How to Handle Various Specimens of The Body
May 30, 2023Uncategorized
How to Handle Various Specimens
- We will discuss precautions for handling the various specimens.
Possible various sources of specimens:
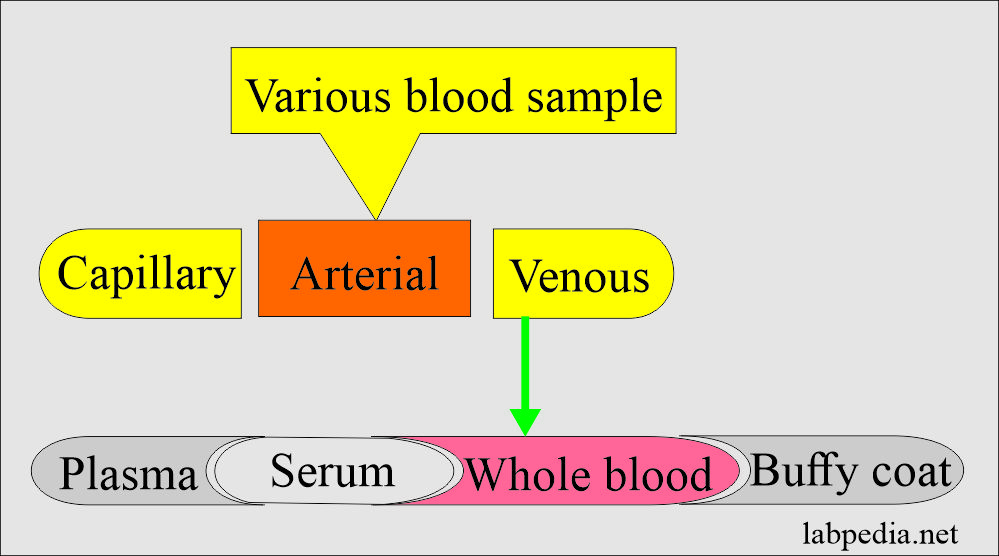
Blood samples types:
- There are the following types of blood samples.
Venipuncture:
- Blood is obtained directly from the vein into the vacuum tubes.
- OR take blood by syringe and transfer it into the tubes.
- Place this tube in a biohazard bag and transfer it to the lab.
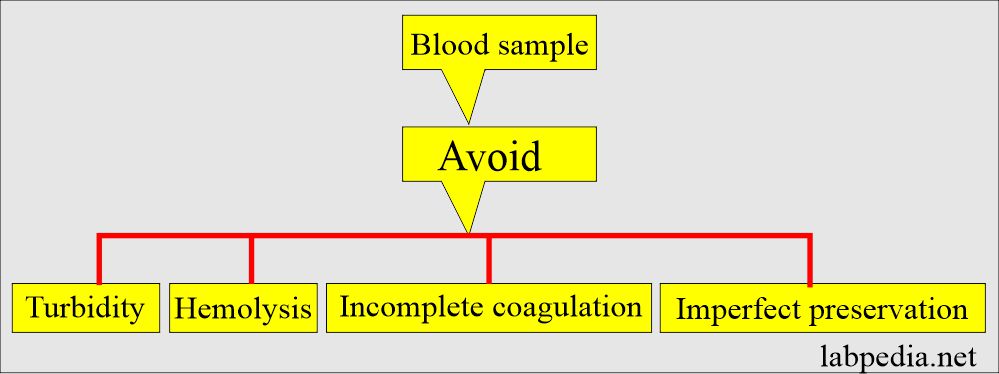
Precautions for blood collection:
- Please look after hemolysis, turbidity, incomplete coagulation, and imperfect preservation.
