Urine Hemoglobin (Hemoglobinuria)
Urine Hemoglobin (Hemoglobinuria)
What sample is needed for Urine Hemoglobin (Hemoglobinuria)?
- It can be done with fresh, random urine.
- A morning sample is preferred.
- Examine immediately.
- If examined later, say for one hour, refrigerate the urine in the fridge to avoid microbial growth.
- Mix urine well before testing the urine for Hb.
What are the indications for Urine Hemoglobin (Hemoglobinuria)?
- To find the cause of hemoglobinuria due to various conditions:
- Hemolytic anemia.
- Other conditions are given below.
What are the precautions for Urine Hemoglobin (Hemoglobinuria)?
- Examine immediately.
- Can refrigerate if delayed.
- Mix well before testing.
How will you define urine hemoglobin (hemoglobinuria)?
- This is the presence of free hemoglobin in the urine, called hemoglobinuria.
- When the level of free hemoglobin in the blood exceeds the renal excretion threshold, it results in hemoglobinuria.
- This lysis of the RBCs takes place in dilute, alkaline urine.
- The lysis of the RBCs in the urine usually shows a mixture of hemoglobinuria and hematuria.
- Urine in hemoglobinuria and myoglobinuria is dark red or brown.
- Hematuria:
- When RBCs are present in the urine, the condition is called Hematuria.
- Myoglobinuria:
- The presence of myoglobin is called myoglobinuria. This is due to myoglobin, a muscle protein.
- Hemoglobinuria:
- When hemoglobin is positive in the urine.
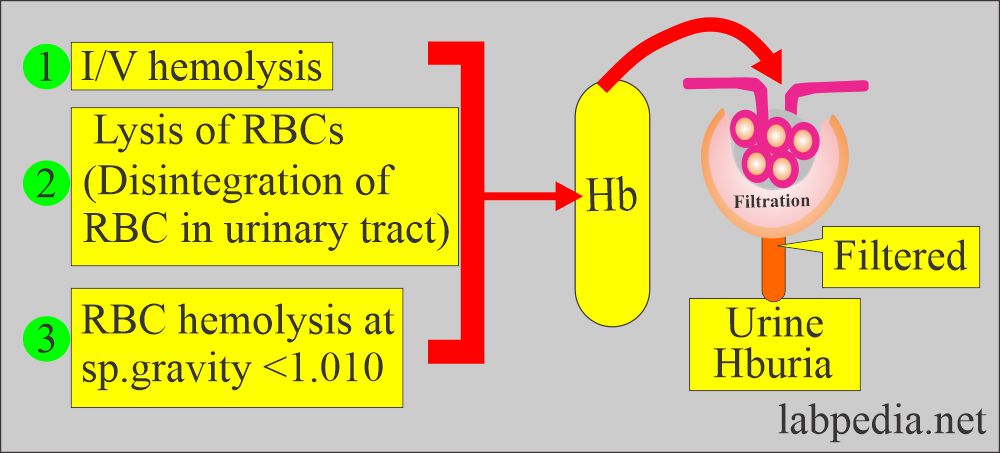
What are the causes of hemoglobinuria?
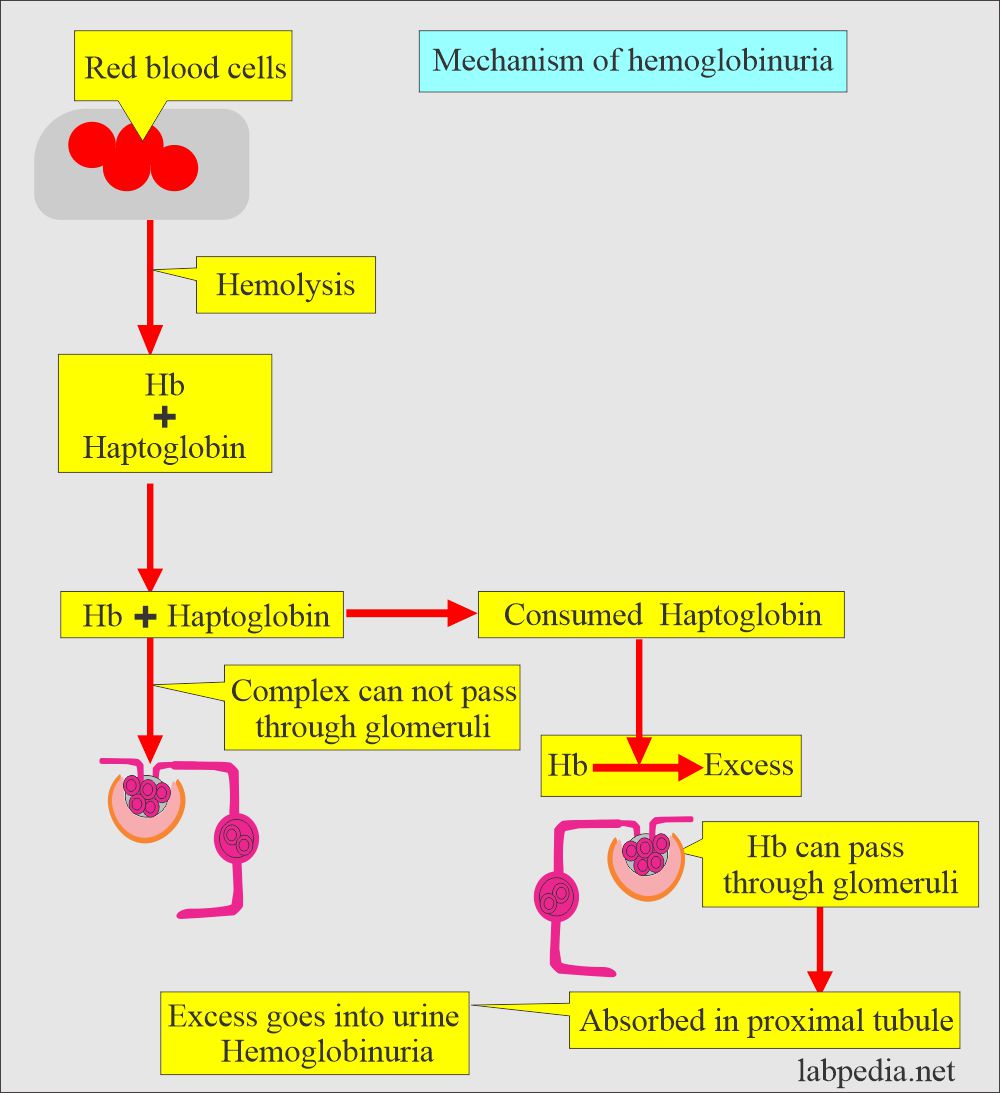
What is the mechanism of hemoglobinuria?
- Erythrocyte lysis occurs at a specific gravity <1.010.
- Hemoglobinuria may occur due to lysis of RBCs in the urinary tract.
- Intravascular hemolysis leads to hemoglobinuria. In such cases, no RBCs are seen.
