Anti-HBs Antibody Significance
What sample is needed for Anti-HBs Antibody (ELISA)?
- The test is done in the serum.
- How to get good serum: Take 3 to 5 ml of blood in a disposable syringe or a vacutainer. Keep the syringe for 15 to 30 minutes at 37 °C and then centrifuge for 2 to 4 minutes to get the clear serum.
- No special preparation is needed.
- This test can be done on a random sample.
What are the Indications for Anti-HBs Antibody (ELISA)?
- An anti-HBS antibody test is done to see whether the patient’s immune status recovered from the infection.
- This test may be done in screening the population for Hepatitis B prevalence.
How will you discuss the pathophysiology of Anti-HBs Antibody (ELISA)?
- The hepatitis B virus is called serum hepatitis.
- The HBV incubation period is 5 weeks to 6 months; there is long incubation.
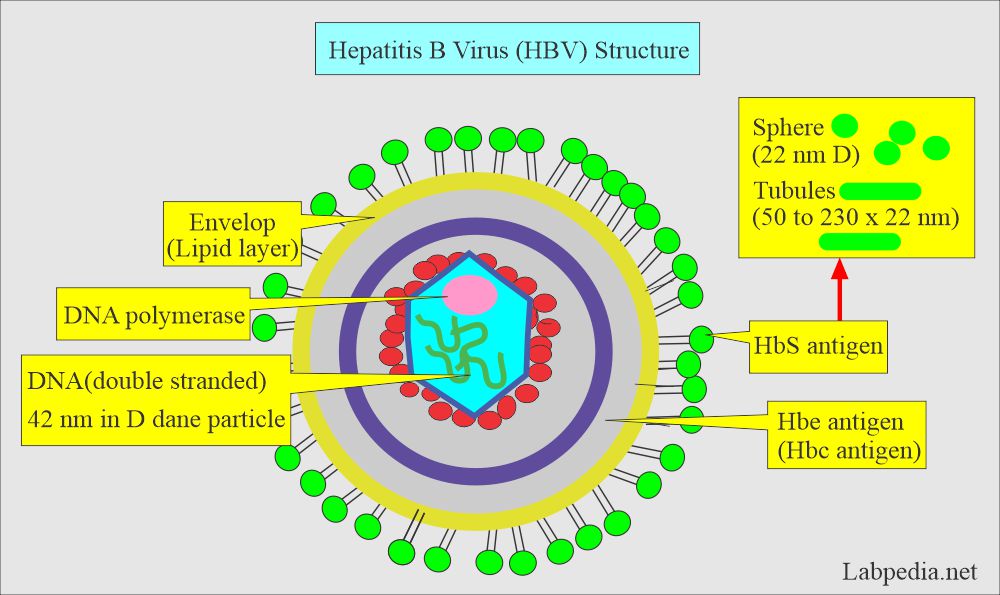
- Patients with Hepatitis B virus infection show hepatitis B surface antigen in the circulation.
- In the case of recovery, Antibodies against these antigens appear in the blood.
- The patient will be Surface ( HBsAg ) antigen negative.
- The following diagram shows the structure of the HB virus. It has three antigens and three antibodies.
What is the significance of Anti-HBs Antibody (ELISA)?
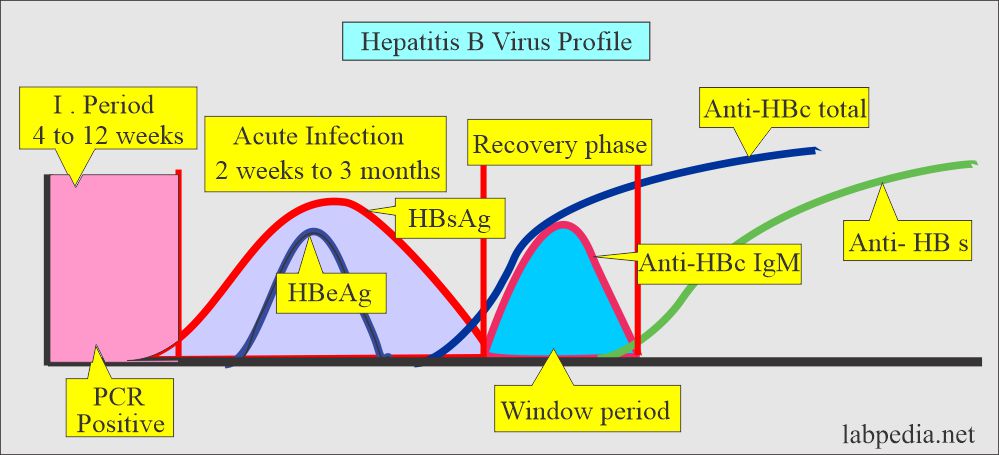
- Anti-HB antibodies are the marker of recovery from the Hepatitis B virus. When positive, it means that the patient has recovered from the disease.
- The presence of anti-HBs antibodies indicates immunity to Hepatitis B viral infection.
- The presence of antibody tite >10mU/mL without detectable HBs antigen indicates:
- Recovery from HBV infection.
- Absence of infectivity.
- Immunity from future HBV infection.
- No need for gamma globulin after exposure to the HBV patient.
- Can donate blood.
- This may occur after blood transfusion, indicating passive transfer of the antibodies.
- It is found in 80% of the patients after recovery.
- After the HBs antigen disappears, anti-HBs antibodies may take several weeks to months to appear in the blood circulation, and this is called a window period ( 2 to 6 weeks) where only anti-HBs IgM is present in the circulation.
- In the window period, the patient is recovering but still infectious.
How will you decide on vaccination of the person based on anti-HB antibodies?
| Patients data | HBs-antigen | Anti-HBs-antibody | Anti-HBc-antibody | Interpretations |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Positive |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|