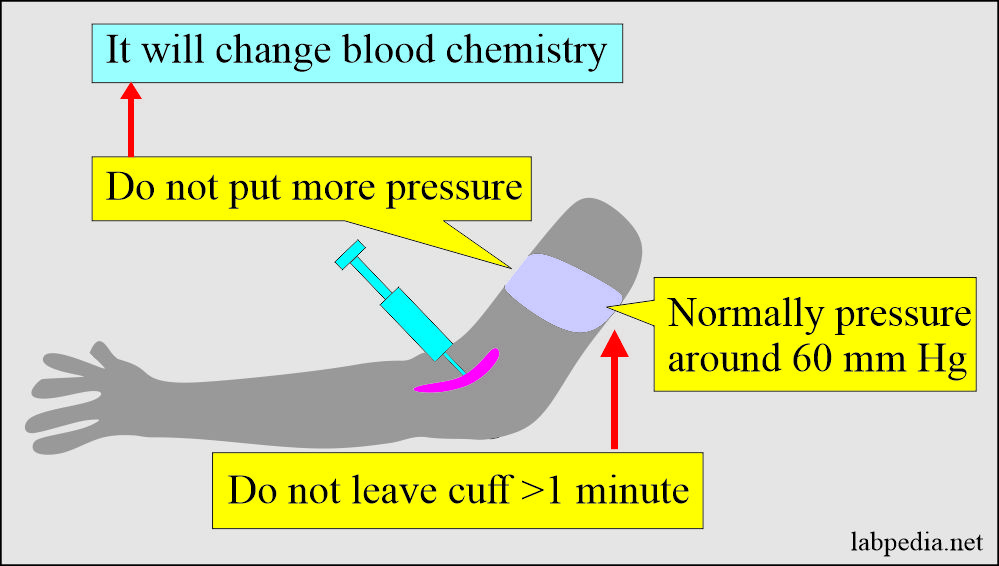
- Avoid too much pressure while collecting the blood samples.
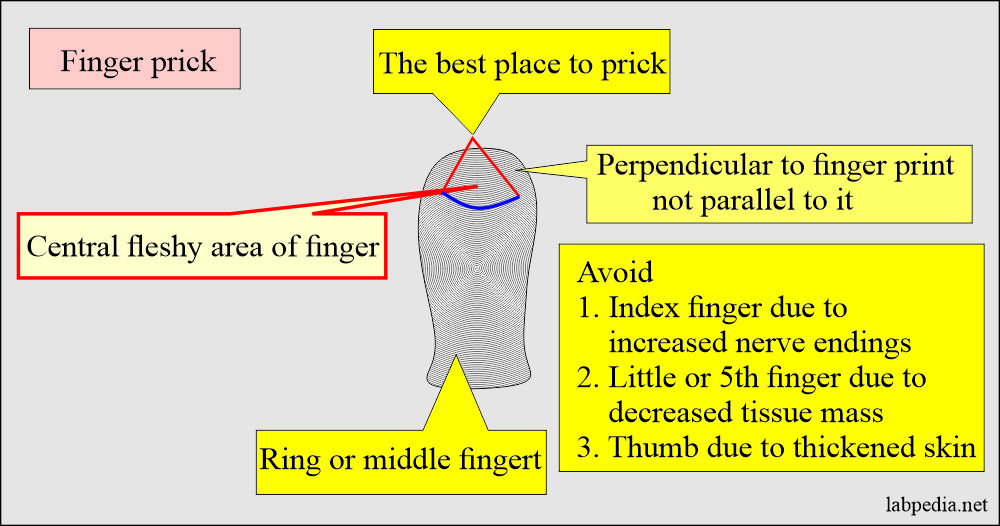
Capillary puncture
- This capillary blood is usually taken in children.
- This site is also used for diabetic patients.
- Precaution: The best area is the lateral side of the finger pulp.