- This will occur when the reticuloendothelial system can not handle or metabolize the hemoglobin by the hemolysis of RBCs (intravascular).
- Under normal conditions, there is a complex of haptoglobin-hemoglobin, which the glomeruli will not filter.
- When the hemoglobin exceeds the amount of haptoglobin in:
- Hemolytic anemias.
- Severe burns.
- Blood transfusion reactions.
- Strenuous exercise.
- Infections
- The free hemoglobin can pass through the glomeruli.
- The excess is absorbed in the proximal convoluted tubules.
- The free hemoglobin can filter out and appear in the urine as hemoglobinuria.
- This may also take place due to hemolysis in the urinary tract system.
- Blood in the urine indicates damage to the kidneys or the urinary tract.
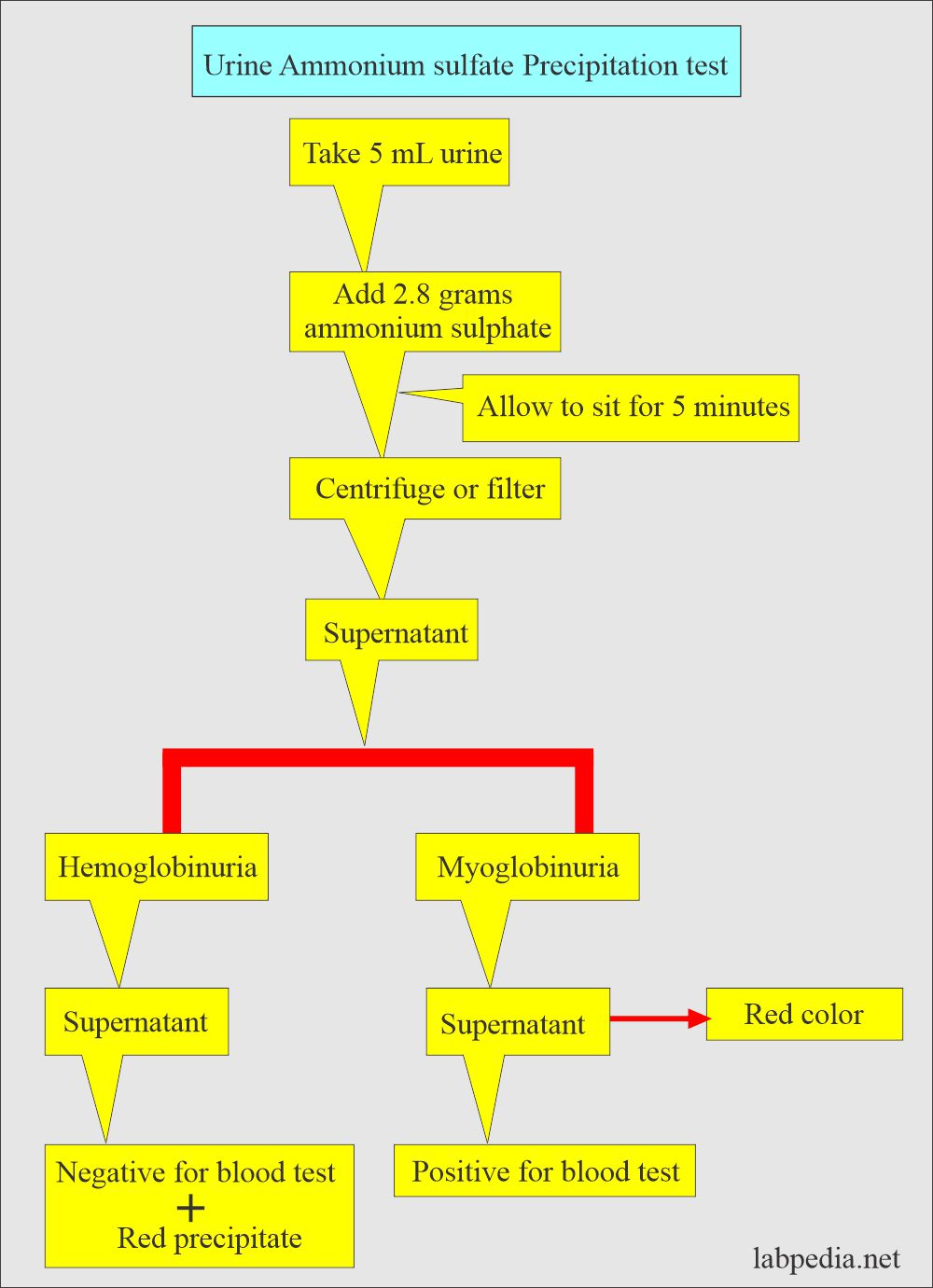
How will you differentiate between hemoglobinuria and myoglobinuria?
- You can differentiate between hemoglobinuria and myoglobinuria by the Ammonium sulfate precipitation test.
How will you detect hemoglobinuria?
- The small amount of hemoglobin in urine does not give a visible color, which can be detected by the dipstick method.
- O-toluidine test:
- It gives a blue color to hemoglobin.
- This also detects myoglobin.
- The false-positive test is seen in the following:
- If the container contains hypochlorite, an oxidizing agent.
- The false-negative test is seen in the following conditions:
- Vitamin C (ascorbic acid).
- Formaldehyde.
- Sensitivity is low when high specific gravity and a high nitrite concentration exist.
- Benzidine test:
- It is not used because it is a carcinogenic agent.
- This test detects:
- RBCs.
- Hemoglobin.
- Myoglobin
| Characteristics | Orthotolidine method | Benzidine method |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Myoglobinuria:
