HbA1c and Diabetes
HbA1c
Sample for HbA1c
- A random blood sample can be taken.
- There is no need for a fasting blood sample.
Indication of HbA1c
- The gold standard for checking diabetes.
- It measures your average blood glucose level over 3 months period.
Precautions for HbA1c
- Hemoglobinopathy can affect the result.
- Ascorbic acid may give false low values.
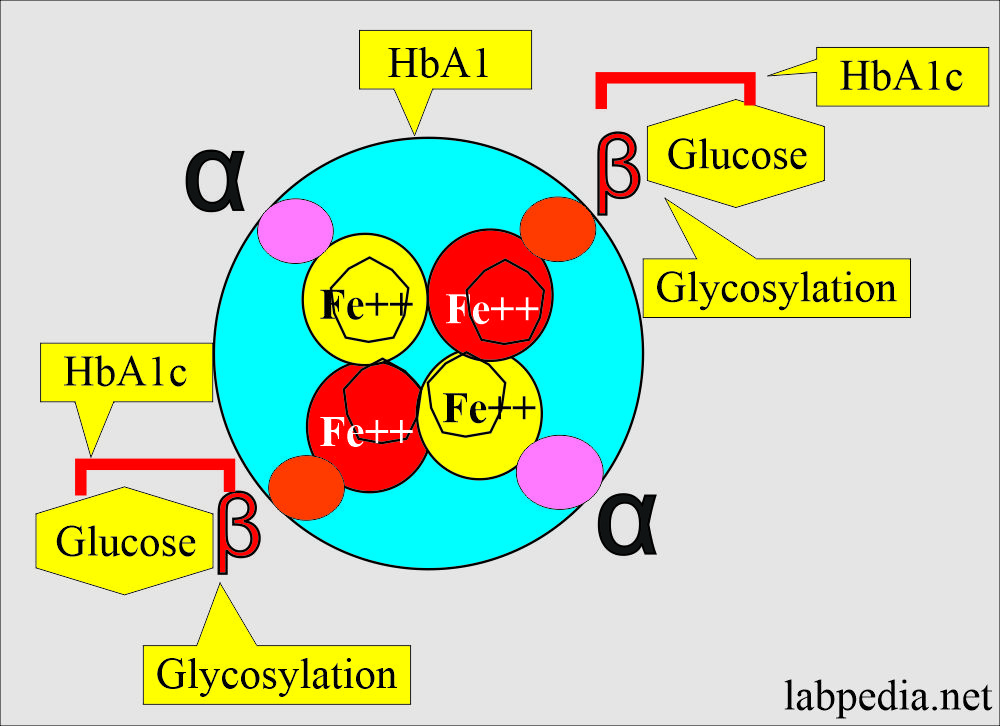
Pathophysiology of HbA1c
- In adults, 98% of the hemoglobin is HbA in the RBCs. Hemoglobin A2 is about 2.5%, and Hemoglobin F is only 0.5%
- About 7% of the HbA consists of HbA1, which can strongly bind glucose, and the process is called glycosylation.
- This glycosylation process in the initial stages is labile and then becomes stable and is not reversible.
- This process of glycosylation takes place when RBCs are exposed to blood glucose.
- HbA1 after glycosylation consists of:
- HbA1a.
- HbA1b.
- HbA1C.
- HbA1c combines with glucose more strongly.
- About 70% of HbA1c is glycosylated.
- At the same time, only 20% of HbA1a and HbA1b are formed.
- This glycosylated hemoglobin HbA1c is the blood RBCs life span is 120 days.
- This glycosylated hemoglobin reflects the average blood sugar level for 100 to 120 days. So please no need to advise before that period.
Normal HbA1c
- Non-diabetic HbA1c = 4% to 5.9%
- Controlled diabetes = <7%
- Fair diabetic control = 8% to 9%
- Poor diabetic control = >9%
| HbA1c% | The mean plasma glucose level | Clinical explanation |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Another reference
| Fasting Glucose Level | HbA1c | Clinical stage |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Another reference
| HbA1c level | The estimated average glucose level |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
For diabetic patients:
- In newly diagnosed cases of diabetes, try to keep HbA1c below 7%.
- In anemic patients, HbA1c will be inaccurate.
- The target range of blood glucose:
- Before a meal, blood glucose should be between 70 to 130 mg/dL
- 2-hours after meals, blood glucose should be <180 mg/dL.
Chat.openai.com recommendations about HbA1c:
- HbA1c gives the mean glucose level over a period of 3 months.
- HbA1c diagnoses diabetes mellitus when the level is 6.5% or higher. This is recommended by the American Diabetes Association.
- HbA1c should be kept within the range to avoid diabetes complications.
- HbA1c helps in the management of medications. When HbA1c is not in the range, then medicine adjustment will be made.
- American diabetes association recommendations are to keep HbA1c below 7%.