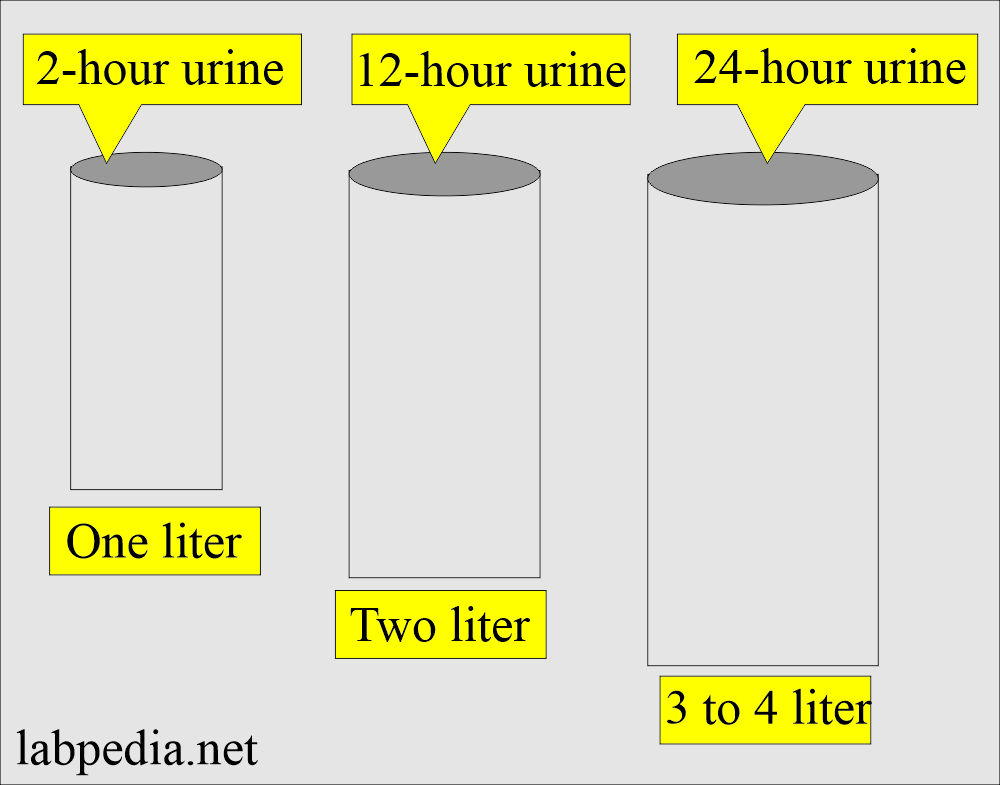
Urine specimens
- Urine needs to be collected in sterile, clean containers for routine examination.
- 24-hour urine is collected in a large container and may need to contain preservatives.
- The urine sample needed to be refrigerated or kept on ice.
- When starting the collection, note the time and discard the first sample.
- When 24 hours are completed, empty the last urine sample in the container.
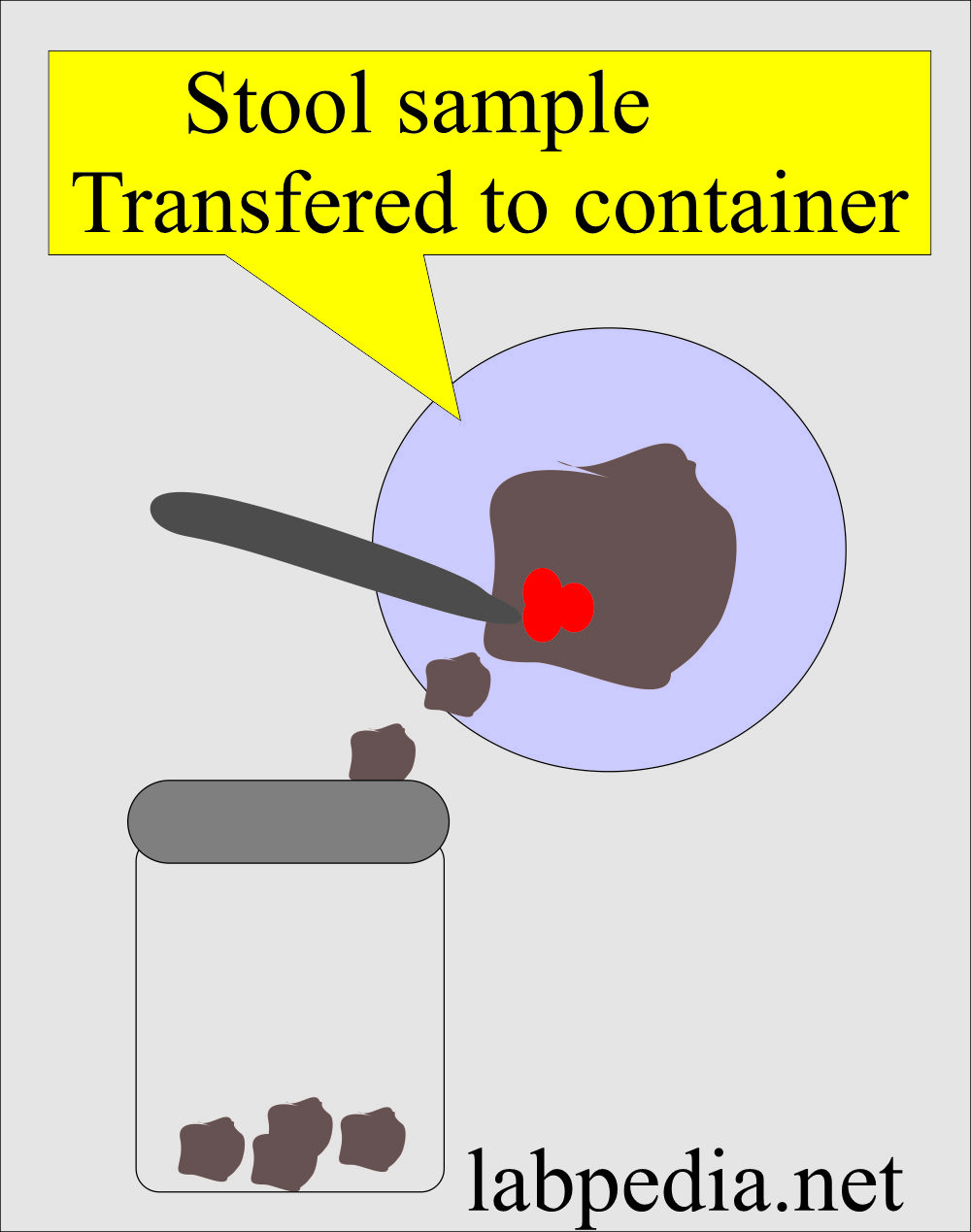
Stool specimens
- Collect the stool in clean and dry containers.
- Can collect stool in a dry clean bedpan.
- Transfer the stool into a biohazard plastic bag.
- Infants can get a stool sample from the diapers.