- In case of positive urine for occult blood but no RBCs are seen under the microscope, suspect myoglobinuria.
- This occurs due to muscle injury, muscle disease disorder, and some poisoning.
What is the normal value of urine hemoglobin?
Source 1
- Normally, Hemoglobin is negative in the urine.
- <0.03 mg free Hb/dL.
What are the causes of Hemoglobinuria?
- It is positive for all causes of hematuria, e.g
- Renal calculi.
- Tumors.
- Exposure to toxic drugs.
- Intravascular hemolysis.
- Pregnancy and in puerpera.
- Transfusion reaction.
- Kidney infarction.
- Extensive burns.
- Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria.
- Drugs and poison, e.g., sulfonamides, quinine, phenylhydrazine, poisonous snake, and fava beans.
- Infections, e.g., malaria, blackwater fever, gas gangrene, yellow fever, and anthrax.
- Direct trauma to RBC like exercise, heart valve prosthesis.
- Microangiopathic hemolytic anemia.
- Disseminated intravascular coagulopathy.
- Hemolysis in the donor blood due to improper storage.
How will you differentiate between Hematuria, Hemoglobinuria, and Myoglobinuria?
| Characteristics tests | Hematuria | Hemoglobinuria | Myoglobinuria |
| Reagent strip for blood | Positive | Positive | Positive |
| Urine color | Cloudy red | Red, clear | Clear, red-brown |
| Plasma color | Normal | Pink to red | Normal |
| Presence of RBCs | Present | Absent (± few) | Absent (± few) |
| LDH | Normal | Raised | Raised |
| LD4 and LD5 | Normal | Normal | Raised |
| LD1 and LD2 | Normal | Raised | Normal |
| Total CK | Normal | A slight increase (10 times the normal) | Markedly increased (40 times the normal) |
Questions and answers:
Question 1: What is the difference between hematuria and myoglobinuria?
Question 2: What is hemoglobinuria?