhosis | Bilirubin | raised |
| Alkaline phosphatase | raised 2 to 10 times the normal value | |
| SGPT / SGOT | moderately raised | |
| Liver malignant tumor | SGPT / SGOT | maybe raised |
| Alkaline phosphatase | raised | |
| Gamma GT | raised to 20 times the normal value | |
| Cholestatic jaundice | Bilirubin | raised mostly conjugated |
| Alkaline phosphatase | markedly raised | |
| SGPT / SGOT | mildly raised | |
| Gamma GT | markedly raised |
What are the Lab tests for jaundice?
- Bilirubin direct and indirect:
- Direct bilirubin is increased in obstructive jaundice.
- Indirect bilirubin increased in hemolytic jaundice, infections, and toxic hepatitis.
- Urobilinogen quantitative:
- Increased urobilinogen is seen in a liver infection, and toxic hepatitis is reabsorbed from the intestine.
- There has also been an increase in various types of hemolytic diseases.
- The absence of urobilinogen is strongly suggestive of posthepatic biliary obstruction.
- Urine bilirubin:
- There is an increase in urine bilirubin due to the excessive production of bilirubin, which is usually due to the posthepatic type.
- Fecal urobilin:
- The absence of urobilin (stercobilin) in the stool indicates that no bilirubin enters the duodenum, leading to a clay-colored stool.
- Alkaline phosphatase:
- It is increased in post-hepatic jaundice, cholangitis, and primary or metastatic cancer.
- There may be a mild increase in hepatic jaundice.
- Cholesterol esters:
- It is a decrease in liver disease.
- Response to vitamin K:
- A poor response to vitamin K is seen in liver disease.
- Flocculation test:
- Positive cephalin flocculation or thymol flocculation tests indicate liver diseases like infections or toxic hepatitis.
- Galactose tolerance test:
- There is decreased tolerance to galactose, which is found in liver disease.
- Liver needle biopsy:
- This will diagnose liver disease.
How will you diagnose Various Types of Jaundice?
| Clinical condition | Urine bilirubin | Urine urobilinogen | Alk. Phosphatase | Bilirubin Direct | Bilirubin indirect | BSP test | Ceph. Flocculation |
| Hepatitis with jaundice | Positive | Increased | Normal or slightly Increased | Normal or slightly increased | Increased | Increased retention | Positive |
| Hepatitis without jaundice | ± | Increased | Normal | Normal | Normal | Increased retention | Positive |
| Hemolytic jaundice | Negative | Increased | Normal | Normal | Increased | Normal | Negative |
| Extrahepatic biliary obstruction | Positive | Decreased or absent | Increased | Increased | Normal | Not satisfactory | Negative |
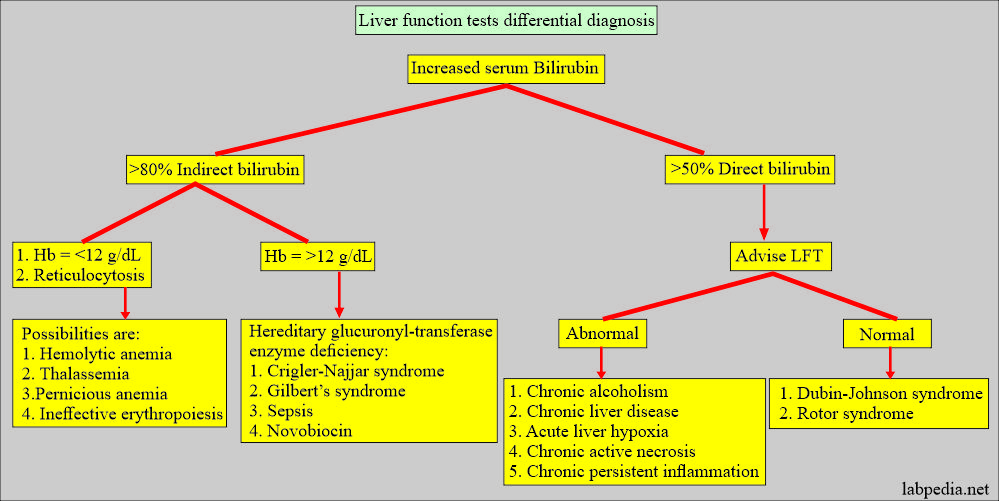
What is the differential diagnosis of increased serum bilirubin?
Please see more details in the LFT.

Excellent D/D
Thanks for the appreciation.
Tnx, excellent work,. Go forward and write more and more
Thanks a lot for the encouraging remarks. We are trying our best to update all the subjects.
My nicee 9 yr old having direct bilirubin 0.3 and sgot 34 what could be the diagnosis
It is normal.