- Transfer the stool with blood, mucus, or pus into a separate container.
- If a suspected case of amoebic dysentery or blood, it should be transferred to the laboratory as soon as possible.
- Precautions: Avoid urine contamination with urine.
- Send the stool sample to the laboratory as soon as possible.
Body fluids
- The possible body fluids are:
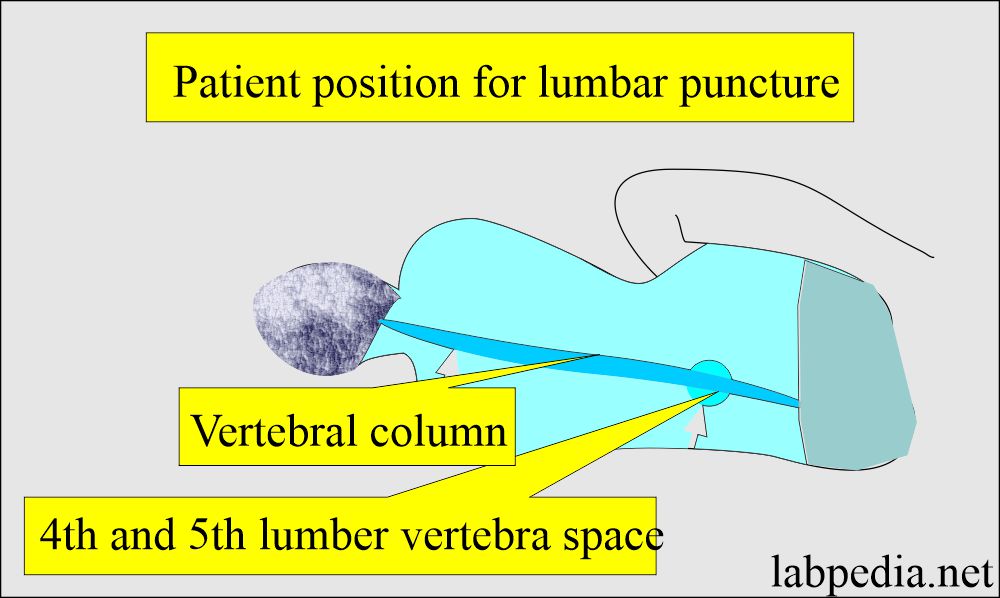
Spinal fluid (CSF examination):
- It is collected by an experienced medical health officer.
- It is collected aseptically to prevent the infection.
- A wide bore needle is inserted between the 4th and 5th lumber vertebrae.
- Collect the sample in sterile test tubes. Usually, CSF is collected into three test tubes.
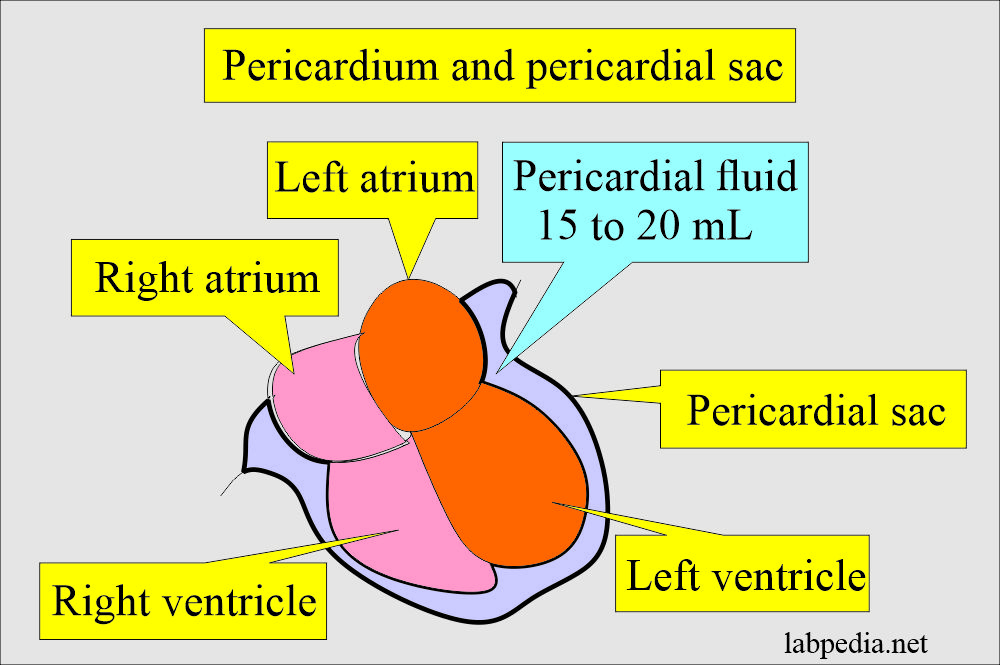
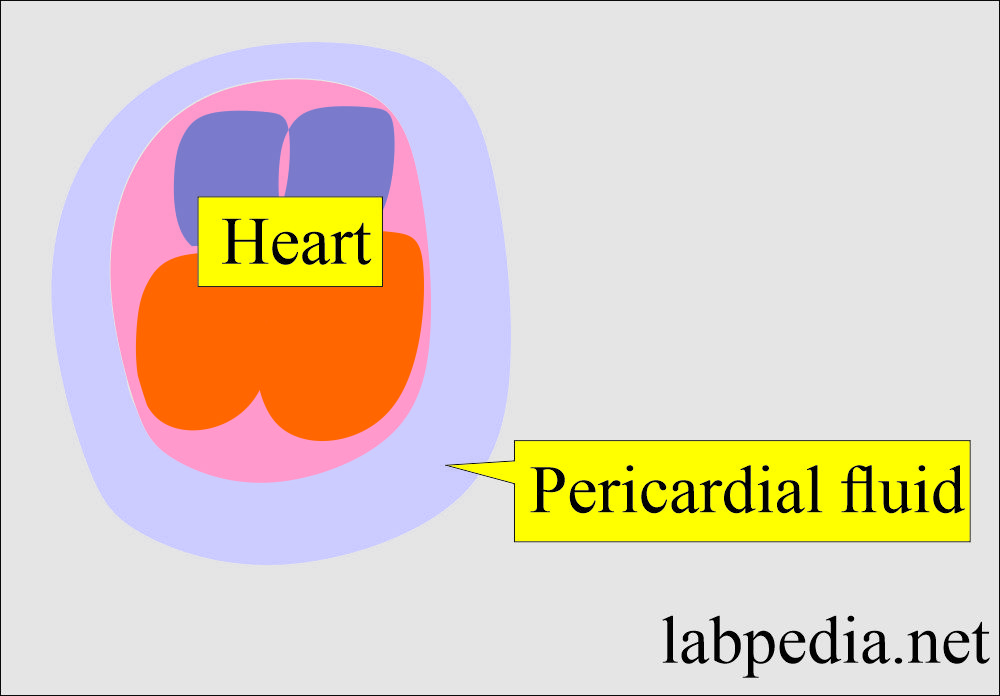
Pericardial fluid.
- Pericardial fluid is aspirated from the pericardial sac, which is the membranous sac surrounding the heart.
- It should be done by an expert in this field, by a cardiologist or interventional radiologist.
- Local analgesia or anesthesia is given to the patient.
- Insert the needle under guidance to enter the pericardial space.
- Once you are in the space, then slowly aspirate the fluid.
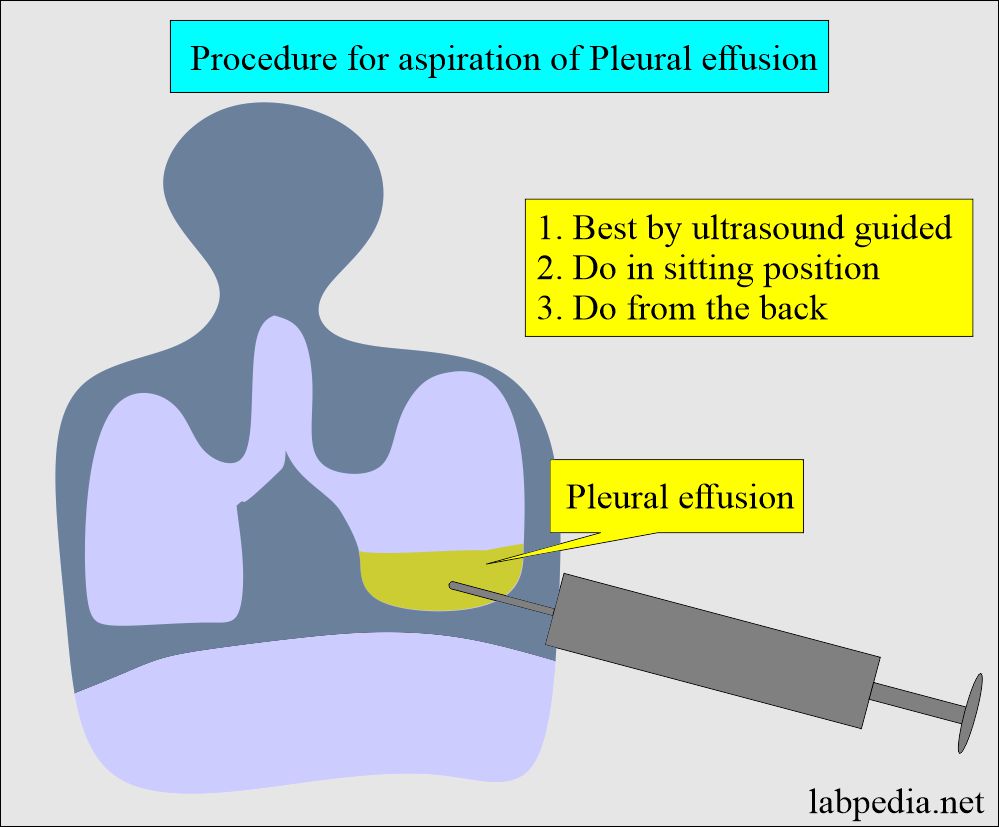
Pleural fluid.
- Pleural fluid is collected between the pleural cavity, that is, the space between the lungs and the inner chest wall.
- Pleural fluid should be aspirated by an expert medical officer. This procedure is called thoracentesis.
- Pleural fluid is aspirated by percussing the chest.
- Insert the needle in the dull area.
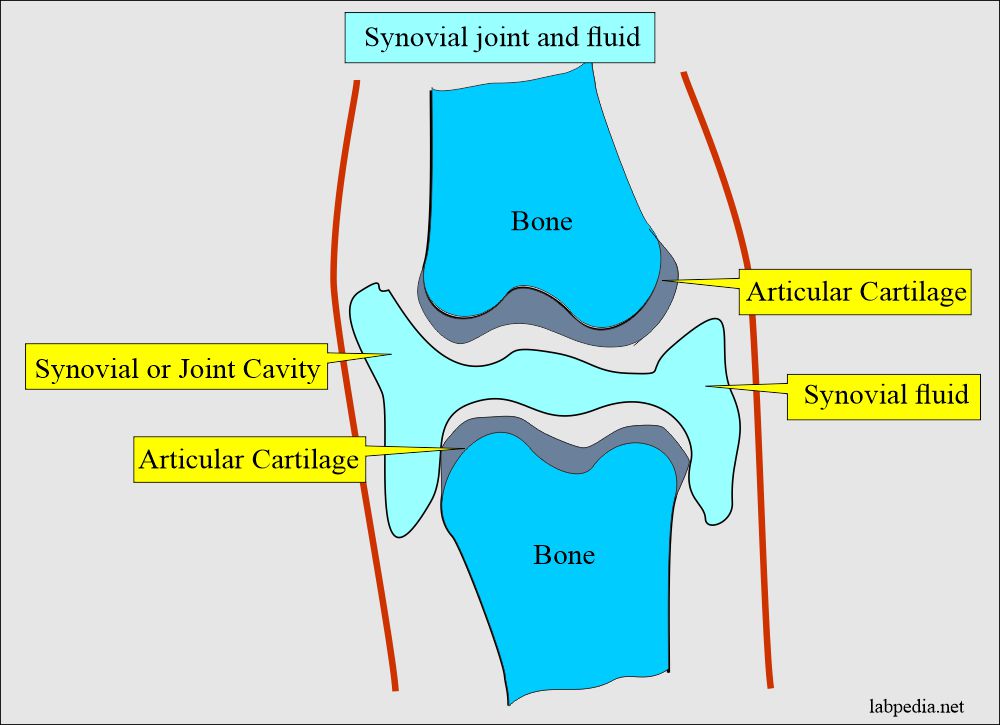
Synovial fluid.
- Aspiration of the synovial fluid is called arthrocentesis.
- These fluids are aspirated by the needle and syringe.
- Can give local anesthesia to make the patient comfortable.
- The aspirated fluid is transferred to a sterile container.
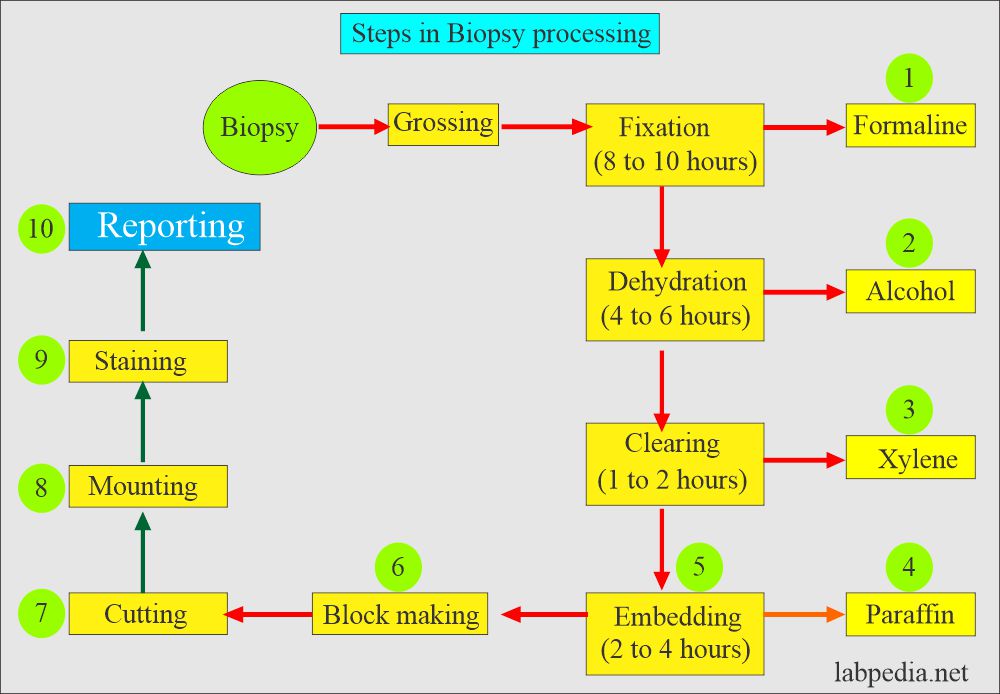
Biopsies
- Always put biopsy in appropriate fixative.
- The most commonly used are formaline.
- The container should be tightly closed to avoid the formaline smell.
- Biopsies need 8 to 12 hours of fixation before starting further processing.
- There are various chemicals through which biopsy will pass through, and ultimately slides are prepared and given to histopathologic for the final diagnosis.
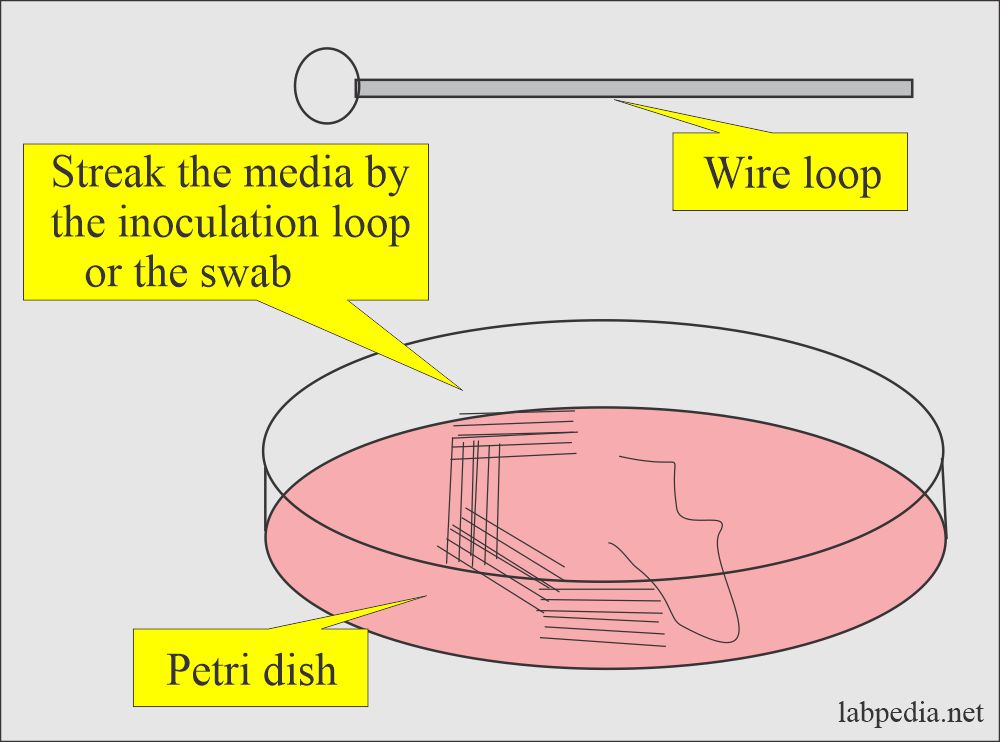
Culture
- There are various sites for the culture specimens.
- It may be throat, eyes, or wounds.
- Urine and stool can also be sent for culture.
- Always take samples for culture in sterile containers.
- There are transport media for the culture.
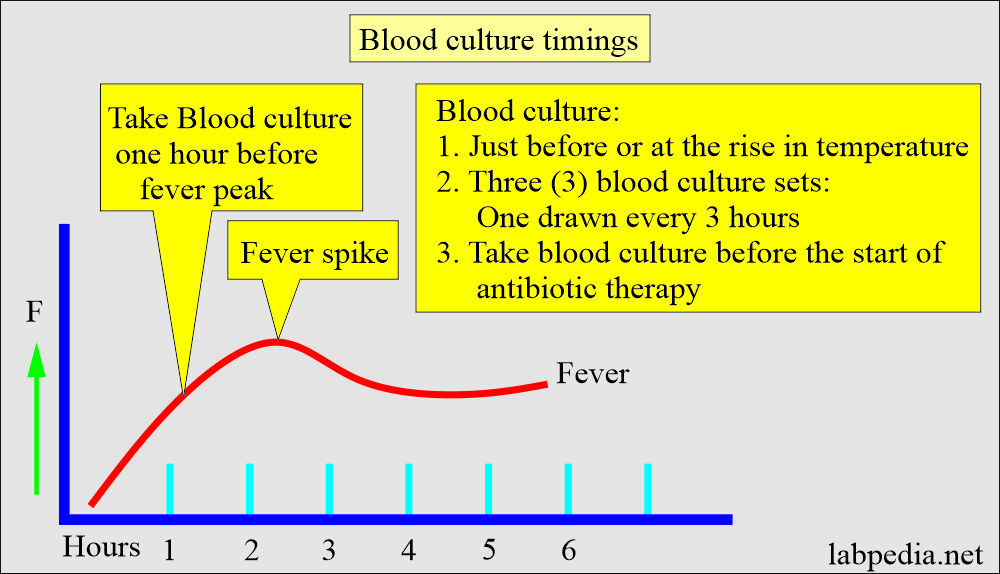
- In the case of blood culture, when the patient has a fever.
- Take a blood sample when the patient has a fever.